AP Psychology Unit 1
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
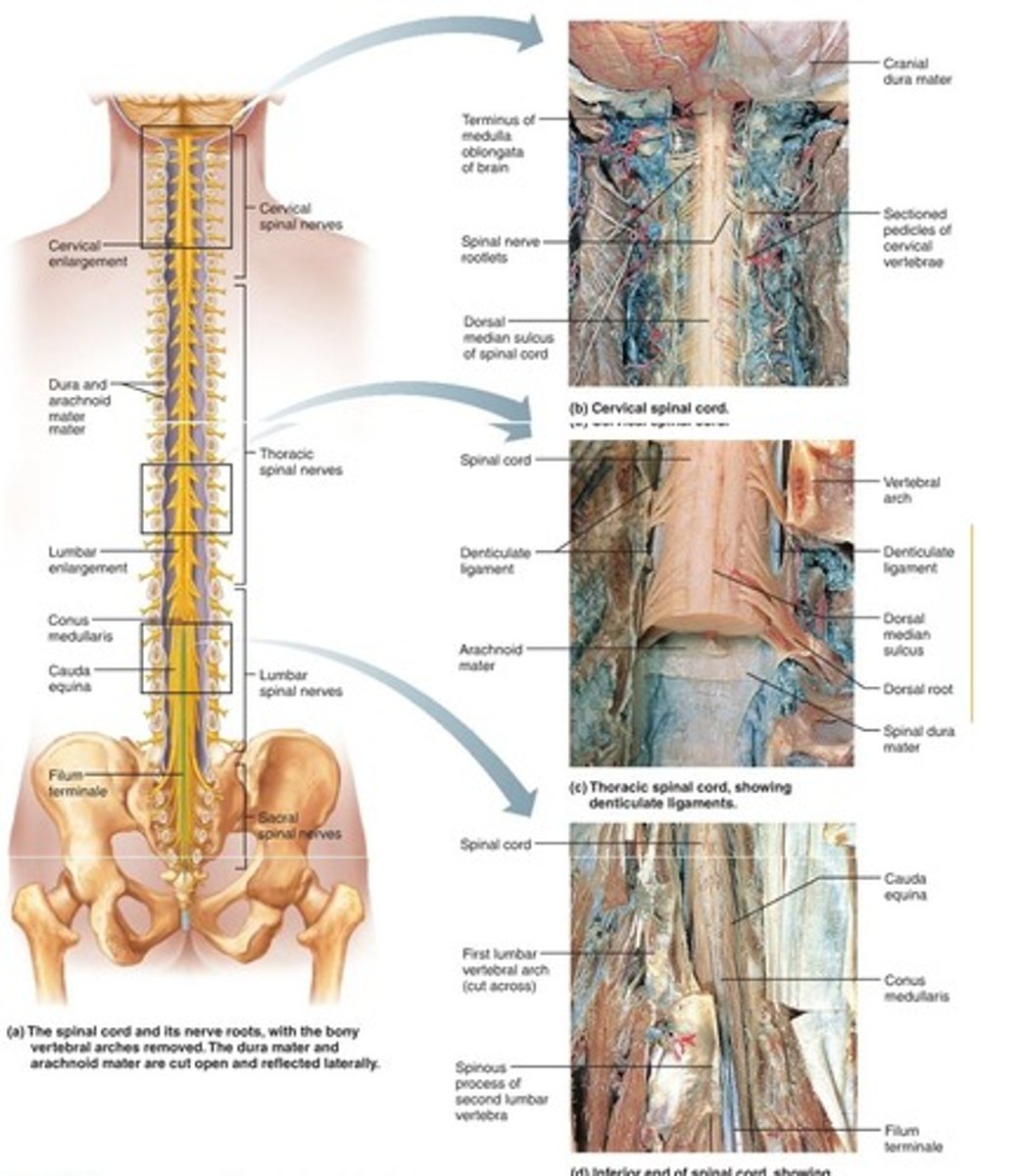
Spinal cord
Communication pathway between brain and body. Ex: Pulling your hand away from a hot stove via a reflex arc.
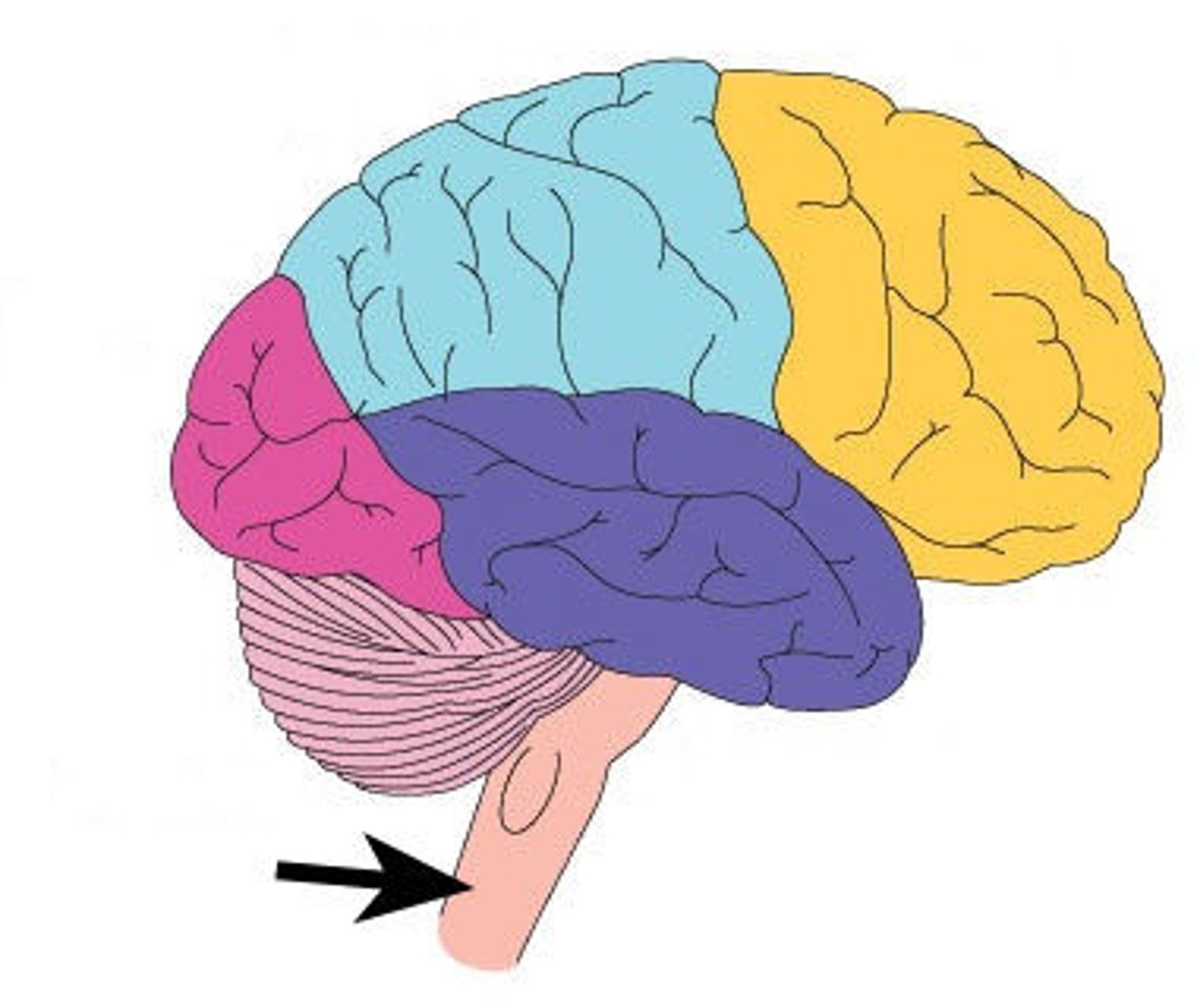
Brain stem function
Controls basic, autonomic functions such as breathing and heart rate. Ex: You do not have to consciously think about keeping your heart beating while you sleep.
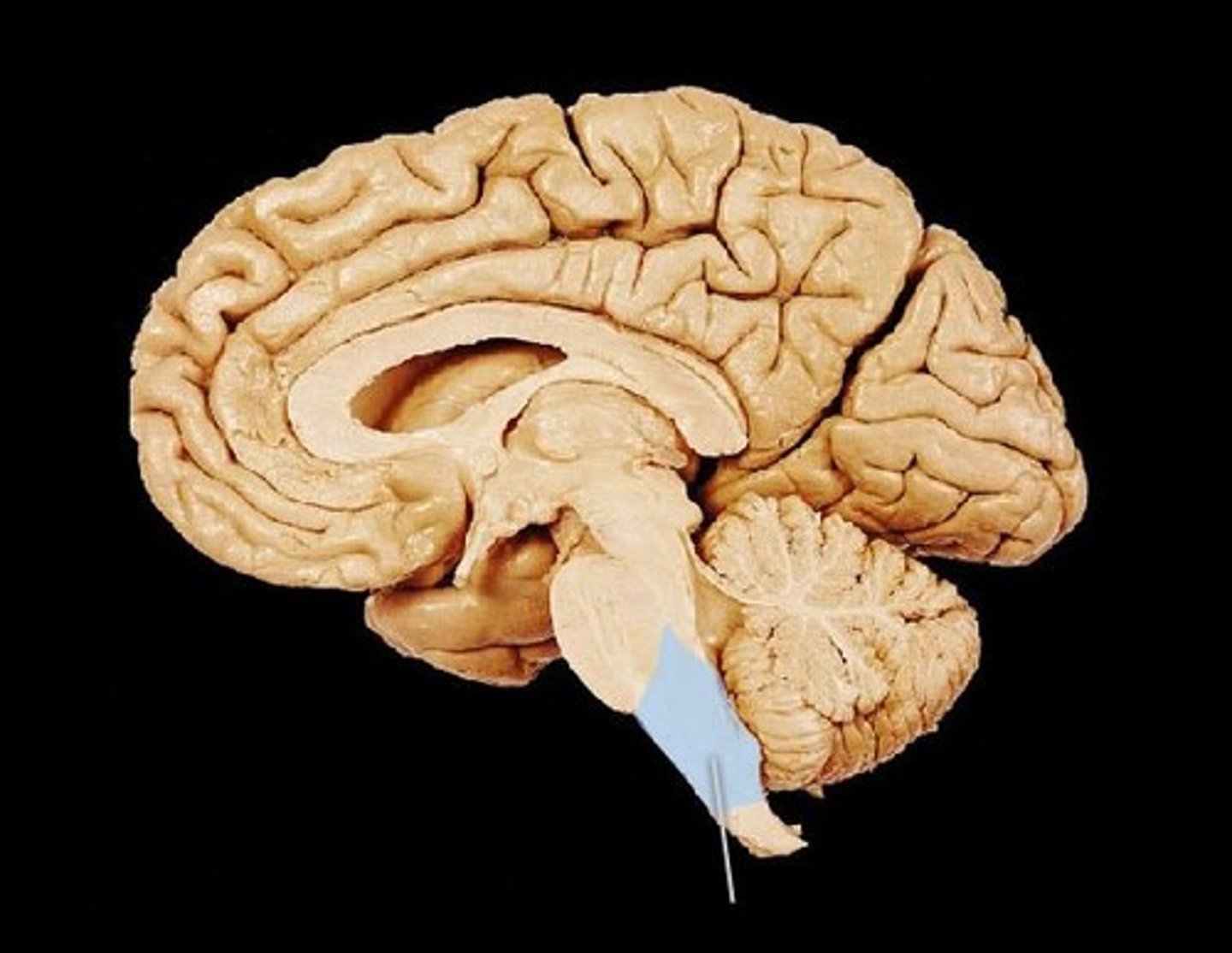
Medula
Part of the brain stem which regulates respiratory and cardiovascular systems. Ex: The medulla automatically increasing your heart rate during a stressful event.
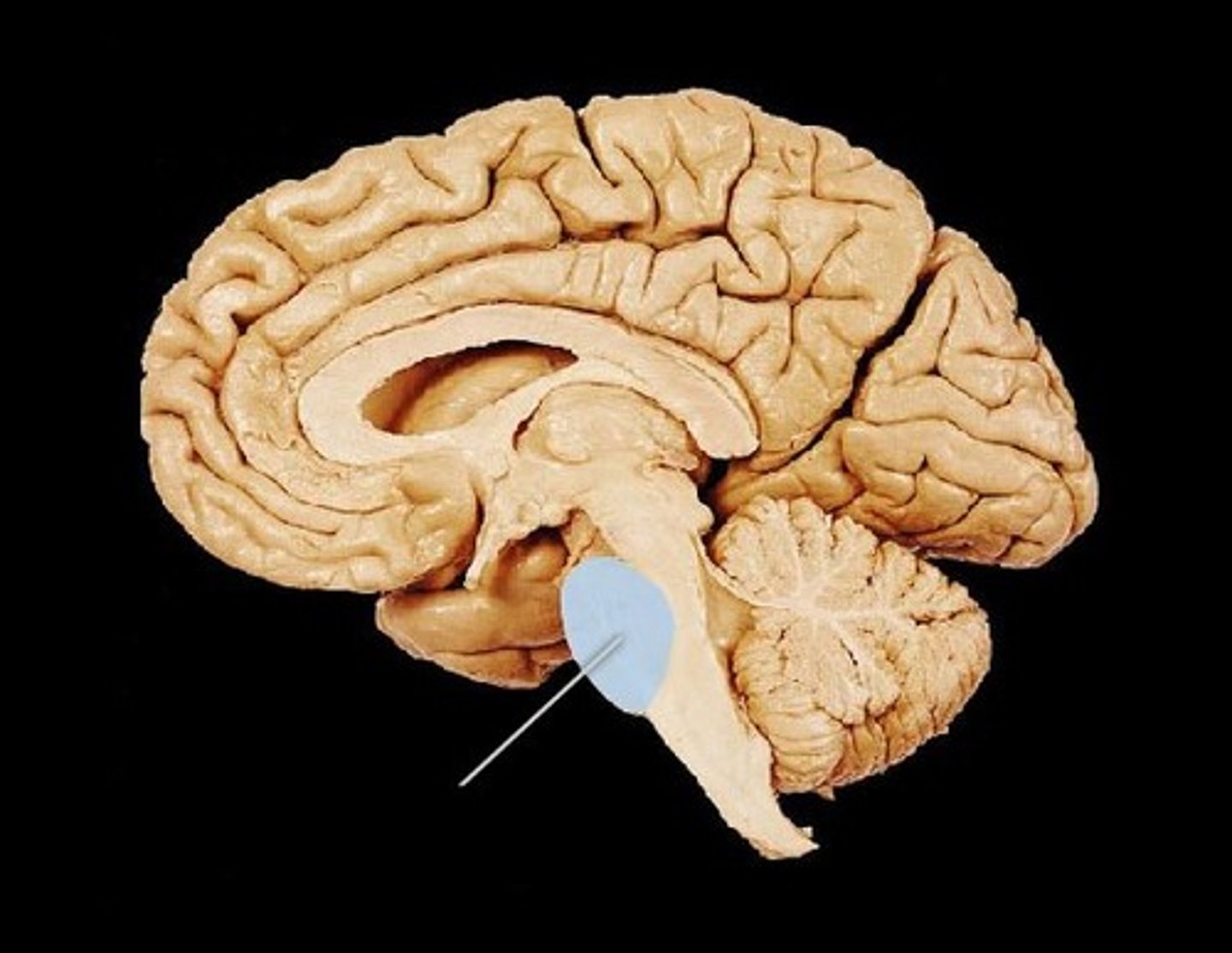
Pons
Part of the brain stem which connects parts of the nervous system, helps with movement. Ex: Coordinating the muscle movements required for facial expressions.
