HCS 2204 Midterm
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
It is what it is.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
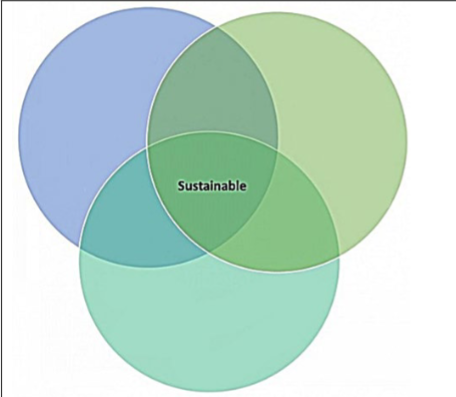
What are the three parts of Sustainability and their components?
Sustainability is the idea that we must conserve the resources we have now for the sake of the future and each individual circle is an aspect greatly impacts the goals of sustainability.
Economy (Blue) - employment of farmers and productivity
Society (Green) - livability and accessibility
Environment (Teal) - Pollution and weather change
What us a dicotyledon?
A flowering plant that has an embryo with 2 cotyledons (seed leaves) (4 to 5 petal flowers) (branched)
Monocotyledons - have an entire/ complete seed like grasses (3 to 6 petal flowers) (Parallel)
Polyploids in Plants (benefits)
Three or more complete sets of chromosomes
They are larger in cell size and plant size
Less tolerant to environmental stress
less subject to the effect of mutation and greater genetic diversity when they sexually reproduce.
Increased vigor
What is the center of origin?
The geographical region from which a species originated
They preserve genetic diversity (germplasm) of crops and their wild relatives
Grafting
A horticultural technique what joins two or more plants together so that they grow as one.
Accession
A distinctly, uniquely identified sample of seeds, that is maintained as a part of a germplasm collection
Germplasm
Genetic resources such as seeds, tissues, and DNA sequences that are maintained for the purpose of animals and plant breeding, conservation efforts, agriculture, and other research.
What are the key phenotypic traits in domestication?
Elimination/ reduction of natural seed dispersal (non-shattering) (most important domestication trait)
Reduction in seed dispersal aids
Trends towards increasing seed/fruit size
Loss of germination inhibition
Synchronous tillering
More compact growth habit
What is the importance of selection in plant breeding?
Selection exploits genetic variation to create distinct plants
It is primarily based on phenotype (plant appearance) and increasingly quantitative measurements are required.
What are some hybridization breeding systems?
Different kinds of pollination systems result in different species changing.
Open pollination - 5-50 elite parents are crossed this occurs with help from wind and pollinators
Self pollination - most common for annual species with limited access to insects (soybeans)
Hand pollination (human intervention) - breeder approach to ensuring that precise crosses of specific plants. good for achieving crosses from self pollinated plants
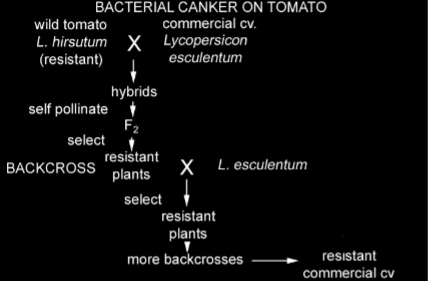
Back-cross breeding hybridization
Where the initial F1 generation is not crossed with itself but with another parent to produce progeny more related to one parent than another.
Double cross hybrids in corn requires inbred parent lines, male sterile lines, and hybridization (within species)
Heterosis (hybrid vigor)
Inbreeding to create a larger crop offspring. Pollen from one plant to pollinate another. They stop the pollination of one plant so that they can cross breed it with another (detasseling - genetically modifying it to be sterile).
Heterosis
the tendency of a crossbred individual to show qualities superior to those of both parents.
occurs when crossing two genetically unrelated inbred parents to create a hybrid.
