GI E2- Study Guide
1/308
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
309 Terms
What condition?
transmitted by food and water; 12-72 hr incubation
profuse watery diarrhea that is prolonged but self limited (1-2 wks)
*can be longer if immunocompromised
look at hx & environmental factors for diagnosis
Acute infectious diarrhea
What pathogen for acute infectious diarrhea does recent hospitalization or abx use suggest?
C. diff
What pathogens for acute infectious diarrhea do recent foreign travel suggest?
Salmonella, shigella, campylobacter, e. coli or v. cholerae
What pathogen for acute infectious diarrhea does an undercooked hamburger suggest?
E. coli 0157:H7
What pathogen for acute infectious diarrhea does an outbreak in a longterm care facility, school, or on a cruise ship suggest?
Norovirus
What pathogen for acute infectious diarrhea does the consumption of fried rice suggest?
B. cereus toxin
What is the treatment for acute infectious diarrhea?
Routine abx not recommended → most self limited
Fluid/elyte replacement, oral glucose rehydration soln, antiemetics
Antibiotics for acute infectious diarrhea could be helpful for with pathogens?
Shigella or campylobacter infections
Acute infectious diarrhea caused by which pathogens would antibiotics worsen the disease?
E. coli 0157:H7 (risk developing HUS)
C. diff (prolongs disease)
What pathogen?
affects all ages, esp kids
MC in summer
transmission: ingestion of contaminated food, drink
vector: domestic pets (dogs, cats, turtles)
large numbers must be ingested to produce illness
Salmonella (salmonellosis)
What are sources that can contain salmonella?
Unpasteurized milk, turkey, chicken, duck, eggs (esp raw), hollandaise sauce, homemade eggnog, caesar salad dressing
What can decrease the possibility of salmonella infection but doesn’t eliminate it?
Cooking contaminated foods (might not reach lethal temperature range / deep in foods like large turkeys or soft cooked eggs)
In general, what amount of shigella is sufficient to induce symptoms?
10-100 bacteria
What pathogen?
Worldwide distribution; common in countries w/o effective sanitation
fecal oral route
source: food or water contaminated with human feces
Shigella aka bacillary dysentery
What pathogen?
infx MC in children and elderly
produces cytotoxin (shiga toxin/STEC) → endothelial damage, hemolysis and renal damage
uncomplicated infx resolves spontaneously in 5-10 days
E. coli 0157:H7 (enterohemorrhagic)
What have E. coli 0157:H7 outbreaks been attributed to?
Undercooked ground beef, unpasteurized apple juice and milk, raw fruits and vegetables
What are complications of E. coli 0157:H7?
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), esp in kids < 5 y/o
Why are antibiotics contraindicated in e.coli 0157:H8 infx?
increases risk of HUS
What does the CDC recommend for all patients with bloody diarrhea or HUS?
Test for E. coli 0157:H7
What condition?
mostly caused by enterotoxigenic e coli, shigella species, or c. jejuni
onset 5-15 days, can occur w/in 2-10 days of travel, esp in area of poor sanitation
contaminated foods or drinks- unpeeled fruits, leafy vegetables, unsanitary drinking water or ice
Traveler’s diarrhea
What is there a significant risk of developing with traveler’s diarrhea?
IBS
What sx are associated with traveler’s diarrhea?
Watery diarrhea (≥ 10 loose stools/day), nausea, abd cramping, fever
Are stool cultures needed for travelers diarrhea?
Nope- no blood or leukocytes present
What is the treatment/prevention for traveler’s diarrhea?
Antimicrobials (cipro/levo/ofloxacin, azithro, or rifaximin) to take if diarrhea occurs during trip
Loperamide 4mg loading dose following by 2mg after each loose stool (max 16 mg/day)
Peptobismol
What condition is a toxin mediate disease caused by C. diff that causes severe inflammatory response with formation of pseudomembranes & is transmitted by fecal oral route?
Pseudomembranous colitis (PMC)
Who is PMC most commonly seen in?
Hospitalized patients receiving abx → ampicillin, lincosamides (clindamycin), 3rd gen cephalosporins, FQs
What pathogen is an obligate anaerobe, gram positive, spore forming bacilli?
