PROKARYOTIC CELLS VS EUKARYOTIC CELL (3rd lesson)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Prokaryotic Cell
- does not have a membrane bound nucleus.
- nuclear materials are scattered.
- does not contain membrane-bound organelles.
- found in a region within the cell called the nucleoid.
prokaryotes
Most _______ have a peptidoglycan cell wall and many have polysaccharide capsule.
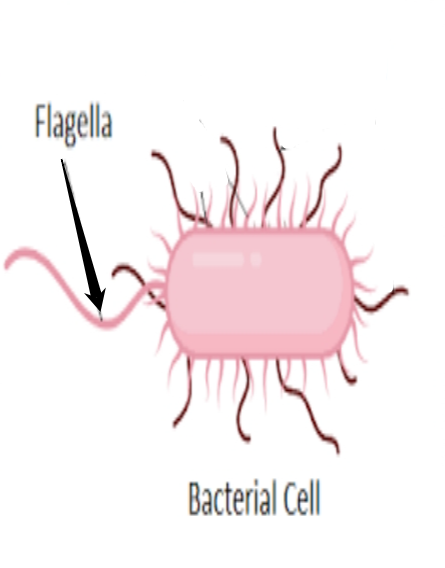
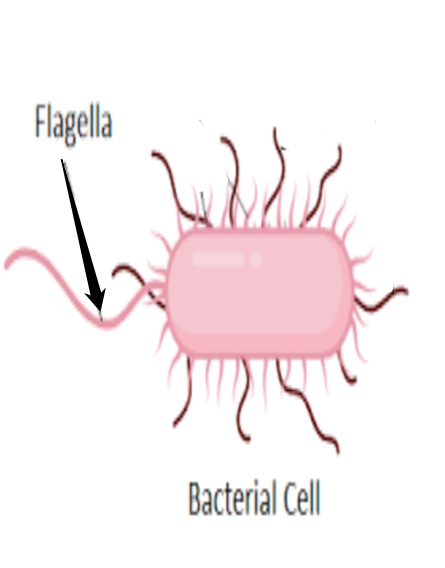
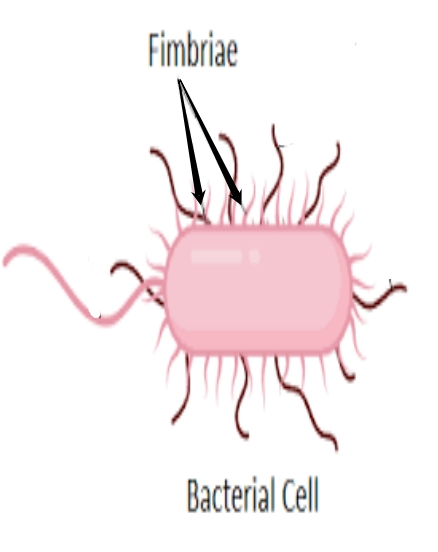
flagella
- used for locomotion (movement)
- allow a cell to move from one place to another
- microscopic hair-like structures (longer hair)
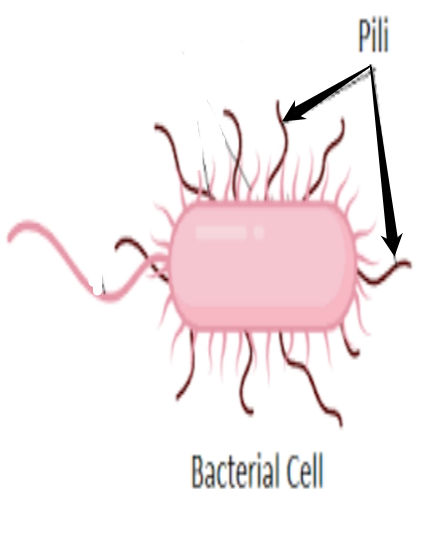
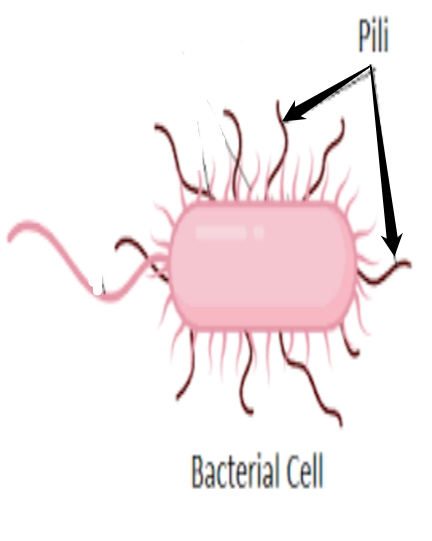
pili
- used to exchange genetic material during a type of reproduction called conjugation (transfer).
