muscular system notes
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
168 Terms
Skeletal Muscle
Muscles attached to the bones that are striated and voluntary.
Cardiac Muscle
Muscle located in the heart that is striated and involuntary.
Smooth Muscle
Muscle found in blood vessels and hollow organs that is nonstriated and involuntary.
Movement of the body
Contraction of skeletal muscles responsible for overall body movements.
Maintenance of posture
Skeletal muscles constantly maintain tone to keep us sitting or standing erect.
Respiration
Muscles of the thorax carry out breathing movements.
Production of body heat
Skeletal muscle contraction releases heat as a by-product, critical for maintaining body temperature.
Communication
Skeletal muscles are involved in speaking, writing, typing, gesturing, and facial expressions.
Constriction of organs and vessels
Contraction of smooth muscle in internal organs and vessels causes constriction.
Contraction of the heart
Contraction of cardiac muscle causes the heart to beat and propel blood throughout the body.
Excitability
The capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus.
Extensibility
The ability of a muscle to be stretched beyond its normal resting length and still contract.
Elasticity
The ability of muscle to recoil to its original resting length after being stretched.
Epimysium
Connective tissue sheath surrounding each skeletal muscle.
Fascicles
Groups of muscle cells within a skeletal muscle.
Perimysium
Connective tissue covering surrounding each fascicle.
Endomysium
Connective tissue covering surrounding each skeletal muscle fiber.
Sarcolemma
Cell membrane of a muscle fiber.
T tubules
Tubelike inward folds of the sarcolemma that connect to the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Sarcoplasm
The cytoplasm of a muscle fiber.
Myofibrils
Bundles of protein filaments within a muscle fiber.
Sarcomere
The basic structural and functional unit of a skeletal muscle.
Actin myofilament
Thin filament within a sarcomere.
Myosin myofilament
Thick filament within a sarcomere.
Z disk
Boundaries of a muscle sarcomere.
H zone
Center of the A band where there is no overlap between thick and thin myofilaments.
M line
Attachment site for the thick myofilaments in the center of the A band and sarcomere.
Troponin
Complex of three regulatory proteins integral to muscular contraction.
Tropomyosin
Two-stranded alpha-helical coiled coil protein found in the cell cytoskeletons.
Excitability of muscle fibers
The ability of muscle fibers to generate and conduct electrical impulses.
Resting membrane potential
The electrical charge difference across the cell membrane of an unstimulated cell.
Action potentials
Rapid changes in the membrane potential that allow muscle cells to perform contractions.
Resting membrane potential
The electrical potential difference across the cell membrane of a resting cell.
Action potential
A rapid change in charge across the cell membrane that allows for the transmission of electrical signals.
Depolarization
The process in which the inside of the cell membrane becomes more positively charged than the outside.
Repolarization
The process in which the cell membrane returns to its resting membrane potential after depolarization.
Motor neurons
Specialized nerve cells that stimulate muscles to contract.
Neuromuscular junction
The synapse where the fiber of a nerve connects to a muscle fiber.
Synapse
The junction between a nerve cell and either another nerve cell or an effector cell, such as a muscle or gland.
Motor unit
A group of muscle fibers that a motor neuron stimulates.
Presynaptic terminal
The end of a neuron cell axon fiber.
Synaptic cleft
The space between the presynaptic terminal and the postsynaptic membrane.
Post synaptic membrane
The muscle fiber membrane or sarcolemma.
Synaptic vesicles
Vesicles in the presynaptic terminal that store and release neurotransmitter chemicals.
Neurotransmitter
Chemicals that stimulate or inhibit the postsynaptic cells.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
A neurotransmitter that stimulates skeletal muscles.
Muscle contraction
The result of an action potential in a muscle fiber, leading to the shortening of the muscle.
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate, the energy currency of cells.
Cross-bridge
The attachment between myosin and actin during muscle contraction.
Krebs Cycle
A series of chemical reactions that occur in the mitochondria to produce ATP aerobically.