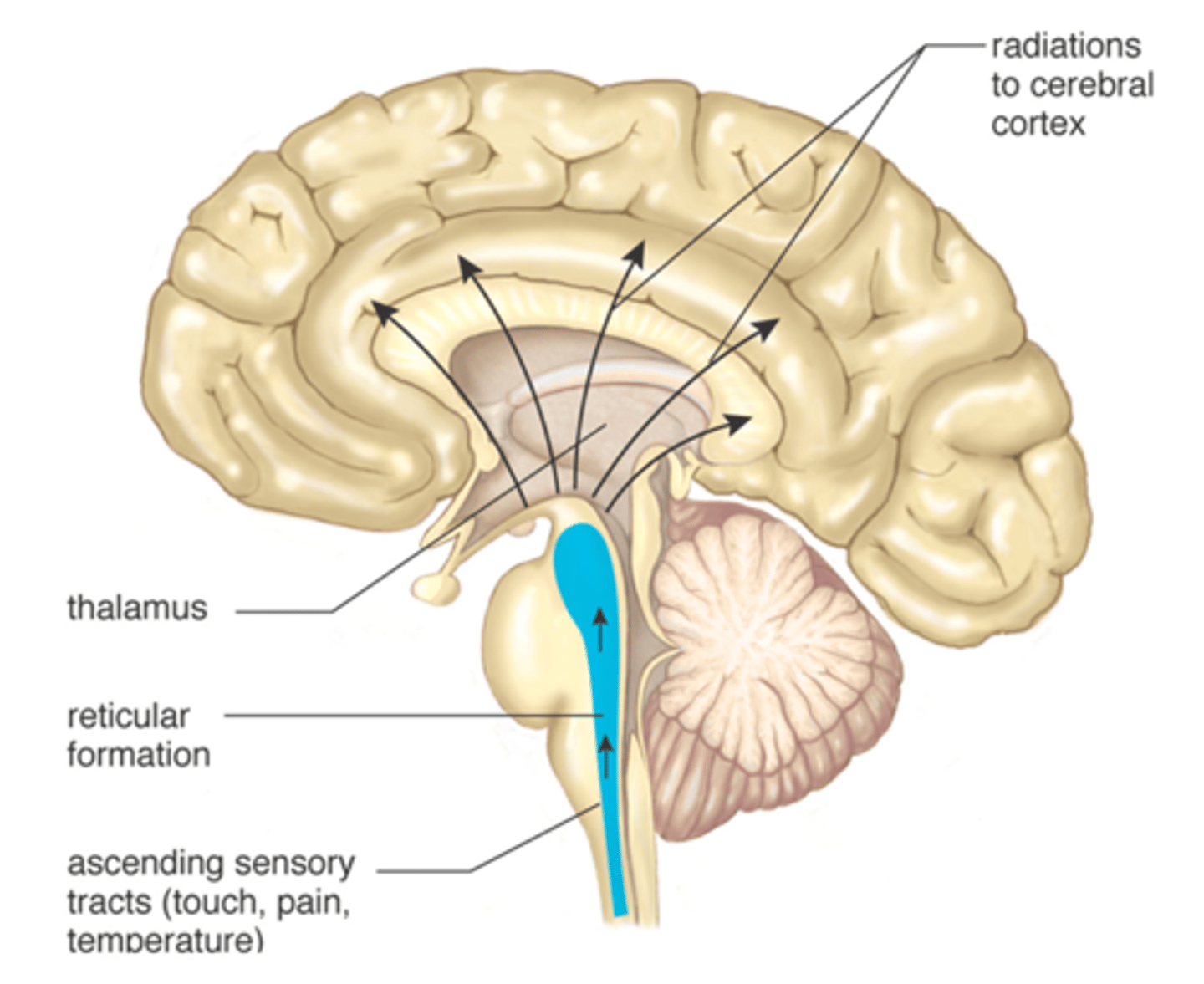
Reticular activating system
Part of the brain stem. Network of neurons which controls alertness, wakefulness, and attention. Ex: Snapping to attention when you hear your name called in a crowded room.
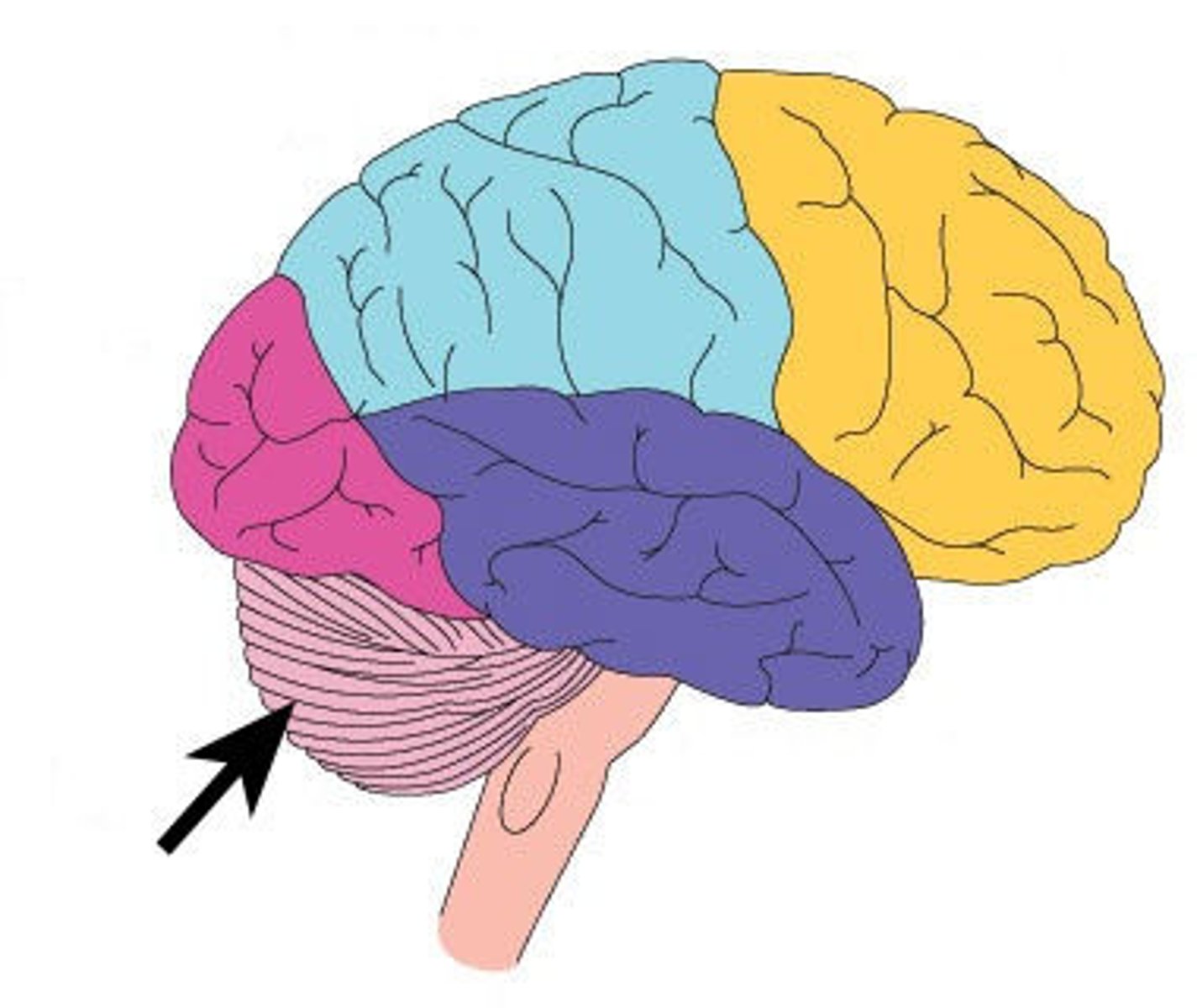
Cerebellum
Part of the brain which controls voluntary functions and motor skills such as coordination. Ex: Maintaining your balance while riding a bicycle.
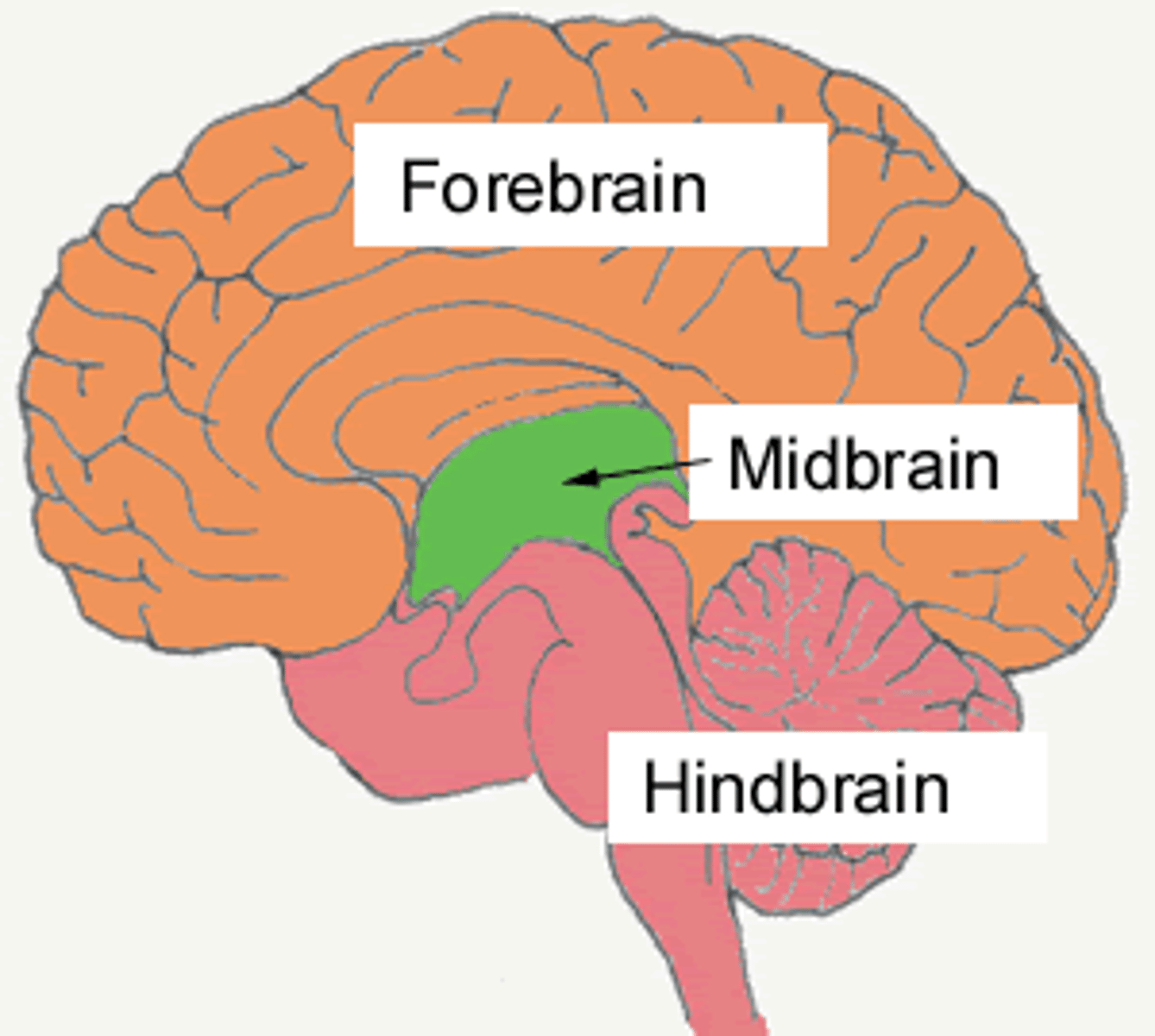
Midbrain
Bridge which connects forebrain and hindbrain. Also processes visual and auditory information and helps with motor control. Ex: Turning your head instinctively toward a sudden loud bang.
