52 Root Caries, Erosion, NCCL + Diff. Diagnosis
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
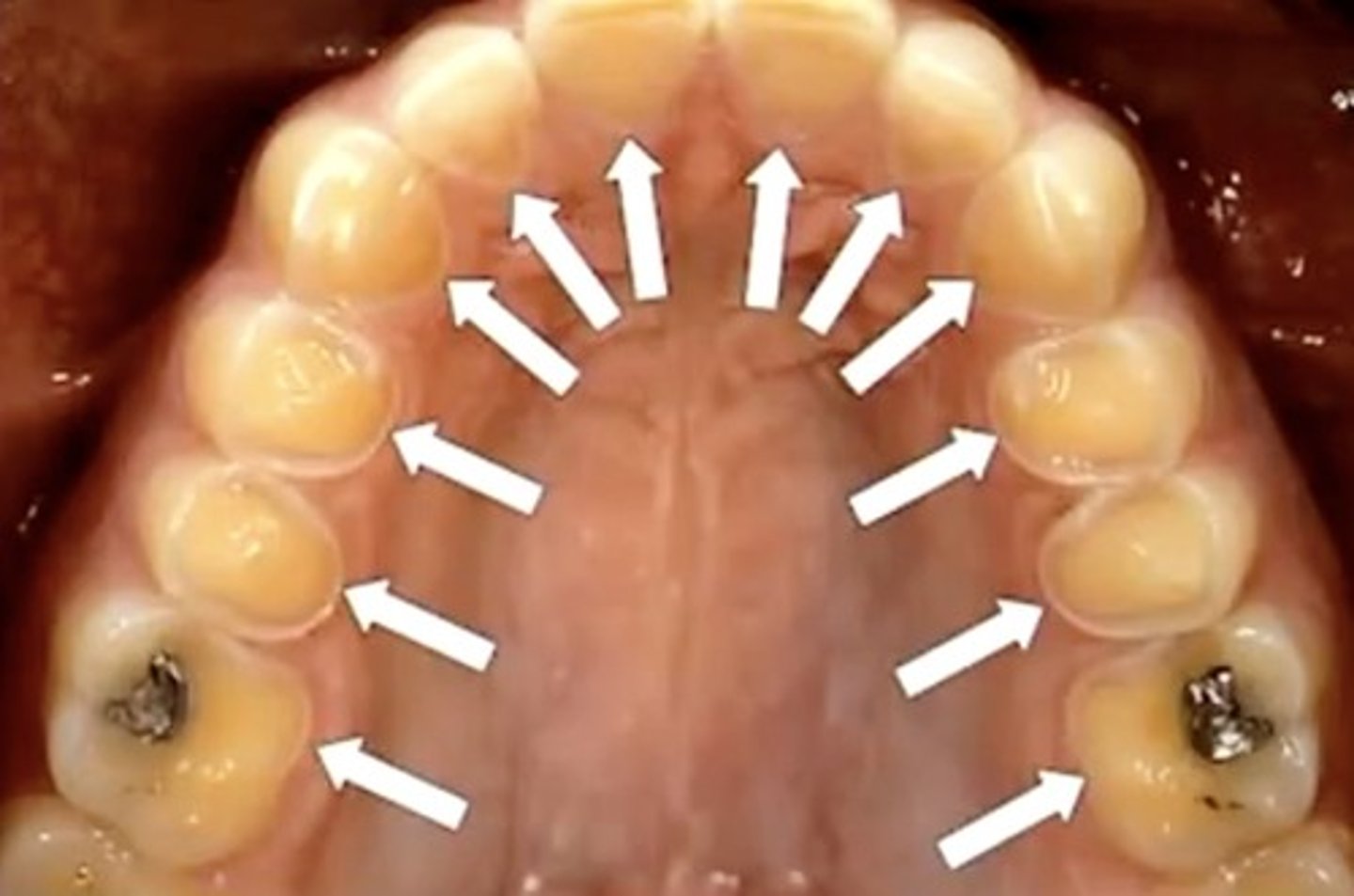
which surface is most at risk for a new caries lesion on a 68 yr old
root surface
a caries lesion originating on the root surface which is exposed due to gingival recession
root caries
where would you find initial lesions on primary teeth
occlusal surface
the more recently exposed tooth surfaces are the ones most likely to have
caries
pH needed for lesion in enamel to develop
5.5
pH needed for lesion in dentin to develop
6.5
biofilm, carbohydrates, and sugars lead to
demineralization
healthy saliva, good oral hygiene, healthy diet, + fluoride intake aid in
remineralization
- encompasses endogenous + exogenous acidic + proteolytic chemical degradation of enamel + dentin
- as well as the piezoelectric electrochemical action on the collagen in dentin