- short hair-like structures
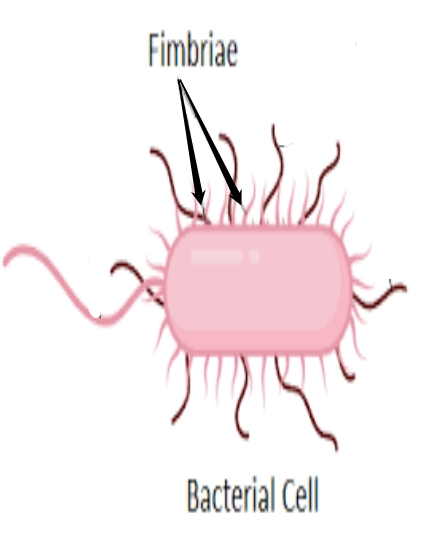
fimbriae
- used by bacteria to attach to a host cell
- are long filamentous polymeric protein structures located at the surface of bacterial cells
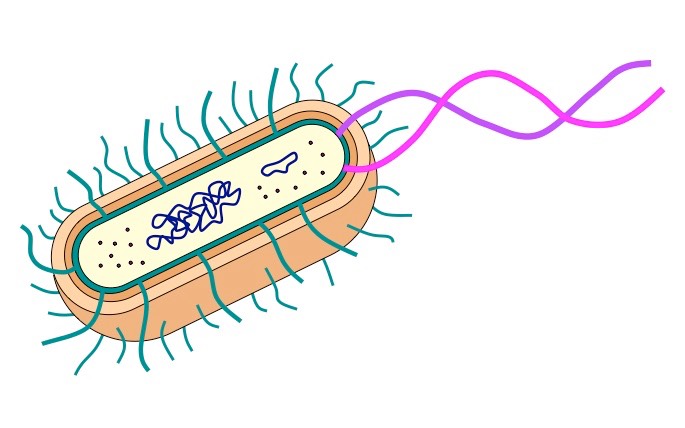
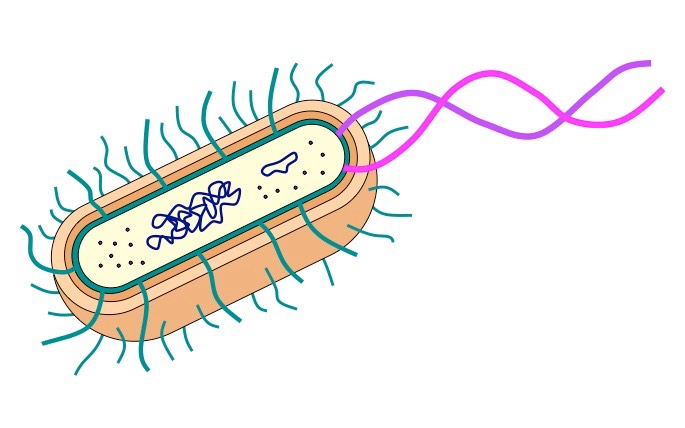
prokaryotic cells
At 0.1 to 10.0 µm in diameter, ________ are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells
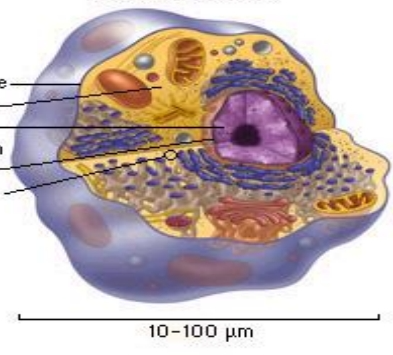
Eukaryotic cells
have diameters ranging from 10 to 100 µm
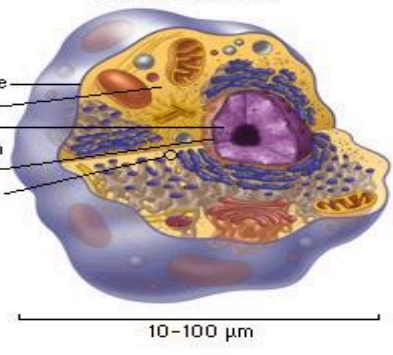
Eukaryotic Cell
- have true, well-defined and clear nucleus.