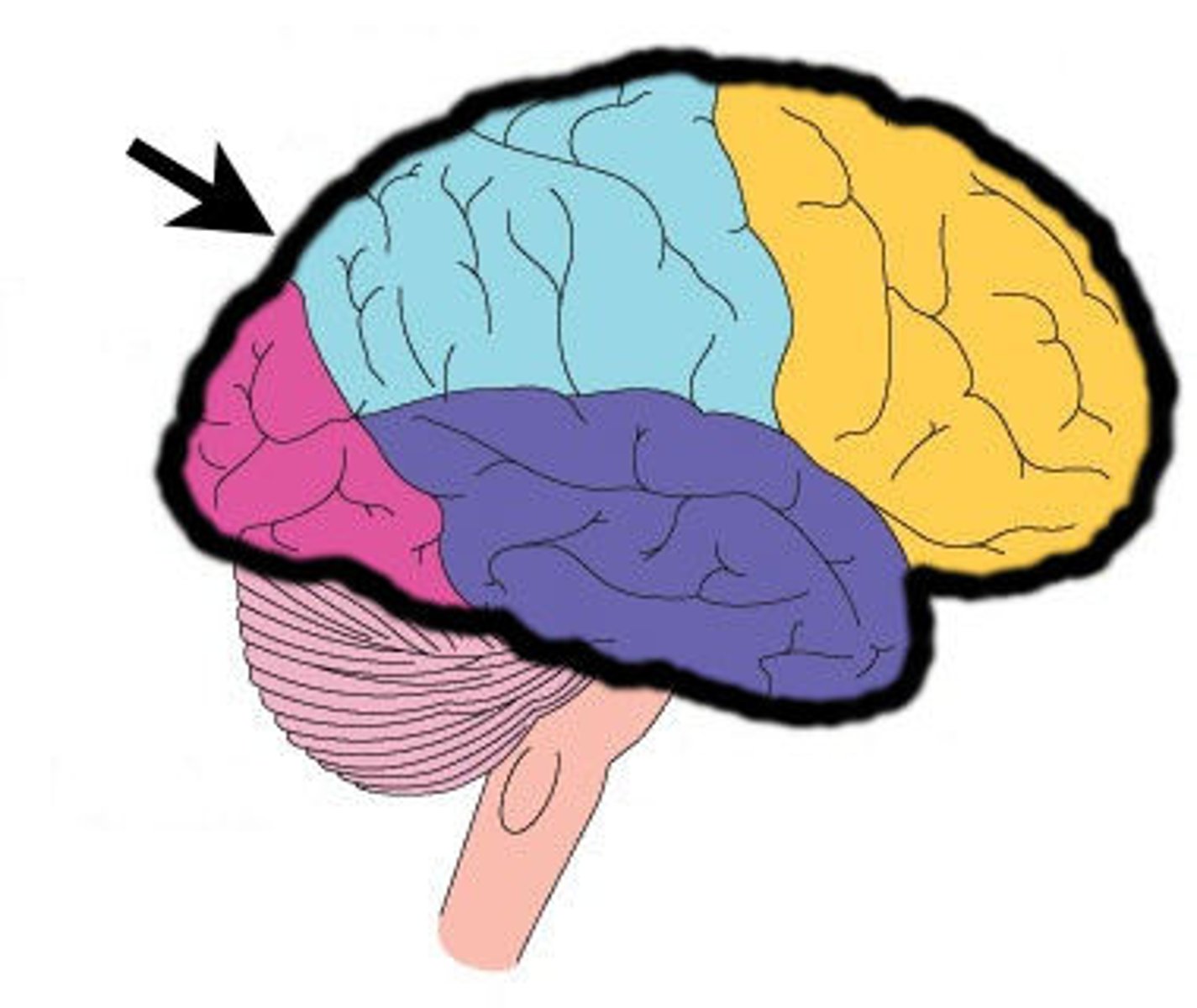
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain. Higher level thinking and functions. Ex: Solving a complex math problem or planning a vacation.
Cerebral cortex
Outer layer of the cerebrum made of gray matter. Ex: The processing of the visual details and colors of a painting.
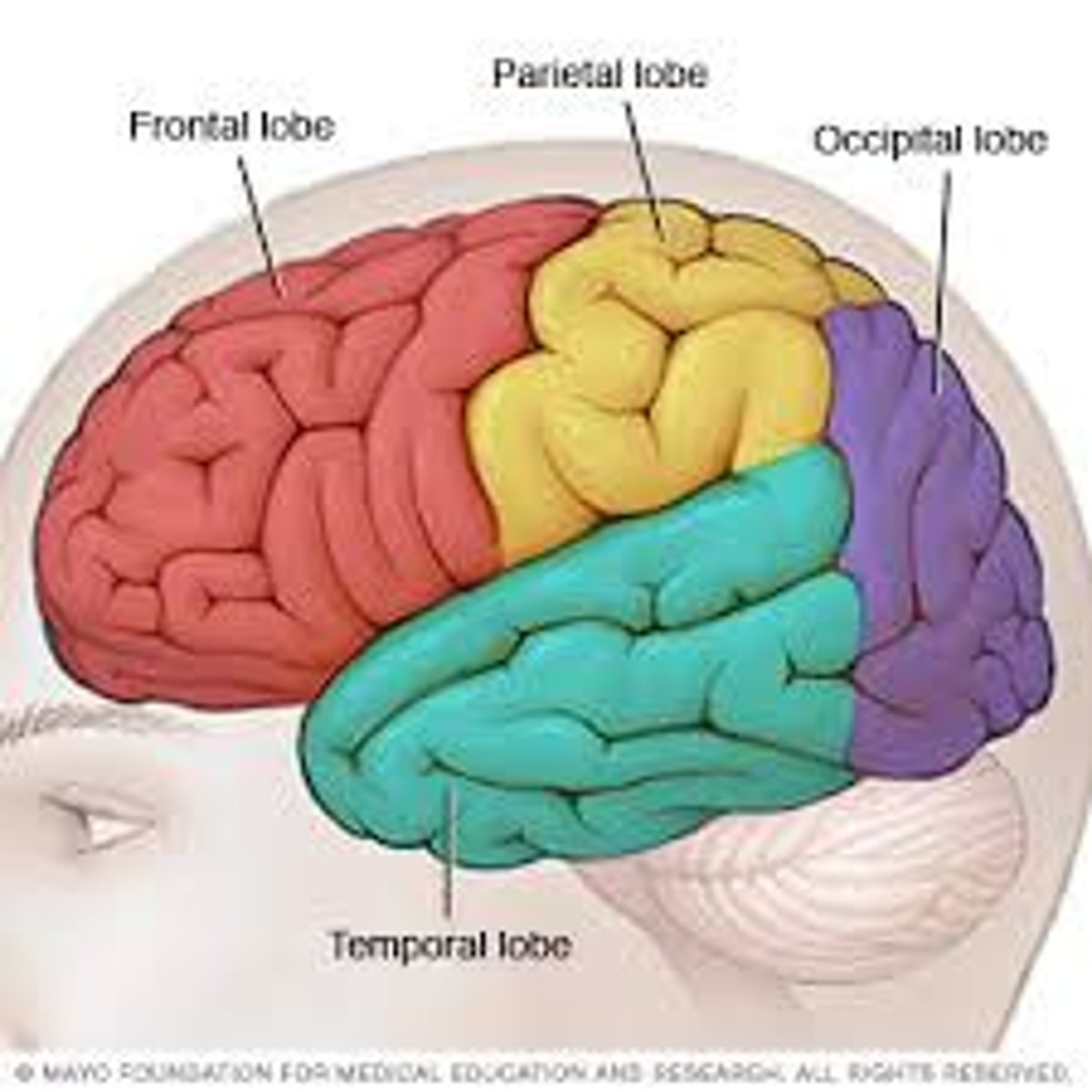
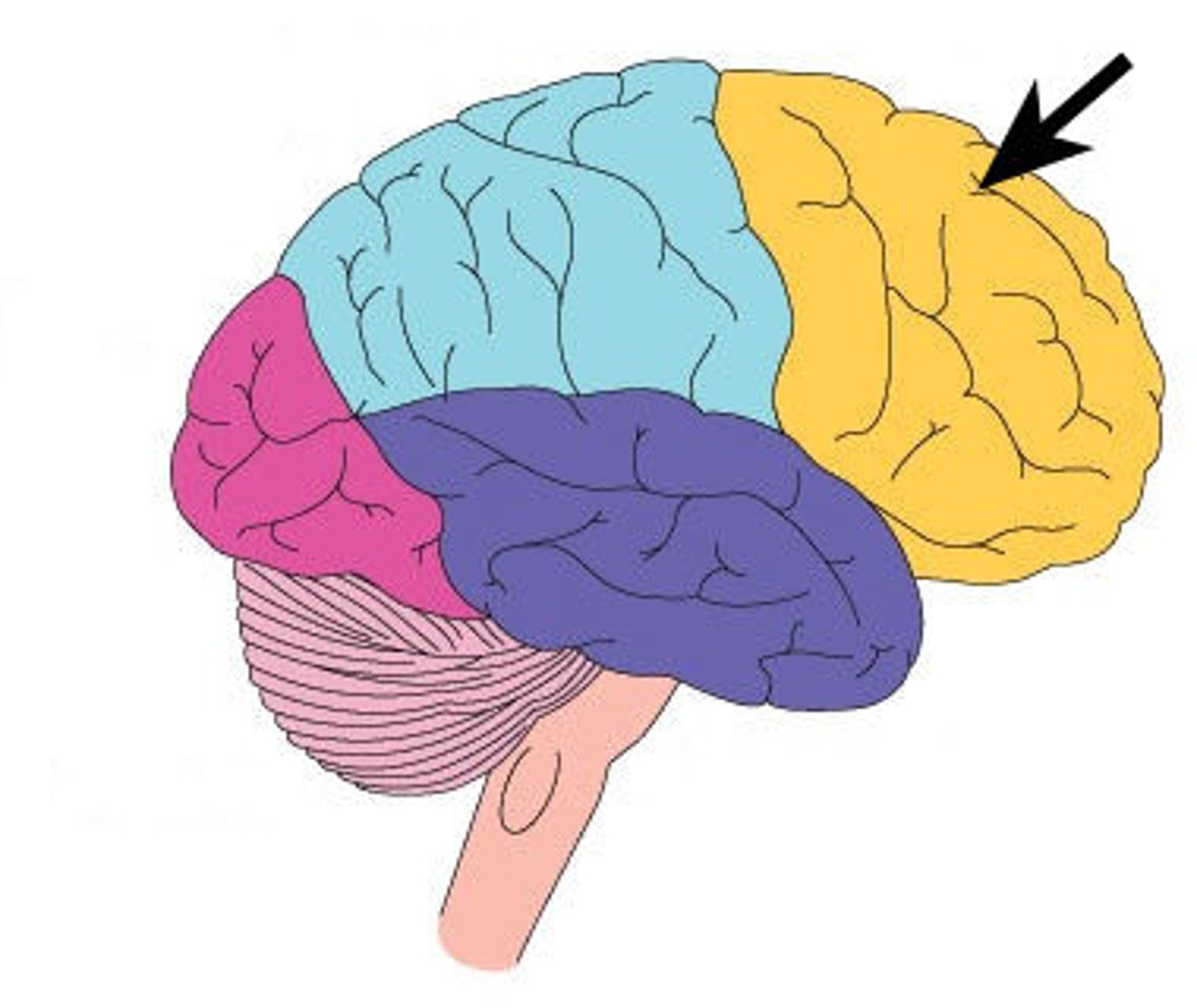
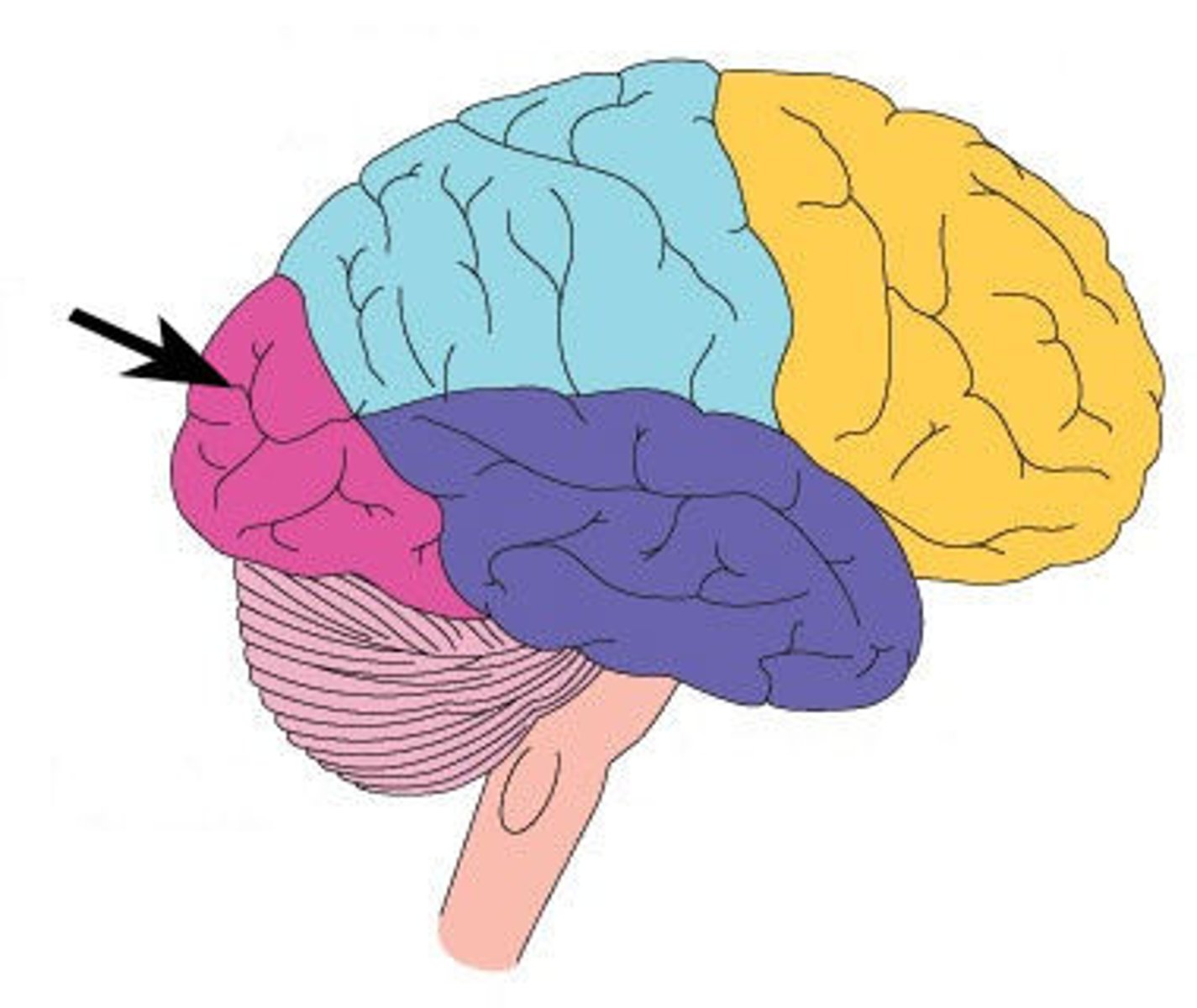
Frontal lobe
Region of cerebral cortex which processes higher level thinking. Ex: Resisting the impulse to eat a cookie when you are on a diet.
