Veterinary Parasitology CH4 P1 - Nematodes of Dogs and Cats
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Part 1 of study material for Chapter 4 of Diagnostic Parasitology for Veterinary Technicians. For class BIO225 at MWCC.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
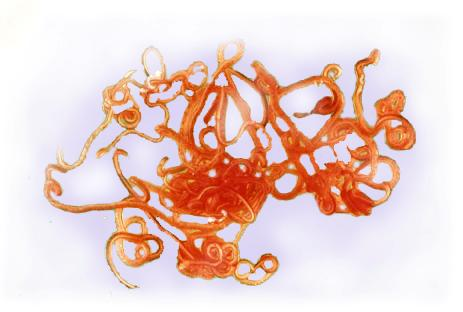
Spirocerca lupi
Esophageal worm - "Coiled tail"
Found: In tropical regions, sometimes Southern U.S.
Affects: Cats and dogs
Paperclip shaped egg; bright red/pink 3-7cm adult worms
Cause of infection: swallowing eggs
Found in fecal flotation or vomit
Causes nodules or granulomas in esophagus or stomach
Symptoms: trouble swallowing, regurgitation, hypersalivation
Prepatent period: 6 months
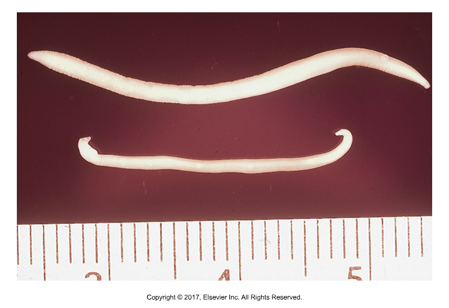
Physaloptera sp.
Stomach worms - "Bladder wing"
Found: Worldwide
Affects: Cats and dogs
Thick-shelled larvated egg; Creamy white, 1.3-4.8 cm adults; Ovoviviparous
Found on fecal flotation if solution has SG > 1.25 (most clinics use 1.2-1.25)
Can be seen in vomit; often mistaken for ascarids if seen grossly — must examine eggs
Stomach or small intestine; suck blood from mucosal surface
Cause of infection: Ingestion of eggs
Symptoms: Vomiting, anorexia, dark stool
Prepatent period: 56-83 days
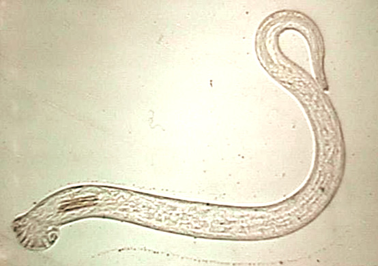
Ollulanus tricuspis
"Small cat hair"
Found: Worldwide
Affects: Felines only
Trichostrongyle
Symptoms: Chronic vomiting
Found in vomit flotation or smears
Adults only 1mm long; have three tail processes
Larviparous — release third stage larvae that are immediately infective
Can be ingested in vomit
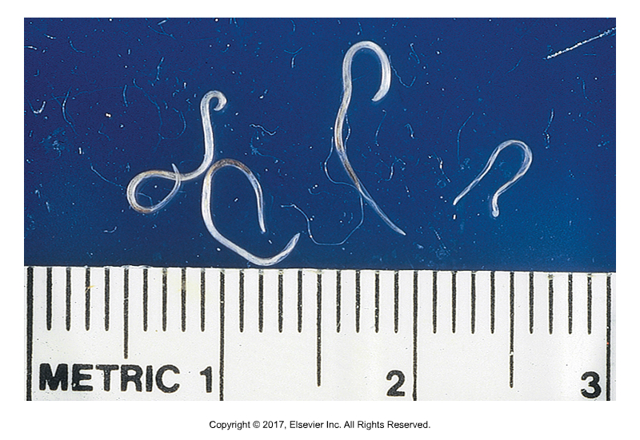