Glycolysis
The breakdown of glucose to produce ATP anaerobically.
Creatine phosphate
A molecule that stores energy in muscle cells and can be used to resynthesize ATP.
Muscle twitch
A single contraction of a muscle fiber in response to a stimulus.
Lag phase or latent phase
The time between the application of a stimulus and the beginning of contraction.
Contraction phase
The time during which the muscle contracts.
Relaxation Phase
The time during which the muscle relaxes.
Slow Twitch Fibers
Muscle fibers that contract slowly, fatigue slowly, have a considerable amount of myoglobulin, and use aerobic respiration. They are darker in color and are used by long-distance runners.
Fast Twitch Fibers
Muscle fibers that contract quickly, fatigue quickly, use anaerobic respiration, and get energy from glycogen. They are lighter in color and are used by sprinters.
Muscle Fatigue
A temporary state of reduced work capacity in muscles, caused by factors such as acidosis, ATP depletion, and oxidative stress.
Isometric Contractions
Muscle contractions that increase tension in the muscle without changing its length.
Isotonic Contractions
Muscle contractions that have a constant amount of tension while decreasing the length of the muscle.
Concentric Contractions
Isotonic contractions in which muscle tension increases as the muscle shortens.
Eccentric Contractions
Isotonic contractions in which tension is maintained in a muscle, but the opposing resistance causes the muscle to lengthen.
Tendon
Connects skeletal muscle to bone.
Aponeuroses
Broad, sheetlike tendons.
Origin
The attachment of a skeletal muscle at the least mobile location.
Insertion
The end of the muscle attached to the bone undergoing the greatest movement.
Belly
The part of the muscle between the origin and the insertion.
Action
The specific body movement a muscle contraction causes.
Agonists
A group of muscles working together.
Antagonists
A muscle or group of muscles that oppose muscle actions.
Synergist
A group of muscles working together to produce a movement.
Prime Mover
A muscle that plays a major role in accomplishing the desired movement.
Fixators
Muscles that hold one bone in place relative to the body while a usually more distal bone is moved.
Muscle Attachment
The point where a muscle is attached to a bone.
Nomenclature
The naming of muscles based on factors such as location, size, shape, orientation of fascicles, origin and insertion, number of heads, and function.
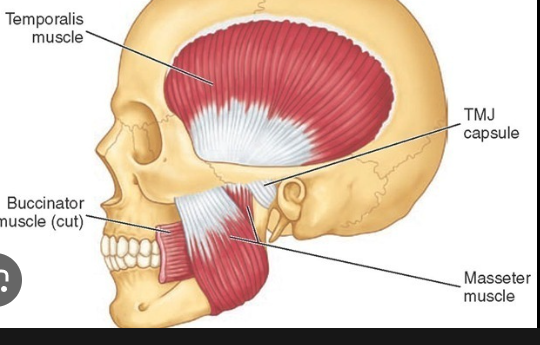
Muscles of Mastication
Muscles involved in the movement of the jaw.
Temporalis
A muscle that elevates and draws the mandible posteriorly, closing the jaw.