- nuclear materials are bound by a nuclear envelope.
- contains membrane-bound organelles which perform unique functions.
- Due to this division of labor among organelles, eukaryotic cells become more efficient, enabling them to be multicellular and grow larger.
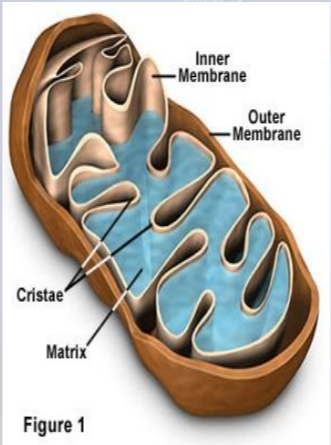
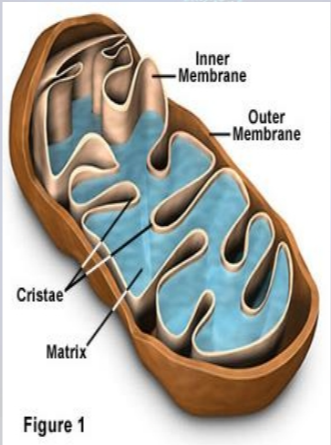
Mitochondrion
- Mito = Mighty/Power
- known as the powerhouse of the cell
- breaks down food molecules so the cell has the energy to perform its processes.
- used in Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production or cellular respiration
- oval-shaped, double-membrane organelles that have their own ribosomes and DNA.
- Each membrane is a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins.
- The inner layer has folds called cristae (sing = crista).
- The area surrounded by the folds is called the mitochondrial matrix. The cristae and the matrix have different roles in cellular respiration.
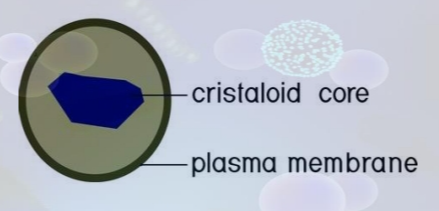
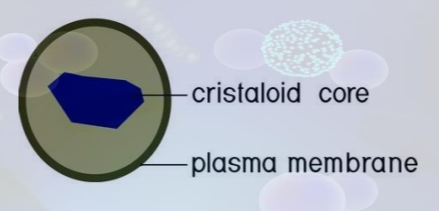
Peroxisomes
- are small, round organelles enclosed by single membranes
- carry out oxidation reactions that break down fatty acids and amino acids
- detoxify many poisons that may enter the body
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
the source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level.
Glyoxysomes
which are specialized peroxisomes in plants, are responsible for converting stored fats into sugars.