biocorrosion
electricity resulting from pressure
piezoelectric
chemical, biochemical, +/or electrochemical action, which causes the molecular degradation of the essential properties in a living tissue
biocorrosion
tooth moves due to forces of chewing, piezoelectricity resulting from that pressure cause degradation
biocorrosion
gingivitis, periodontitis, + bone less can lead to an
increase in root caries
cementum on root surfaces is very
thin
dentists should provide even more proper oral hygiene instruction for patients who have gingival recession and the development of caries on the root since the nerve is closer to the _________ towards the apex of the tooth
outside surface
what are the best toothbrushes to use
soft, narrow bristles and electric
differential diagnosis of other conditions that cause loss of tooth structure on cervical region (3aE)
attrition, abrasion, abfraction, erosion
the loss of tooth structure caused by wear in functional + parafunctional modes
attrition
attrition is typically seen in patients who
clenching/grinding (teeth are worn down)
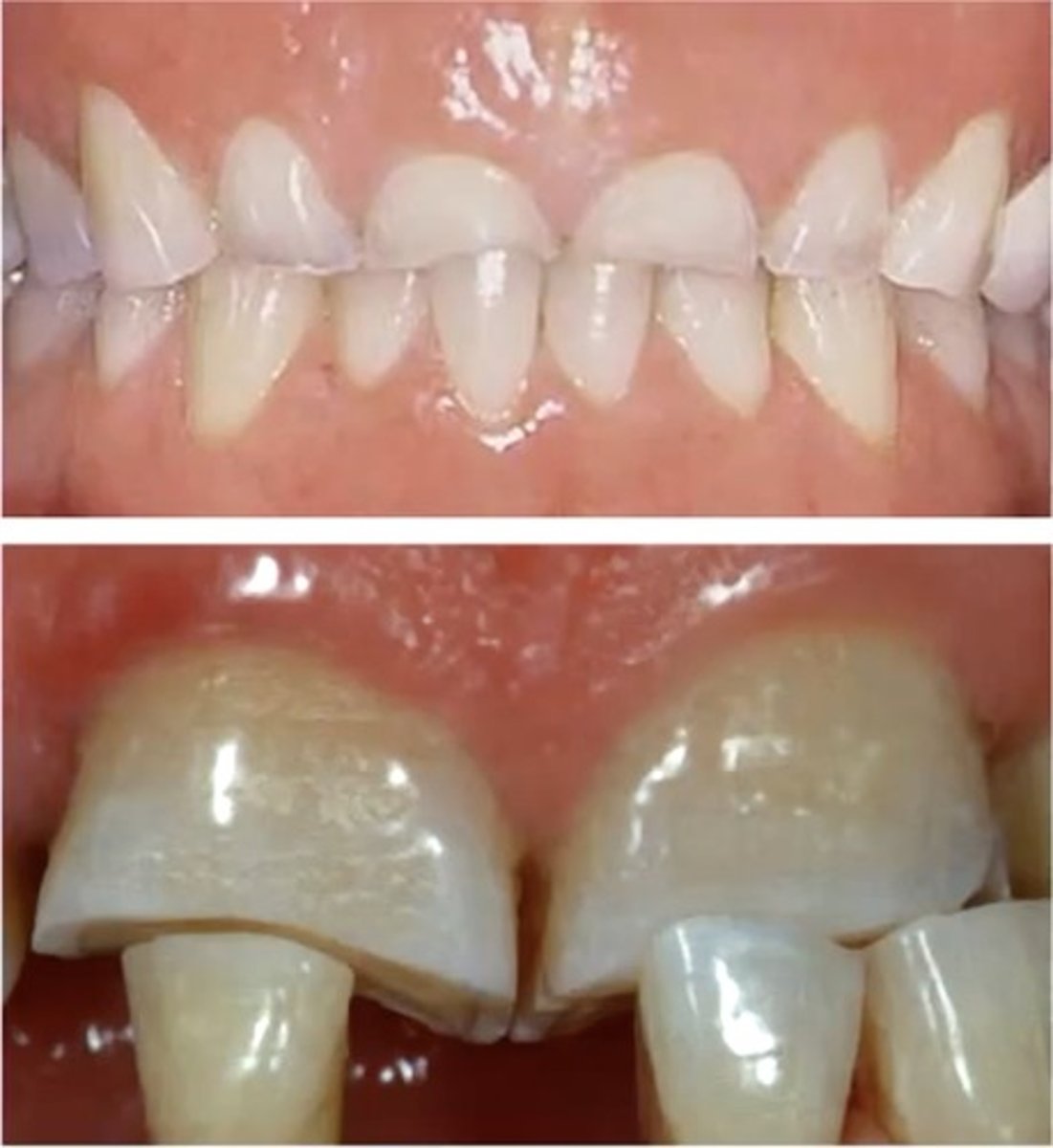
identify the type of differential diagnosis
attrition
the loss of tooth substance through mechanical means (ie tooth brushing, type of toothpaste); characterized by rounded lesions
abrasion
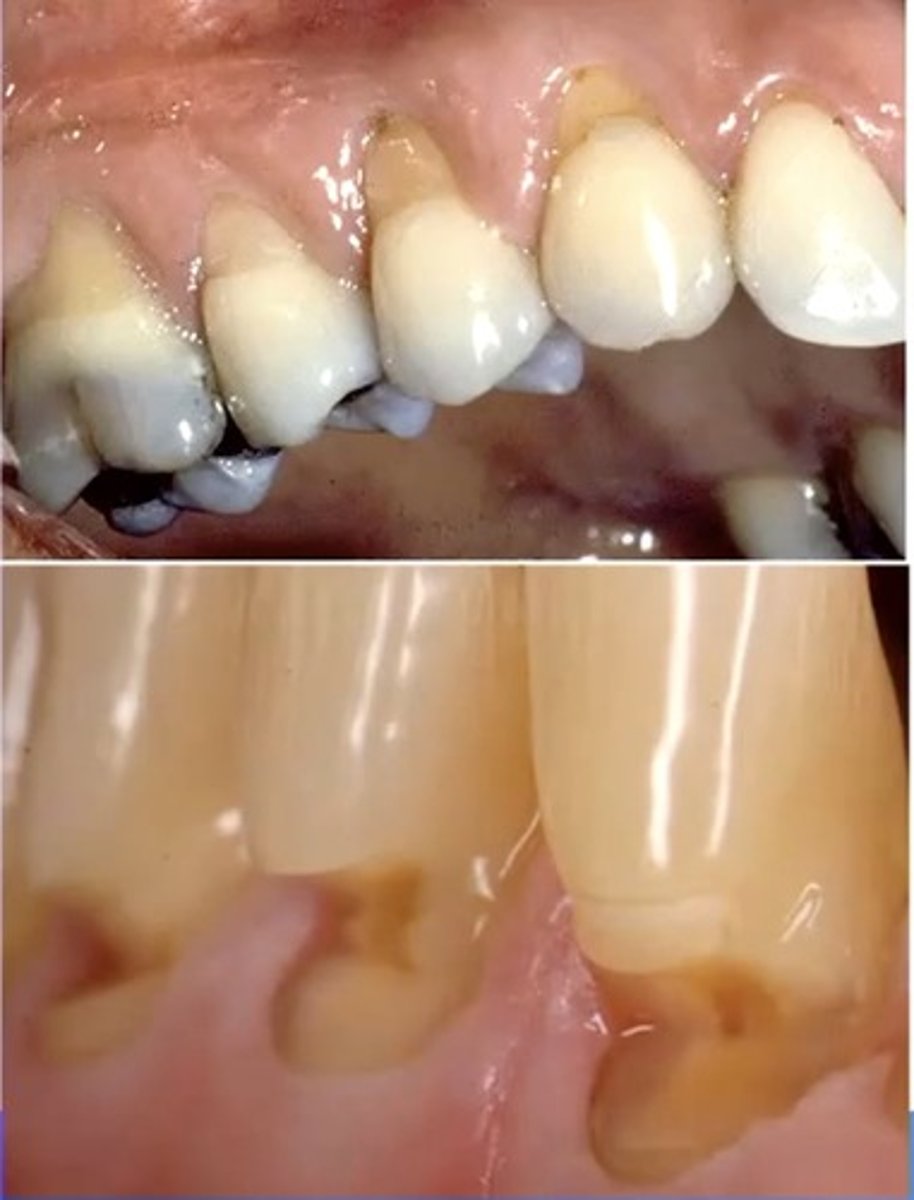
identify the type of differential diagnosis
abrasion
is abrasion caused by the toothpaste or the toothbrush
both (but more the toothbrush)
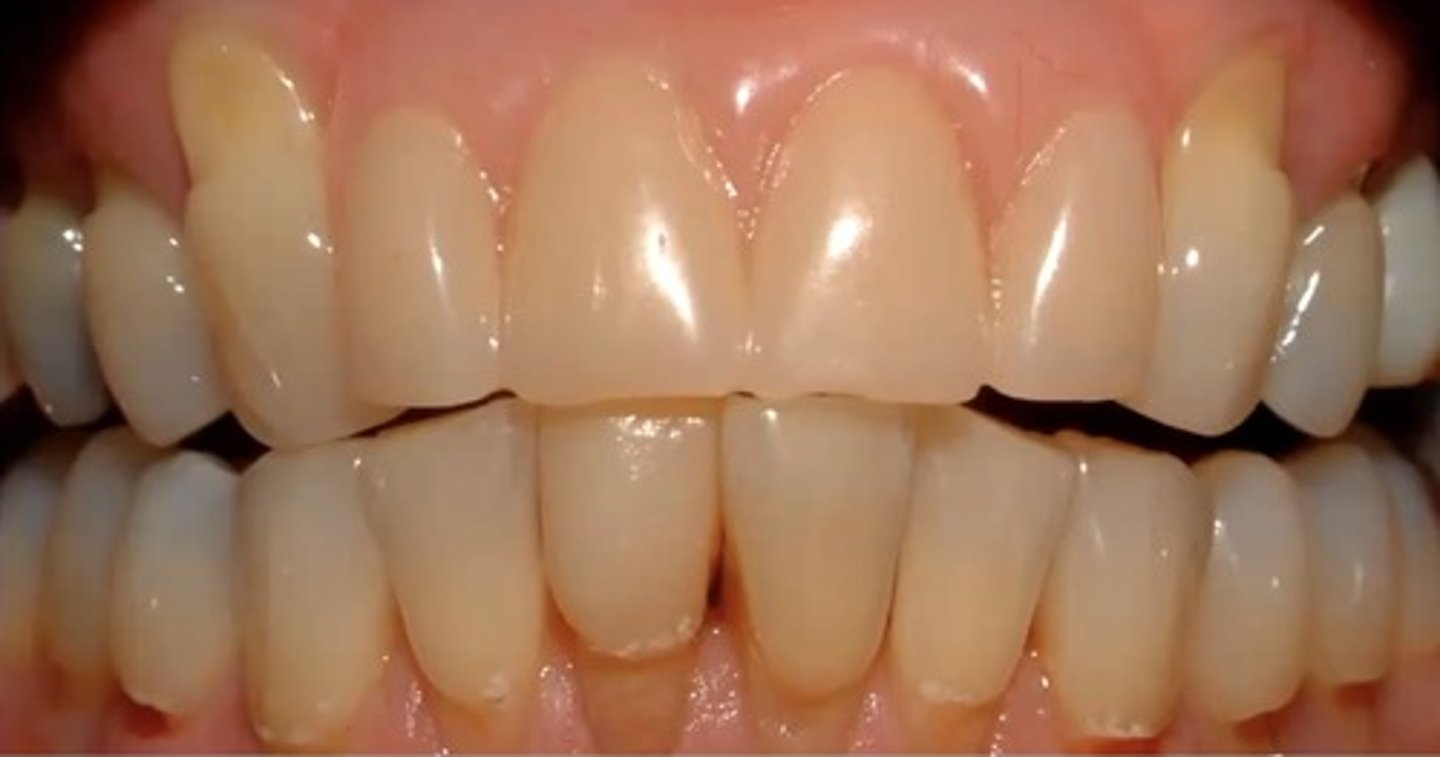
identify the type of differential diagnosis
abrasion
which teeth in the dentition would have the most pronounced abrasion
canines
a right handed patient will have more lesion on which side of their mouth
right side