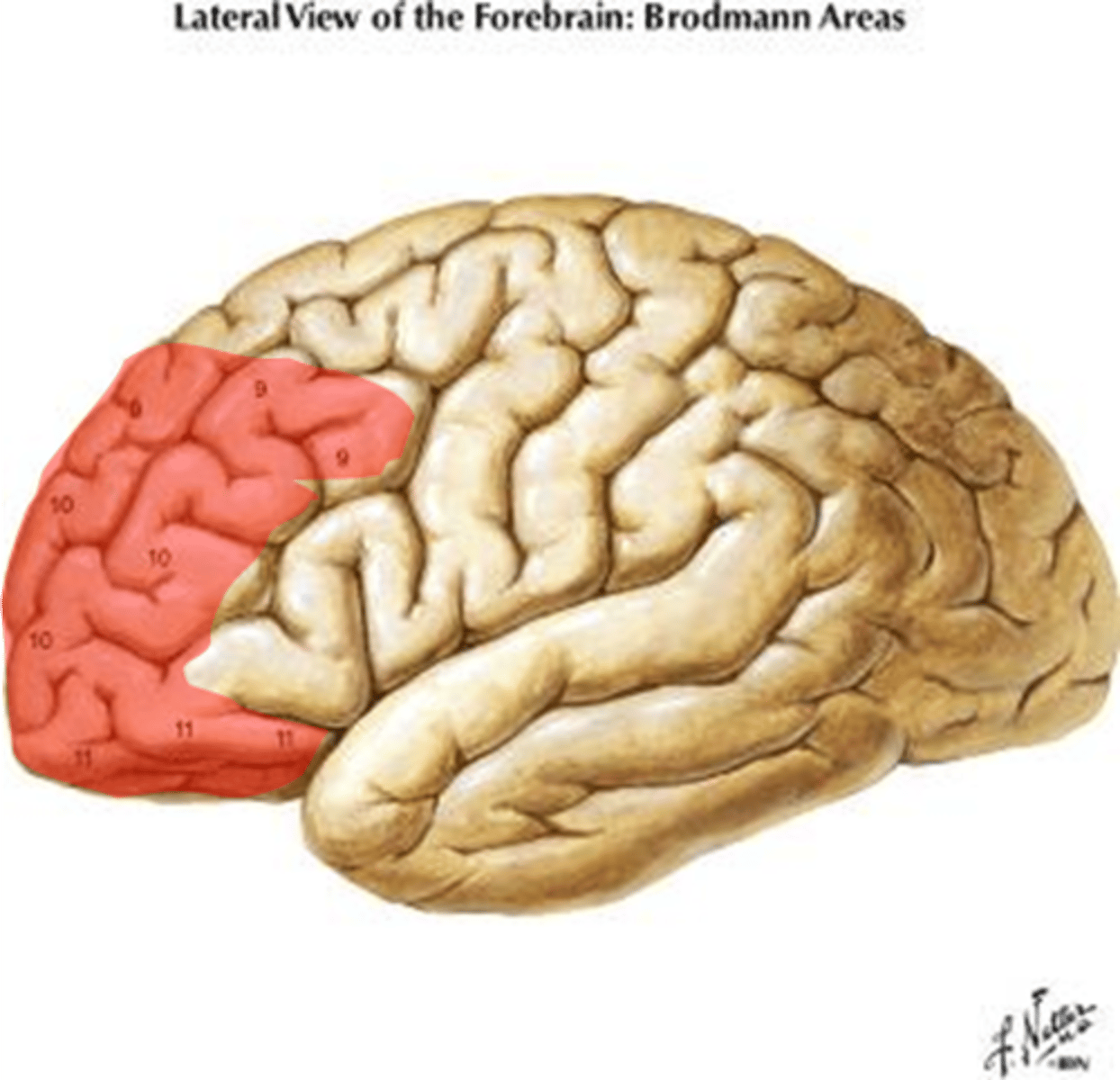
Prefrontal cortex
Area of the frontal lobe responsible for language, judgement, and high level thinking. Ex: Making a long-term financial decision for your retirement.
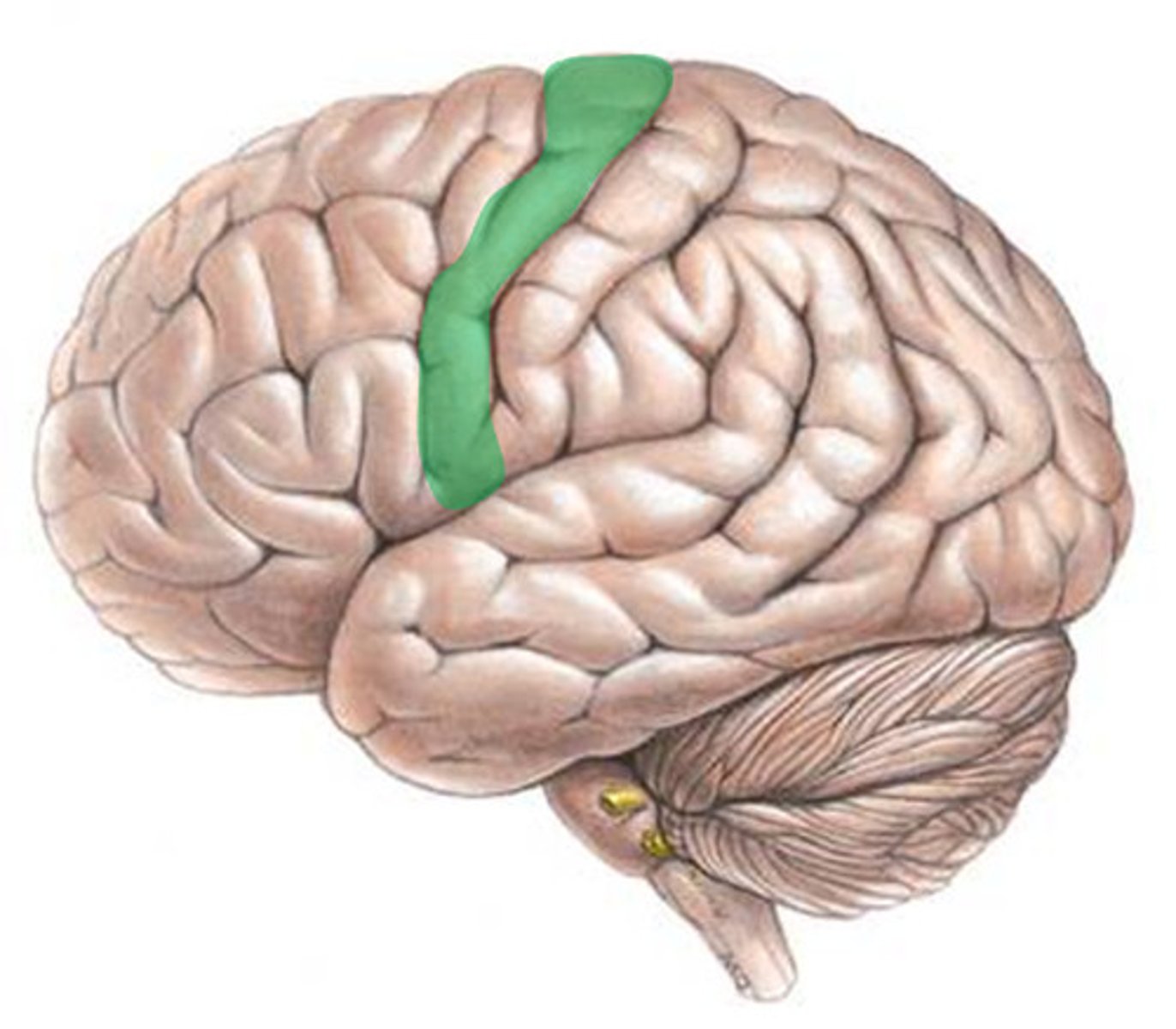
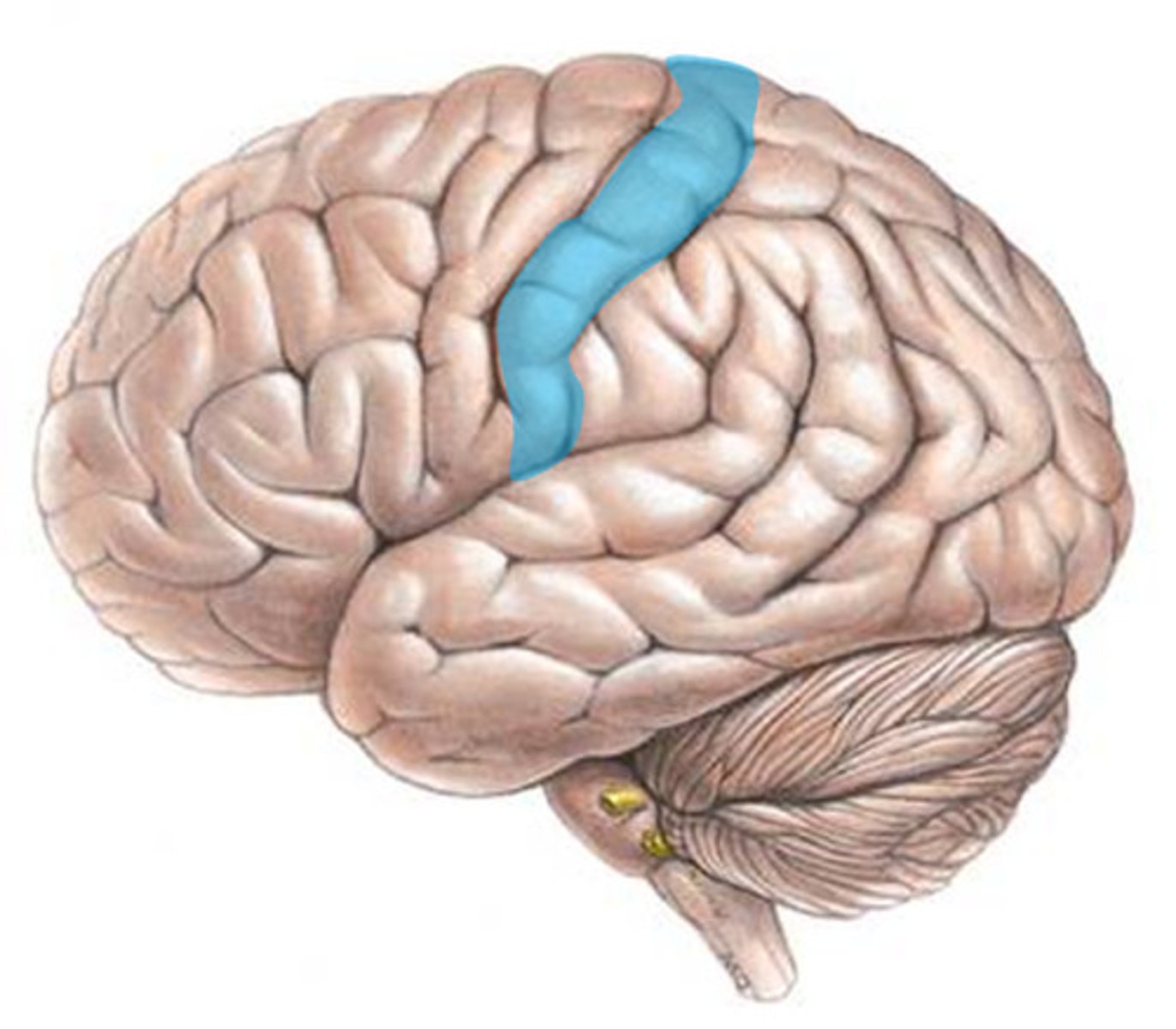
Motor cortex
Area of the frontal lobe that controls voluntary movements. Ex: Raising your arm to wave hello to a friend.
Parietal lobe
Region of cerebral cortex which processes sensory information from the body such as touch and spatial orientation. Ex: Feeling the soft texture of a velvet blanket.
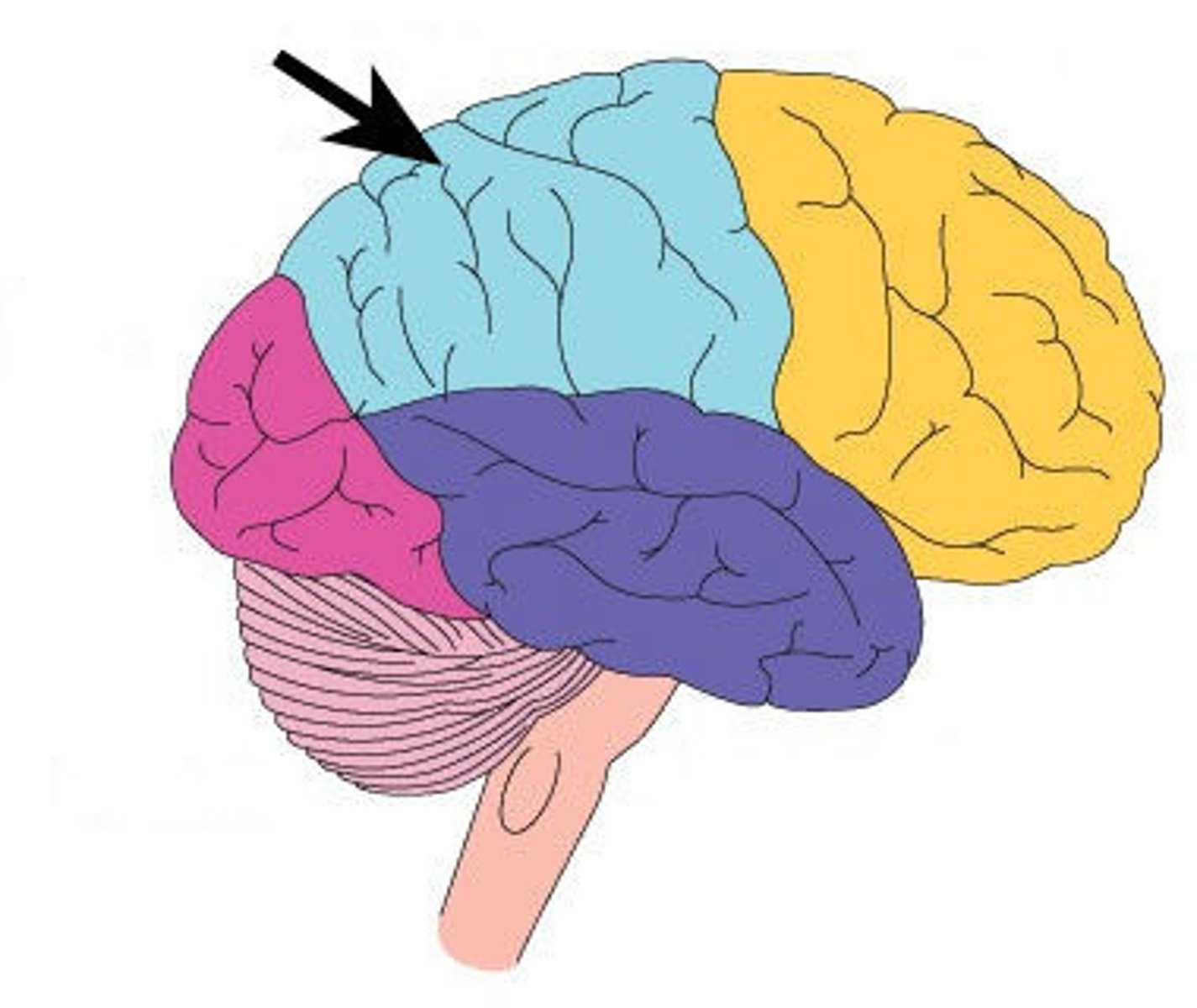
Somatosensory cortex
Area of the parietal lobe which processes touch sensitivity. Ex: Recognizing that a mosquito has landed on your forearm.
