EOC Economics Review
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
Scarcity
Unlimited Wants, limited resources (the basic problem of economics)
Factors of Production
Land, Labor, Capital, Entrepreneurship
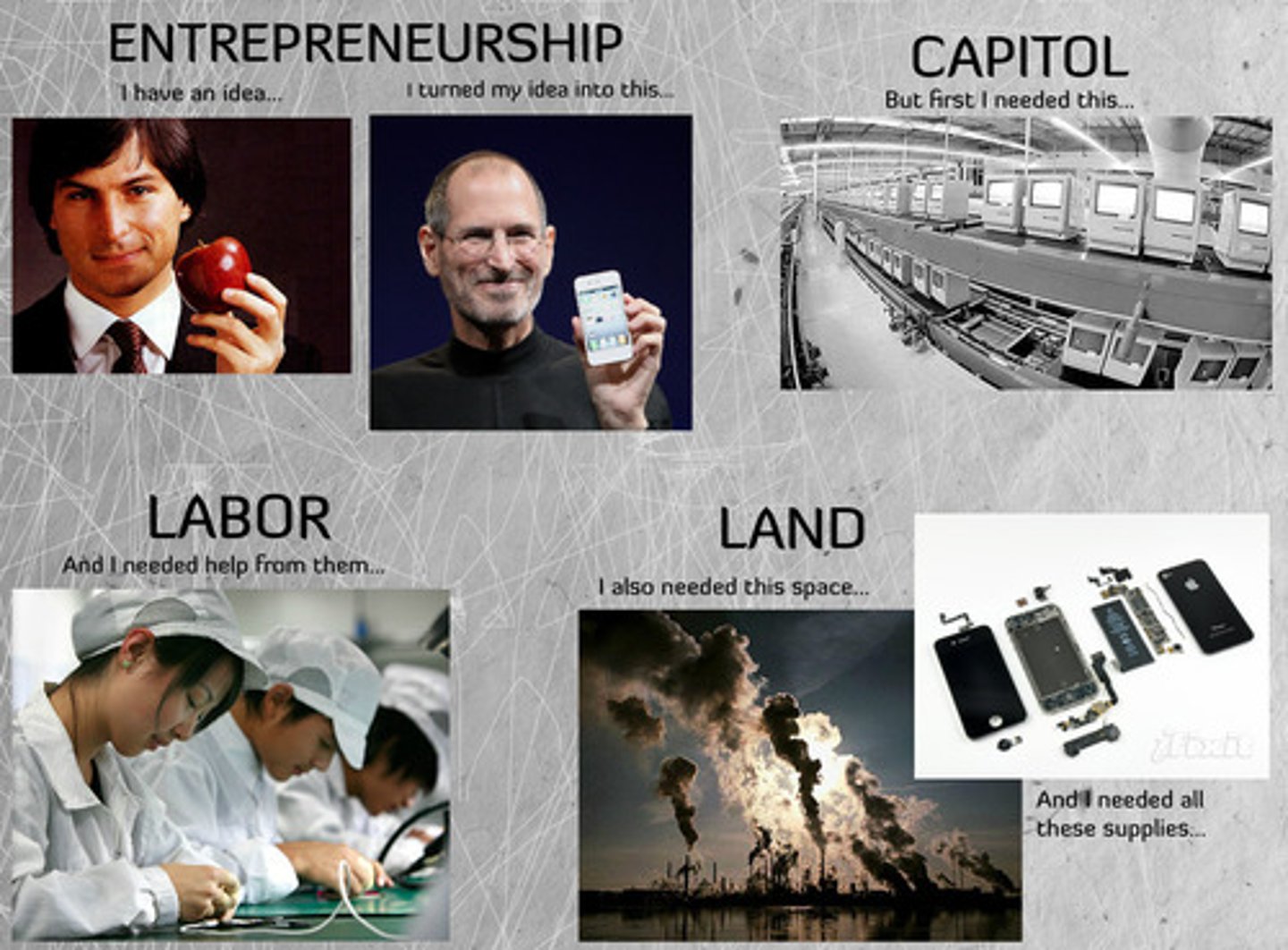
Entrepreneurship
An individual, motivated by profit, who chooses to open their own business
Human Capital
Human knowledge to perform a task (ex: Brain surgeon having the knowledge to preform surgery)

Physical Capital
Man-Made Tool (part of the factors of production)

Opportunity Cost
Second best alternative given up
Marginal Cost
The cost of creating an additional item
Marginal Benefit
What you gain from creating an additional item/ preforming a certain task
Rational Decision
When Marginal Benefit exceeds the Marginal Cost
Positive Incentive
Benefits that are offered to individuals to get them to behave a certain way (offering rewards)
Negative Incentive
Avoiding a situation to escape punishment