Insertion: Anterior portion of the Mandibular Ramus and Coronoid Process
Origin: Temporal fossa
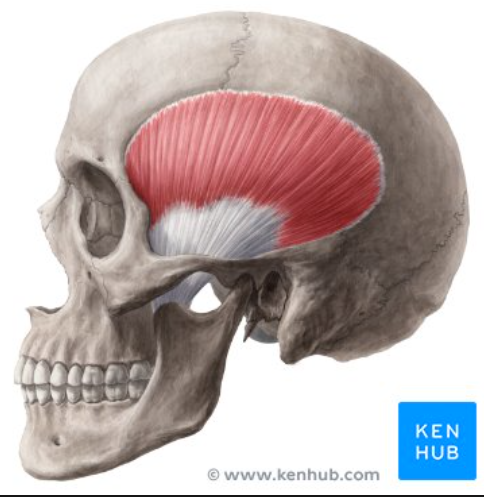
Masseter
• Origin: Zygomatic arch
• Insertion: Lateral side of mandibular ramus
• Action: Elevates and pushes mandible anteriorly; closes jaw
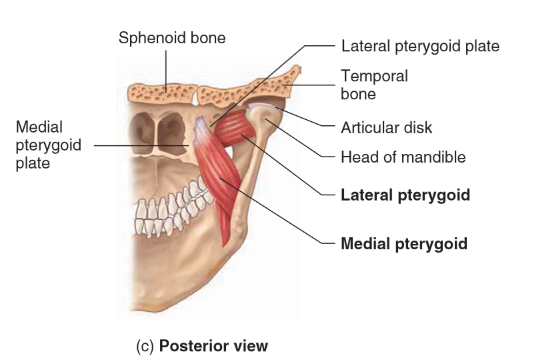
Lateral Pterygoid
Origin: Lateral pterygoid plate and greater wing of sphenoid
Insertion: Condylar process of mandible and articular disk
Action: Pushes mandible anteriorly and depresses mandible; closes jaw
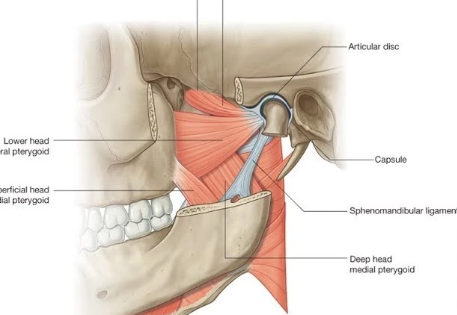
Medial Pterygoid
• Origin: Lateral pterygoid plate of sphenoid and tuberosity of maxilla