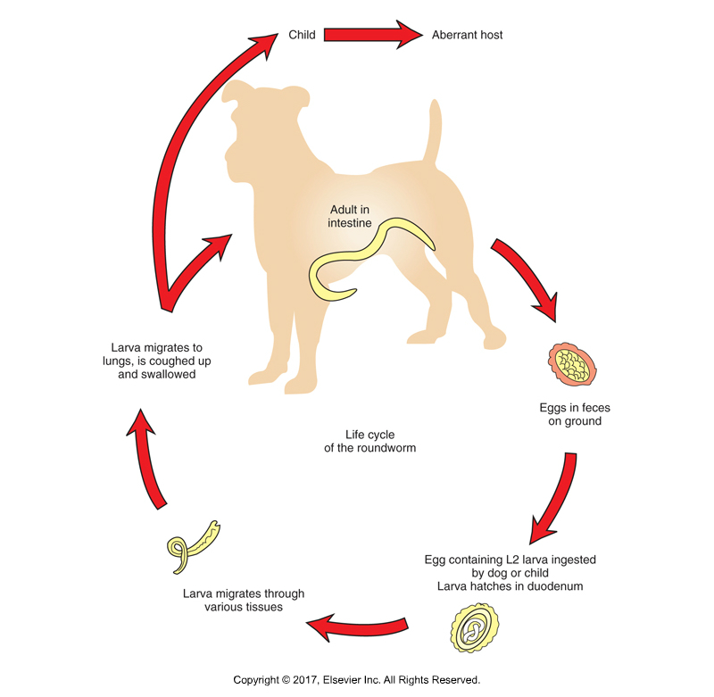
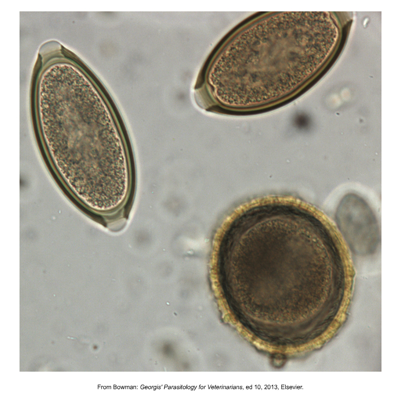
Toxocara canis, T. cati, Toxoscaris. leonina
Roundworms - "Arrowhead"
Found: Worldwide
Affects: Canines and felines
Cause of infection: Ingestion of larvated eggs
Adults 3-18 cm, usually coiled in feces or "spaghetti vomit"
Symptoms: Vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, bowel obstruction, "pot-belly"
Does not attach, undulates to stay in the intestine
Oviparous; single cell egg released; larvae develop on ground to L2 and ingested
L2 released from eggs and migrate to host lung, coughed up and swallowed
Adults mature in host small intestine; dormant in adult female host- become active due to pregnancy hormones of host
T. canis can cross placenta and milk and can infect babies; also zoonotic
Treatment: vermifuge (piperazine or pyrantel) — paralyzes adults, pass in feces
Treatment: vermicide - (thiabendazole or mebendazole) —kills parasite in host and broken down
Baylisascaris procyonis
Raccoon roundworm
Found: North America (MS-OH basin)
Affects: Raccoon host but can parasitize many species
Cause of infection: Ingestion of eggs
Egg similar to T. canis but slightly smaller
Symptoms: Can cause bowel obstruction in raccoon or dog
Zoonotic infection can lead to neurologic larva migrans
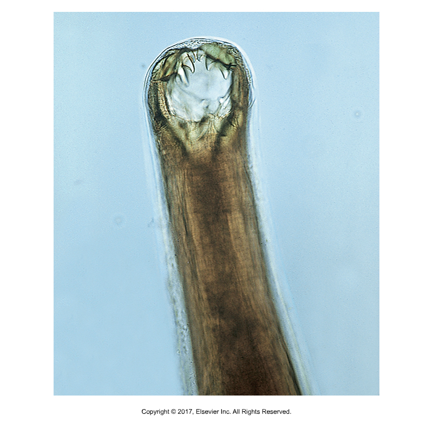
Ancylostoma caninum, A. tubaeform, A. braziliense, Uncinaria stenocephala
Hookworm
Ancylostoma: worldwide, Uncinaria: N. America
Ancylostoma: curved mouth; Uncinaria: hooked nose
A. caninum: dog, A. tubaeform: cat, A. braziliense: cat and dog, Uncinaria: dog only