C. difficile
Describe the toxins associated with PMC
Raised yellowish-white plaques (pseudomembranes) in patches loosely adherent to the colonic mucosa, destroying it
*Can occur in any part of colon but MC in rectosigmoid
The following sx are associated with what condition?
mild-mod greenish, foul smelling, watery diarrhea
5-15 stools/day
lower abd cramping, LLQ tenderness
positive for mucous in stool but no blood
PMC
What is the diagnostic workup for PMC?
Cytotoxicity assay (definitive), EIA, rapid PCR, fecal WBC, flex sig
What is the treatment for PMC?
D/c offending antibiotic
Vancomycin PO or fidaxomicin (if both not available → flagyl)
Fecal microbiota transplant
*avoid antimotility agents & narcotics → delays clearance of toxin
What is the treatment for a relapse of PMC?
Retreat with same therapy
Multiple relapses → 7 week tapering regimen of vancomycin & concomitant probiotics
What condition is caused by rotaviruses or norovirus and is spread fecal-oral, with water/food borne outbreaks being common?
Viral gastroenteritis
Rotavirus or norovirus (Norwalk)?
MC winter months
infants & children 6-24 mos
24-72 hr incubation
abrupt onset of watery diarrhea, V, low fever, ± abd pain
Rotavirus
Rotavirus or norovirus (Norwalk)?
family & community wide outbreaks, esp on cruiseships
school age children, family contacts, and adults
1-3 day incubation
abrupt onset of D, N, V, mild abd cramps
Norovirus (Norwalk)
What pathogen?
Causes protozoal gastroenteritis
1-3 wk incubation
prevalent in areas with poor water treatment → water contaminated w/ cyst-infested feces from humans or animals
MC after camping or backpacking trip (mountainous west)
Giardia lamblia
What is the presentation/diagnosis for protozoal gastroenteritis caused by Giardia lamblia?
Pale, explosive diarrhea & cysts or trophozoites found in stool
What is the treatment for protozoal gastroenteritis?
Tinidazole (TOC) or metro
*tx empirically, tx close contacts, report to board of health
What AST-ALT ratio suggests alcohol injury / alcohol hepatitis?
≥ 2:1
What is a useful marker to diagnose specific liver diseases?
AST-ALT ratio
What level of AST-ALT elevations would be due to ETOH alone?
< 300 IU/L
What common digestive disease consists of gallstone and is most often asymptomatic and found incidentally during abd sonography?
Cholelithiasis
What are RF for cholelithiasis in adults (> 40)?
Fat, forty, female, fertile
What are RF for cholelithiasis in children?
CF, sickle cell disease
The following ssx are associated with what condition?
biliary colic- steady epigastric or RUQ pain that radiates to R scapula or shoulder
lasts 15min-5 hrs
often develops after eating fatty foods
nocturnal awakening is common
N, +/- V
most will have recurrent attacks (stone usually returns back to GB after attack)
Cholelithiasis
How is uncomplicated symptomatic gallstone disease characterized?
Episodes of biliary pain < 5 hrs
How is complicated gallstone disease characterized?
Biliary pain lasts > 5 hours + findings might indicate acute cholecystitis, acute biliary pancreatitis, or biliary obstruction
What is the diagnosis for cholelithiasis
Preferred: abd US → GB wall thickening, cystic duct dilation
Other: HIDA scan (GB contractility), CT, ERCP, PTC
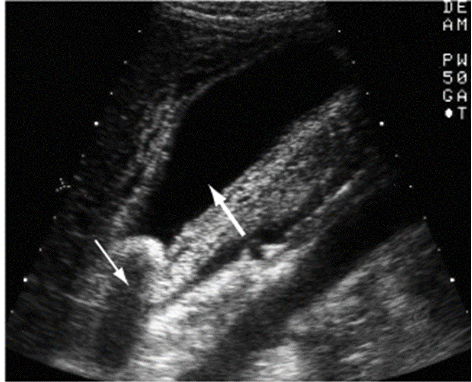
What condition is an acute GB wall inflammation due to mechanical, chemical, or bacterial causes and can be a complication of cholelithiasis?
Acute cholecystitis
The following PE findings are seen in what condition?
progressively worsening biliary colic localizes to RUQ
N, V
palpable gallbladder, peritoneal inflammation
Murphys sign
Triad: RUQ pain, fever, leukocytosis
Acute cholecystitis
What is the triad for acute cholecystitis?