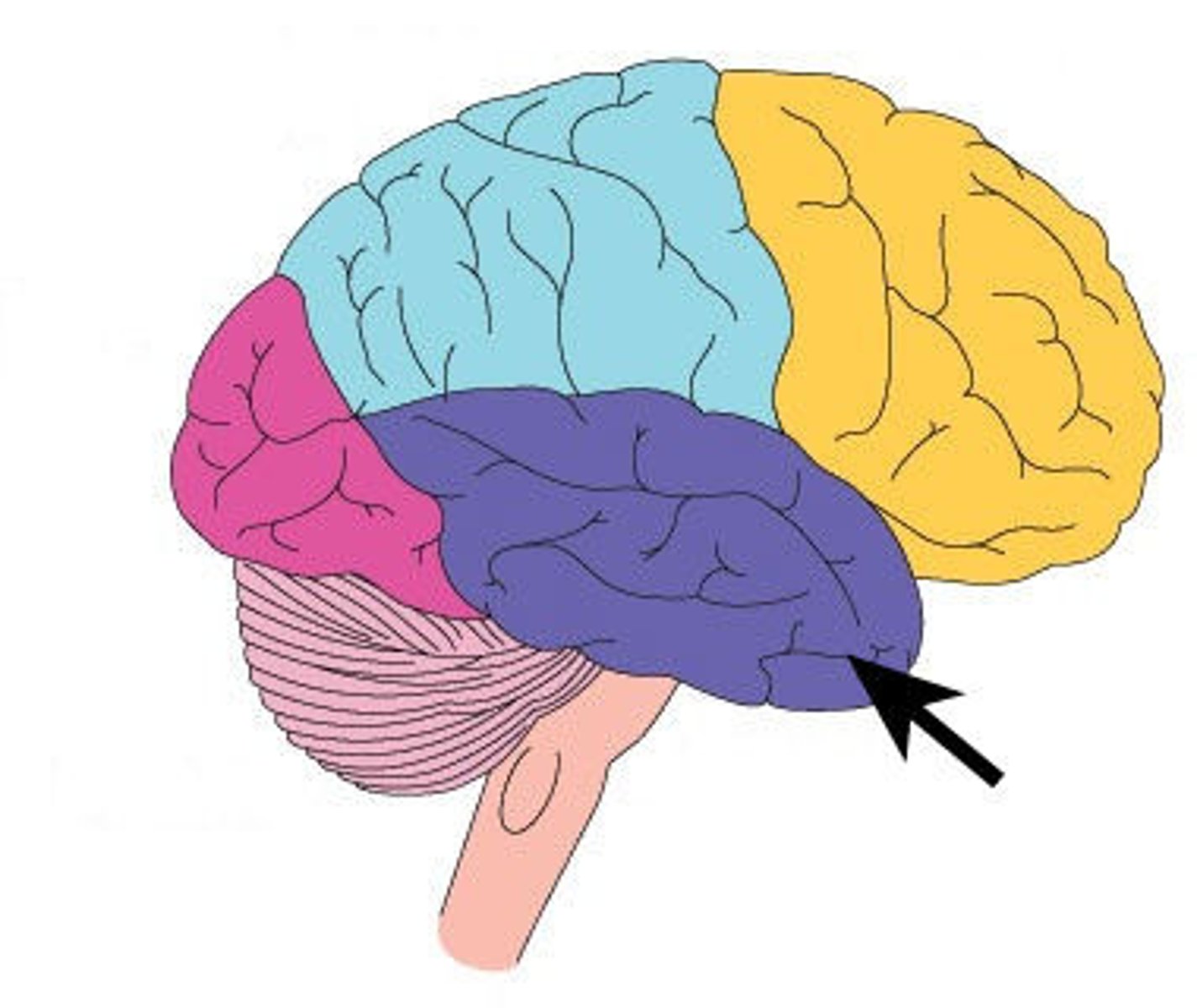
Temporal lobe
Region of cerebral cortex which controls auditory and linguistic processing. Ex: Listening to and understanding the lyrics of your favorite song.
Occipital lobe
Region of the cerebral cortex which processes visual information. Ex: Recognizing the shape and color of a stop sign while driving.
Limbic system
Part of the brain which connects different parts together and performs essential life functions. Ex: Feeling a surge of fear when you see a snake.
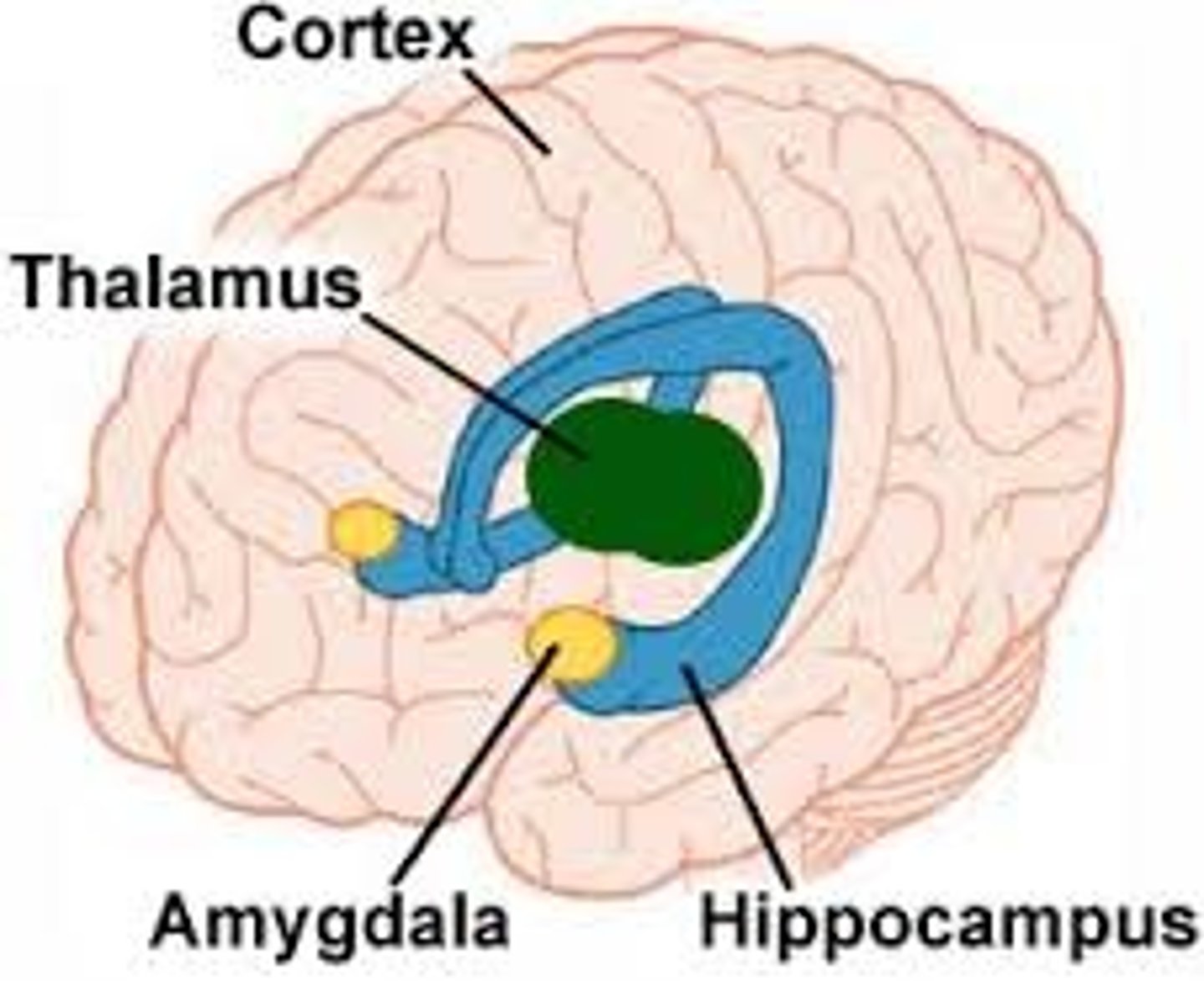
Thalmus
Part of the limbic system which receives sensory information such as vision, touch, audio, and sends it to the appropriate lobe for processing. Ex: Routing visual data from the eyes to the occipital lobe.
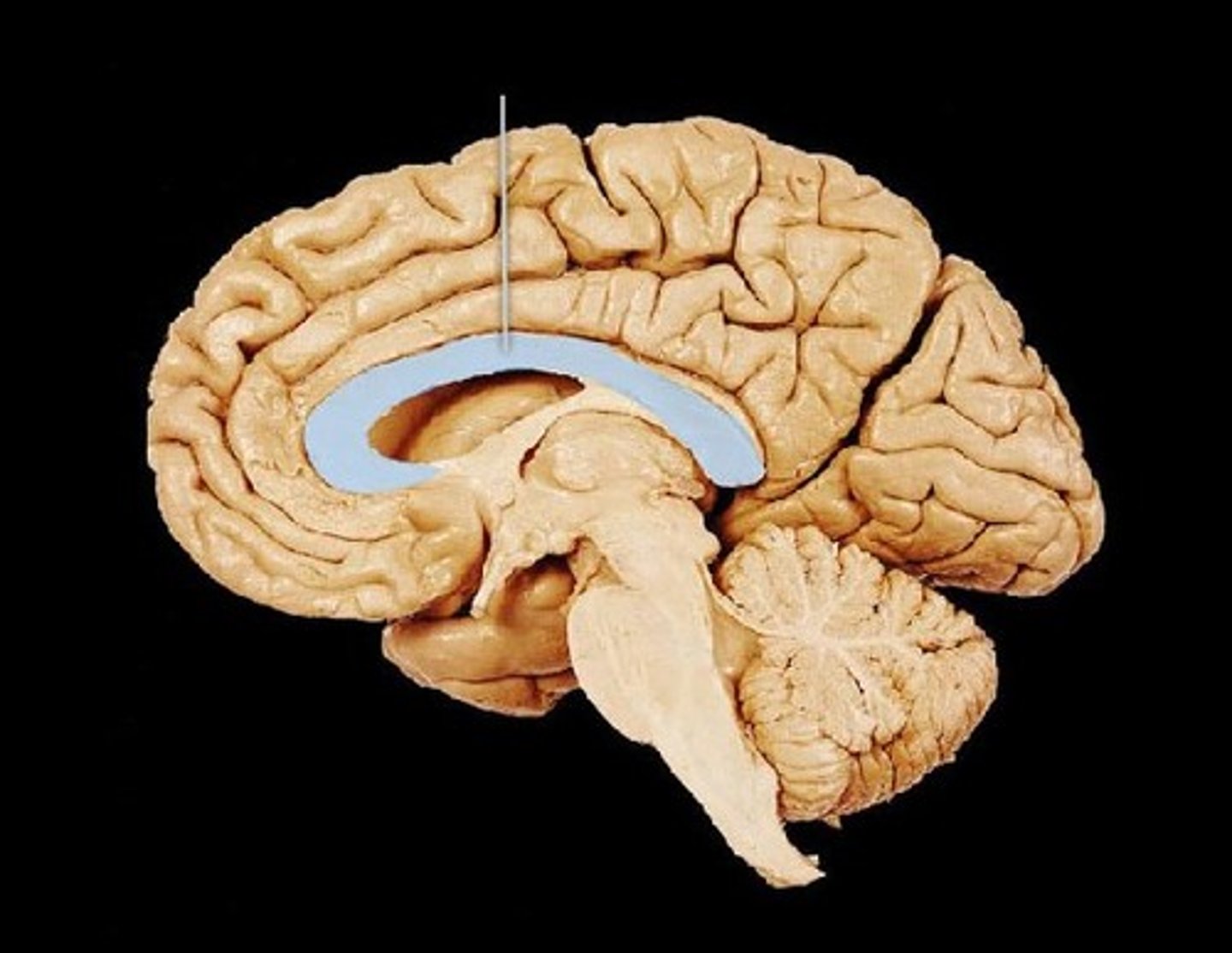
Corpus Callosum
Part of the limbic system. Band of nerve fibers which connect the 2 hemispheres of the brain. Ex: Allowing the left hemisphere to verbalize the name of an object seen in the right visual field.