• Insertion: Medial surface of mandible
• Action: Pushes mandible anteriorly and elevates mandible; closes jaw
Muscles of Facial Expression
Muscles involved in facial expressions.
Buccinator
• Origin: Maxilla and mandible
• Insertion: Orbicularis oris at corner of mouth
• Action: Draws corner of mouth posteriorly; compresses cheek to hold food between teeth
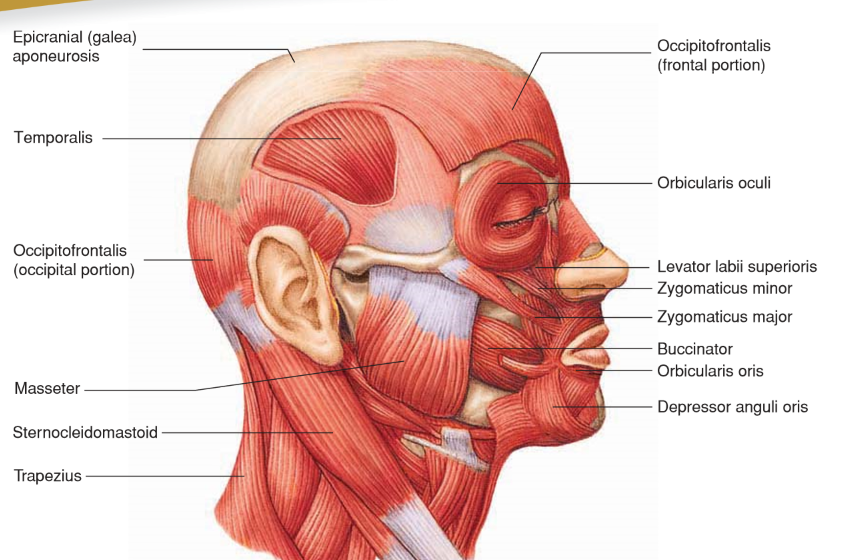
Depressor Anguli Oris
• Origin: Lower border of mandible
• Insertion: Skin of lip near corner of mouth
• Action: Lowers corner of mouth; “frown”
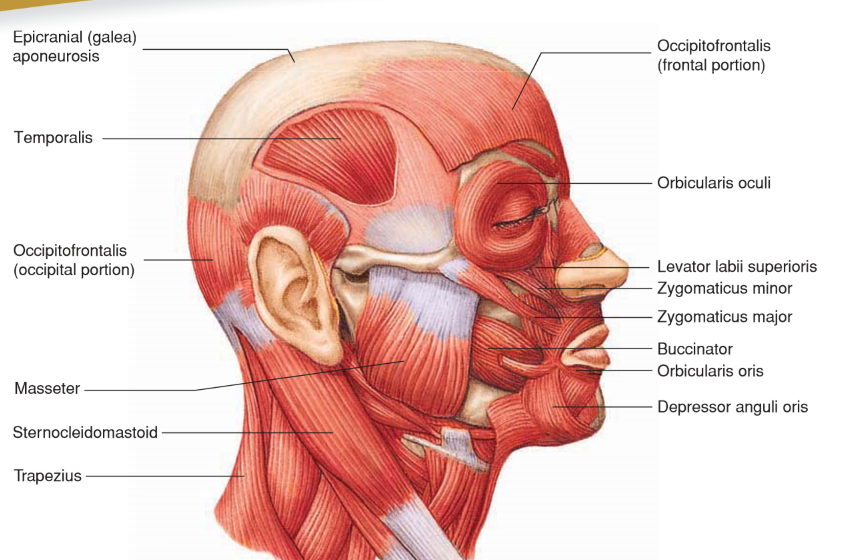
Levator Labii Superioris
Origin: Maxilla