RUQ pain, fever, leukocytosis
What sign?
Pt exhale → place hand below costal margin on right side at MCL → pt inhale
positive = pt stops breathing in & winces w/ a catch in breath
d/t inflamed gallbladder palpated as it descends → acute cholecystitis
Murphy’s sign
What is the dx for acute cholecystitis?
Abd US, leukocytosis, mild elevation in AST/ALT, amylase, bili
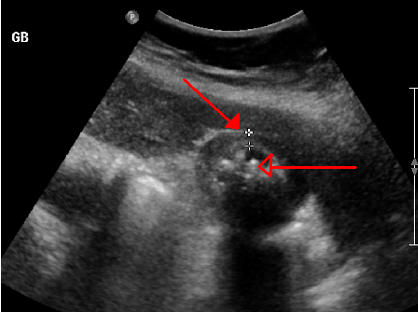
What condition is chronic inflammation of the GB wall that results from repeated attacks of acute/subacute cholecystitis OR mechanical irritation of GB mucosa by gallstones?
Chronic cholecystitis
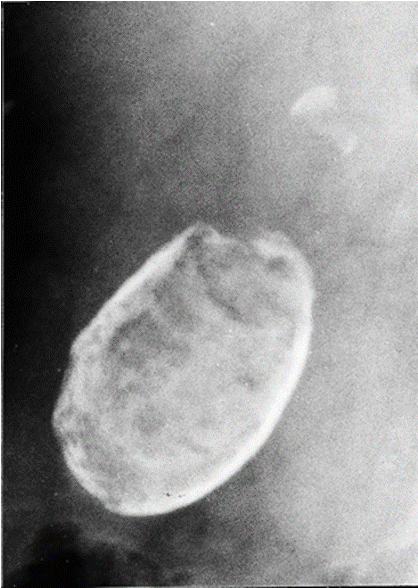
What condition?
Calcium salts are deposited w/in wall of chronically inflamed GB (comp of chronic cholecystitis)
Dx: plain films
Rx: cholecystectomy
Porcelain gallbladder
What does porcelain gallbladder have a high association with?
Carcinoma of gallbladder
What is an acute necroinflammatory disease of the GB, presents with NO gallstone, & has a high morbidity/mortality?
Acalculous cholecystitis
Who is acalculous cholecystitis MC in?
Males over 50
What is acalculous cholecystitis associated with?
Major surgery, critical illness, burns, trauma, TPN
*GB stasis & ischemia → local inflammatory response, distension, necrosis, secondary infx
What condition is characterized by calculus in the common bile duct (CBD) from gallstones or formed spontaneously in CBD s/p cholecystectomy?
Choledocholithiasis
The following presentation is associated with what condition?
MC “silent”- no sx unless obstruction
Frequently occur in pts w/ hx of biliary colic episodes
+/- abd tenderness
Jaundice develops later on
Choledocholithiasis
How is choledocolithiasis diagnosed?
Labs: elevated LFTs & GGT, later → elevated ALP & bili
Imaging: abd US, ERCP
What diagnostic modality is highly sensitive & specific for choledocholithiasis, allows for stone extraction, & is completed preoperatively or if cholangitis or acute pancreatitis is also present?
ERCP
What condition is a bacterial infection superimposed over an obstructed biliary tree due to a gallstone, stricture, or neoplasm (uncommon, can develop after ERCP)?
Acute cholangitis
What is the triad associated with acute cholangitis?
Charcot’s triad → RUQ pain, jaundice, fever w/ chills
What is a complication of acute cholangitis?
Acute suppurative cholangitis (pus in biliary ducts)
What is the pentad associated with acute suppurative cholangitis?
Reynold’s pentad → charcot’s triad + hypotension + mental confusion
What is the treatment for acute cholangitis?
Emergent ERCP, cholecystectomy, or percutaneous cholecystectomy if others can’t be done
What condition is pancreatic inflammation due to the passage of stones through the CBD during acute cholecystitis or in patients with choledocholithisis?
