End of the Bronze Age/Homer/Iron Age
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Iliad
Epic composed through oral tradition
not a history book
Presents a collection of cultures from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age
Equipment: boar-tusk velvets , tower-shields , silver-studded swords , and weapons belong to the Bronze Age (2nd millennium)
Catalogue of ships (books 2) lists Mycenaean ships/many which
are unattested later)
Rock-cut ditches are talked about in the epic
No reference to Hilties or Meletus (Achean stronghold)
Acreans united in language (Panhellenism) → reflects the 8th century → Iron Age, Trojans speak different languages (8th cent .= Luwian ,Greek , Lydian , Phrygian) in the Iron Age
Bronze Age Collaspe
The end of Troy VIIA occurred roughly at the time when Mycenaean palaces
and Hattusa were destroyed in c. 1200 BC -> identity of the attackers is unknown
The only place to survive the collapse was Egypt
were attacked these times: 1208, 1178, 1175 BC
were attacked by the “sea people”
Evidence of Bronze Age Collaspe
widespread destructions
- Earthquake
- Palaces destroyed (many sacked and burned down)
- Never rebuilt
- abandonment of settlements
- migrations
- collapse of trade
- economic depression
- depopulation of certain regions
Explanations
natural disasters: Earthquake? Drought?
- attack by outsiders
• Dorians? “Sea Peoples”? Warrior bands from the Danube?
- internal strife; civil war?

Large Bowl from Mycenae
1200BC → around the type the fortifications were built
image of ranked soldiers
shows that militarism was on the rise

Image - Lion Gate
Cyclopean masonry
c. 1250 BC
Akkadian Cuneiform Letters
found in the ruins of Uganit, destroyed in c. 1180 BC
letter between the King of Cyprus to Ammurapi, King of Uganit
asking for reinforcement against a force that came from the sea
Myth-history of the Bronze Age
setting for Homeric epics and heroic ancestry
Trojan War
Age of heroes and gods
Model of virtue (ideal behavior)
texts like the Homeric epic are used as guides for virtuous behavior
warrior ethos → glory in war, being courageous in battle
Arete
Arete
excellence, being the best
part of the warrior ethos
Iron Age
1100 - 900 BC
c. 1050: smelting and working of Iron develops
by c. 950: most tools and weapons made of iron
they started to use iron for jewelry, then tools, and lastly weapons
Bronze was still around
They were making steel by alloying iron with carbon
Iron Age Pottery
Submycenaean, c 1100 - 1000 BC
bands around the base and shoulder
very simple
Protogeometric , c. 1050-950 BC
geometric designs
ex. concentric circles
beginning of the use of black slip → a different diluted clay that was painted onto the original clay
There is new equipment that is made to make pottery with more consistent designs
Submyceanean Pottery
1100 - 1000 BC
bands around the base and shoulder
very simple
The designs were done with freehand
Protogeometric Pottery
c. 1050-950 BC
geometric designs
ex. concentric circles
beginning of the use of black slip → a different diluted clay that was painted onto the original clay
Designs would be done with technology, like a compass
Black Slip
a different diluted clay that was painted onto the original clay
is a very complex process
Belly Handled Amphora
used for female cremation
refers to the handle being on the “belly” of the amphora
were used as cinerary urns
With the Iron Age came a new form of burial → cremation
Karphi
1100-1000 BC
Iron Age site
located on the island of Crete
is on a mountain-side
has a shrine and a potential “big house”
Karphi goddess

Karphi goddess
1100-1000 BC
seems to have horns of consecration on her headress
is potentially wearing a flounced dress
was 2ft tall
was something that was worshipped
has exposed breasts
is definently more simple and rudimentary than statues from the Bronze Age

