5) Central Dogma of Biology
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Frederick Griffith
Responsible for the discovery of DNA’s genetic role.
He was trying to develop a vaccine against pneumonia.
He was observing two strains of the pneumonia bacteria:
one that is harmless and the other causes the disease in mammals (it is pathogenic).
He killed the pathogenic ones and mixed the remains with the harmless strain and was surprised that some of the living strains became pathogenic.
Furthermore, descendants of the transformed bacteria also acquired the ability to cause the disease.
Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase
experimented and showed that DNA is the genetic material, specifically of the bacteriophage (or simply phage), viruses that exclusively infect bacteria.
DNA
What is the molecule for heredity?
Rosalind Franklin
James Watson
Francis Crick
These are the three people who determined the shape of DNA as a double-stranded helix.
Rosalind Franklin was able to take an X-ray image of the DNA, and the two men expanded on it.
Watson and Crick proposed that the specific pairing of the DNA’s bases account for its ability to be copied.
James Watson & Francis Crick
These two men expanded on Rosalind Franklin’s theory, their model predicted that when a double helix replicates, each of the resulting strands will have one old strand from the parental molecule and another newly created strand.
This model came to be known as the semiconservative model because half of the parental strand is maintained in the daughter strands (hence it is conserved).
Semiconservative model
What do you call the model which predicted that when a double helix replicates, each of the resulting strands will have one old strand from the parental molecule and another newly created strand.
Basically, half of the parental strand is maintained in the daughter strands (hence it is conserved).
Origins of replication
Replication of DNA begins at particular sites called ______, which are short stretches of specific DNA sequences.
Proteins attach at the sites to separate the strands of the helix and replication ensues in both directions, creating replication “bubbles
How does DNA copy itself?
Imagine you have a zipper on your jacket. The zipper is like DNA, made up of two sides that are stuck together.
Now imagine some little helpers (proteins) come in. They unzip the zipper at one spot, making a small bubble where the two sides are not stuck anymore. This bubble is like a space where work is being done!
As the helpers keep unzipping more and more, the bubble grows bigger, and new matching zippers (new strands) start forming next to the old ones.
Eventually, the entire zipper is unzipped—but now, instead of just one zipper, you have two zippers! Each one has one old side and one brand new side.
In terms of chemical composition, a DNA strand has two ends called?
3’ (three-prime end)
5’ (five-prime end) which refers to the carbon atom of the nucleotide sugar.
The 3’ carbon atom is attached to an -OH group while the 5’ carbon is attached to the phosphate group.
DNA Polymerase
These are proteins that add new DNA strands (daughter strands) during replication, only to the 3’ end.
It also proofreads to remove bases paired incorrectly during replication.
Together with DNA ligase, the two proteins also repair DNA damaged by radiation or other toxic chemicals from the environment.
3’ to 5’ Parent Strand
The DNA strand that is copied continuously because DNA polymerase can easily follow its direction.
5’ to 3’ Parent Strand
The DNA strand that is copied in short pieces since DNA polymerase can’t move in this direction.
Okazaki Fragments
Short pieces of DNA formed on the 5’ to 3’ parent strand during replication.
DNA Ligase
The protein that connects Okazaki fragments to form a continuous daughter strand.
Gene Expression
This process goes from DNA to RNA to Protein
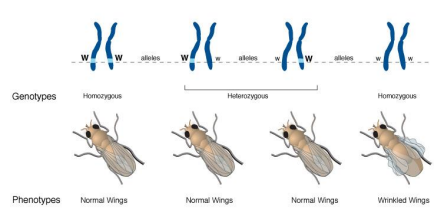
Genotype
an organism’s genetic makeup and is the heritable information stored in the nucleotide sequences of DNA.
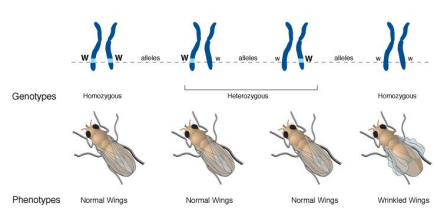
Phenotype
This is the organism’s physical traits.
Central dogma of biology
Genes alone do not build proteins directly.
This refers to the flow of genetic information and therefore its expression.
This tells us that the molecular chain of command is from the DNA in the cell, to RNA, to protein synthesis in the cytoplasm.
Transcription (the synthesis of RNA based on instructions from DNA)
Translation (the synthesis of protein under the direction of RNA)
These are the two main stages of the central dogma
Transcription
The process of copying a DNA strand to make an RNA molecule.
RNA Polymerase
The enzyme that builds the RNA strand by following base-pairing rules.
Template Strand
The DNA strand used by RNA polymerase to create a matching RNA strand.
Promoter
A specific DNA sequence where RNA polymerase binds to start transcription.