Biliary pancreatitis
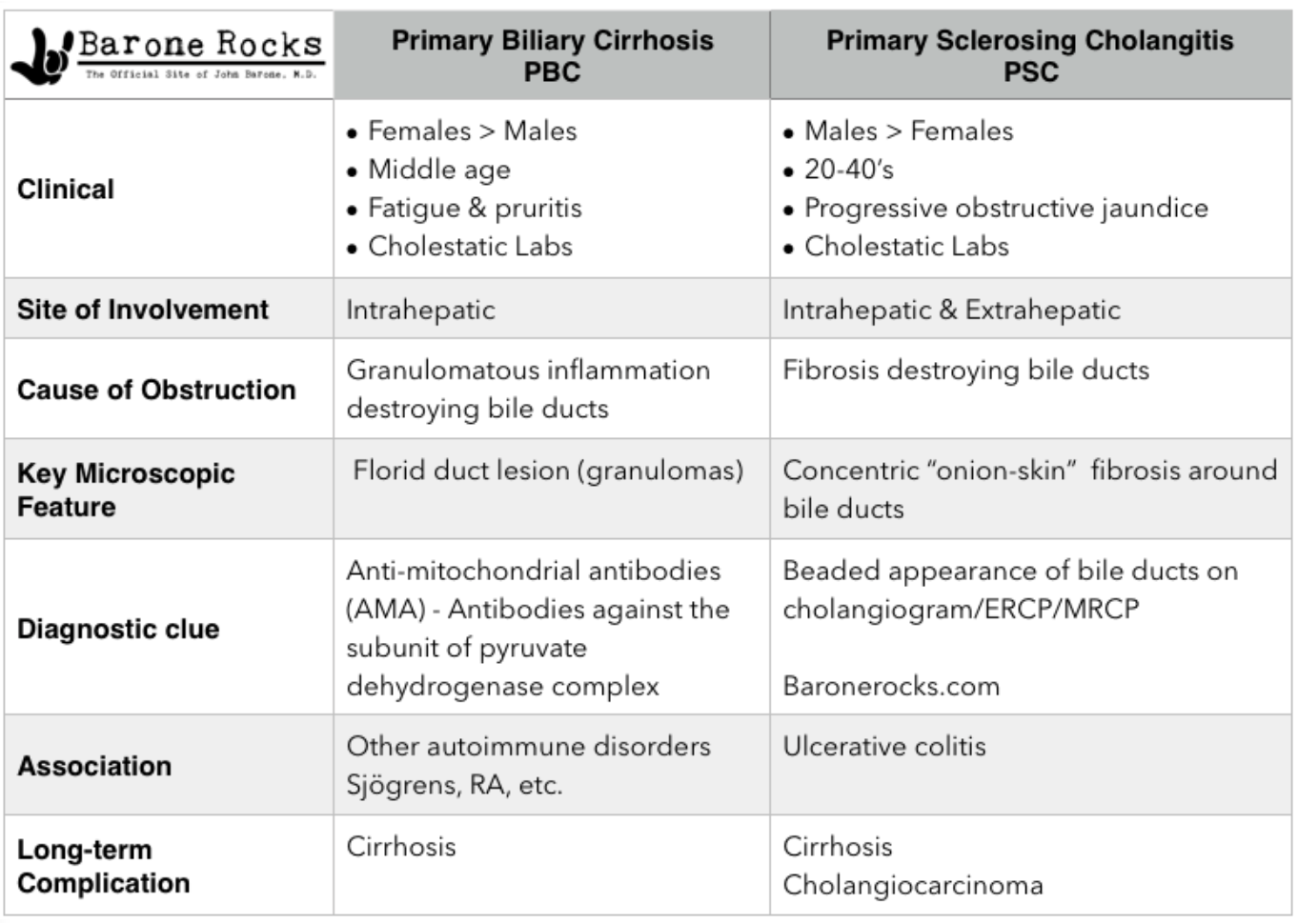
What condition is an autoimmune destruction of intrahepatic bile ducts by antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA) & cholestasis?
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)
Who is PBC MC in?
Middle aged women
The inflammation & fibrosis associated with PBC can lead to what?
Portal HTN and eventual cirrhosis (in 10-12 yrs)
What is the onset of PBC?
Insidious- often asx and found incidentally w/ inc LFTs on annual labs
The following symptoms are associated with what condition?
insidious onset, often asx
Fatigue, dry eyes & mouth
pruritus (excoriations)
unexplained RUQ discomfort → hepatomegaly
xanthelasma- yellow plaques around eyes
d/t dec LDL receptors in damaged hepatocytes
late finding → jaundice
PBC
What is the dx for PBC?