Insertion: Skin and orbicularis oris of upper lip
Action: Raises upper lip; sneer
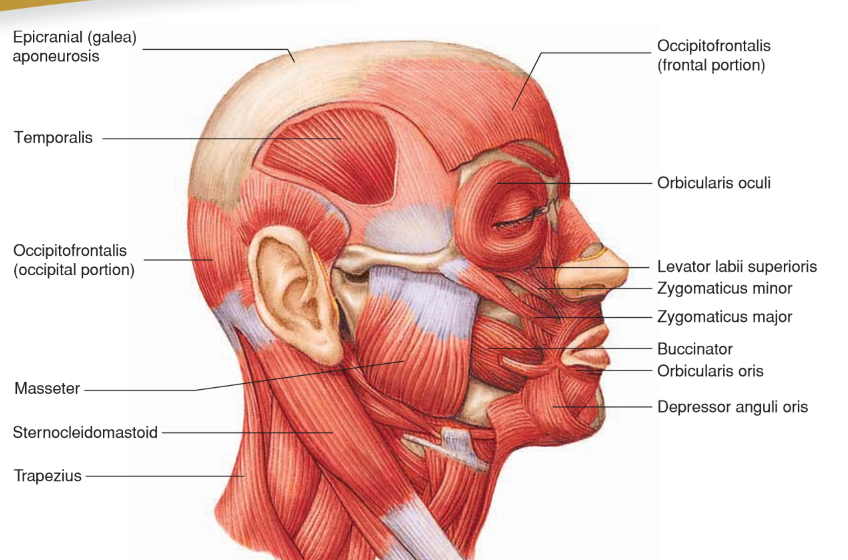
Occipitofrontalis
• Origin: Occipital bone
• Insertion: Skin of eyebrow and nose
• Action: Moves scalp; raises eyebrows
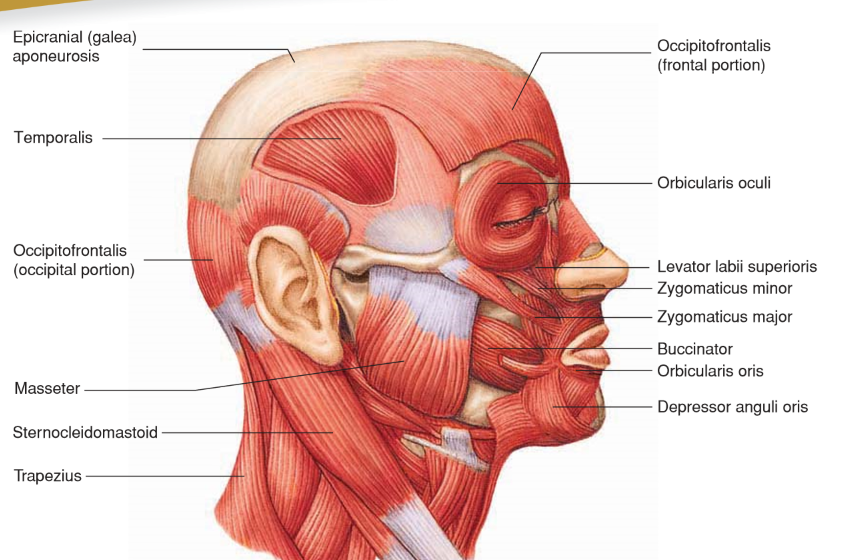
Orbicularis Oculi
• Origin: Maxilla and frontal bones
• Insertion: Circles orbit and inserts onto SKIN around eyelids
Action: Closes eyes; blinking, winking, squinting
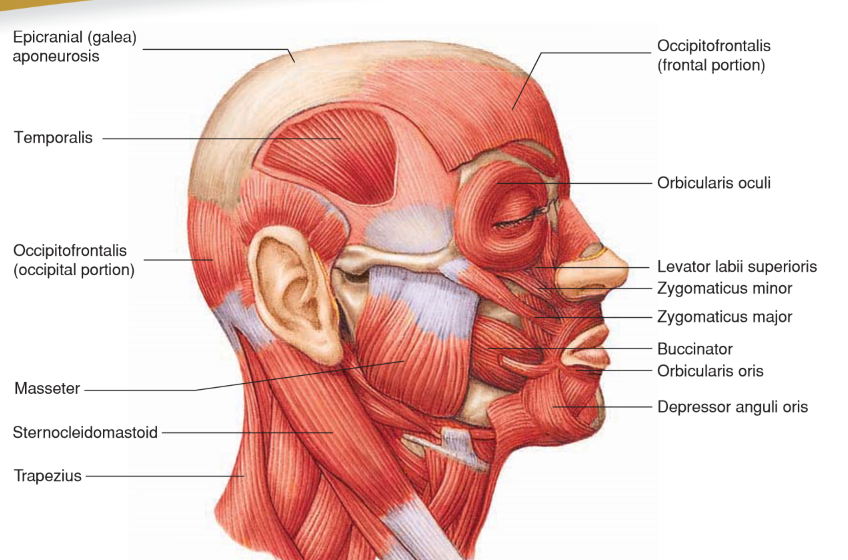
Orbicularis Oris
Origin: Nasal septum, maxilla, and mandible
• Insertion: Fascia and other muscles of lips
Action: Closes and purses lips; “kissing”
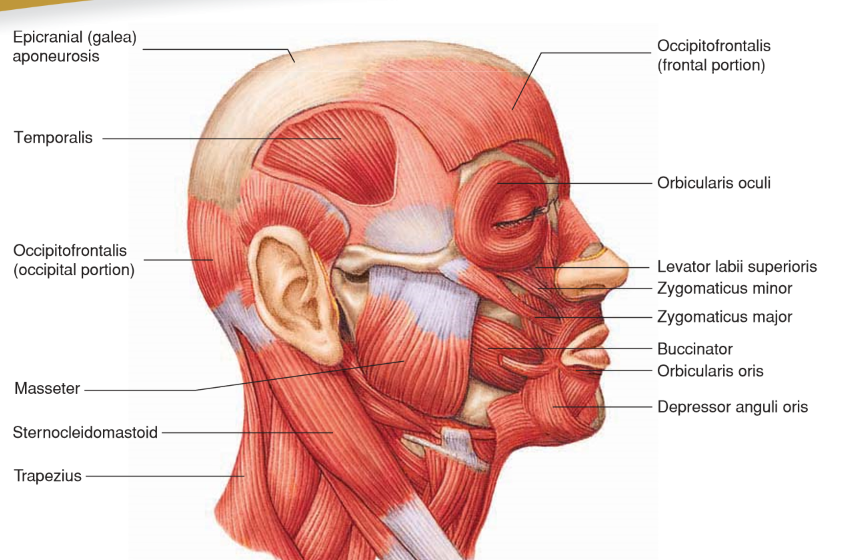