Terminator
A DNA sequence that signals RNA polymerase to stop transcription.
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
What are the three major steps in gene transcription?
Initiation
This step involves the attachment of RNA polymerase to the promoter to start RNA synthesis.
Elongation
This step is where the newly formed RNA strand grows with the growing RNA peeling away from its DNA template.
This allows the separated DNA strands to come back together in the region already transcribed
Termination
When RNA polymerase reaches the terminator DNA, the polymerase molecule detaches from the newly formed RNA strand and the gene.
Genes
What provides the instructions for making specific proteins?
RNA
What do you call the bridge / nucleic acid linking DNA and protein synthesis?
Transcription
FIRST!!
What do you call the process when DNA forms RNA?
Uracil
DNA uses thymine to avoid mutation from cytosine deamination and to improve long-term stability.
RNA uses uracil because it's more energy-efficient and stability is not as critical.
What pyrimidine base replace Thymine in the RNA?
Pyrimidine base
A type of nitrogenous base with a single-ring structure found in DNA and RNA; includes cytosine, thymine (DNA), and uracil (RNA).
Codons
What do you call the triplet code which are instructions for the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide are a series of nonoverlapping three-base “words”
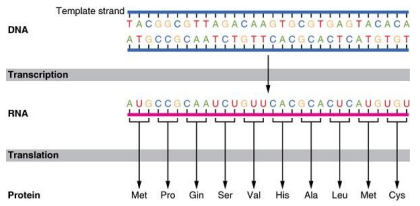
Codon
a sequence of three nitrogenous bases in mRNA that codes for a specific amino acid or a start/stop signal during protein synthesis.
20
Proteins are made up of how many amino acids?
AUG
This three base unit has the following functions:
it codes for the amino acid methionine (Met)
provides the signal for starting the polypeptide chain. You can say it is the start codon.
UAA
UGA
UAG
These 3 codons do not code for amino acids because they mark the end of translation (thus, being referred to as stop codons).
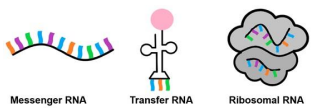
Messenger RNA
Transfer RNA
Ribosomal RNA
What are the three types of RNA?
Messenger RNA
– Delivering Instructions from the DNA.
This kind of RNA encodes for amino acid sequences because it conveys instructions from DNA to the translation mechanism of the cell.
This is transcribed from DNA with the information within used to translate into polypeptides.
Cytoplasm
In prokaryotes where do both transcription and translation happen since they have no nucleus?
Nucleus
in the nucleus, then processed and sent to the cytoplasm for translation.
In eukaryotes, where is mRNA made?
5’ Cap and 3’ Tail
These are extra sequences added to mRNA—a cap at the 5’ end and a tail at the 3’ end—to help export and protect the mRNA.
Introns
Non-coding sequences in mRNA that are removed during processing.
Exons
Coding sequences in mRNA that are kept and joined together to form the final message used in translation.
RNA splicing
The cut-and-paste process that removes introns and joins exons; ensures accuracy in mRNA processing.
Transfer RNA
– Picker of Proteins
This kind of RNA acts as an interpreter, transferring amino acids to a growing protein during translation.
tRNA performs two main tasks:
Picks up the correct amino acid from the cytoplasm
Matches its anticodon to the correct codon on the mRNA
What is the role of tRNA in Translation?
Anticodon
A triplet of bases on tRNA that pairs with a complementary codon on mRNA.
tRNA molecule
It is the site where one specific kind of amino acid attaches. These type of molecules occur for different amino acids and each also has specific enzymes that assist in joining the correct tRNA to its corresponding amino acid, with the use of ATP
Ribosomal RNA
– Facilitator of Translation
What type of RNA helps build ribosomes and facilitates translation by linking mRNA and tRNA to form proteins?
Ribosomes
What is the final component of translation?
These structures in the cytoplasm that coordinate both mRNA and tRNA and catalyze the production of polypeptides.
a large and small subunit, each made up of proteins and a kind of RNA called ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
What are the two subunits of ribosomes?
Eukaryotic ribosomes are slightly larger than bacterial ones. These differences allow antibiotics like streptomycin to target bacteria without harming human cells.
How are eukaryotic and bacterial ribosomes different from each other?
Translation
It is the process of converting the genetic code in mRNA into a chain of amino acids, which folds into a protein. It occurs in the ribosome, using the instructions copied from DNA during transcription.
Transcription occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells.
Where does transcription occur?
🧠 Remember:
Transcription = DNA → mRNA
Translation = mRNA → Protein
🧠 Remember:
Transcription = DNA → mRNA
Translation = mRNA → Protein
Just like transcription;
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
What are the three steps in translation?
Initiation
Which phase in translation is being described?
mRNA binds to the small ribosomal subunit, and an initiator tRNA carrying methionine (Met) pairs its anticodon (UAC) with the start codon (AUG).