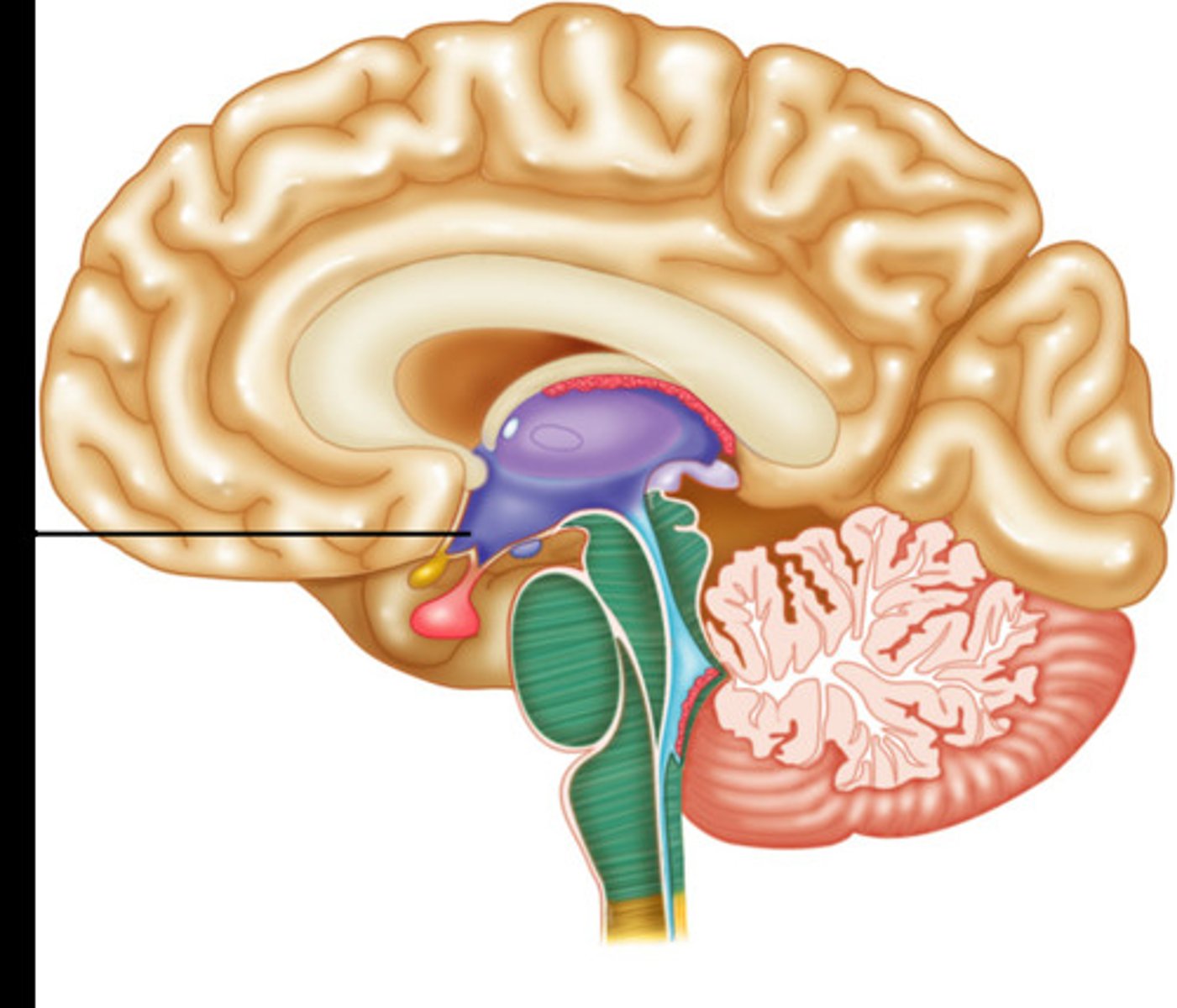
Hypothalmus
Part of the limbic system. Helps body to maintain balance and homeostasis. Controls drives such as thirst and hunger. Ex: Triggering the feeling of hunger when your blood sugar drops.
Pituitary gland
Regulates hormones which release glands to regulate bodily function. Ex: Releasing growth hormones into the bloodstream during puberty.
Left hemisphere of brain
Words, letters, interpreting language. Ex: Reading a book or applying logic to a scientific problem.
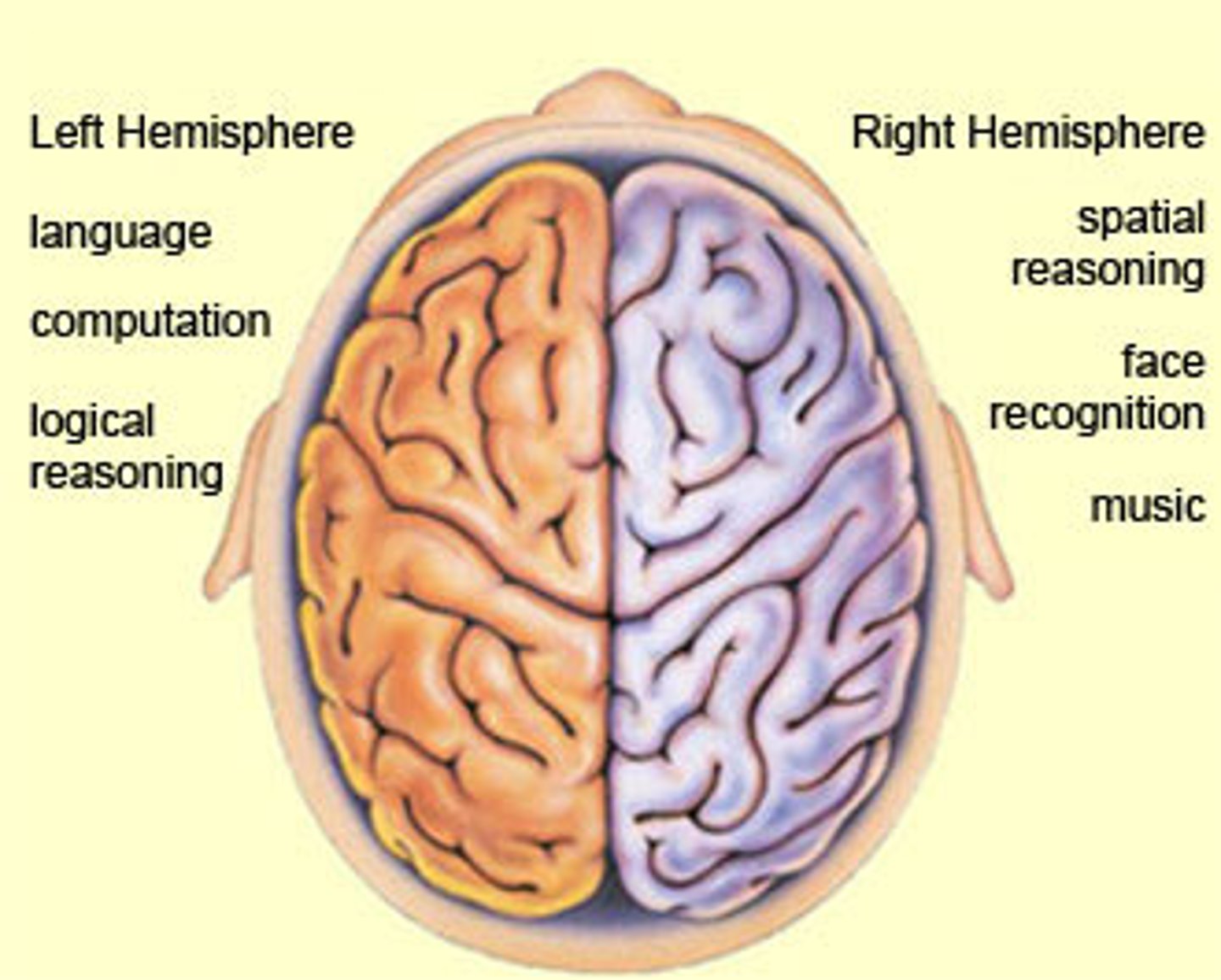
Right hemisphere of brain
Spatial concepts, facial recognition, discerning direction. Ex: Recognizing the face of a childhood friend in a large crowd.
Broca's area
Region of brain in the frontal lobe which deals with the production of speech. Ex: Being able to physically articulate the words "I am tired."
Wernicke's area
Region of brain in the temporal lobe which deals with the comprehension of speech. Ex: Understanding what a person means when they ask you a question in conversation.
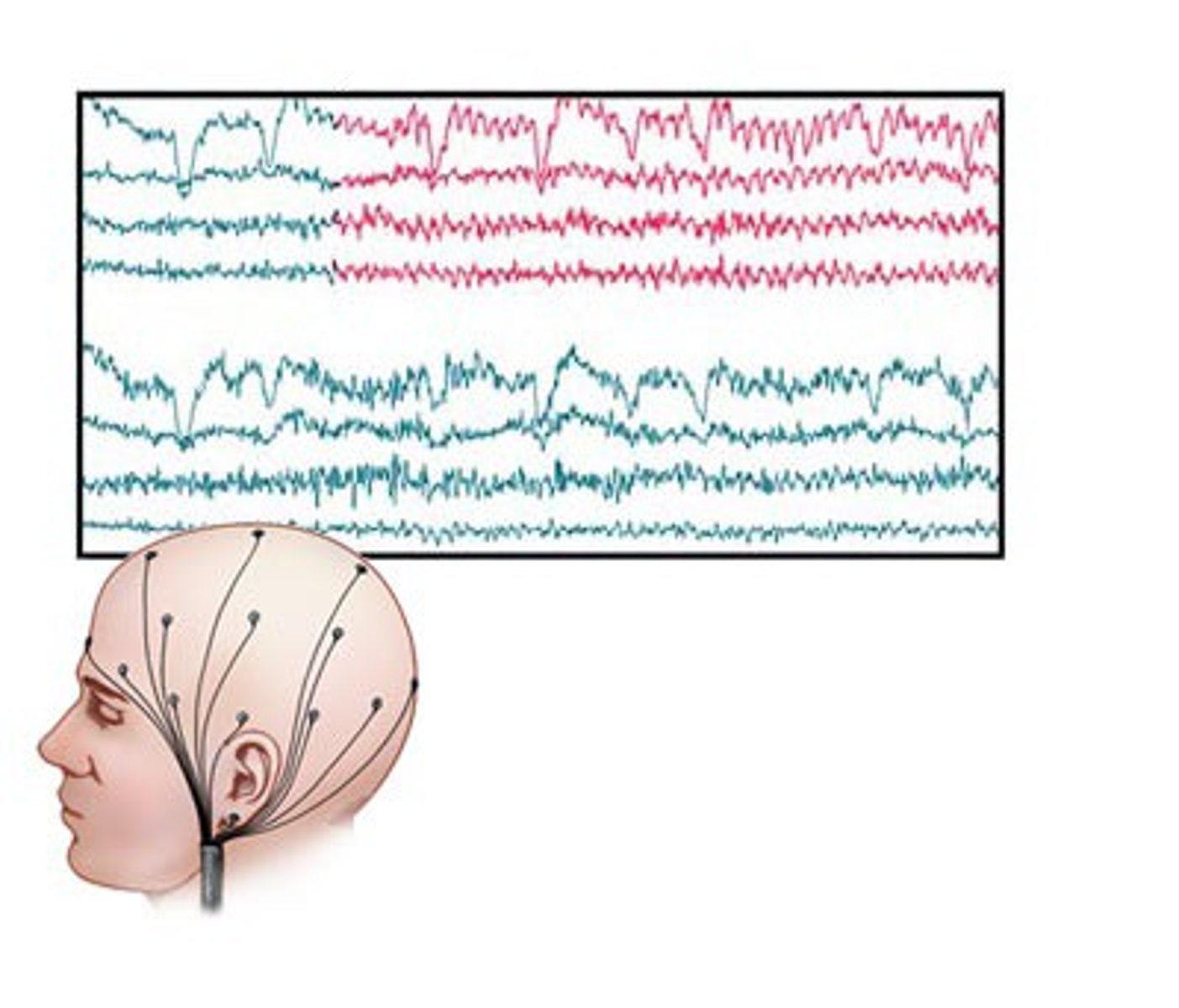
EEG
Electrodes are placed on an individual's scalp to record the electrical signals from neuron firing. Ex: Tracking brain activity to identify the onset of a seizure.
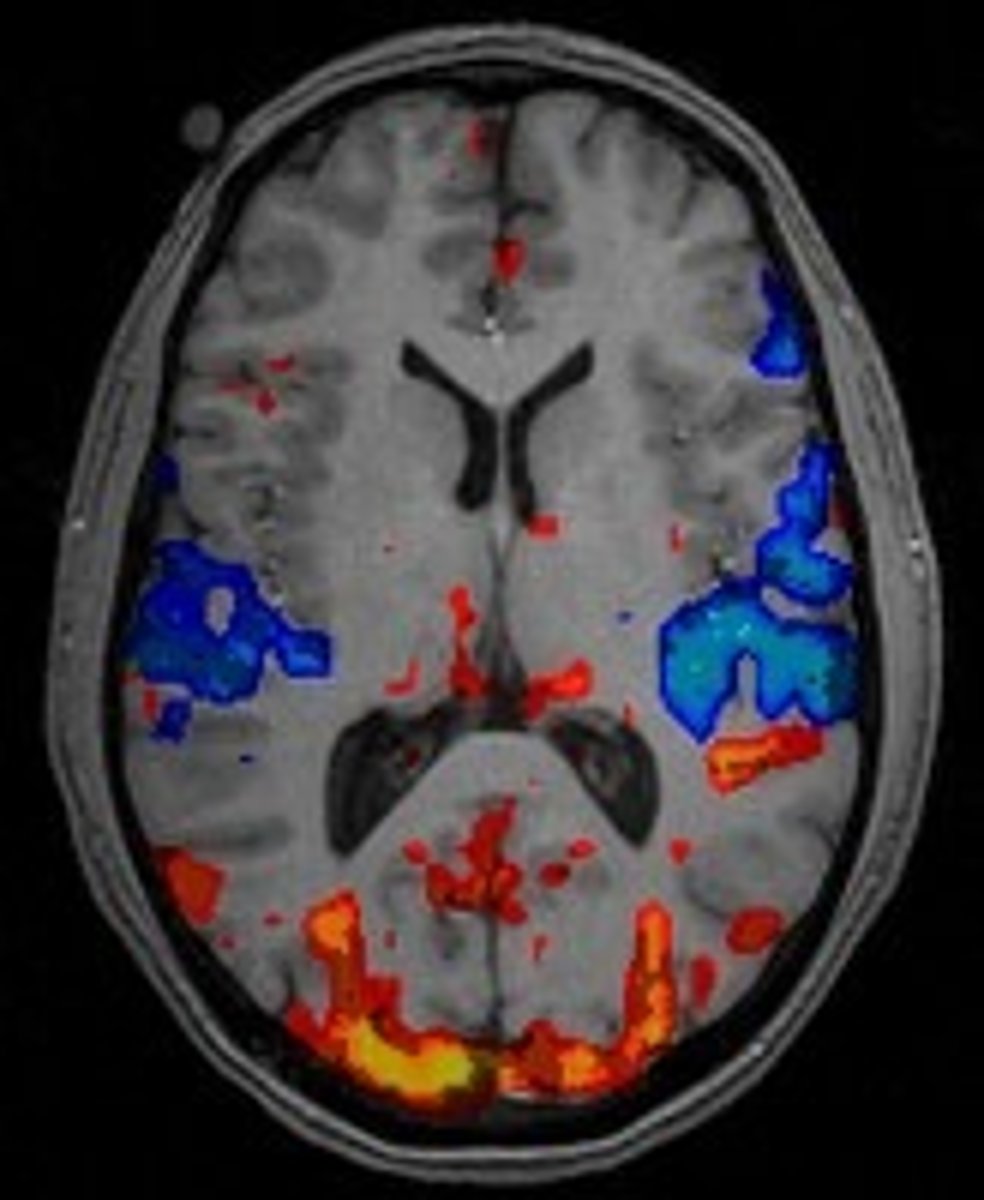
fMRI
Magnetic imaging of the brain which shows active areas of the brain. Ex: Seeing the visual cortex light up on a monitor while a patient looks at photographs.