the loss of tooth structure by chemical or idiopathic processes where patients remove a lot of their enamel; characterized by cupping lesions
erosion
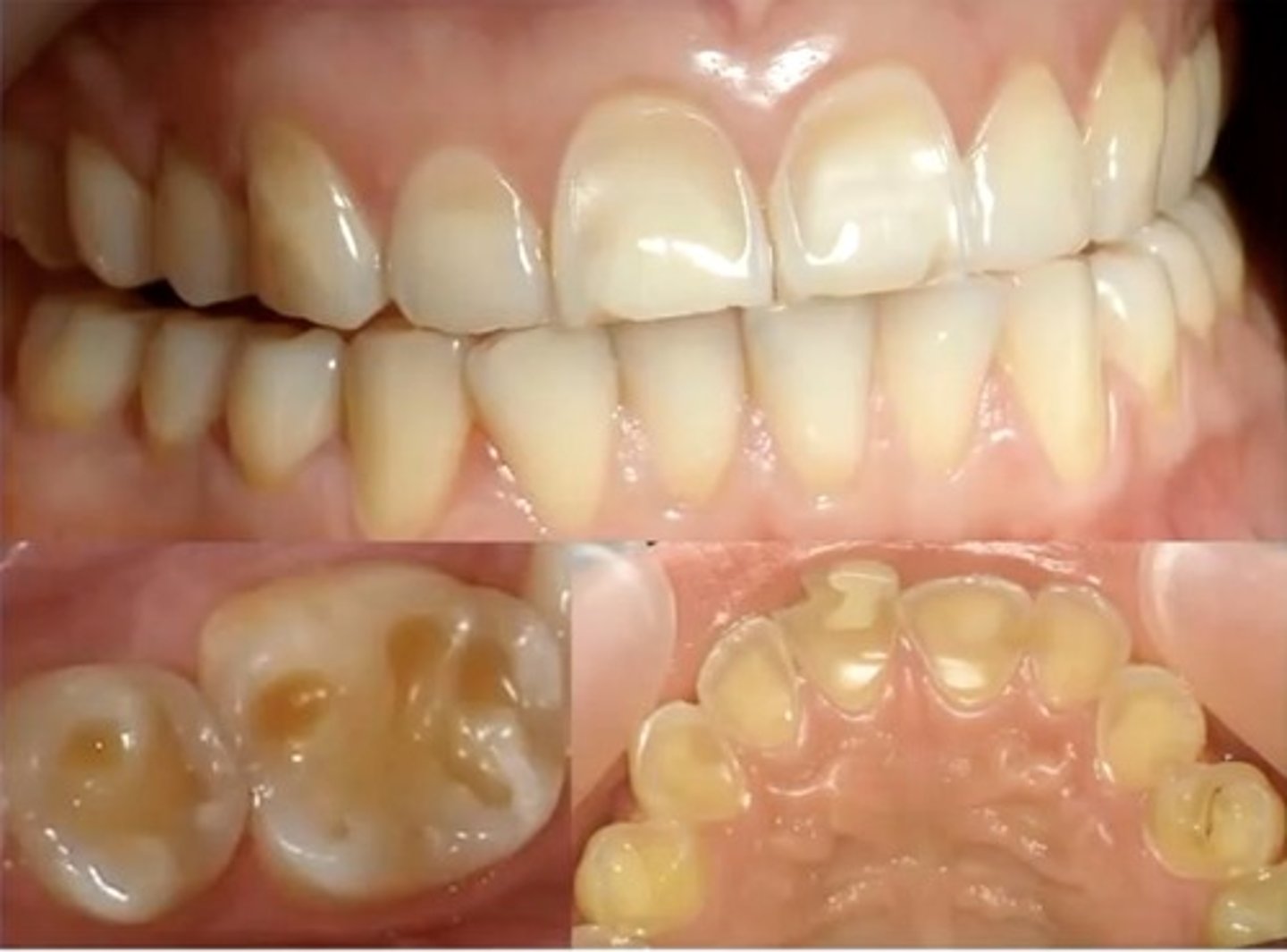
identify the type of differential diagnosis
erosion
6 dental erosion causes (DI REEF)
dietary, idiopathic, regurgitation, environmental, exposed dentin, flow of saliva
food-based dental erosion can be caused by all _______ beverages + ________-based drinks
carbonated; citrus
erode teeth with a pH as low as 3.0-3.8
wine
the acid produced in the stomach during the digestive process that can dissolve bone + teeth
regurgitation
sources of erosion from regurgitation
eating disorders, GERD (gastrointestinal disorder), chronic alcoholism
a patient population where regurgitation leads to erosion
bulimics
this is a clinical presentation of
regurgitation/erosion