Cause of infection: Ingestion of eggs or through skin
Attach to mucosa of small intestine, feed on blood, secrete anticoagulants
Ancylostoma: three pairs of ventral teeth
Symptoms: anemia, dark tarry stool, especially kittens and puppies
Can spread through placenta and milk
Oviparous: morulated egg released in feces, develop into L1 in environment
L1 hatch, grow and molt into L2, grow and molt into infective L3
Migrate to lungs, coughed up, swallowed
Matures in small intestine
Prevention: Interceptor and Heartgard Plus
Treatment: mebendazole or fenbendazole
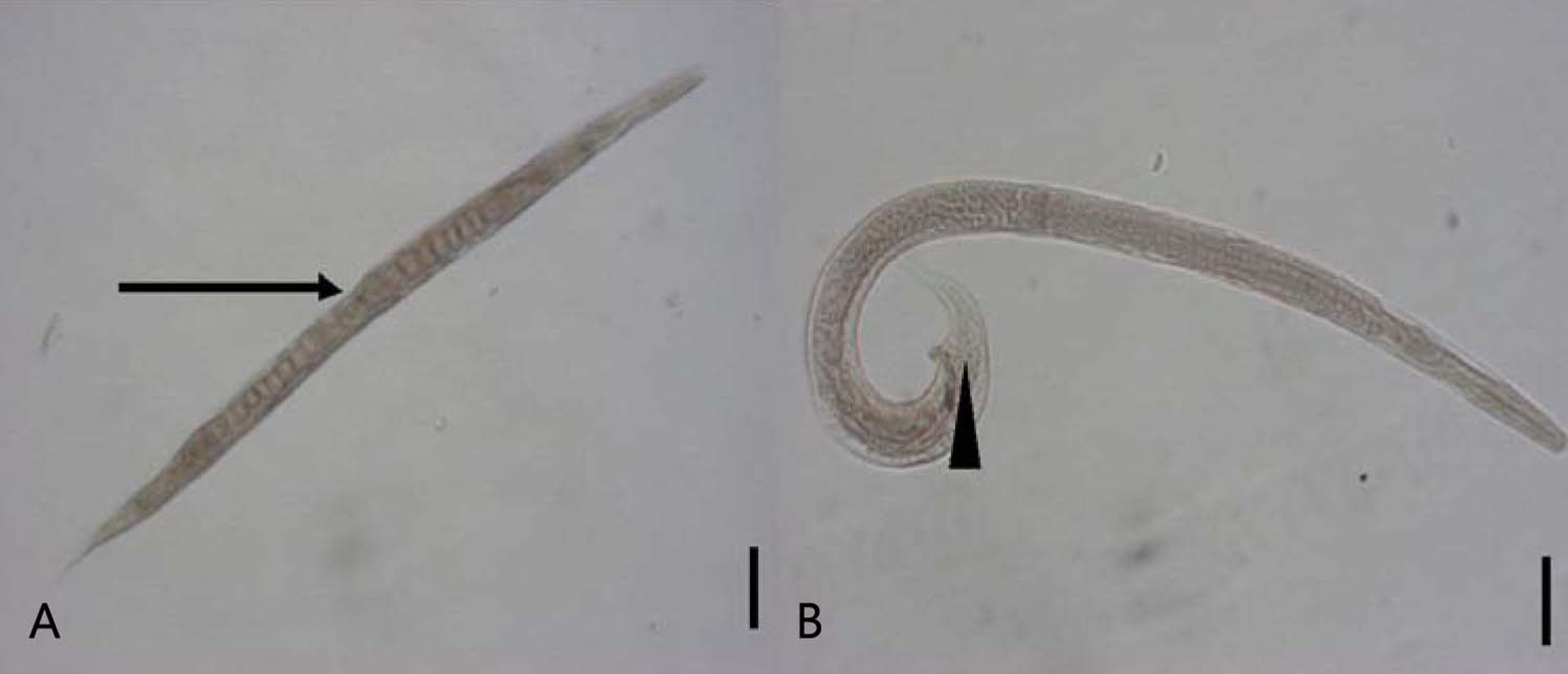
Strongyloides stercoralis, S. tumefaciens
Threadworms - "Round-like shape"
Found: Worldwide
Affects: Dogs, cats and humans
Cause of infection: Skin infection or placenta or milk passage
Symptoms: diarrhea, especially in puppies, zoonotic
Parthenogenesis: female produces viable ova without fertilization
No parasitic males
Adults found in small intestine
Adult female has cylindrical esophagus
Larvated eggs released but hatch in host intestine releasing L1 often found in feces
Larvae have rhabditiform esophagus
L1 are free-living in environment, L3 are infective
Prepatent period: 8-14 days
Trichuris vulpis, T. campanula
Canine whipworm, Cat whipworm - "Hair tail"
Found: Worldwide (Trichuris vulpis/canine whipworm common in USA)
Adults attach to wall of cecum and colon of dog, suck blood
Elongated, trichurid egg, single cell, bipolar plugs visible
Prepatent period: 70-90 days
Eggs only released every third day
Found in feces but heavy and don't float well; fecal centrifugation preferred
Eggs hatch in environment, grow into L1