NREM 1
The first stage of sleep which lasts 5-10 minutes. Body will start to relax and mind will slow. Alpha waves. Ex: Feeling like you are floating right as you begin to drift off.
NREM stage 2
Second stage of sleep which lasts 10-20 minutes. Body will experience bursts of mental activities called sleep spindles and K-complexes. Theta waves. Ex: Being easily awakened by a quiet floor creak during this light stage of sleep.
NREM stage 3
Third stage of sleep which lasts around 30 minutes. A deep sleep where growth hormones are produced and an individual may experience sleep walking. Delta waves. Ex: A person being very difficult to wake up even if a loud alarm goes off.
Hypnogogic sensations
Imaginary images or sensations that seem real and occur as a person is falling asleep. Ex: The common sensation of falling that causes your body to jerk awake suddenly.
REM (rapid eye movement) sleep
The fourth stage of sleep. Ranges from 10 minutes to an hour. External muscles are paralyzed while internal systems are active. Dreams are experienced. Beta waves. Ex: Dreaming of running through a forest while your actual legs remain perfectly still.
REM Rebound
The tendency for REM sleep to increase in length after a person is deprived of REM sleep. Ex: Experiencing unusually intense and frequent dreams after a night of only 3 hours of sleep.
Activation-synthesis Theory
Proposes that dreams are the brain's way of making sense of random neural activity during sleep. Ex: Dreaming of a siren because your brain is trying to interpret a random electrical signal from the auditory cortex.
Consolidation theory
Proposes that dreams help process and strengthen our memories and experiences. Ex: Dreaming about the vocabulary you studied for your psychology exam earlier that day.
Restoration theory
Proposes that we sleep because we are tired and need to restore our energy. Ex: Feeling physically and mentally refreshed after a full night of uninterrupted rest.
Sleep apnea
A disorder where an individual has trouble sleeping due to breathing issues. Ex: Loudly snoring and then momentarily stopping breathing multiple times throughout the night.
REM sleep behavior disorder
A disorder where an individual physically acts out dreams in REM sleep. Ex: Punching or kicking in bed because you are dreaming of being in a boxing match.

Somnambulism
Sleepwalking. Ex: Getting out of bed and walking to the kitchen while still in a deep stage of NREM sleep.
Narcolepsy
A disorder where a person has trouble falling asleep at night, but suffers from uncontrollable sleep attacks in the day. Ex: Suddenly falling into a deep sleep while in the middle of a classroom lecture.

Sensory transduction
The process of converting stimuli into sensation. Ex: Light waves striking the retina and being converted into electrical signals the brain can interpret as an image.
Absolute threshold
The smallest amount of stimulus which can be detected by an organism 50\% of the time. Ex: Detecting the scent of a single drop of perfume in a three-room apartment.
Sensory adaptation
Constant exposure to an unchanging stimulus leads to reduced sensitivity. Occurs in the body. Ex: No longer noticing the feeling of your socks on your feet after wearing them for an hour.
Habituation
Repeated exposure to the same stimulus leads to a reduced response. Occurs in the brain. Ex: No longer hearing the steady hum of a nearby air conditioner after being in the room for a while.
Difference threshold
Minimum difference between two stimuli required for a person to detect the change. Ex: Determining the smallest amount of sugar that must be added to a coffee to make it taste sweeter.
Weber-Fechner law
For us to notice a difference between two stimuli, they must differ by a constant percent, not a constant amount. Ex: Noticing the difference between a 10-ounce weight and an 11-ounce weight, but not between a 10-pound weight and a 10-pound-1-ounce weight.
Synesthesia
A neurological condition where one sense is experienced through another. Ex: A person who "sees" specific colors whenever they hear different musical notes.

Pupil
A part of the visual sensory system. The part of the eye which helps focus light to the retina. Ex: The pupil dilating in a dark room to allow more light to enter.
Retina
A part of the visual sensory system. A layer of photo receptor cells which convert light into neural impulses. Ex: The retina acting like the film of an old camera to capture the visual world.
Optic nerve
A part of the visual sensory system. The nerve which transmits the neural impulses from the retina to the brain. Ex: The physical "cable" connecting the eyeball to the brain's processing centers.
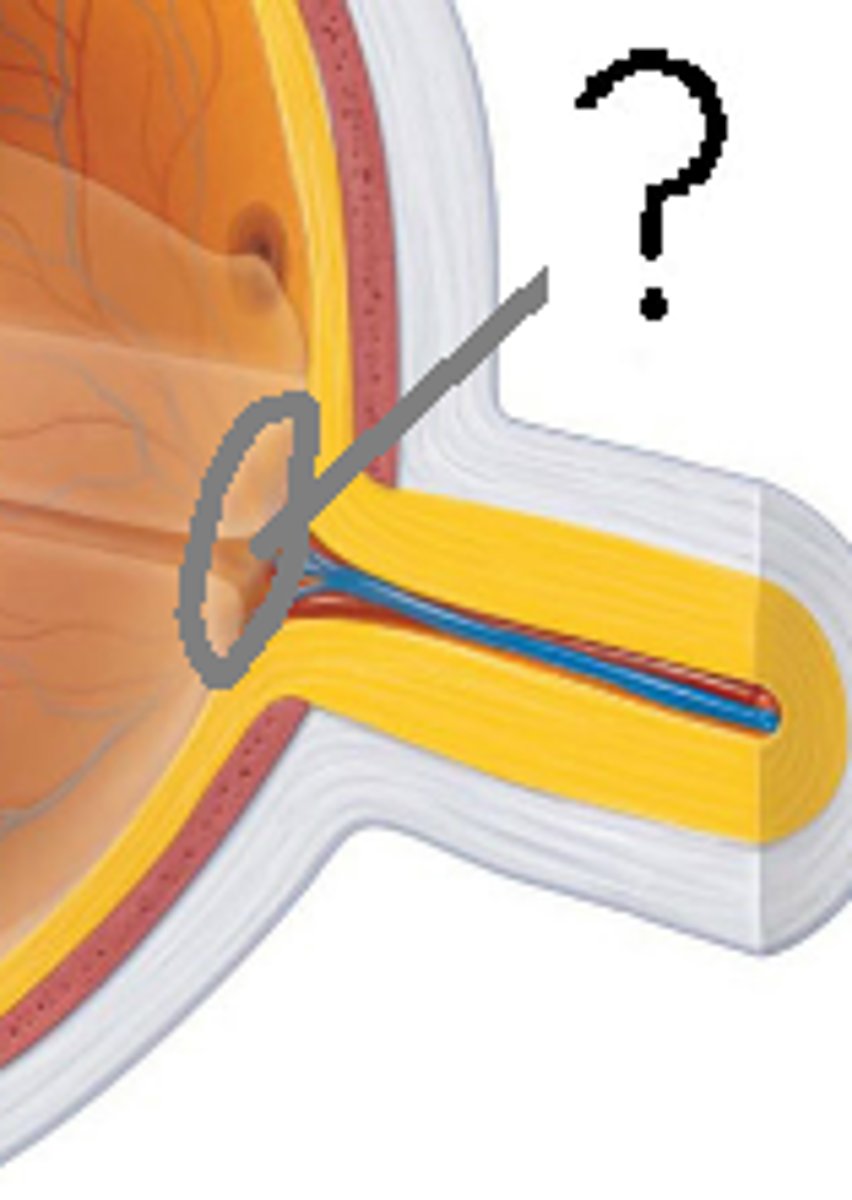
Blind spot
The point where the optic nerve leaves the eye. No photo receptors are here. Ex: Moving a dot on a piece of paper until it disappears from your field of vision.
Rods
Photoreceptor cells located in the periphery. They become active in low light but do not process color. Ex: Seeing the gray shadows of furniture in a room lit only by moonlight.
Cones
Photo receptor cells located in the fovia. They allow a person to see fine details and color. Ex: Discriminating between different shades of paint in a brightly lit hardware store.
Trichromatic theory
Color vision results from combinations of 3 color receptors: red, blue, and green. Ex: Seeing yellow because the red and green cones are both partially stimulated.
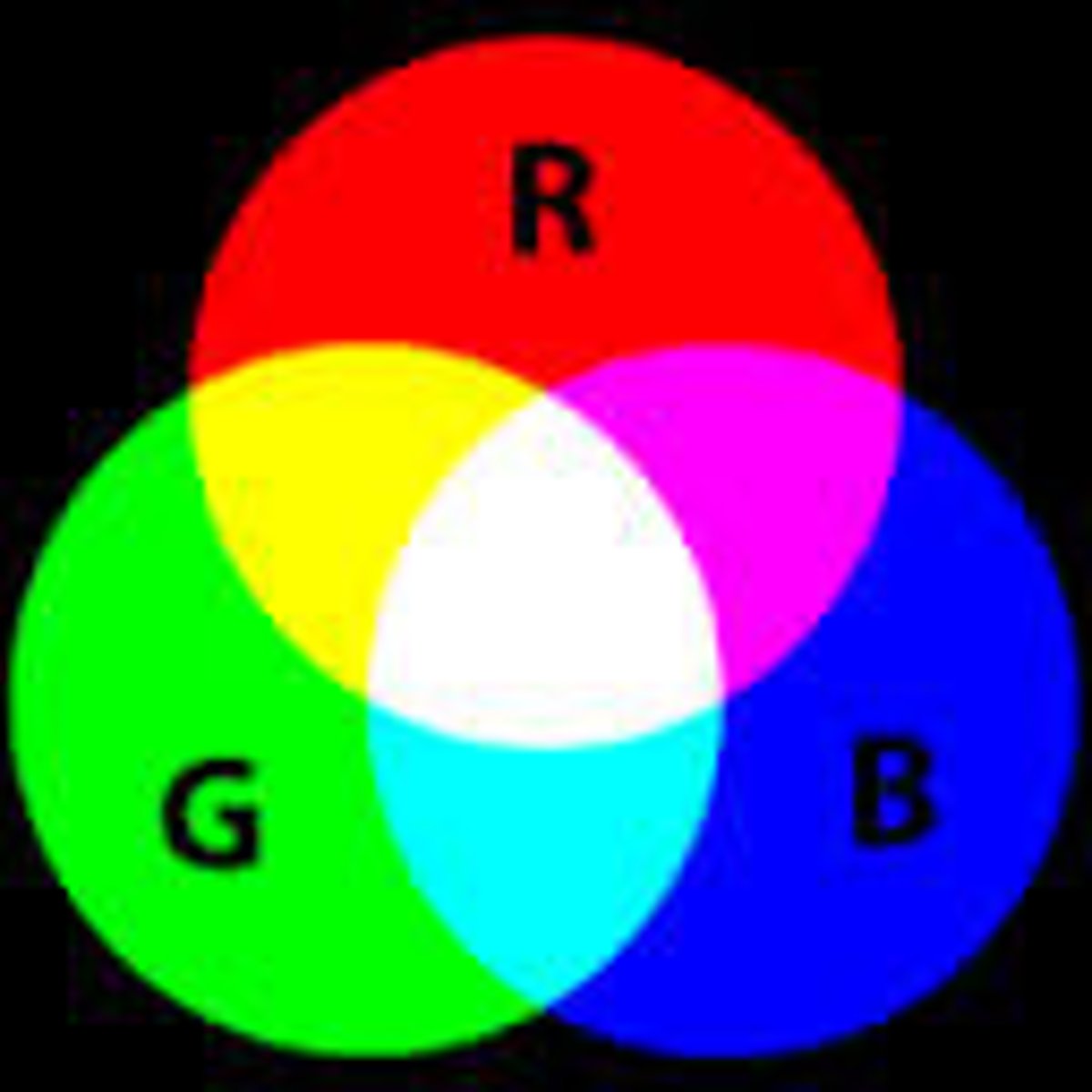
Opponent processing theory
Opposing retinal processes (red-green, etc.) enable color vision. Ex: Staring at a green square for a minute and then seeing a red afterimage when you look at a white wall.
Color blindness
Color blindness is caused by damage or lack of cones. Ex: An individual being unable to distinguish between the colors in a red-green color deficiency test.
Dichromatism
Caused by only having 2 out of the 3 cones. Ex: A person seeing the world primarily in shades of blue and yellow because they lack red cones.
Monochromatism
Caused by having 1 cone or no cones at all. Full color blindness. Ex: Experiencing the world entirely in black, white, and gray tones.
Accommodation
The ability for the eye to change shape to focus light on the retina. Ex: Your lens thickening to focus on a book you are reading up close.
Myopia/nearsightness
The lens focuses light in front of the retina. Ex: Being able to read the fine print on a phone but finding road signs miles away blurry.
Hyperopia/farsightedness
The lens focuses light behind the retina. Ex: Seeing distant mountains clearly but needing reading glasses to see a menu.
Prosopegnosia
A condition where a person is no longer able to recognize faces. Ex: Not being able to recognize your own reflection or your mother's face in a photo.
Blindsight
A condition where a blind person can still detect visual stimuli without conscious awareness. Ex: A blind individual correctly guessing the direction of a moving dot without actually "seeing" it.
