Topic 5 - Forces
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What are Vector and Scalar quantities?
Vector - A quantity with a magnitude and a direction - Force, Velocity, Displacement, Acceleration, Moment, etc
Scalar - A quantity with a magnitude and no direction - Speed, Distance, Mass, Temperature, Time
What are Contact and Non-Contact Forces?
Contact Force - When two objects have to be touching for a force to act - Friction, Air Resistance, Normal Contact Force, etc
Non-Contact Force - If the objects do not need to be touching - Magnetic, Electrostatic, Gravitational, etc
What is the formula for weight?
Weight (N) = Mass (Kg) x Gravitational Field Strength (N/Kg)
What is the formula for Work Done?
Work Done (J) = Force (N) x Distance (S)
What is the formula for Force?
Force (N) = Spring Constant (N/m) x Extension (m)
Describe a practical to investigate the link between Force and Extension?
Setup a apparatus using a stand, clamp and a spring
Measure the natural length of the spring with a ruler and record the length in metres
Then add a 100g mass and measure the new length of the spring
Repeat until you have all your desired results
Then take away the natural length from each result to find the extension
Repeat it all if you want repeat reading for greater accuracy and less anomalies
What is a moment and the equation?
A moment is the turning effect of a force.
Moment (Nm) = Force (N) x Distance (m)
If the total anticlockwise moment is equal to the total clockwise moment about a pivot, then the object is balanced.
The greater the distance from a pivot means less force needs to be put in. This is good for things like levers.
What is a Fluid?
A substance that can flow because their particles are able to move around (Liquids and Gases). This results in pressure from collisions.
What is the formula for Pressure?
Pressure at Surface: Pressure (Pa) = Force (N) x Area (m²)
Pressure in liquids: Pressure (Pa) = Depth (m) x Gravitational Field Strength (N/Kg) x Density (Kg/m³)
What is Upthrust?
The resultant force equal to the weight of fluid that is displaced. This is due to pressure exerted in all directions underwater, and pressure being greater at the bottom from the greater depth.
An object can float if the upthrust is equal to the weight
What are these typical speeds?
Walking - 1.5 m/s
Running - 3 m/s
Cycling - 6 m/s
Car - 25 m/s
Train - 30 m/s
Plane - 250 m/s
What are the two equations for Acceleration?
Acceleration (m/s²) = Change in Velocity (m/s) / Time (s)
V² - U² = 2as
What is Terminal Velocity?
The maximum velocity a falling object can reach without any added driving forces. It’s the velocity at which the resistive forces acting on the object match the force due to gravity.
What is Newton’s First Law?
If the resultant force on a stationary object is zero, the object will remain stationary. If the resultant force on a moving object is zero, it will keep the same velocity. (Inertia)
What is Newton’s Second Law?
The larger the resultant force acting on an object, the more the object accelerates.
Force (N) = Acceleration (m/s²) x Mass (Kg)
What is Newton’s Third Law?
When two objects interact, the forces they exert are equal and opposite.
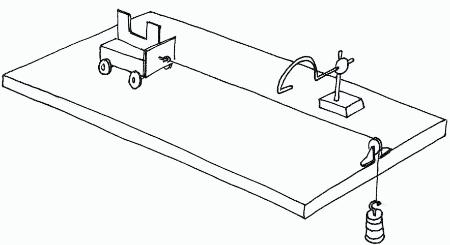
Describe a practical to investigate how Mass and Force affect Acceleration (Newton’s Second Law)?
Setup a apparatus with a trolley, card with a gap in the middle, light gate, pulley and mass
Measure the length of the gap in the card with a ruler
Connect the trolley to the mass over the pulley
Mark a starting line for your trolley
Add a 100g mass, hold the trolley so the string is not loose and release
Record the acceleration from the data logger
Repeat with more masses
Take repeat readings for more accuracy and to eliminate anomalies
What is the formula for Stopping Distance?
Stopping Distance = Thinking Distance + Braking Distance
What is the formula for Momentum?
Momentum (Kg m/s) = Mass (Kg) x Velocity (m/s)
Momentum is conserved throughout in a closed system
What is another formula for Force?
Force (N) = Chang in Momentum (Kg m/s) / Change in Time (s)