Unit 5 - Political Participation
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Rational Choice Voting
voting rationally
Retrospective Voting
Looking at past record of politician in question
Prospective Voting
Look at how the party or candidate will perform in the future.
Party-line Voting
Voting down the line of party.
Voter Turnout
structural barriers
a policy or law can prevent or encourage people for voting
political efficacy
belief of weather their vote matters
demographics
age
type of election
national get more than state or midterm
Factors affecting vote
party/ideology
candidate characteristics
political issues
religion, sex, race
Linkage Institution
Societal structure that connects people to their government or the political process
The 4 Linkage institutions
political parties
interest groups
elections
media
Party and Ideology
Democratic is liberal ideas
Republican is conservative ideas
Coalition
a demographic group
Party Realignment
Rearranging stuff if you lose or win
Why can’t 3rd parties win?
Winner takes all
whoever has the popular vote in the district gets all electoral vote and 3rd party will never get popular vote
Two parties incorporate third-party ideas
Interest Group
A group of people who gather around a policy issue to try and persuade policy makers to pass legislation that is favorable to the group.
Why interest groups exist
Lobbying - pushing, educating
Going door to door in the capitol and pushing for their goal
Asking for the support of congress people
Electioneering/Campaigning ($)
Donate time and support certain people running for office
Tell people in their group hey vote for this person they support our policy/agenda
Litigation - lawsuits, amicus curiae
File lawsuits
Help out with lawsuits
File out amicus curiae briefs to help if they think the case has to do with their agenda
Going Public - Spread awareness
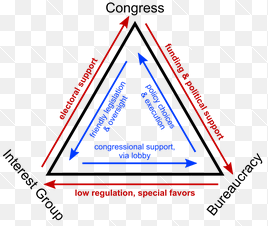
Iron Triangle
The strong, mutually beneficial relationship between interest groups, congressional committees, and government agencies
Members of Congressional committees are especially helped by interest groups
provide them with policy information
provide campaigns donations if the representative is the sympathetic to the group’s goals
Types of Interest Groups
Single issue
Devoted to one thing (ex: pro-choice)
Corporate
Defense contractors
Union
Teachers unions
Firefighters unions
Electricians unions
Electing a President
candidates first have to earn their party’s nomination through primary elections
elections in which members of a party vote on which candidate they want to represent them in the general election
Some states hold open primaries
Any registered voter can vote in either party’s primary—but not both
Some states hold closed primaries
Only people registered with the party can vote in those primaries
Caucus
Same as the primary but instead of using secret ballots to cast their vote, voter at a caucus discus and debate together and then vote publicly.
National Convention
A big party for the winning candidate and their choice for president and that’s the beginning of the general election
Incumbent vs Challenger
Incumbent has already been there, challenger is a newbie
incumbent>challenger
Election Day
First Tuesday of November
Electoral College
Winner takes all system for each state
faithless electors vote against popular vote
almost never happens
How many votes does the candidate need to win?
At least 270/538 electoral votes.
Congressional elections
every 2 years
members of the house of reps have 2 year terms
senators have 6 year terms
1/3 are up for reelection every 2 years
90% of incumbents win reelection
What effects campaign spending?
election cycles (starting campaign as early as possible)
complexity of campaigns (hiring multiple people to handle it)
advertising
FECA
federal elections campaign act
created new federal commission called FEC (federal election commission)
FEC created to oversee and regulate the money being spent in political campaigns
established limits on
how much money a person could give a candidate
how much money candidates could spend on their campaign
Hard Money
given directly to the political candidate
Soft Money
money donated to a party or interest group that can buy advertising on the candidate’s behalf
not subject to campaign finance laws
Political Action Committee (PAC)
organizations that raise money for the sake of influencing the population to vote for their preferred candidate
Connected PAC
formed by corporations or other entities like labor unions
only collect funds from the members of their organization
money can be donated directly to candidates in limited quantities
can raise unlimited amounts of money provided the individual limits are obeyed
Non-connected PAC
formed independently of an organization, usually around a specific public interest
donations to non-connected PACs are limited by law
can accept donations from the public and donate directly to candidates
Super PAC
can be formed by anyone
can accept unlimited donations
cannot directly coordinate with a candidate