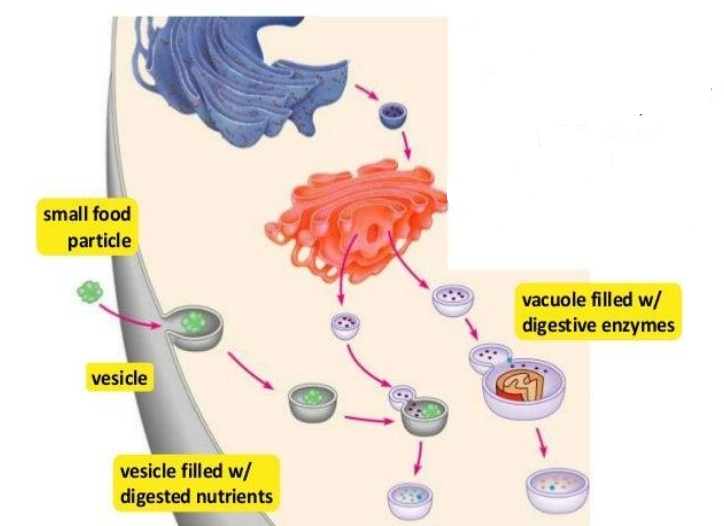
Vesicles and Vacuoles
- are membrane-bound sacs that function in storage and transport.
- moving material around cell
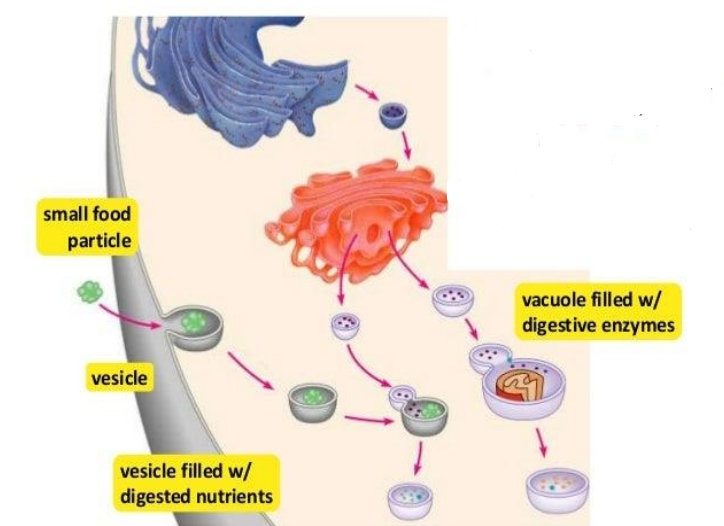
vesicles
- The membranes of _____ can fuse with either the plasma membrane or other membrane systems within the cell.
vacuole
- The membrane of a ______ does not fuse with the membranes of other cellular components.
Endomembrane System
- (endo = “within”) is a group of membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells that works together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins.
- includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, and vesicles, and the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus.
-not technically within the cell, the plasma membrane is included in the ______ because it interacts with the other endomembranous organelles.
- does not include the membranes of either mitochondria or chloroplasts.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- a series of interconnected membranous sacs and tubules that modifies proteins and synthesizes lipids.
- The membrane of the _______, which is a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins, is continuous with the nuclear envelope
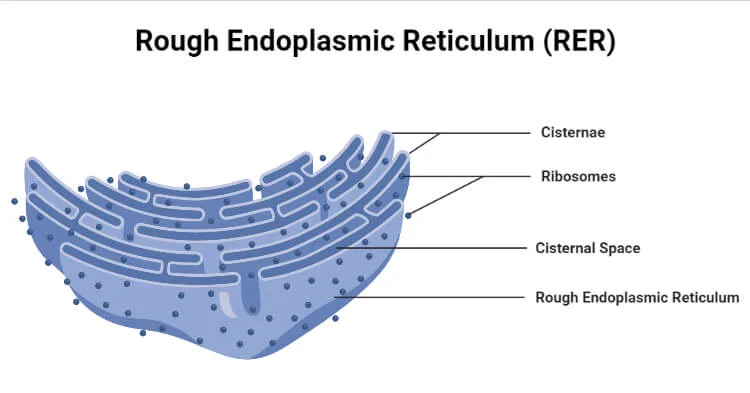
lumen or cisternal space
hollow portion of the ER tubules is called ______
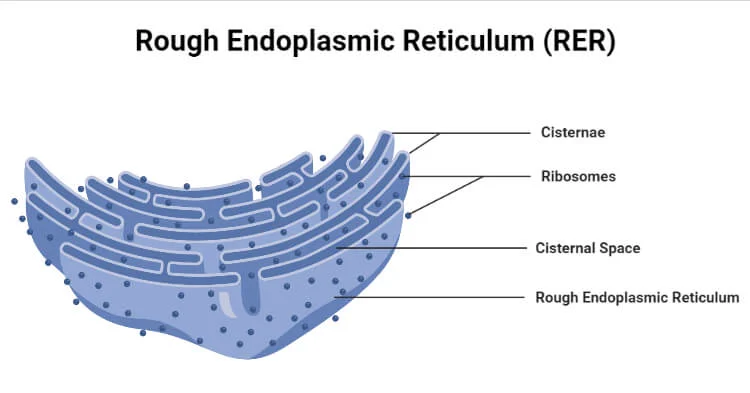
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
- the ribosomes attached to its cytoplasmic surface give it a studded appearance when viewed through an electron microscope.