Specialization
To become very skilled in one particular task/job (Ex: Teaching specifically Economics)
Voluntary Exchange
Exchanging money for a good at a benefit for both parties

Three Economic Questions
What to produce, How to produce, For whom to produce it for

Profit Motive
Motivated towards making a profit (money)- The reason why entrepreneurs usually enter into business
Government Regulation
Government laws/rules (usually make products more expensive in order to comply)
Economic Security
Providing safety from economic hardship (Welfare, social programs, etc.)
Economic Efficiency
Being efficient/productive with scarce resources
Economic Sustainability
Sustaining Economic Growth
Public good/service examples:
Parks, sidewalks, schools, roads (paid for by tax dollars)
Market Failure
When a third party is harmed by the failure of the government to regulate an industry (ex: pollution)
Regulation
Creating a law involving a business (usually results in price increases)
Deregulation
The lifting of government restrictions on business, industry, and professional activities.
Productivity
Not wasting resources/time
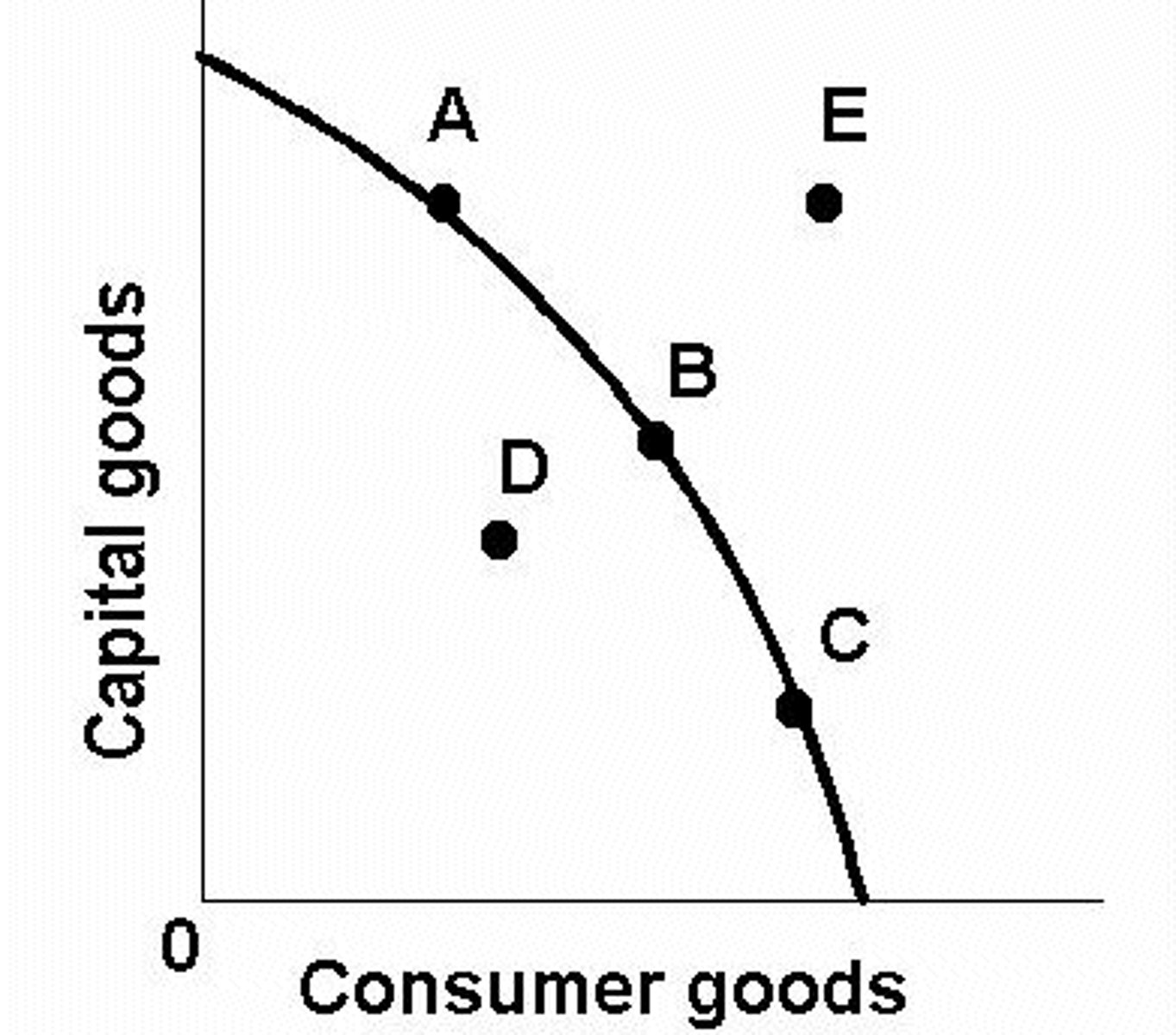
Production Possibility Curve
a graph that shows alternative ways to use an economy's productive resources
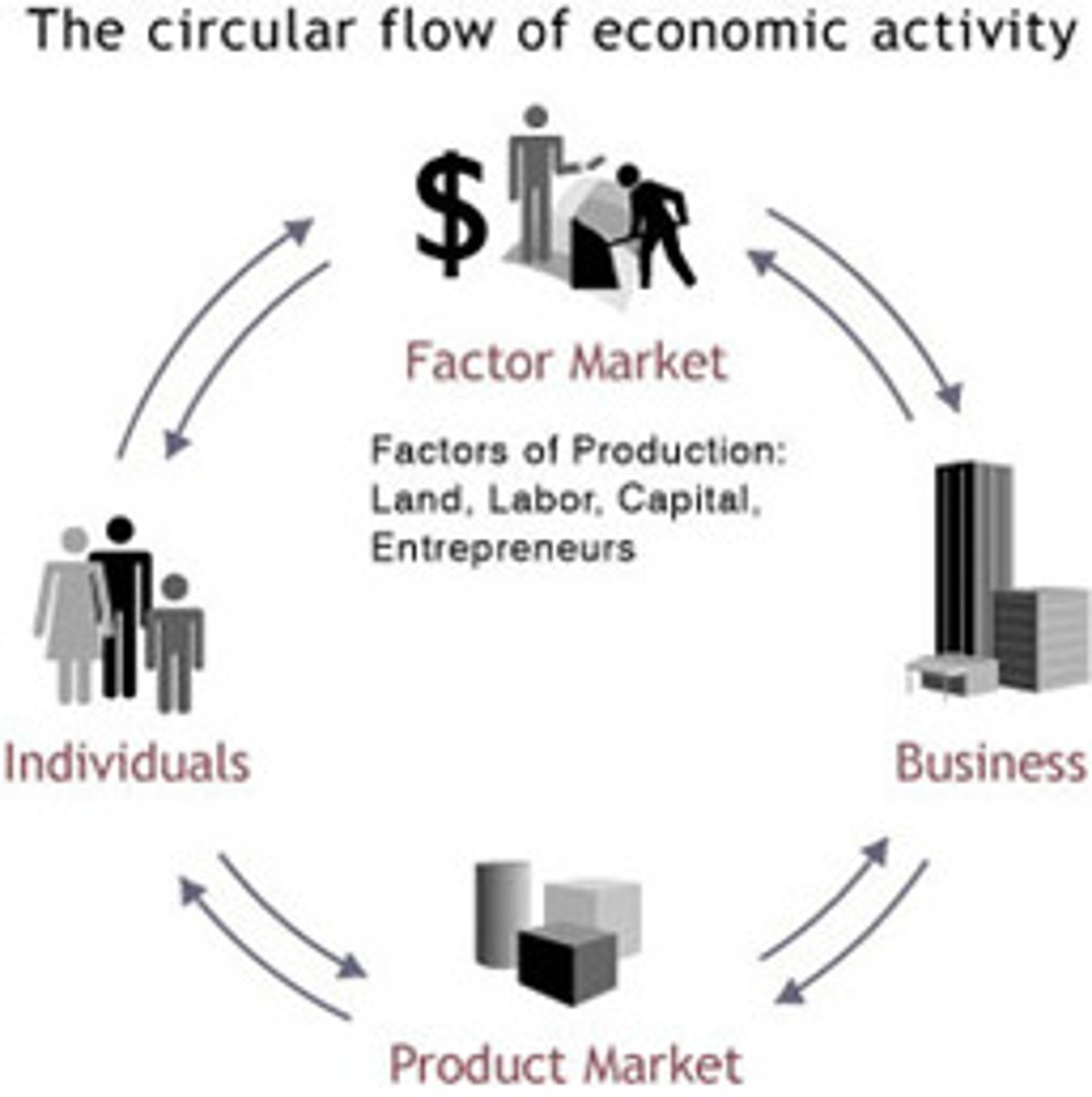
Product Market
the market in which households purchase the goods and services that firms produce

Factor Market
market in which firms purchase the factors of production from households
Law of Demand
consumers buy more of a good when its price decreases and less when its price increases
Law of Supply
Produces make more of a good when its price increases, and less when its price decreases
Demand
Amount willing and able to bought of an item at all price levels
Aggregate Demand
Total amount demanded in the whole economy
Supply
Amount willing and able to be produced of an item at all price levels
Aggregate Supply
