ECELAWSCESS Chapter 3 Ethics
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:18 PM on 2/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
1
New cards
Ethics
a discipline or area of study dealing with moral problems
2
New cards
Engineering Ethics
The discipline or study of moral issues arising in and surrounding engineering
3
New cards
Morality
Study of human behavior as a consequence of beliefs about what is right or wrong (Descriptive Ethics)
4
New cards
Morality
Study of what is thought to be right and what the general public, group, culture, or society would generally do.
5
New cards
Ethics
define whether it is right or wrong for one person to kill another in a dispute over property
6
New cards
Morals
define whether I should kill my neighbor Joe when he steals my tractor
7
New cards
The End Justifies the Mean
The result of some actions taken is more important than the other repercussions of the said actions. As long as the desired result is achieved, it doesn’t matter what you do to get those results
8
New cards
The End Justifies the Mean
Satanic Doctrine teaching that we may do evil without becoming evil if our motive is good enough
9
New cards
Ethics
are beliefs regarding what is right and wrong behavior
10
New cards
Morality
refers to social convention about right and wrong
11
New cards
Virtues
are habits that incline us to do what is acceptable
12
New cards
Vices
are habits that incline us to do what is unacceptable
13
New cards
Moral
A category of moral action if they reflect a person’s values and those of society
14
New cards
Immoral
A category of moral action if they go againts a person’s values or those of society
15
New cards
Amoral
A category of moral action if they do not reflect choices based on values or social norms
16
New cards
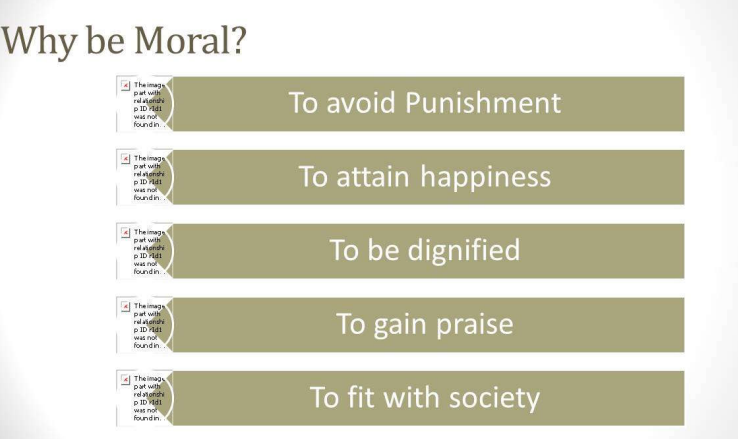
Why be Moral?
17
New cards
The Ethical of Moral Dilemma
Situations where two or more moral obligations, duties or rights are in conflict. Often, not just a choice between right or wrong or good and evil. Greater of goods, Lesser of evils
18
New cards
Virtue Ethics Approach
The ethical choice is one that best reflects moral virtues in our selves and our communities .
19
New cards
Utilitarian Approach
The ethical choice is the one that approach produces the greatest excess of benefits over harm
20
New cards
Fairness Approach
The ethical choice is the one that treats everyone the same and does not show favoritism or discrimination
21
New cards
Common good Approach
The ethical choicen is the one that advances the common good
22
New cards
Hedonism
Humans are ends in themselves and not means
23
New cards
Result Oriented
Humans are ends in themselves and not means
24
New cards
Utilitarianism
The rightness of the Act is based in results.
Welfare. Consequence
Welfare. Consequence
25
New cards
Utilitarianism
The right thing to do is that which is likely to produce the greatest happiness for the greatest number of people
26
New cards
The Act Utilitarian Test
A part of the utitilitarian test where it measures the consequence if a single act
27
New cards
The Act Utilitarian Test
A part of the utitilitarian test where you ask yourself, “Will this course of action produce more utility than any alternative course of action that I could take?”
28
New cards
The Act Utilitarian Test
A part of the utitilitarian test where the rightness or wrongness of the act is based on the premise that the probable benefit is maximized
29
New cards
The Rule Utilitarian Test
A part of the utitilitarian test where onme asks “Would utility be maximized if everyone did the same thing in the same time?”
30
New cards
The Rule Utilitarian Test
A part of the utitilitarian test where it would consider the consequence of an action in the long run if it is repeated over and over such that it becomes a “rule”
31
New cards
Cost-Benefit Test
Resolves moral problems by converting the negative and positive utilities to monetary terms.
Mostly used by the government and business sector when making a decision.
Mostly used by the government and business sector when making a decision.
32
New cards
Universal criterion in resolving a moral issue
to be ethically valid, we must be willing for others to do similar course of action in similar circumstances
33
New cards
The Golden Rule Test

34
New cards
Self Defeating test (Kantian Ethics)
Asks the questions: Which actions are inherently good? Simply focus on the deed itself.

35
New cards
The Question you ask yourself when facing a moral dilemma
Can I will that all human beings should act in the same way I am about to act now if they are confronted with the same problem?
36
New cards
A universalized action can be self-defeating in two ways:
\

37
New cards
The Rights Test
In this approach, the rights of the people must be respected.
38
New cards
Right
An entitlement to act in a certain way
39
New cards
Right
Serves as a protective barrier, shielding individuals from unjustified infringements of their moral agency by others.
40
New cards
Rights to Freedom and Rights to well-being
The two types of Essential Rights
41
New cards
Valid Consent
It is when the consent was given voluntarily.
42
New cards
Valid Consent
The consent was based on the information that a rational person would want, with the information presented in understandable form.
43
New cards
Valid Consent
The consenter was competent and rational to process information.
44
New cards
An experiment is valid if
The participants give their consent subject to the following:

45
New cards
Hindrance to Ethics in Business
Operating ethically does not always guarantee business success.
46
New cards
Fostering good business ethics
Why is it important that the company foster good business ethics?

47
New cards
Code of Conduct
Is a guide that highlights an organization’s key ethical issues and identifies the overarching values and principles.
48
New cards
Lotus
A _____ remains beautiful even as it lingers in the filthy waters of the pond.
49
New cards
Good Will
____ is only good withot qualification
50
New cards
Good Will
is a will that acts for the sake of duty, as a “good-in-itself”
51
New cards
Duty
is the necessity of acting out of reverence for universal law
52
New cards
Moral Obligation
Arising from conscience or the sense of right and wrong:
53
New cards
Moral Victory or Support
Having psychological rather than physical or tangible effects
54
New cards
Moral Certainty
Based on strong likelihood or form conviction, rather than on the actual evidence
55
New cards
Moral Scrutiny or Quandary
Of or concerned with the judgment of the goodness or badness of human action and character:
56
New cards
Moral Lesson
Teaching or exhibiting goodness or correctness of character and behavior
57
New cards
Moral Life
Conforming to standards of what is right or just in behavior; virtuous
58
New cards