Zygomaticus Major
• Origin: Zygomatic bone
• Insertion: Angle of mouth
• Action: Elevates and abducts upper lip and corner of mouth; “smile”
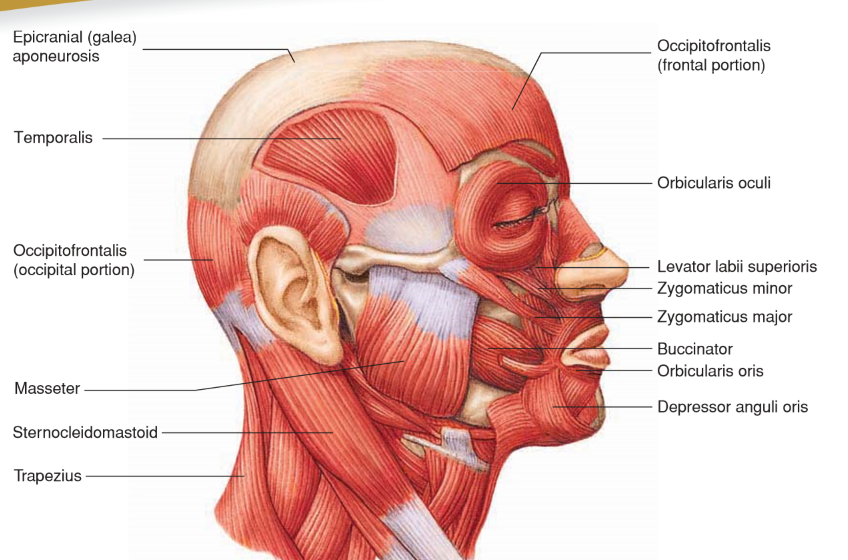
Zygomaticus Minor
• Origin: Zygomatic bone
• Insertion: Orbicularis oris of upper lip
• Action: Elevates and abducts upper lip; “smile”
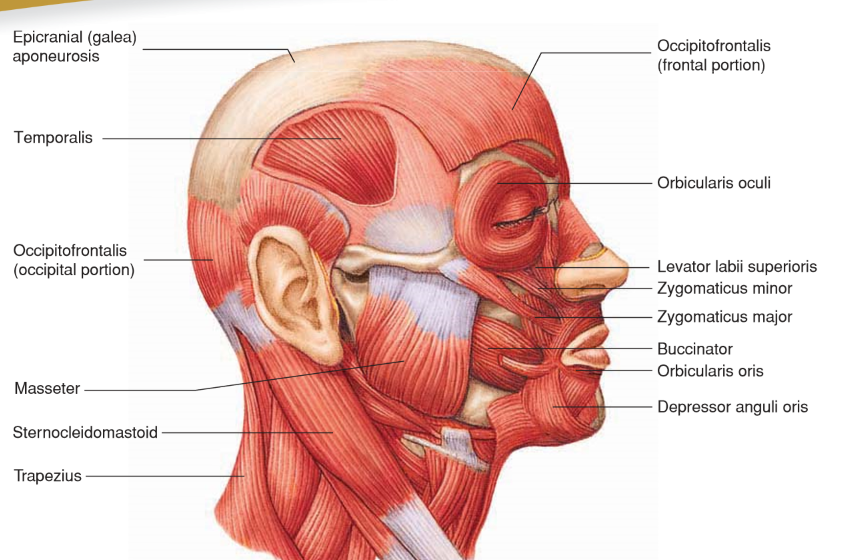
Flexors (Muscles of the Neck)
• Origin: Anterior side of vertebrae
• Insertion: Base of skull
• Action: Flex head and neck
Extensors (Muscles of the Neck)
Originates from the posterior side of vertebrae and inserts into the base of the skull. They extend the head and neck.