- also makes phospholipids for cellular membranes.
- engaged in modifying proteins (such as enzymes) that will be secreted from the cell, it would be correct to assume that the ____ is abundant in cells that secrete protein
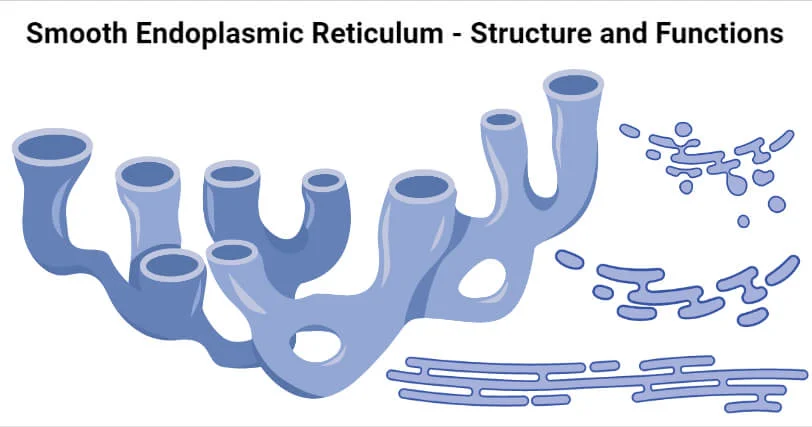
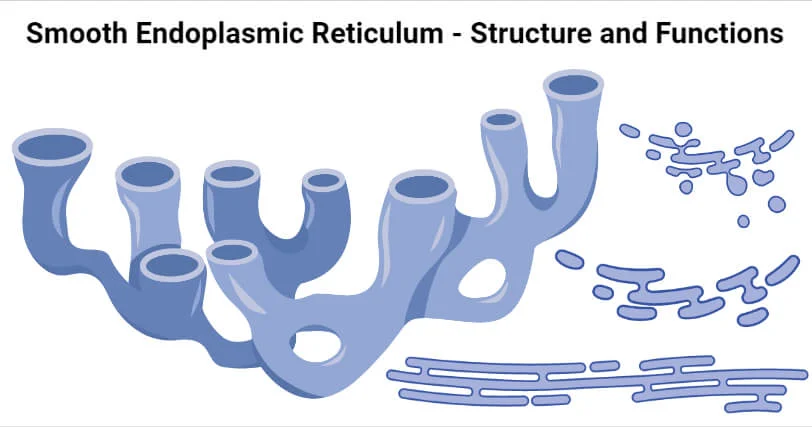
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
- is continuous with the RER but has few or no ribosomes on its cytoplasmic surface.
- synthesis of carbohydrates, lipids, and steroid hormones; detoxification of medications and poisons; and storage of calcium ions.