The large ribosomal subunit joins, forming a complete ribosome with two sites:
P site: holds the initiator tRNA and growing polypeptide
A site: accepts the next tRNA carrying a new amino acid
Elongation
Which phase in translation is being described?
A new tRNA anticodon pairs with the mRNA codon at the A site.
The polypeptide detaches from the tRNA in the P site and forms a peptide bond with the amino acid in the A site.
The empty tRNA in the P site leaves, the A site tRNA moves to P, pulling the mRNA with it, and a new tRNA enters the A site. This cycle repeats.
Mutation
This term refers to any change to the genetic information of a cell
Nucleotide substitution
What occurs when one nucleotide in mRNA gets replaced?
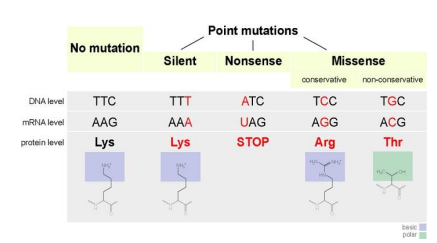
Silent mutation
This type of mutation results when the substituted nucleotide still encodes for the same amino acid, this will have no effect at all leading to a ____
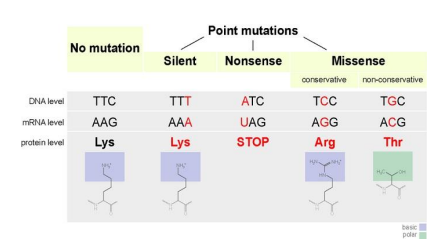
Missense mutation
This type of mutation results when the substituted nucleotide causes a change in the amino acid sequence.
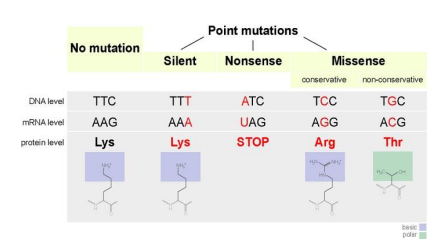
Nonsense mutation
This type of mutation results when the substitution causes the codon to be one of the stop codons which results in a prematurely terminated protein that may not function properly
Frameshift mutation
This type of mutation occurs whenever the mRNA gets inserted or deleted by a nucleotide that is not a multiple of three, resulting in the nucleotide sequences regrouping into different codons.
“The cat ate the rat”
If we remove c the result is a nonsensical message:
“The ata tet her at.”
These mutations in a way will most likely produce nonfunctional polypeptides and often have disastrous effects.
Mutagens
Mutations can arise in many ways: from errors during DNA replication or recombination; or due to effects of physical or chemical agents called ______.
Viruses
These are infectious particles consisting of nucleic acids wrapped in a protein coat called a capsid and in some, a membranous envelope. Unlike other organisms, viral genomes can be DNA or RNA and usually consist of a single molecule of nucleic acid, which may be linear or circular
Bacteria are living organisms. They are made of cells, can reproduce, grow, and use energy on their own.
Viruses are not truly living. They don’t have cells and can only reproduce inside a host. Outside a host, they are inactive.
Are bacteria and viruses living?
lytic cycle
lysogenic cycle.
Both cycles begin when the phage enters the bacterium and forms a loop.
What are the two routes that viruses take once they are inside cells?
Lytic cycle
A viral reproduction cycle where the virus takes over a host cell, makes copies of itself, and bursts (lyses) the cell to infect others.
Lysogenic cell
A viral cycle where viral DNA integrates into the host's chromosome (as a prophage) and is copied every time the cell divides, without killing the host.
Prophage
Viral DNA that is inserted into a bacterial chromosome during the lysogenic cycle.
A lytic virus that targets alveoli in the lungs, causing respiratory symptoms.
What type of virus is COVID-19?
Single circular chromosome
Where are most bacterial DNA stored?
Binary Fission
An asexual reproduction method where a bacterial cell replicates its chromosome and splits into two identical cells.
Transformation
Transduction
Conjugation
Although binary fission is asexual, bacteria can still create genetic variation through:
Transformation – Uptake of foreign DNA from the environment.
Transduction – Transfer of DNA between bacteria using bacteriophages.
Conjugation – Direct DNA transfer between bacteria through sex pili. The donor cell, guided by the F factor, replicates and shares DNA with the recipient cell.
Transformation
A process where bacteria absorb foreign DNA directly from their environment.
Transduction
Gene transfer between bacteria using bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria).
Conjugation
A process where bacteria exchange genes through direct contact using sex pili, transferring DNA from a donor to a recipient cell.
F Factor (Fertility Factor)
A specific piece of DNA that allows a donor cell to form sex pili and carry out conjugation.