Total amount produced in the whole economy
determinants (shifters of demand)
Population
Expectation of future price
popularity/preferences
Substitutes (related goods)
Income
Complements (related goods)
Substitutes
Items bought in place of each other (Coke and Sprite)
Complements
Items bought typically together (milk and cereal)

Increase in demand: Shift to the __________
RIGHT
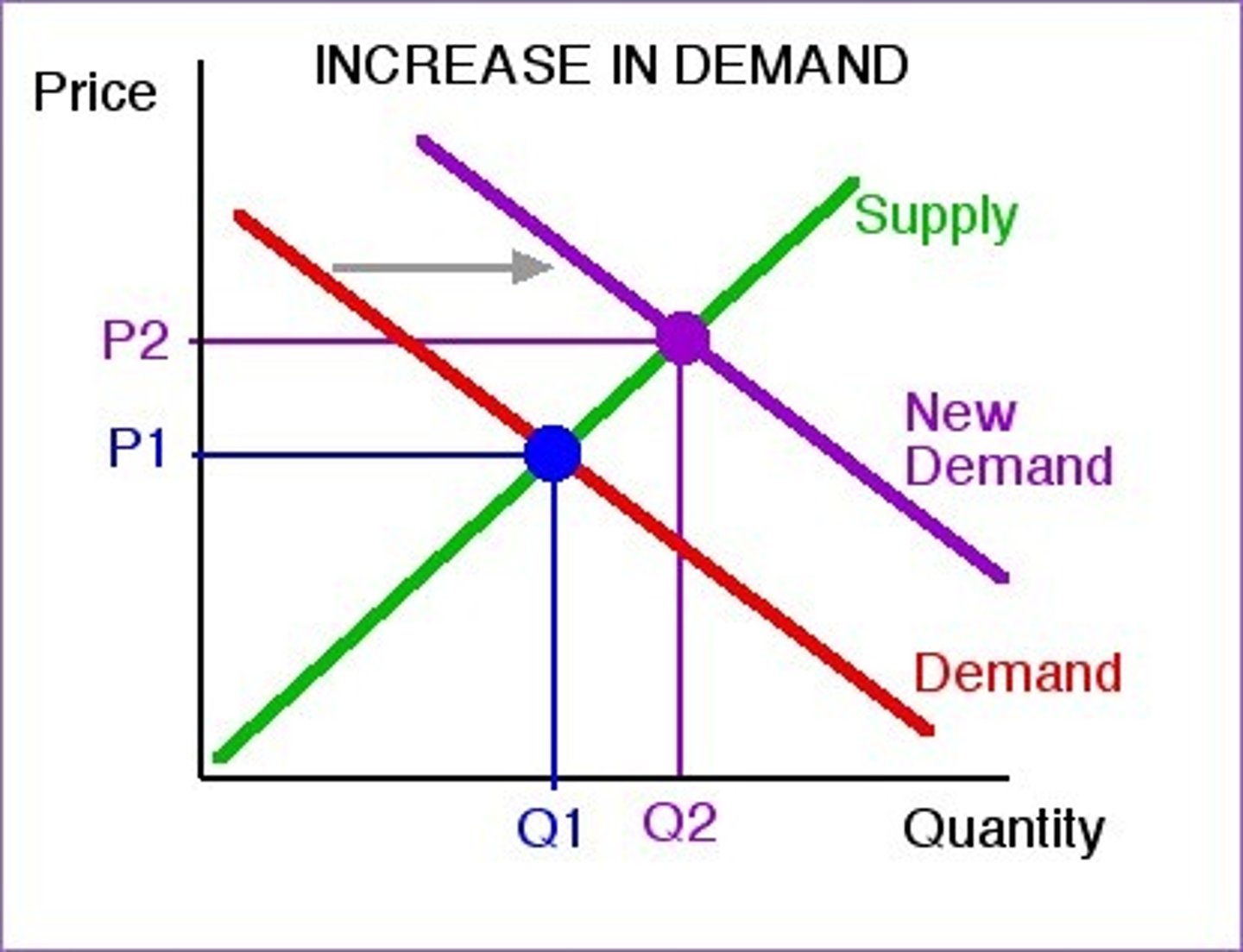
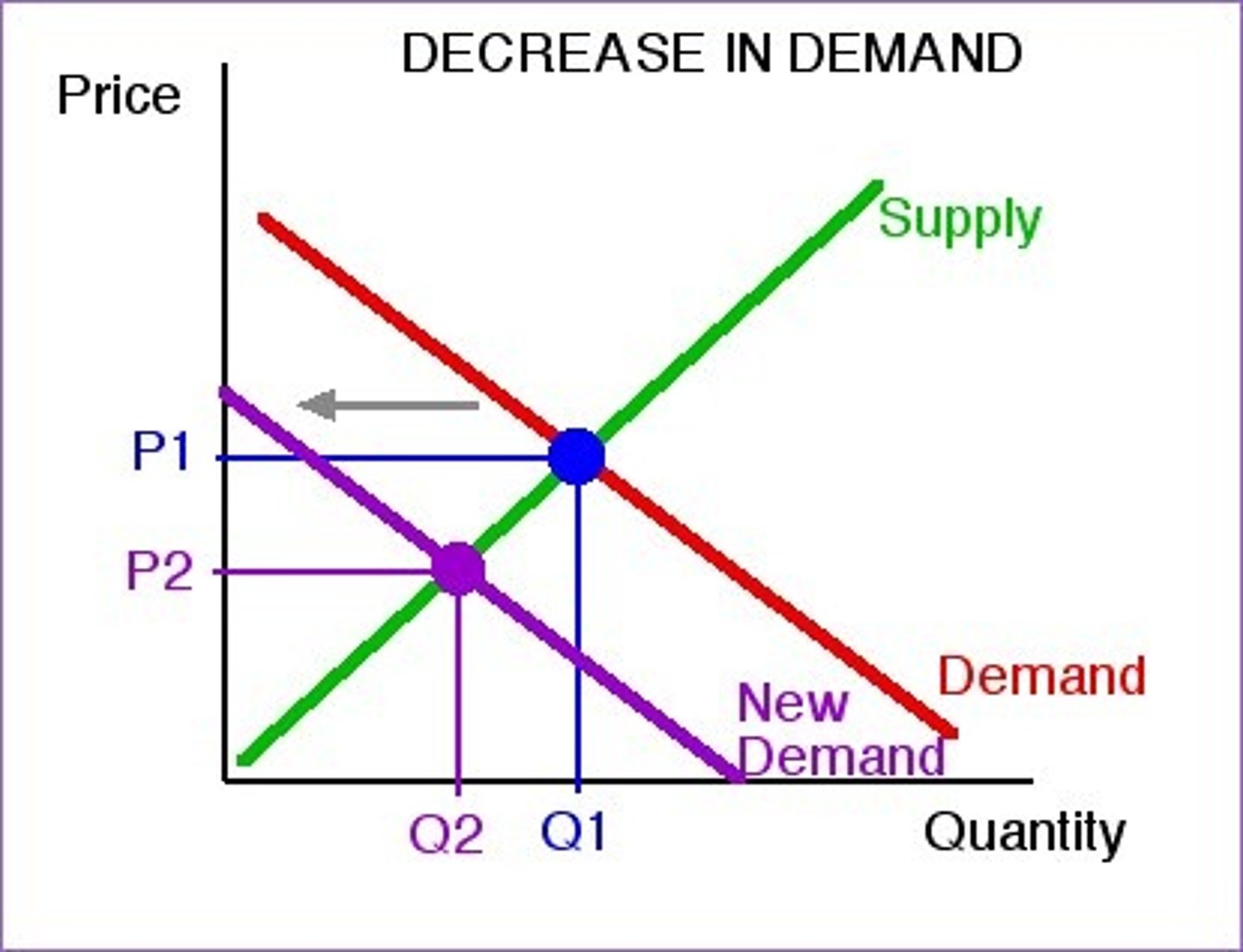
Decrease in demand: shift to the ___________
LEFT
Increase in supply: Shift to the __________
RIGHT
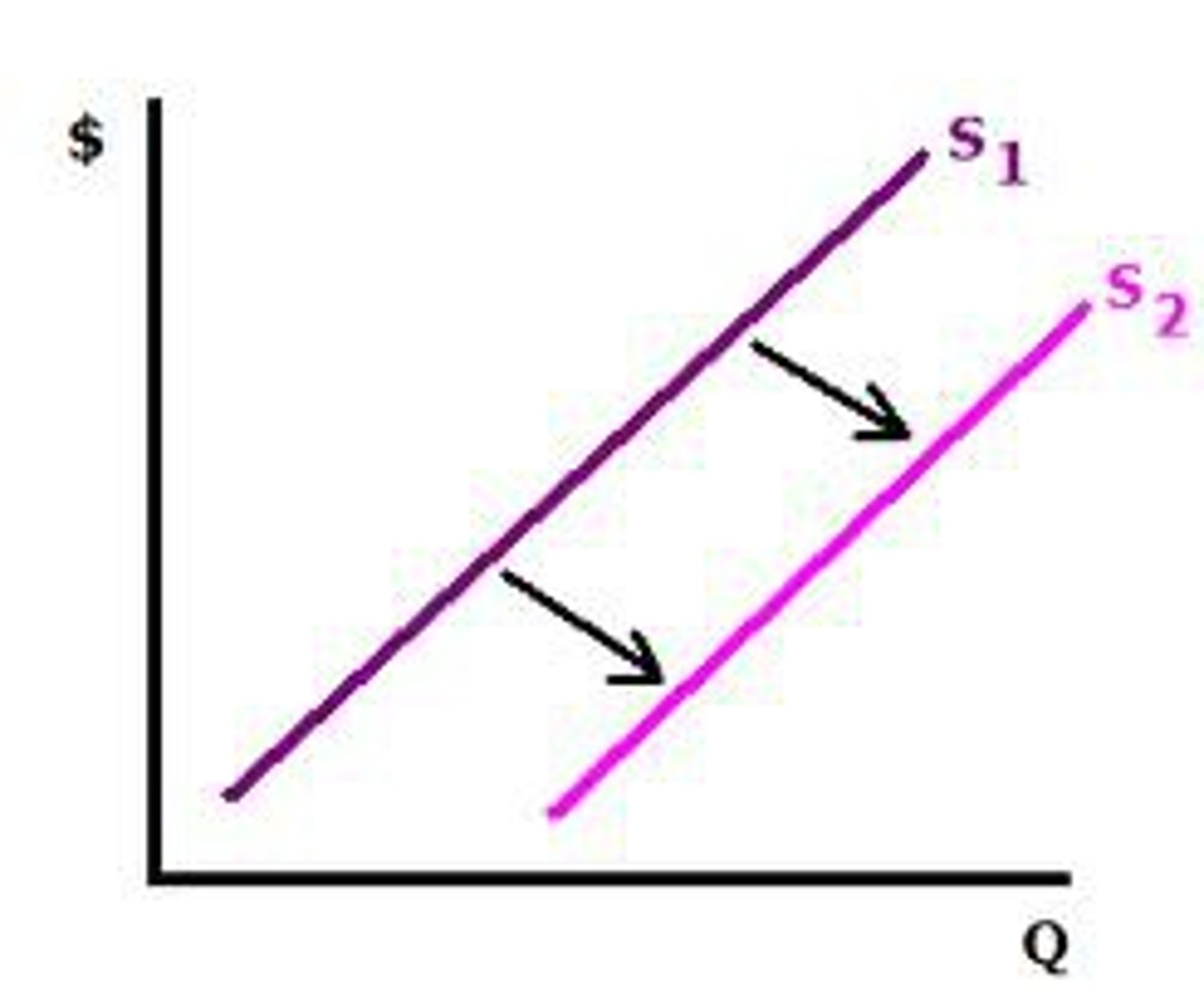
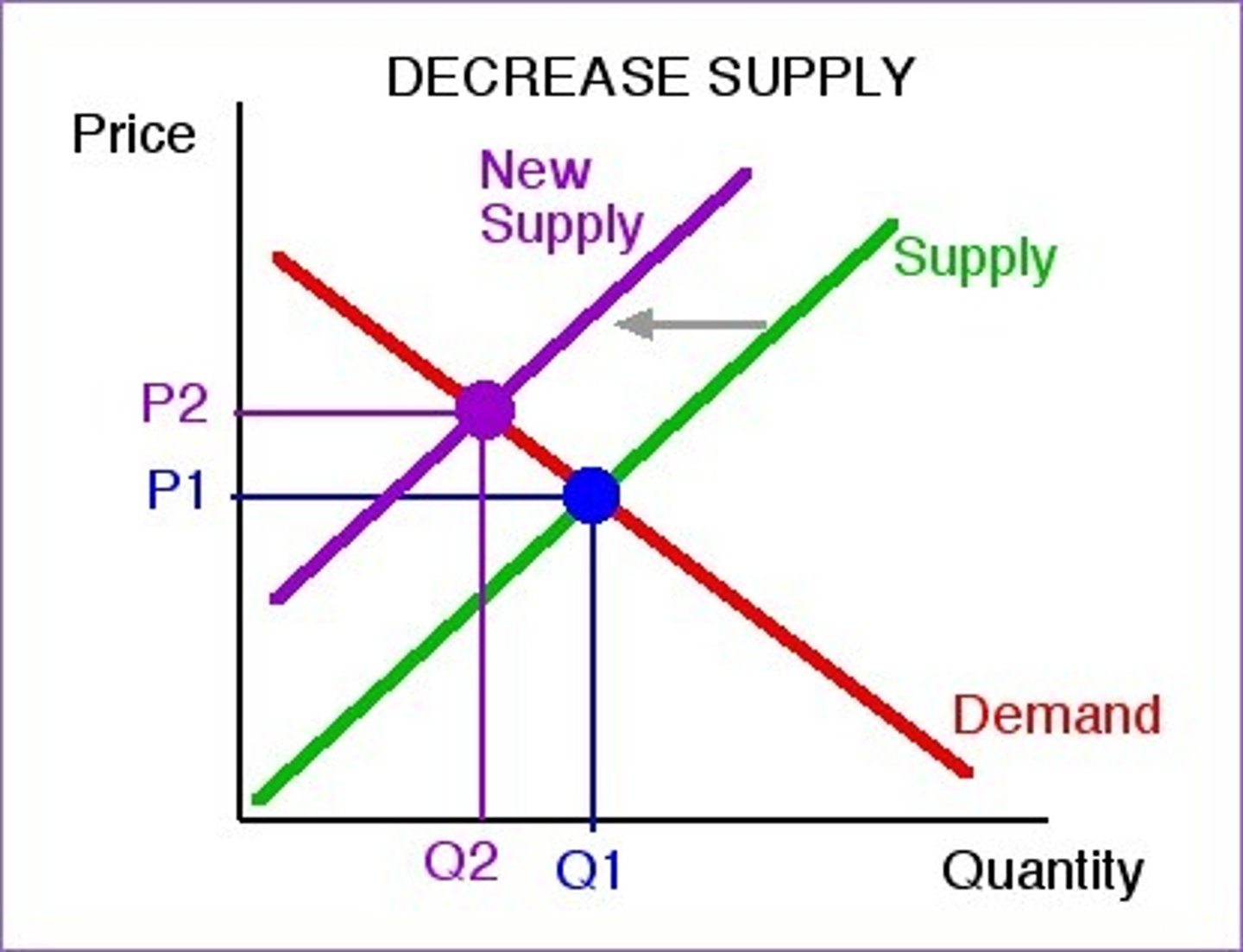
Decrease in supply: Shift to the ________-
LEFT
Determinants (shifts) of Supply:
# of sellers
Technology
Government regulation
Cost of Inputs
Future Price/expectation of future profit
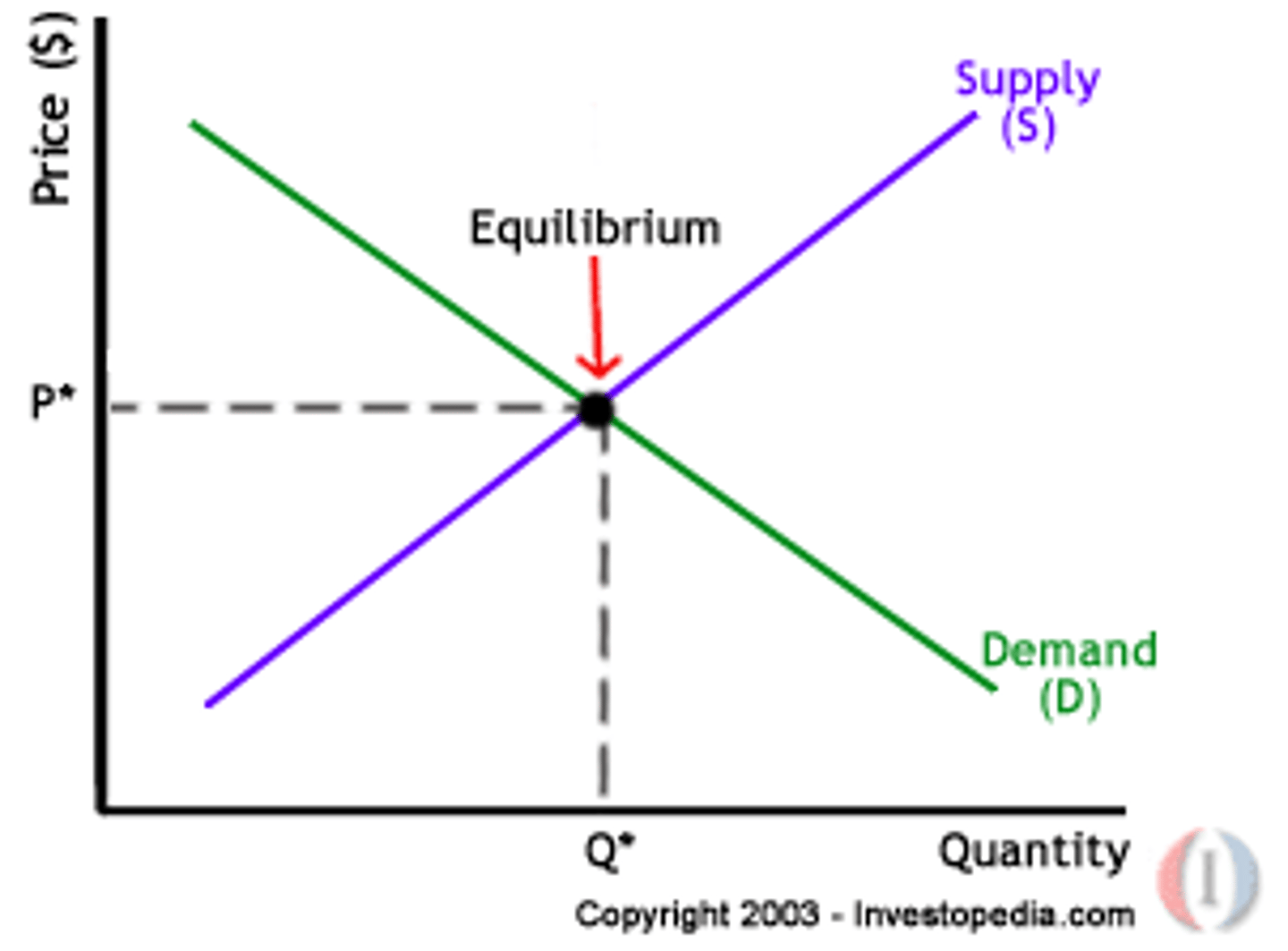
Market Clearing Price
Price where the amount supplied in a market matches exactly the amount demanded.