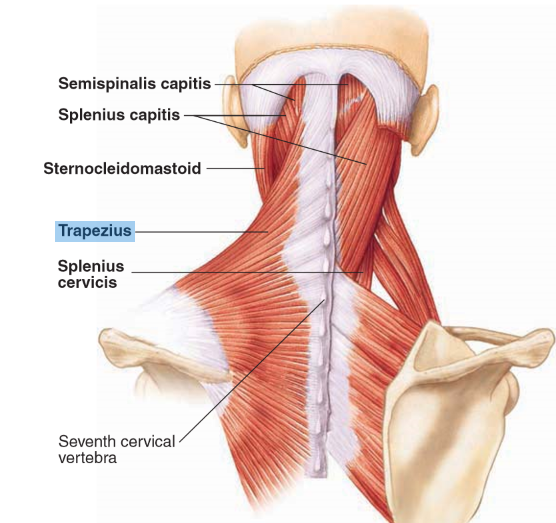
Sternocleidomastoid
• Origin: Manubrium of sternum and medial part of clavicle
• Insertion: Mastoid process and nuchal line of skull
• Action: Individually rotate head; together flex neck
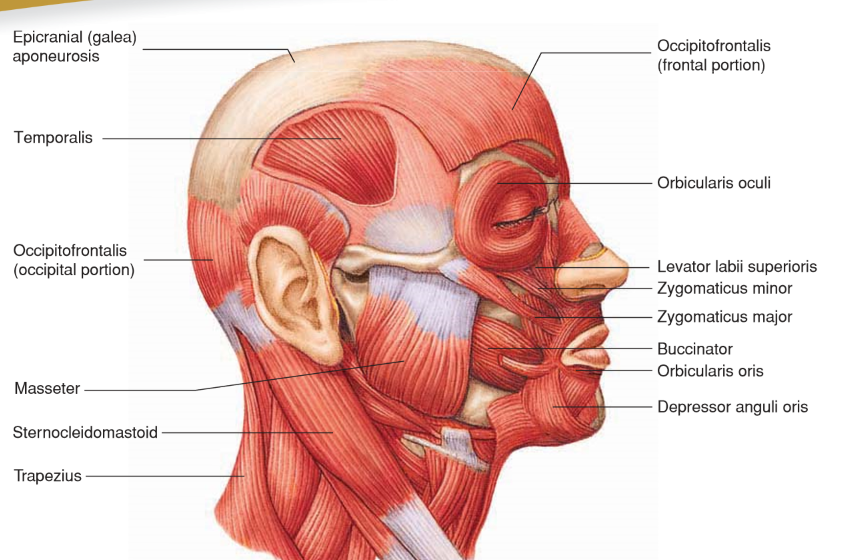
Trapezius
Originates from the posterior surface of the skull and upper vertebral column (C7-T12), and inserts into the clavicle, acromion process, and scapular spine. It extends and laterally flexes the neck.
INTRINSIC
• Origin: Inside tongue
• Insertion: Inside tongue
• Action: Changes shape of tongue
EXTRINSIC
Origin: Bones around oral cavity or soft palate
•Insertion: Onto tongue
Action: Moves tongue
Suprahyoid muscles (geniohyoid, stylohyoid, and hyoglossus)
• Origin: Base of skull, mandible
• Insertion: Hyoid bone
• Action: Elevates or stabilizes hyoid
INFRAHYOID
• Origin: Sternum, larynx
• Insertion: Hyoid bone
• Action: Depresses or stabilizes hyoid
ELEVATORS
• Origin: Soft palate and auditory tube
• Insertion: Pharynx
• Action: Elevate pharynx
CONSTRICTORS
• Origin: Larynx and hyoid
• Insertion: Pharynx
• Action: Constrict pharynx