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
responsible for storage of the calcium ions that are needed to trigger the coordinated contractions of the muscle cells
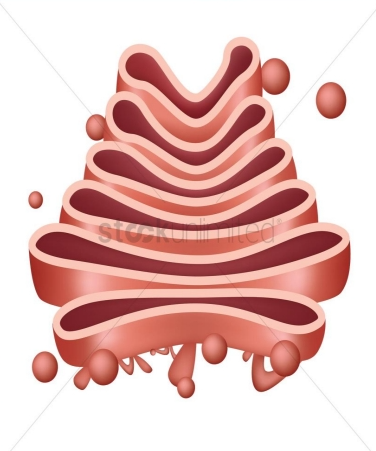
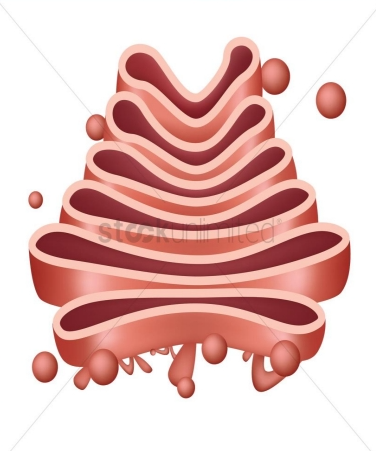
Golgi Apparatus (Golgi body)
- Sorting, tagging, packaging, and distribution of lipids and proteins take place in the______, a series of flattened membranes.
- Before reaching their final destination, the lipids or proteins within the transport vesicles still need to be sorted, packaged, and tagged, so that they wind up in the right place.
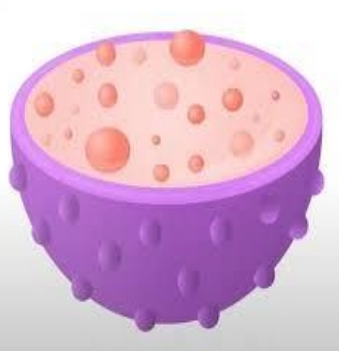
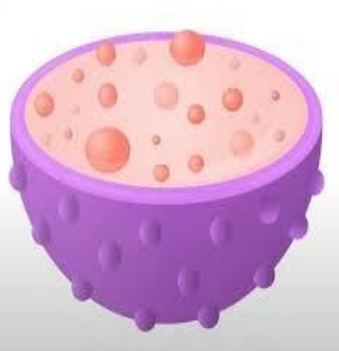
Lysosomes
- use their hydrolytic enzymes to destroy pathogens that might enter the cell.
- considered to be parts of the endomembrane system.
- the digestive component and organelle recycling facility of animal cells
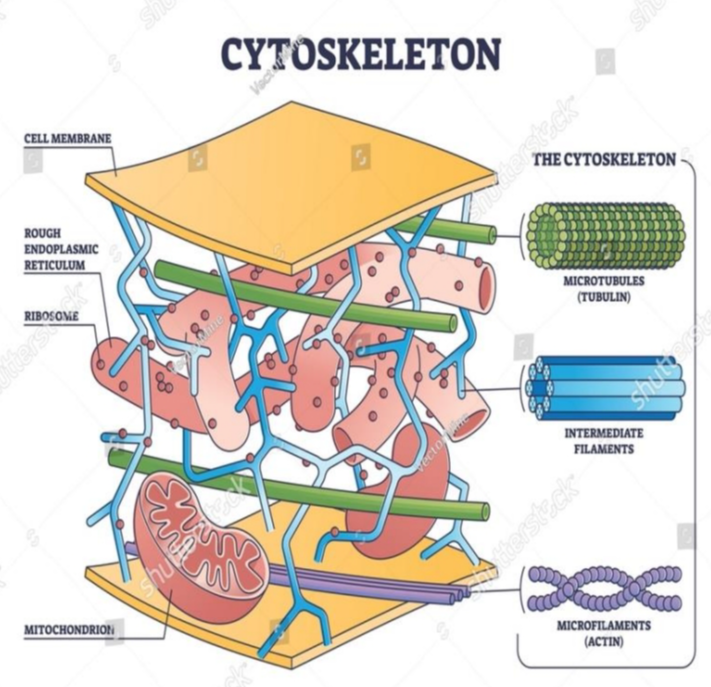
Cytoskeleton
- this network of protein fibers is known as the ________
- a network of protein fibers that help maintain the shape of the cell, secure some organelles in specific positions, allow cytoplasm and vesicles to move within the cell, and enable cells within multicellular organisms to move.