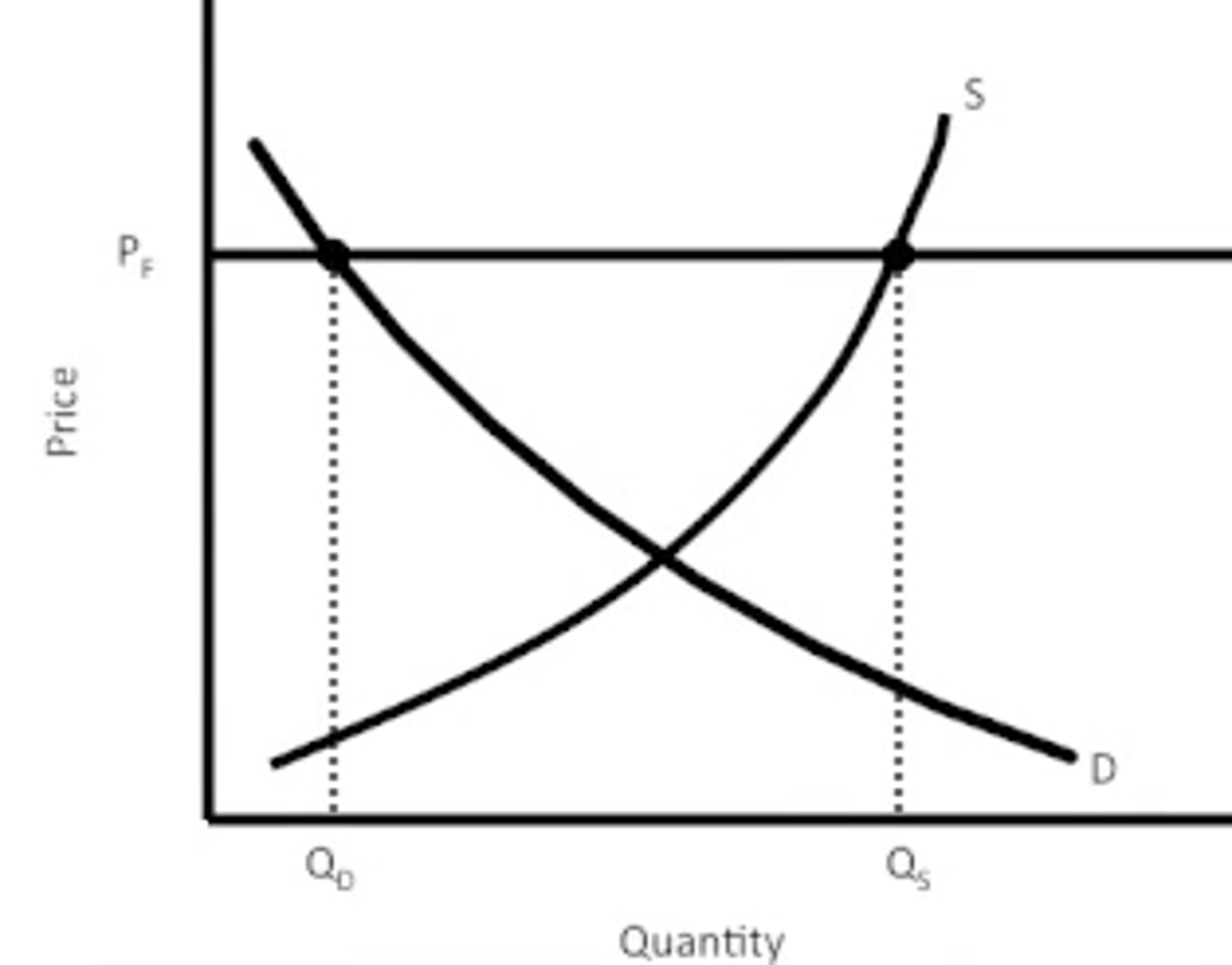
Price Floor
A legal minimum on the price at which a good can be sold (Ex: minimum wage)
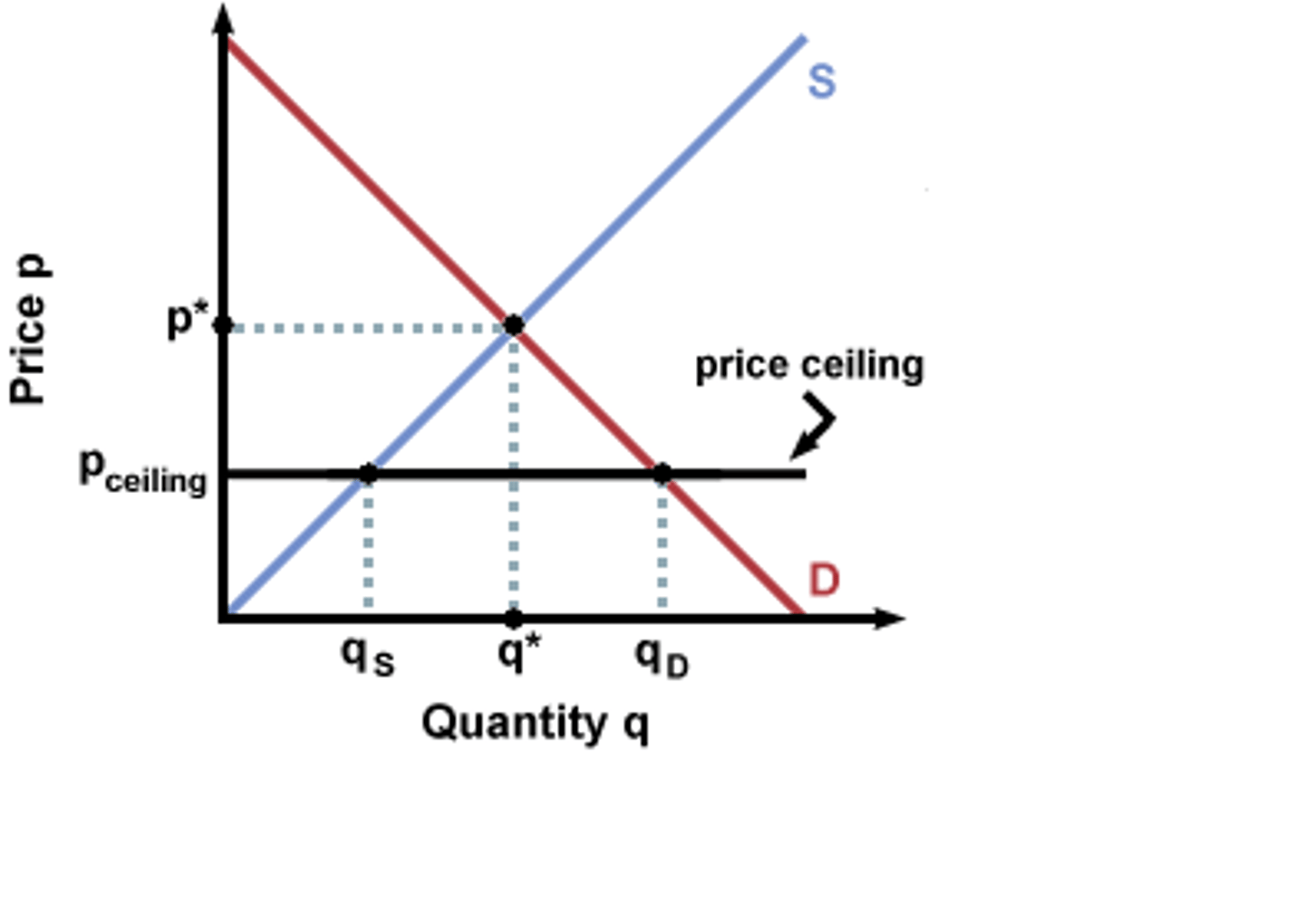
Price Ceiling
A legal maximum on the price at which a good can be sold (Ex: Rent Control)
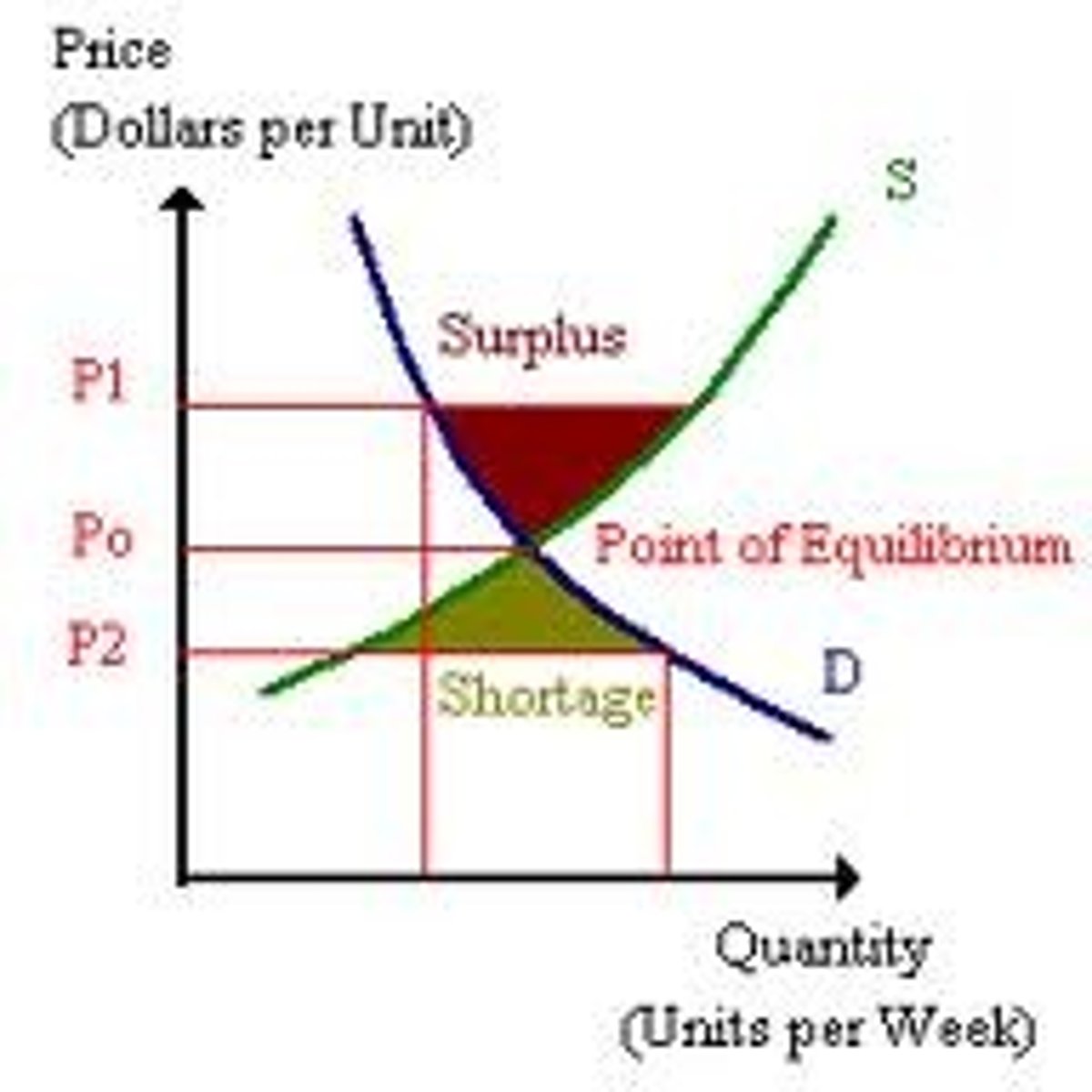
Surplus
A situation in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded
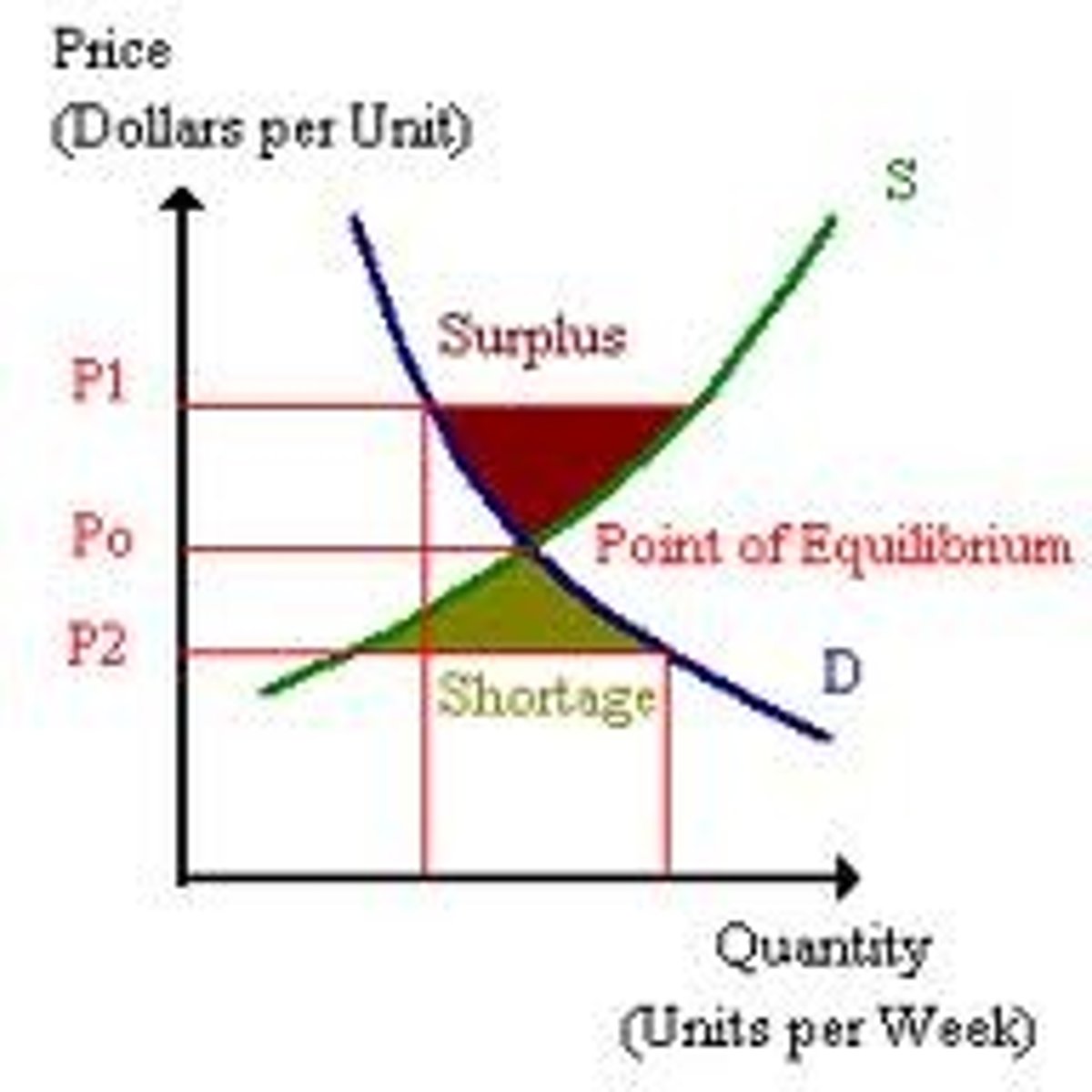
Shortage
A situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied
Sole Proprietorship
A business owned by one individual
Has unlimited liability
Complete control over business
Most numerous type of business
Easiest to start/shut down
Partnership
A business owned by two or more individuals
Unlimited (usually shared) liability
Can disagree over business decisions
Corporation
A business owned by shareholders (stock holders)
Run by a board of directions
limited liability
double taxed (income + dividends)
Limited Liability
Cannot lose personal belongings due to business debt
Unlimited Liability
The owner is personally and fully responsible for all losses and debts of the business
Perfect Competition
A large amount of businesses compete with identical products (fruits/vegetables)
Have no control over price
Easy barriers to entry
Monopolistic Competition
A large number of firms compete with similar products (fast food/clothing/etc.)
Have some control over price
Easy barriers to entry
Compete using non-price competition (advertising)

Non Price Competition
a way to attract customers through style, service, or location, but not a lower price
Oligopoly
A market structure in which a few large firms dominate a market
High barriers to entry
Can set own prices
Cannot collude (come together to set prices)

Monopoly
A market in which there are many buyers but only one seller.