contributes greatly to the high productivity in maize
Inter-species breeding systems
Breeding Between different species
Intra-species hybrid
Breeding between the same species
Inbreeding Depression
reduced phenotypic expression (lost yield) resulting from homozygosity
Hybrid Vigor
Increased phenotypic expression (increased yield) resulting from heterosis
GMO Mechanisms
Roundup Ready (RR) - transgenic plants that include a gene (extracted from bacteria) that confers resistance to glyphosate. Blanket-sprayed glyphosate to RR crop to kill of susceptible weeds but not the crop
Bt - transgenic plants that include a gene (extracted from bacteria) that produces a enzyme that digests caterpillar gut wall. Predominantly used for corn and cotton (reduced insectide use by 30%)
What are the pros and cons or GMO in plants
Pros
yield protection (prevent yield loss due to weeds and insects but do not increase yield)
Improved nutritional value
Longer shelf life
Weather resistant
Cons
Lack of public awareness
additional expense
resistant weeds
loss of biodiversity
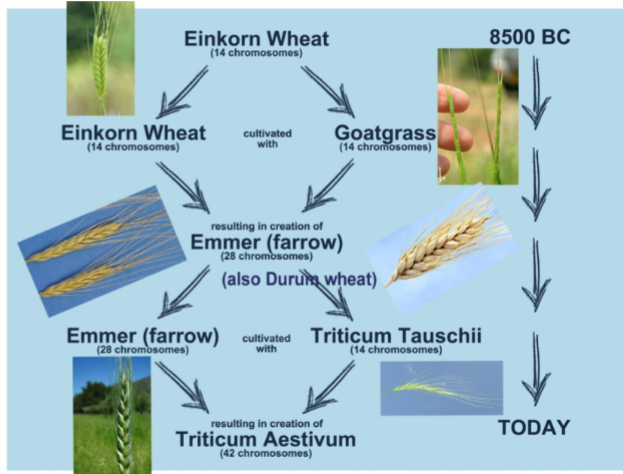
Crop evolution of wheat
The ancestral wheat is a diploid 2n=14
become hybridized with goat grass and became tetraploid
Goat grass is hybridization with another species creating a triploid
Finally, further chromosome doubling produced the hexaploidy Triticum aestivum (6n=42)
In what way might humans have contributed to the evolution of crop plants? What are characteristics (or traits) of domesticated crops that differ from their wild relatives?
Humans have contributed to the evolution of plant through artificial selection favoring more desirable traits like large fruit/ grain size, uniform ripening, and increased yield. Domestication. non-shattering.
Plant Variety Rights and their significance in plant systems
A form of intellectual property protection for new plant varieties, granting breeders exclusive right sto control commercial use of their creations such as sale and reproduction.
This encourages innovation and investment because it incentivizes the development of improved plants overall.
Plant Taxonomy and their significance in plant systems
The identification, description, classification, and naming of plants
important for organizing and keeping track of plant knowledge. accuracy and communication become easier with a standard system
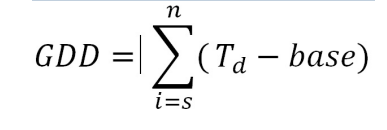
Growing degree days equation and importance in agricultural science
Used to provide a metric for tracking crop development, predicting harvesting times and optimizing resource application which reduces variable cost
GGD = growing degree days
s = Start date of measurements
n = End date of measurements
Td = base temperature for each day
base = base temp for the crop in question
The importance of light for plant systems
light is a key determinant of seasonality
cloudiness
canopy management (avoid shade, optimize planting density and breed for short plants)
Greenhouse lighting - reduced energy costs LED and different wavelengths like red and blue lights
Evapotranspiration (ET)
water is lost by leaves because the stomata opens during photosynthesis. as CO2 enters the leaf, H2O leaves the leaf
ET = plant transpiration (surface evaporation) and soil evaporation
primary way of plant cooling
What are some management options to reduce water use?
Low vs high volume irrigation - drip rather than flood
Mulch - eliminates soil evaporation
Species selection - high water efficiency crops and plants
canopy management - weed removal and dense canopy
What is the composition of air?
Nitrogen - 78%, Oxygen - 21%, Carbon Dioxide - 0.04%
How do plants benefit from shelter (from wind)?
Reduced wind speeds (mechanical abrasion)
Conserve water loss (lower ET)
Can promote wild life (both birds and small rodents)
What is the plant boundary layer?
A micro-layer of static air that surrounds all stationary objects
Can slow down the movement of water vapor out the leaf and result in warming on a cool day.
Heat absorption can also lead to differences in leaf temp and air temp.
In what ways does wind affect plants?
1) Air movement affects plant temp and water loss. Increase air movement = more water loss.
2) Mechanical Disturbance caused by wind moving over plants which slow stem elongation
3) Wind reduces Plant boundary layer
4) Low air flow (and high humidity) can promote the development of fungal and bacterial diseases.
5) Wind Erosion cause cause losses of top soil and make soil more sandy and dry.