regurgitation/erosion can be first be noticed on which tooth surface
lingual
possible sources of erosive acids are from exposure to chlorinated swimming pool water
environmental
seen in batter plant workers, picklers, + miners who are around the acidic fumes
erosion
in some individuals, saliva itself may be the cause of
erosion
in some individuals, salivary pH is _____ b/c of medications like vit. C, aspirin, + iron preps that alter the saliva
lower
lower salivary pH leads to more instances of
erosion
patients with dentin that is dissolving typically show _____ erosion on the ____ surfaces of the teeth
cupping; occlusal
erosion that we cannot find a definable cause
idiopathic
4 signs + symptoms of erosion (GDCT)
glossy/silky appearance, surface gloss dulling, "cupping", enamel texture loss
"cupping" erosion is seen most often on which teeth
mandibular (especially molars + premolars)
- angular (like a cutout)
- non-carious cervical lesion (NCCL)(no decay)
- subgingival (b/c of pivot point at neck of tooth = root)
- tooth flexion, multifactorial, maybe caused by tooth brush
abfraction
erosion is more _____, whereas abfraction is more _____
rounded; angular
abfraction is caused by which forces
clenching/grinding
best preventative measure and non operative procedure for a patient with abfraction
night guard
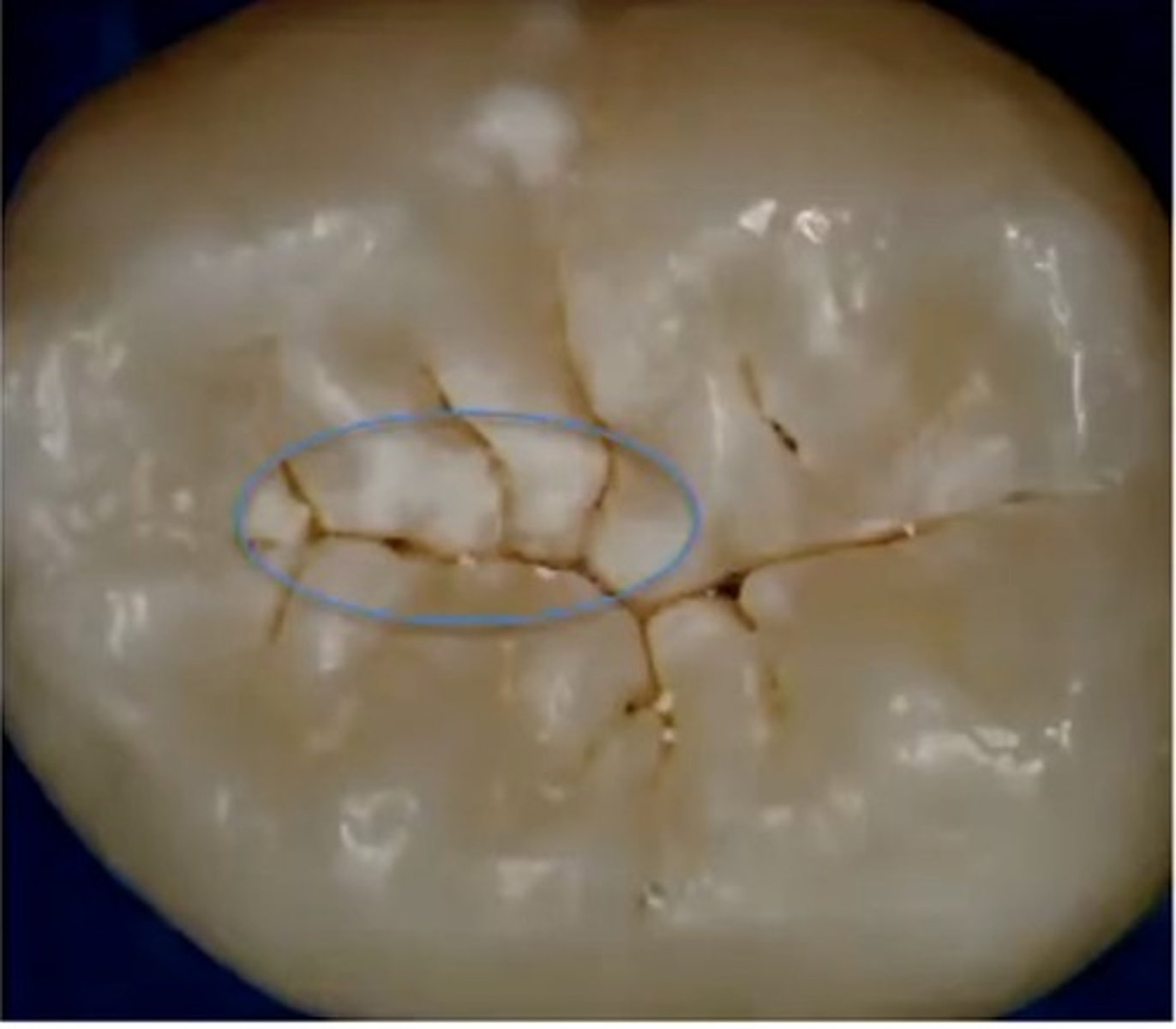
identify the lesion
initial
caries lesions are associated with
biofilm
caries lesions may become more ______ when dried
opaque
will follow the enamel development pattern + occur across multiple teeth
fluorosis
will usually occur in homologous teeth (teeth that developed at the same time)
hypoplasia
lesion not associated with a restoration
primary caries
caries left over by the dentist during restorative treatment
residual caries
lesions associated with a restoration
secondary caries/recurrent caries
secondary caries, fracture, marginal deficiencies, wear, + postoperative sensitivity
main reasons for direct + indirect restorations
can develop on exposed root surfaces and have the same etiological factors as primary coronal caries
root caries
longer retention of teeth + increase life expectancy often with comorbidities has led to an
increase in root caries diagnosis
the 2 classification for root caries
initial/non-cavitated lesions + extensive lesions
root caries can be
arrested
abrasion, abfraction, erosion, or non-caries cervical lesions (NCCL) need to be _________ from root caries
differentiated
refer to lesions around restorations
CARS/secondary caries/recurrrent caries
need to be differentiated from caries
non-caries opacities
opacity, hypoplasia, and fluorosis are examples of
enamel defects