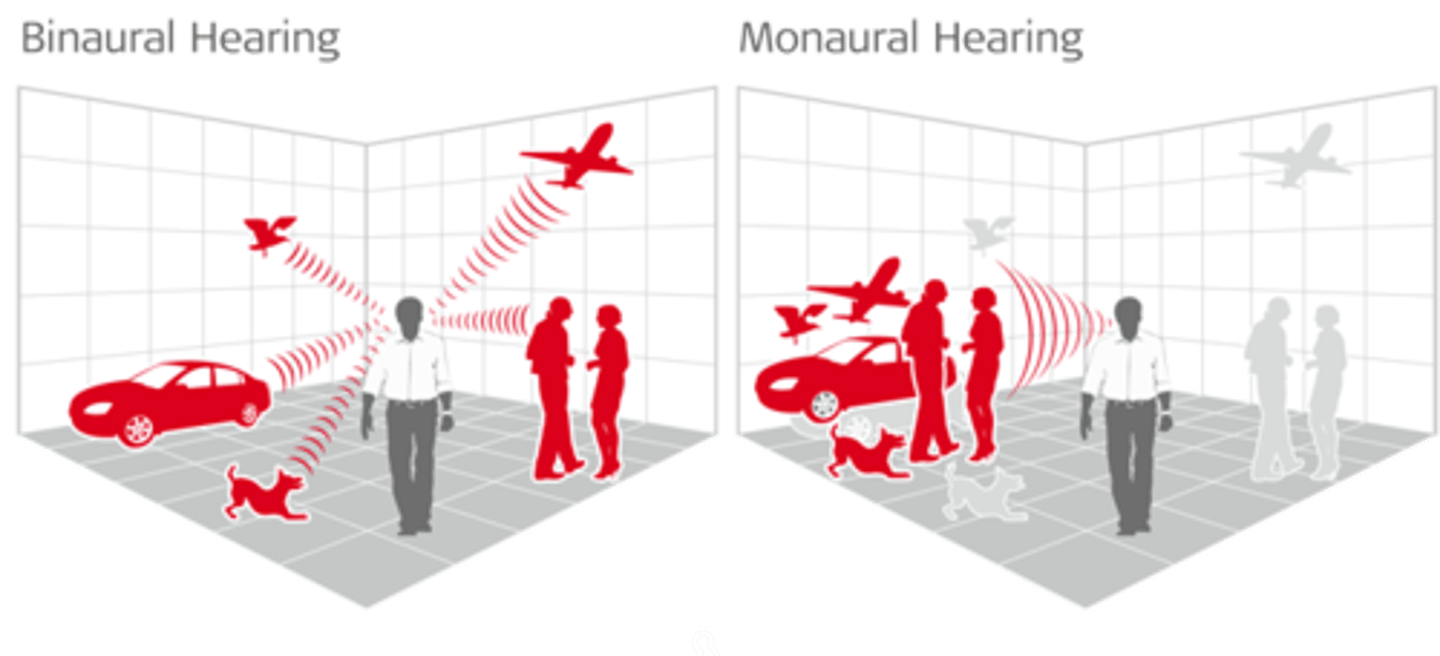
Sound localization
The process by which our brain determines where sounds are coming from. Ex: Instinctively looking to the left when you hear a car door slam on that side of your body.
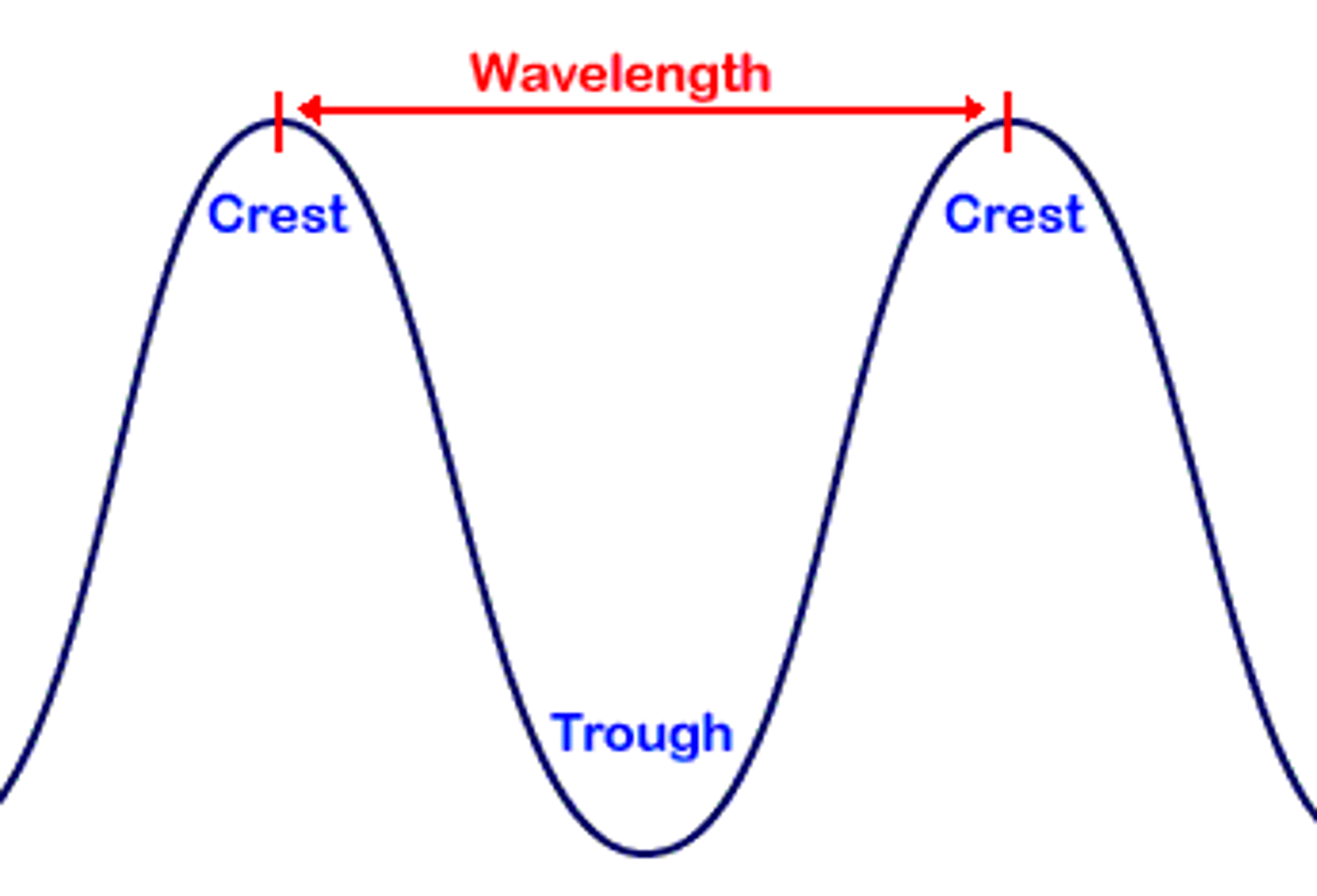
Wavelength
Higher wavelength=higher pitch, lower wavelength=lower pitch. Ex: A high-pitched flute note having a much higher wave frequency than a low-pitched tuba note.
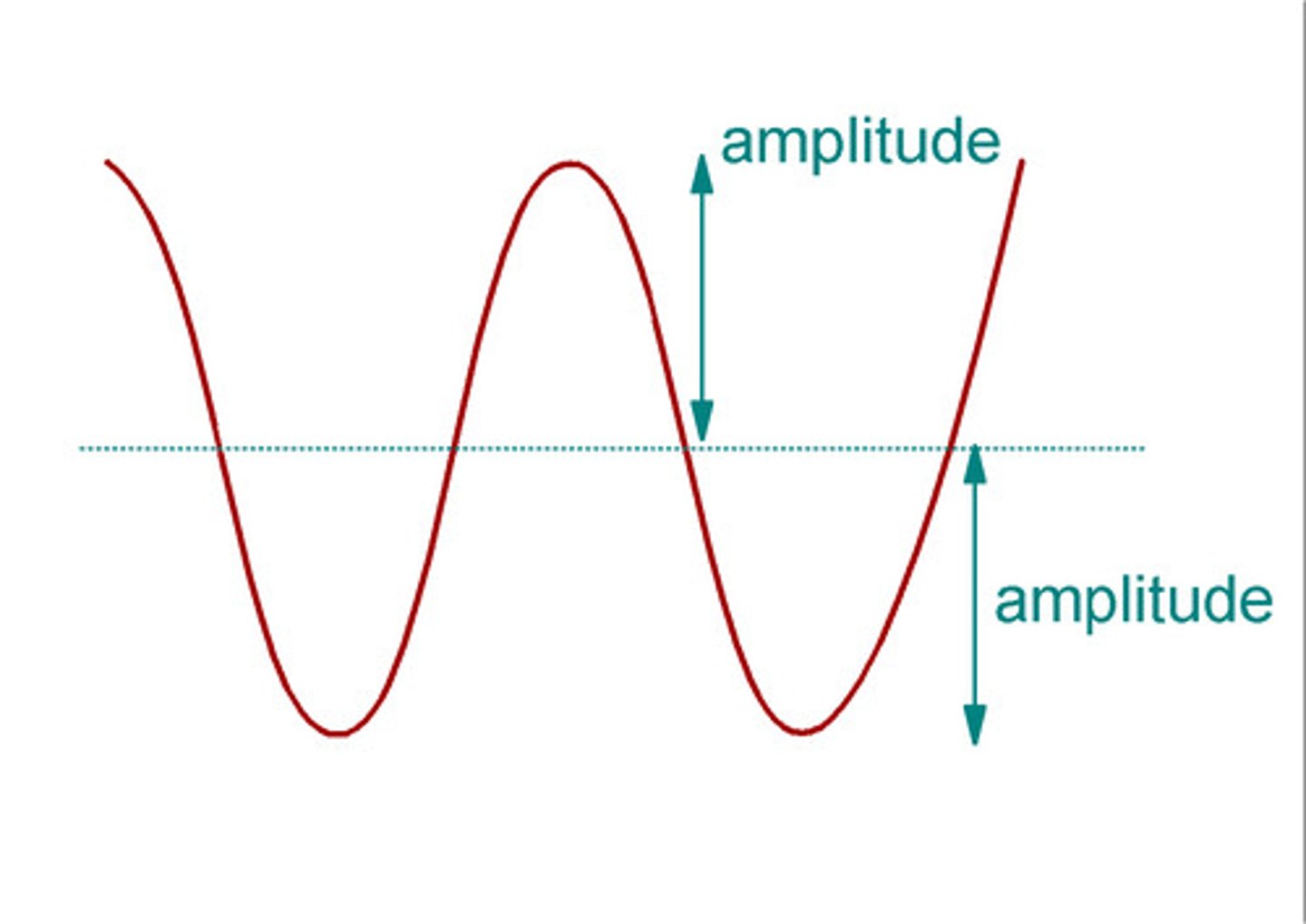
Amplitude
Higher amplitude=Louder, lower amplitude=quieter. Ex: Turning up the volume knob on a radio increases the height of the sound waves.
Place theory
Certain hair cells respond to certain frequency based on their location in the cochlea. Ex: High-pitch sounds triggering hair cells at the base of the cochlea.
Frequency theory
The frequency of the auditory nerve's impulses corresponds to the frequency of a sound wave. Ex: A tone of 100 Hz causing the auditory nerve to send 100 pulses per second to the brain.
Volley theory
Groups of neurons fire in a staggered manner to match high frequency sound waves. Ex: Multiple neurons alternating their firing to represent a high-pitched 3000 Hz whistle.
Sensorineural deafness
Inner ear or auditory nerve is damaged. Ex: Permanent hearing loss caused by prolonged exposure to extremely loud music at concerts.
Conduction deafness
A blockage prevents sound from traveling to the inner ear. Ex: Losing hearing temporarily because a foreign object or wax is stuck in the ear canal.
Olfactory receptors
Receptors in the nasal cavity that convert chemical particles into electrical signals. Ex: Molecules from a flower binding to receptors in the nose to signal the scent of a rose.
Pheremones
Chemical signals released by an individual which affect the behavior of others. Ex: Ants releasing chemicals to mark a trail for other ants to follow to a food source.
Gustation
Sense of taste (sweet, sour, bitter, salty, umami, oleogustus). Ex: Savoring the sweetness of a piece of chocolate as it hits your tongue.

Taste sensitivity factor
The amount of taste buds present. More taste buds leads to greater ability to taste. Ex: A "supertaster" finding the taste of broccoli intensely bitter due to a high density of taste buds.
Mechanoreceptors
Sensors in the skin which respond to pressure. Ex: Feeling the firm pressure of a firm handshake from a colleague.
Thermoreceptors
Sensors in the skin which respond to temperature changes. Ex: Feeling a pleasant warmth when you place your hands near a fireplace.
Nociceptors
Sensors in the skin which cause pain when detecting harmful stimuli. Ex: Feeling an immediate sharp pain after accidentally touching a hot iron.
Gate control theory
Spinal cord contains a neurological "gate" which can block or allow pain signals. Ex: Rubbing a stubbed toe to provide competing sensory input and "close the gate" on the pain.
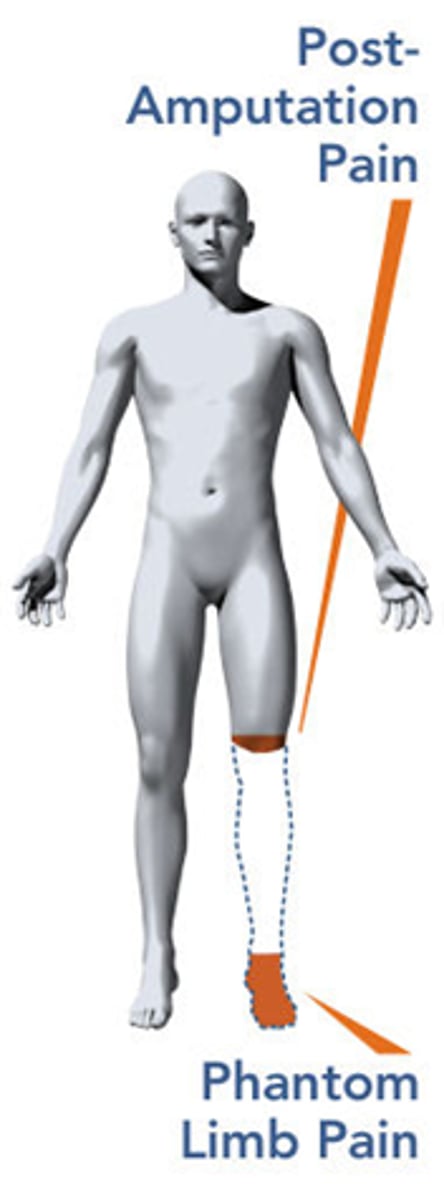
Phantom limb sensation
An individual experiences pain where a lost limb once was. Ex: A veteran feeling a phantom itch or cramp in a leg that was surgically removed.
Vestibular sense
Movement of fluid in semicircular canals allows the brain to understand movement and balance. Ex: Feeling dizzy and losing your balance after spinning around rapidly in a circle.
Kinesthesis
Sense of one's body movement. Ex: Being aware of the location and movement of your legs as you run through a dark room.

Proprioceptors
Sens