Cholestatic LFT pattern → 3-4x inc ALP
Positive AMA & ANA, liver bx (dz not uniform throughout)
What is the first line and only proven therapy for PBC?
Ursodiol (URSO) → decreases ALP
What are additional treatment options for PBC?
Cholestyramine for pruritus, Osteoporosis agents (Ca, Vit D), vaccines, hepatology referral, no alcohol
What is the only effective treatment for end stage PBC?
Liver transplant
What condition is a progressive, inflammatory, sclerosing & obliterative disease of the extrahepatic and/or intrahepatic bile ducts, in which the progression of the disease cannot be halted?
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)
Who is primary sclerosing cholangitis MC in?
Men 20-50 y/o & often associated with UC (check in pts w/ IBD + persistent & unexplained elevated ALP)
What are PSC patients at an increased risk for developing?
Cholelithiasis, choledocholithiasis, cholangitis, & cholangiocarcinoma
The following ssx are associated with what condition?
often asx
fatigue & pruritus are common
RUQ pain
progressive jaundice
anorexia, indigestion
acute cholangitis
PSC
The following diagnostic workup is for what condition?
cholestatic LFT pattern → 4-10x inc ALP
liver bx → fibrous obliteration of connective tissue in onion skin pattern
fibroscan
MRCP (preferred) & ERCP→ narrowing & beading of bile ducts
PSC
What is the tx for PSC?
Ursodiol (URSO), cholestyramine for pruritus, ERCP (to distinguish from PBC), liver transplant if advanced
Quick reference PBC vs PSC
What is the most common gallbladder carcinoma?
Adenocarcinomas
What RF are associated with GB carcinoma?
Hx chronic cholecystitis, porcelain gallbladder** (calcification of GB itself)
MC in elderly women
The following ssx are associated with what condition?
early → usually asx, incidental finding
advanced → RUQ pain & mass, wt loss, malaise, jaundice
dx w/ radiologic imaging
GB carcinoma
What condition is an acute, reversible pancreatic inflammation with enzymatic release into the parenchyma, which activates enzymes that lead to autodigestion of the pancreas?
Acute pancreatitis
What is the “I get smashed” mnemonic for causes of acute pancreatitis?
Idiopathic
Gallstones
Ethanol
Trauma
Steroids
Mumps
Autoimmune
Scorpion sting
Hypercalcemia or Hypertriglyceridemia (serum TG > 1000 mg/dl)
ERCP
Drugs (cannabis, codeine, enalapril, furosemide, 5ASA, metro, simvastatin)
At what serum TG levels would hypertriglyceridemia associated pancreatitis occur?
≥ 1000 mg/dL
The following ssx are associated with what condition?
Epigastric / LUQ pain that radiates to the back
steady, boring pain, increases in intensity
often bends forward or pulls knees to chest
N, V, abd distension, restless, ± fever
very tender to palpation
dec bowel sounds
Acute pancreatitis
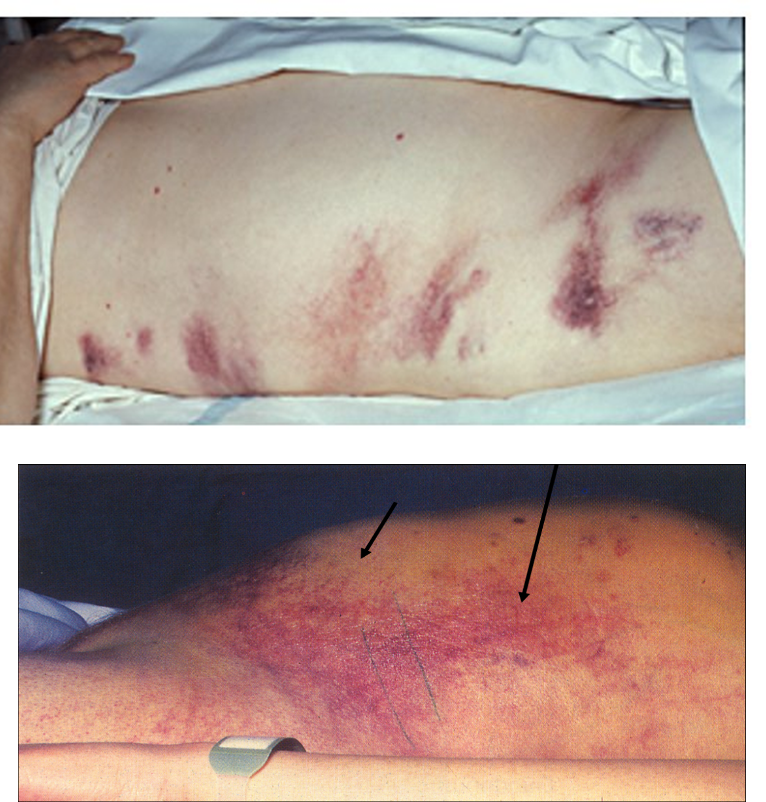
What is Cullen’s sign?