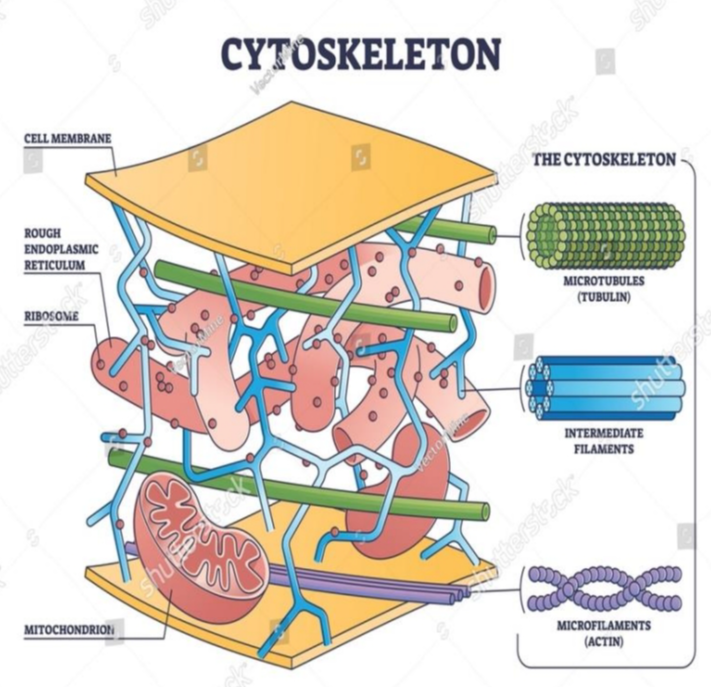
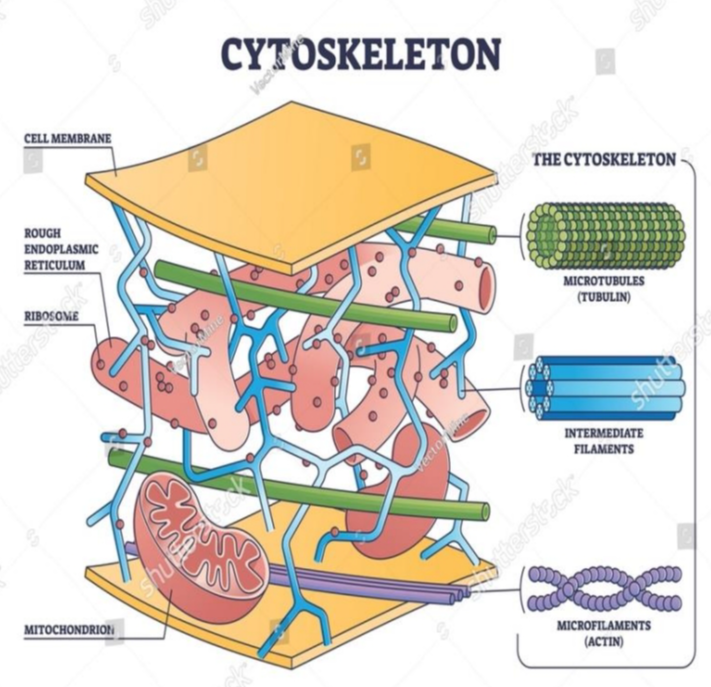
3 types of fibers within the cytoskeleton
microfilaments
intermediate filaments
microtubules
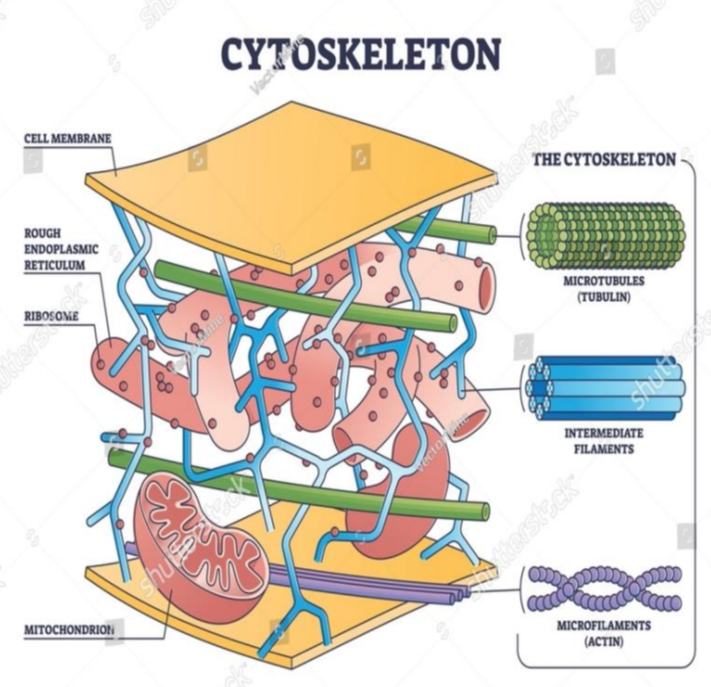
Microfilaments
provide rigidity and shape to the cell
Intermediate Filaments
- have no role in cell movement
- Their function is purely structural maintaining the shape of the cell, and anchor the nucleus and other organelles in place.
Microtubules
- help the cell resist compression, provide a track along which vesicles move through the cell, and pull replicated chromosomes to opposite ends of a dividing cell.
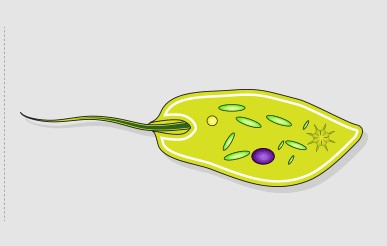
Flagella
singular = flagellum
- a las-like appendage that protudes from the cell body
- are long, hairlike structures that extend from the plasma membrane and are used to move an entire cell (e.g., sperm cell, Euglena).- cell has just one _____
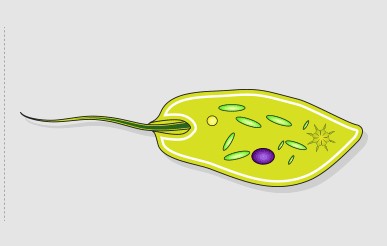
Cilia
singuler = cilium