High barriers to entry
Sets own price and people have to pay
Gross Domestic Product
The sum total of the value of all the goods and services produced in a nation in one year
*must be brand new *
GDP: Formula
C + I + G + Xn
Consumption Goods
Investment Goods (business spending)
Government
Imports-Exports
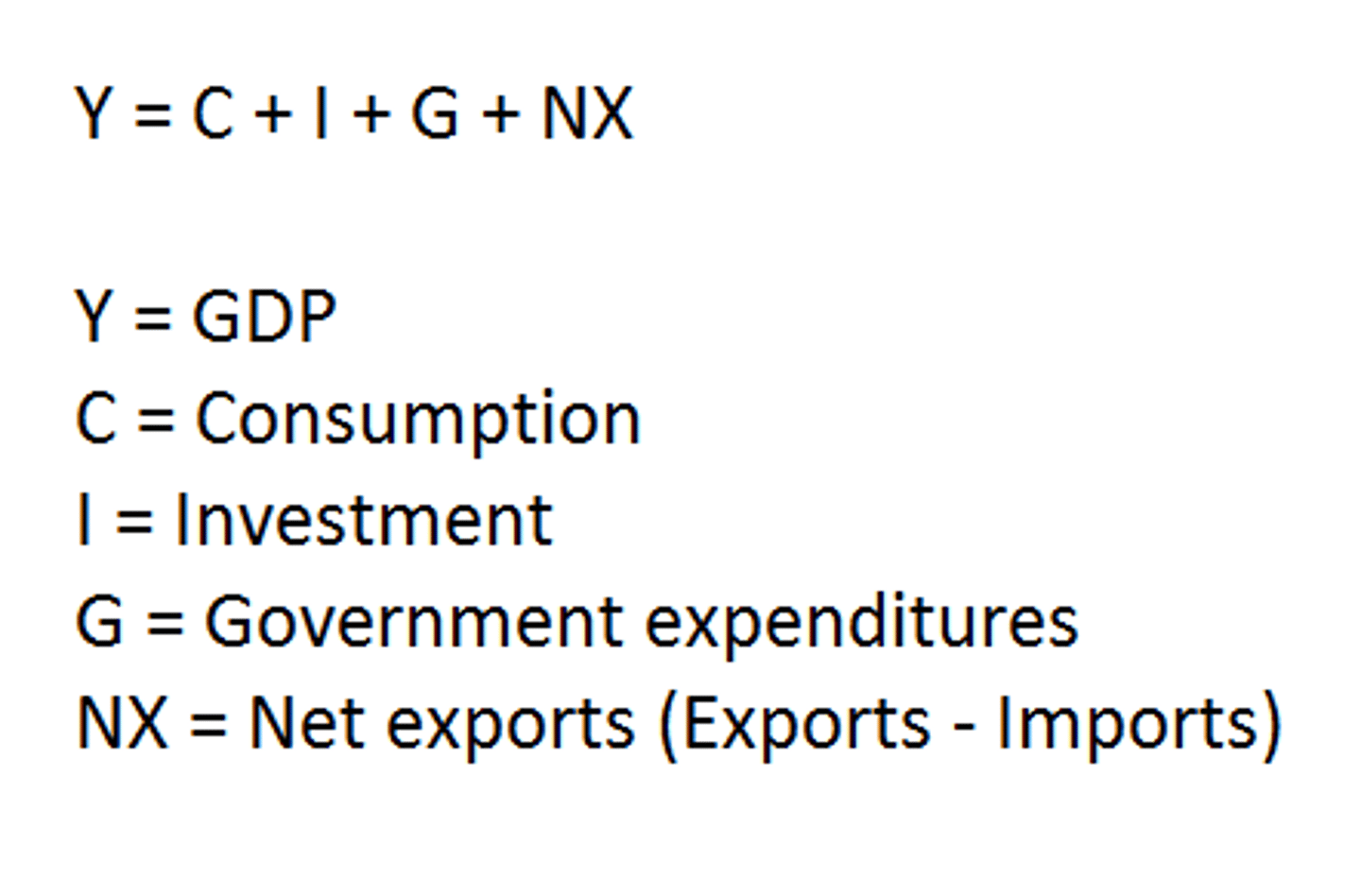
Real GDP
GDP which has adjusted for inflation over time
Unemployment
When an individual does not have a job who is willing and able to work
-Above the age of 16
-Not a full-time student
-Has to be looking for work

Discouraged Worker
An individual who has given up looking for work
Seasonal Unemployment
Unemployment caused by seasonal changes in the demand for certain kinds of labor

Frictional Unemployment
unemployment that occurs when people take time to find a job (first job, quit, fired)

Structural Unemployment
unemployment that occurs when workers' skills do not match the jobs that are available
Cyclical Unemployment
unemployment that rises during economic downturns and falls when the economy improves
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
Measures the rate of inflation
Inflation
General rise in prices

Market Basket
representative group of goods and services used to compile the consumer price index (typical goods bought by a household)
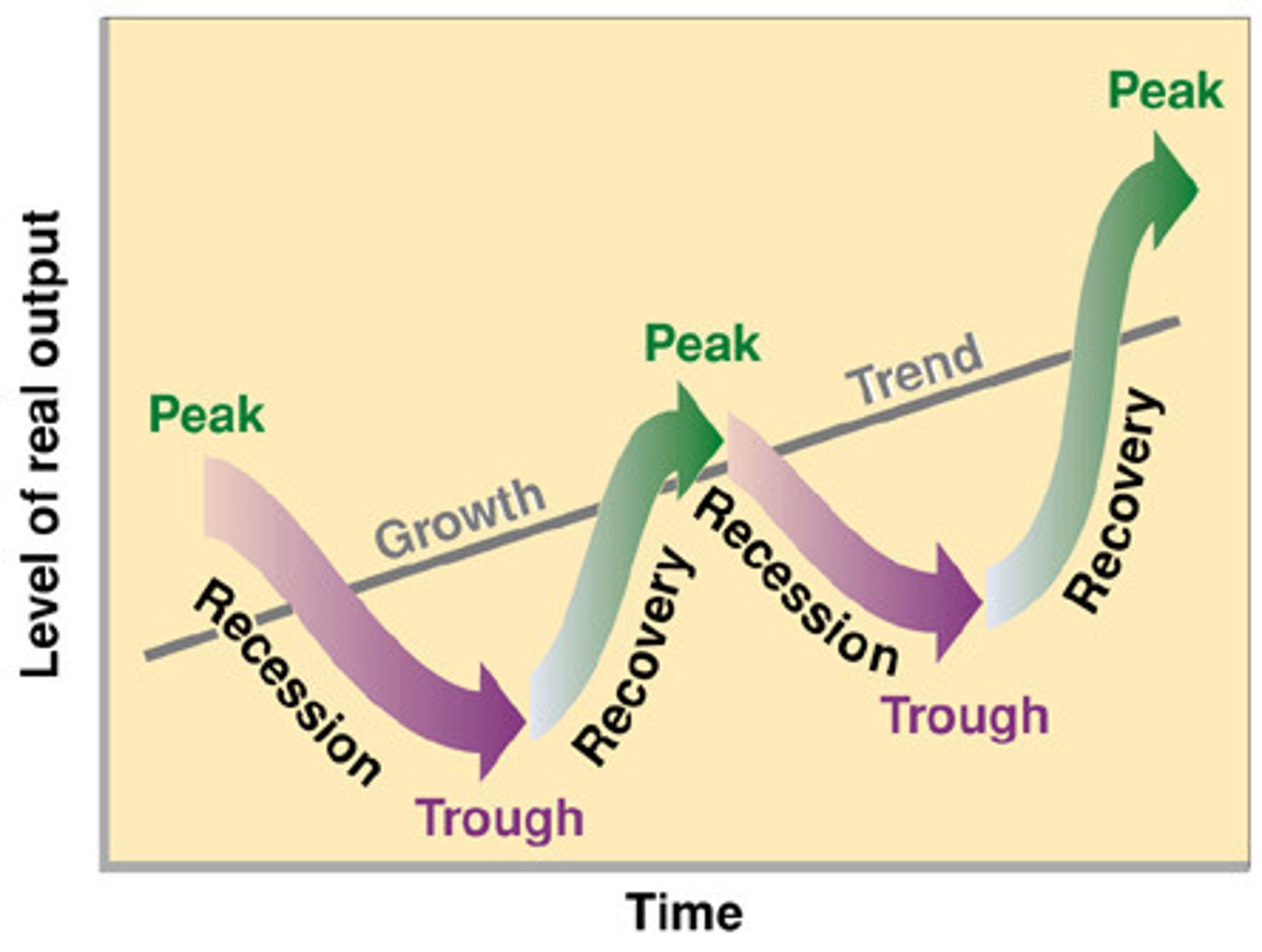
Business Cycle
Alternating periods of economic expansion and economic recession
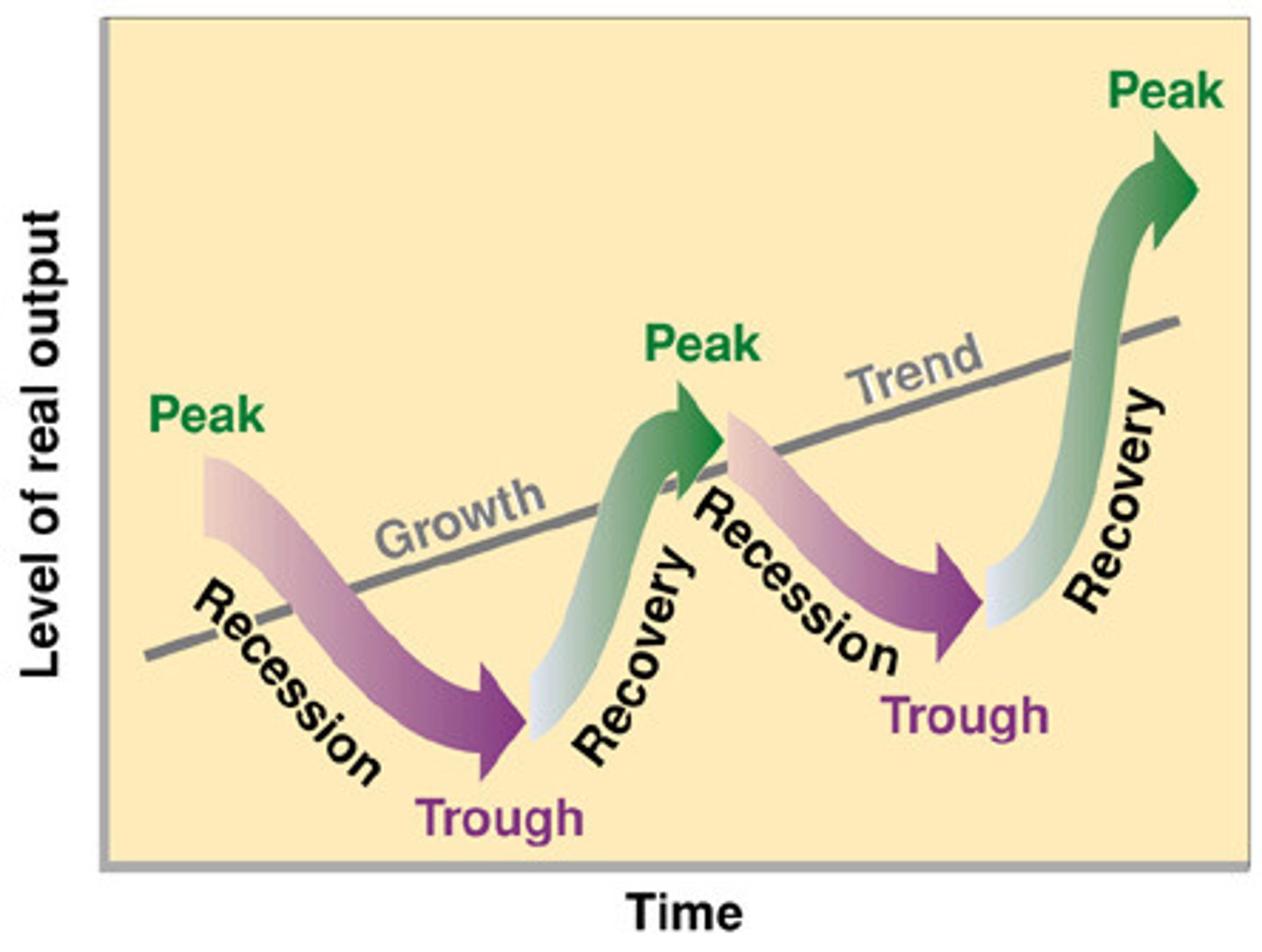
Expansion
A period of economic growth as measured by a rise in real GDP
Peak
the height of an economic expansion, when real GDP stops rising
Contraction
a period of economic decline marked by falling real GDP
Trough
Lowest point of economic contraction, when real GDP stops falling
Recession
A period of declining real GDP, accompanied by lower real income and higher unemployment. 6 months or more
Depression
A period of low economic activity (recession) and rising unemployment. Record levels of unemployment and inflation
Medium of Exchange
anything that is used to determine value during the exchange of goods and services (dollars in the US)
Store of Value
Something that keeps its value if it is stored rather than used
Unit of Account