Only pass by ingestion of egg
Symptoms: Diarrhea, anemia, mucus-coated stool
Resistant, needs follow up treatment to kill all adults
Not zoonotic
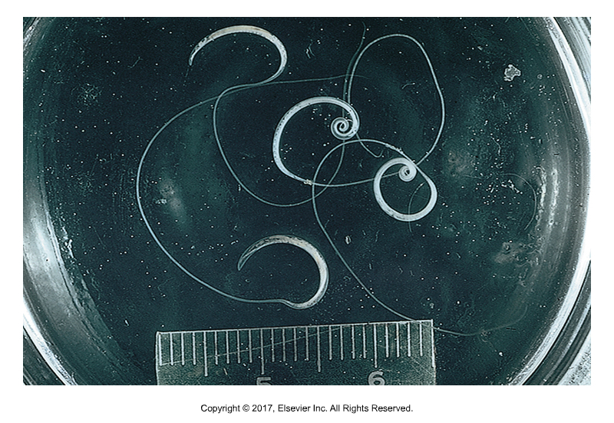

Dirofilaria immitis
Heartworm - "Dread thread"
Found: Warm climates worldwide
Affects: Dogs, cats, ferrets, humans (incidental only)
Definitive host: Dog
Intermediate host: Female mosquito
Adults found in right ventricle and pulmonary arteries of dog
Commonly found in aberrant sites: brain, eye, skin
Prepatent period: 6 months
Larviparous: microfilariae released into host bloodstream, picked up by female mosquito
Molt into L2 and L3 in mosquito digestive tract
L3 passed into dog by mosquito, mold into L4, L5, adults in heart
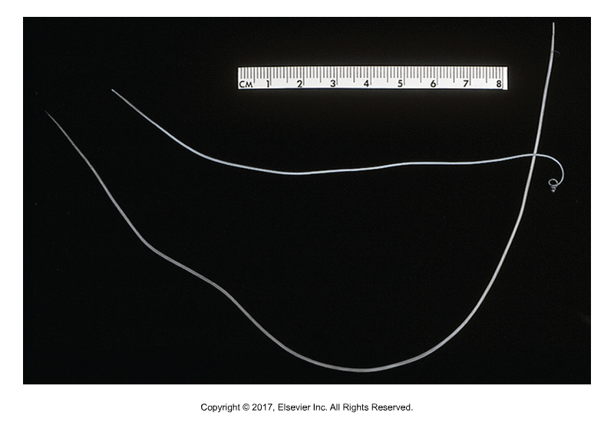

Aelurostrongylus abstrusus
Feline lung worm
Affects: Cats only
Found: Worldwide
Cause of infection: Ingestion of larvae (360mm long)
Adults live in respiratory bronchioles
Larvated eggs
S-shaped curve and dorsal spine on larvae
Larvae present in fecal or tracheal wash
Prepatent period: 30 days
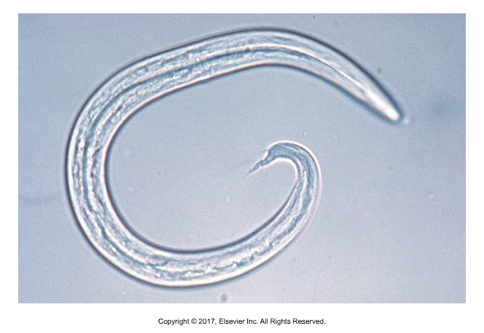
Oslerus osleri
Unique in that L1 phase is infective
No outside development is necessary
Dogs are definitive host
Cause of infection: Ingestion of larvae 232-266 um, often from mom to puppies via the mouth
Adults found at the bifurcation of trachea in nodules
Prepatent period: 10 weeks
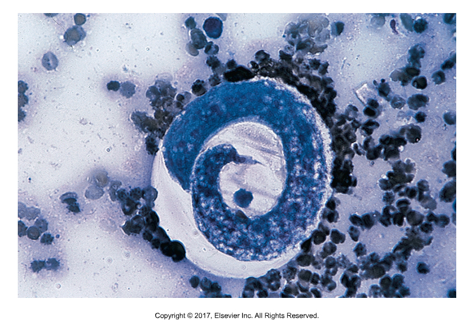
Dioctophyma renale
Canine giant kidney worm
Adults found in right kidney
Found: In North America and Europe