Blue discoloration to umbilicus form retroperitoneal bleeding in pancreatic necrosis
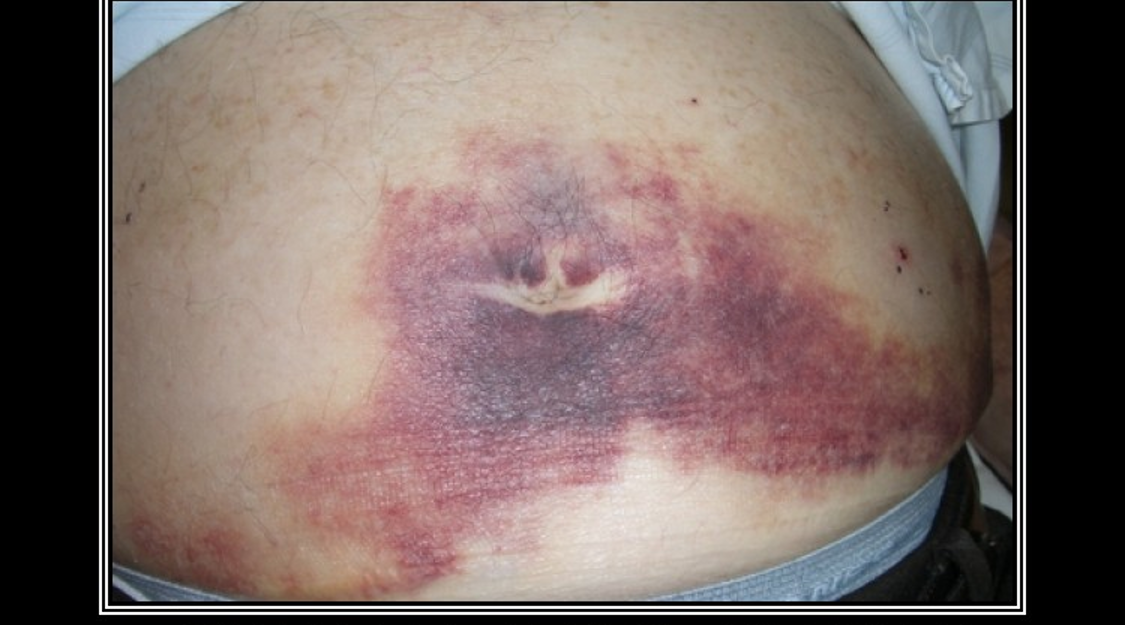
What is Grey Turner’s sign?
Green brown discoloration to flanks seen with severe, necrotizing pancreatitis
How might a patient with acute pancreatitis appear on physical exam?
Cullens & Grey turners sign, erythematous nodules (fat necrosis), dec/absent bowel sounds, rales/atelectasis/effusions, pt may appear anxious or shocky
The following labs are likely to be seen in what condition?
Amylase & lipase elevated >3x upper limit
lipase preferred
Hypocalcemia bc necrotic fat binds calcium
ALT > 150 (highly specific for stones)
possible protein casts in UA
Acute pancreatitis
What is the preferred lab test for acute pancreatitis because it is most specific, sensitive, & remains elevated the longest?
Lipase
What should you think of with increased ALP & bilirubin?
Biliary disease
What are the imaging studies used to dx acute pancreatitis?
Abd CT (gold standard), flat plate (shows ileus & sentinel loop), US
What are the different criterias used in the evaluation of acute pancreatitis?
Ranson’s criteria (predict mortality), APACHE II (ICU mortality), & BISAP (preferred, assess severity)