Gazi goddess
Post-Palatial Phase → LMIIIC
Crete
also has the horns of consecration and raised hands
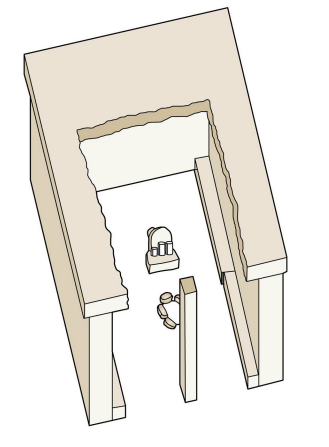
Phoenician “Temple” at Kommos
925-600 BC
a bit iffy to called it a temple
has a block with three stones on it, some think it represents deities
But that isn’t how deities are typically represented
unless it’s a meteorite
Phoenicians
peoples from the Levant
Were traders and merchants
They thrive from the Iron Age onwards
Lefkandi
on the island of Euboea
Toumba building at Lefkandi
10th century (900s) BC
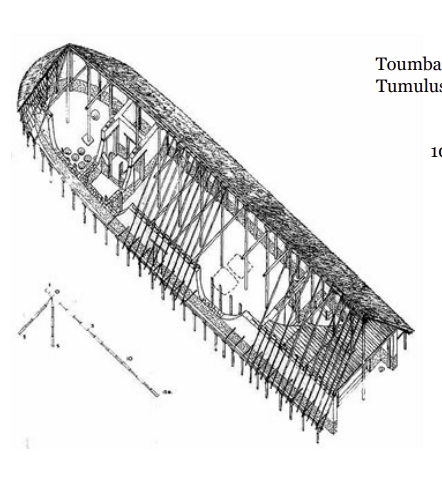
Toumba at Lefkandi
tumulus over the chief’s “house”
was a heroon
home of the basileos → would have been someone who attempted to live up to the heroic ideal
There’s no evidence that toumba building was used as a house
There was no kitchen
the idea that the Chief house would be dismantled is problematic
is potentially just a burial chamber in a tumulus that collapsed
· at the time they were made of perishable material
Heroon
the burial place of a hero
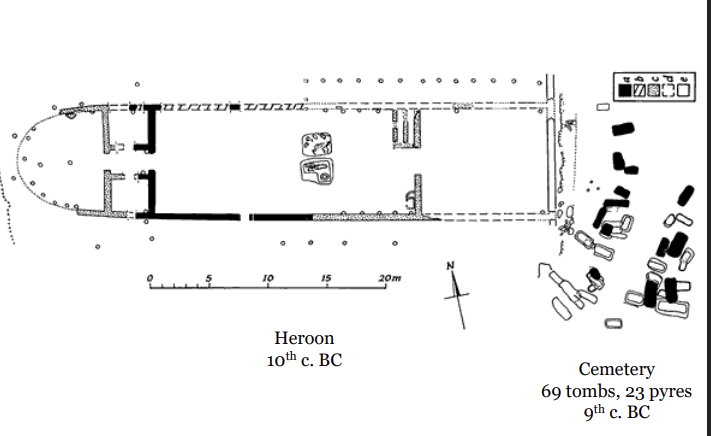
Heroon at Lefkandi
There were two shaft graves in the middle of the building
The chief (basileos) was in a cinerary urn → a bronze urn → an heirloom form the Bronze Age
The chief’s wife was also buried there
She was in her 30s
Four horses
There is a cemetery near the Heroon → 9th century BC (800s)
69 tombs
23 pyres
Heroon Grave Goods
Cremation (Chief)
Amphora w/sword , wooden scabbard, razor, and whetstone
Inhumation (Wife)
gold earrings ,gold necklace , faience and crystal , gold pendant, gold disks over breasts ,bronze and iron fibulae = pins
Bronze cremation urn
12th cent . BC
Found in the heroon
was from Cyrus
bowl decoration on rims and handles → Hunting lions and bulls
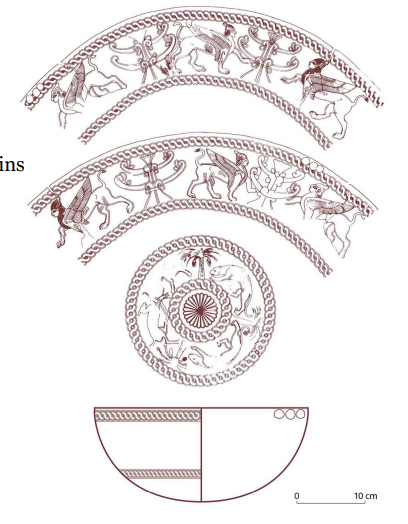
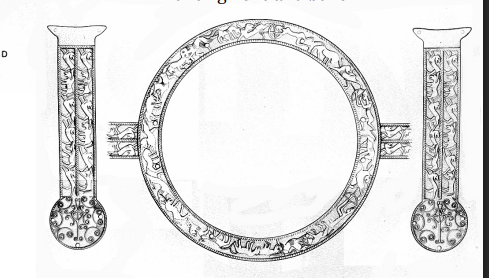
Phoenician Bowl
10th cent. BC
decorated with panthers, griffins, palm trees, and concentric circles
demonstrates that there was contact with the Levant and the near east.
Fibulae
pins used for clothing

Centaur from Lefkandi
900 BC
Could be an image of Cheiron
-Was the mentor of Achilles
-Has a notch on the knee
is painted with a geometric design → everything was painted and with geometric patterns
Diagnostic pottery
pottery that are able to be dated

Euboian Sub-Protogeometric Skyphos
10th-8th century BC
Is black glazed
Pendant semicircles
Is an example of diagnostic pottery
Are found in the Levant, the Cycladic islands, islands off of Italy
Was manufactured around the same time the Tumba was built
Skyphos
a cup