A means for comparing the values of goods and services (price tags)
Monetary Policy
Managing the economy by altering the supply of money and interest rates
Organization of the Federal Reserve
Board of Governors: 7 (run by the chairman)
FOMC: Board of governors + bank presidents
District Banks: 12
Member Banks: 25,000+
Federal Open Market Committee
Oversees the buying and selling of bonds
Open Market Operations
Buying & selling government securities (bonds) to change the supply of money
Required Reserve Ration
The ratio of reserves to deposits that banks are obligated by regulation to hold.
Discount Rate
The interest rate on the loans that the Fed makes to banks
Interests on Reserves
The Fed pays banks interest to hold money in reserve
Contractionary Monetary Policy
the federal reserve's adjusting the money supply to increase interest rates to reduce inflation
Increase RRR
Increase DR
Increase IOR
Sell Bonds
Expansionary Monetary Policy
the federal reserve's increasing the money supply and decreasing interest rates to increase real GDP
Decrease RRR
Decrease DR
Decrease IOR
Buy Bonds
Fiscal Policy
Government policy that attempts to manage the economy by controlling taxing and spending.
Expansionary Fiscal Policy
An increase in government spending or a reduction in taxes
Contractionary Fiscal Policy
A decrease in government spending or an increase in taxes
National Debt
The sum of government deficits over time.
Government Deficit
The dollar amount that a country is over budget within a given fiscal year
Budget Surplus
An excess of tax revenue over government spending (government makes money- takes away from debt)
Absolute Advantage
the ability to produce more of a given product using a given amount of resources

Comparative Advantage
The ability of a country to produce a good at a lower cost than another country can.
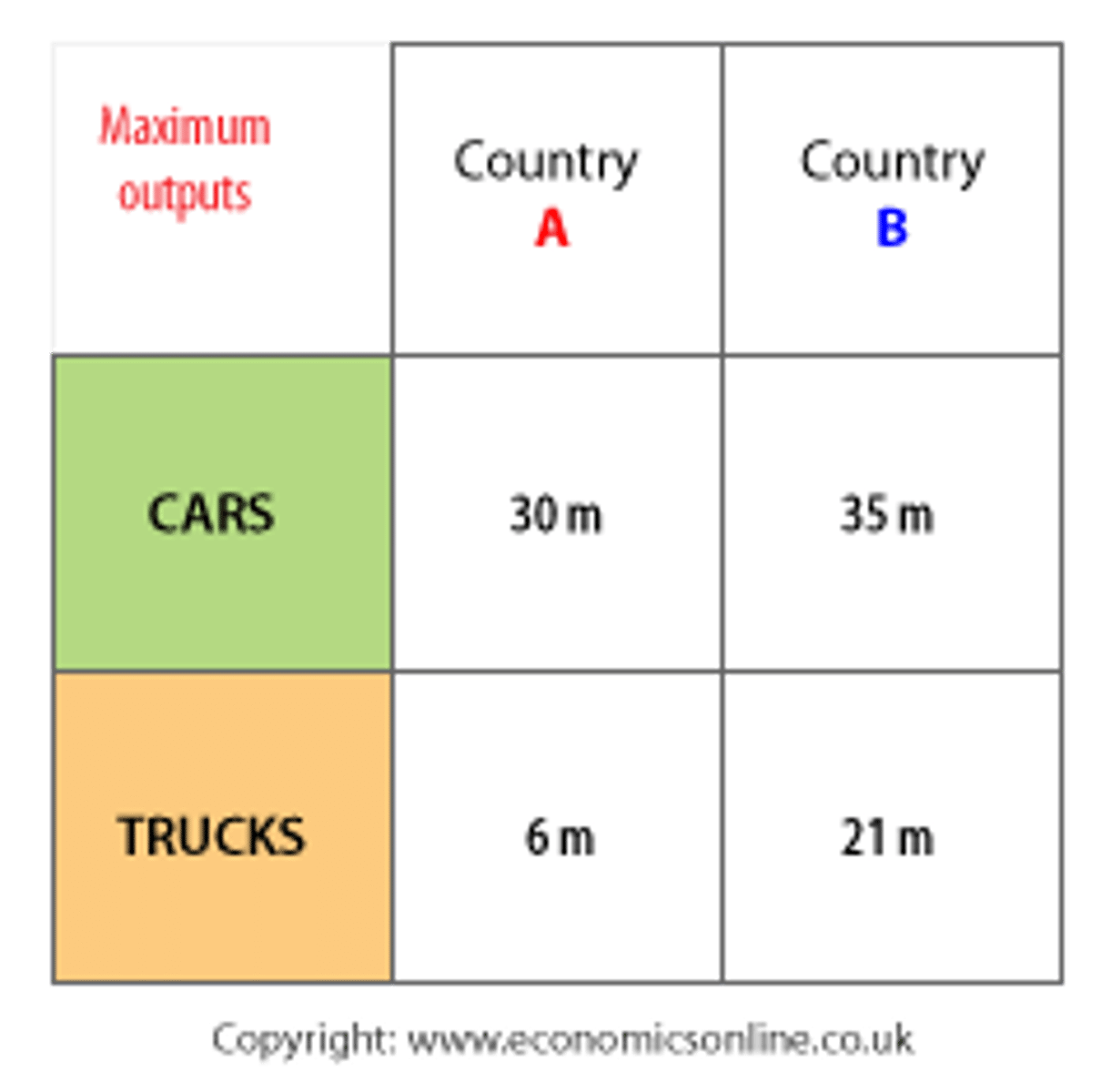
Trade Surplus
when a country exports more than it imports
Trade Deficit
An excess of imports over exports
Balance of trade
the difference between a country's total exports and total imports
Trade Barriers
Taxes, quotas, and other restrictions on goods entering or leaving a country.
Tariff
A tax on imported goods (makes items more expensive)