- are slender protuberances that project from the much larger cell body
- are present, however, many of them extend along the entire surface of the plasma membrane.
- short, hair-like structures that are used to move entire cells (such as Paramecium) or substances along the outer surface of the cell (for example, the cilia of cells lining the Fallopian tubes that move the ovum toward the uterus, or cilia lining the cells of the respiratory tract that trap particulate matter and move it toward your nostrils).
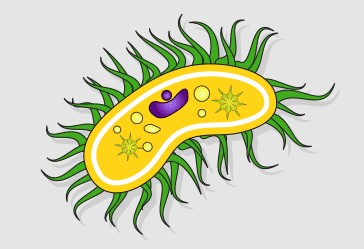
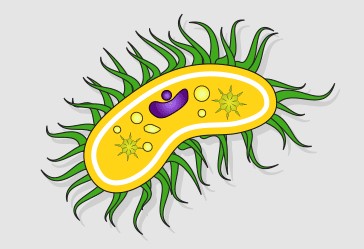
prokaryotic cell
cell membrane is present
prokaryotic cell
Nuclear membrane, membrane-bound organelles, chloroplasts, and mitochondria are absent
prokaryotic cell
it has small ribosomes
prokaryotic cell
has singular and circular chromosomes
eukaryotic cell
cell membrane, nuclear membrane, membrane-bound organelles, chloroplasts, and mitochondria are present
eukaryotic cell
has large ribosomes
eukaryotic cell
chromosomes are multiple; double helix