Cause of infection: Ingestion of larvae in annelid worm (ringed worms including earthworms and leeches) - can go through fish or frogs as paratenic hosts
Parasite eats through the parenchyma of kidney, leaving only capsule behind
Largest nematode. Males 30-40cm, Females can be 1m
Barrel shaped bipolar yellow brown egg found in urine sediment
Can "wander" into peritoneal cavity
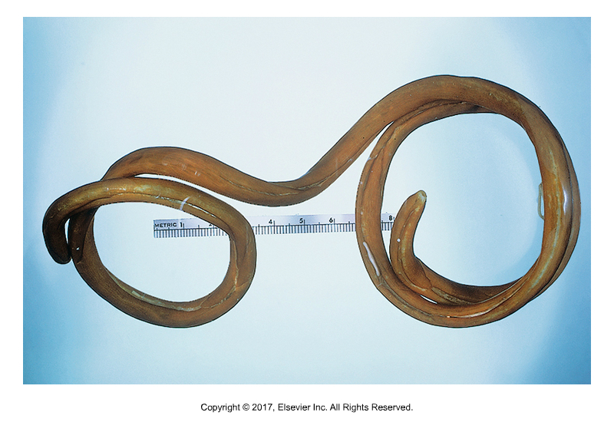

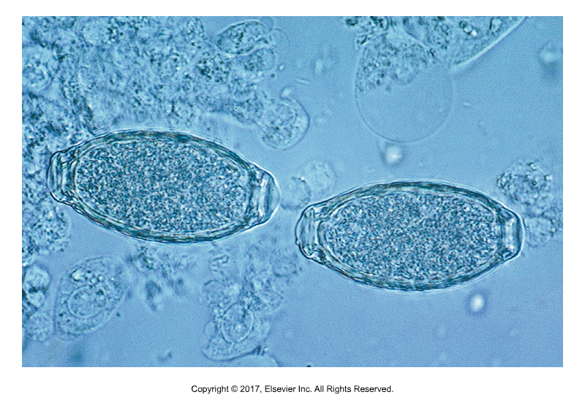
Pearsonema plica (dog), Pearsonema feliscati (cat)
Bladder worm
Adults found in bladder
Larvae get into Earthworms
Definitive host ingests worms
Eggs can be confused with whipworms
Bipolar flattened plugs
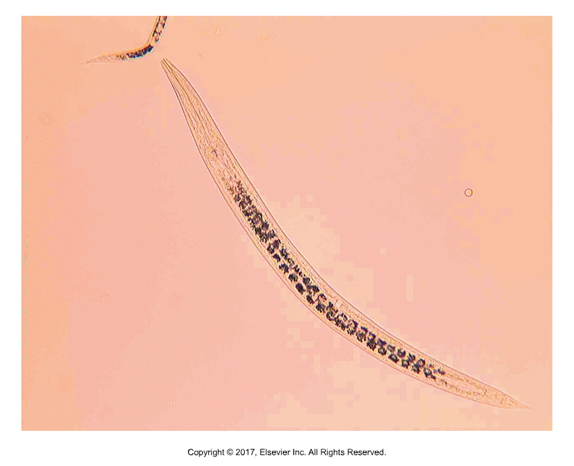
Rhabditis strongyloides
Facultative parasites — usually live in soil
L1 larvae get in through skin — red, crusty, loss of hair where inflamed
Larvae can be seen on skin scraping, even on cattle
L1 can look like microfilariae of D. immitis if taken from a bloody skin scraping
Dracunculus insignis
Guinea worm - "Small dragon"
Adult found in subcutaneous tissues of dog
Female 120cm; Male 2-3cm
Female produces draining ulcer on dog's skin; end of female comes out of ulcer
When she comes in contact with water, uterus prolapses and releasing L1 in water
L1 ingested by microscopic crustaceans (copepods) as intermediate host and molt to L3
Dogs infected by drinking water with these crustaceans
Female must be surgically removed
L1 must be differentiated from D. immitis and R. strongyloides
Thelazia californiensis
Eyeworm - "Nipple saliva"
Found: In North America
Adults found in conjunctiva and lacrical duct
Larvae passed by face fly, Musca autunmalis
Surgically removed from eye