Human Anatomy & Physiology Lab Exam 1
1/157
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
Transport across this surface must occur through simple diffusion
Found in:
Alveoli of the lungs
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Necessary in absorption and secretion
Found in:
Kidney tubules
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Necessary for absorption and extensive secretion
Found in:
Digestive track
Simple Columnar Epithelium
May bear cilia and goblet cells
Found in:
Trachea
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Functions in protection
Found in:
The largest ducts of sweat glands
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Functions in protection and secretion
Found in:
Lining the male urethra
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Functions to allow organs to stretch
Found in:
Urinary bladder
Transitional Epithelium
Gel-like matrix composed of fibroblasts
Loose arrangement of collagen and elastin fibers
Found in:
The lamina propria of mucous membranes
Areolar Connective Tissue
Gel-like matrix composed of adipocytes (fat cells)
Loose arrangement of collagen and elastin fibers
Found in:
Around the kidneys
Adipose Connective Tissue
Loose reticulin fibers composed of lymphocytes
Filters blood and lymphatic fluid
Found in:
Within the lymph nodes
Reticular Connective Tissue
Densely packed parallel bundles of collagen composed of fibroblasts
Provides a large amount of strength along the parallel axis of the bundles
Found in:
Ligaments
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Irregularly arranged bundles of collagen composed of fibroblasts
Provides a moderate amount of strength in many directions
Found in:
Dermis
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Contains large amounts of elastin fibers
Dominated by fibroblasts
Able to stretch and recoil when needed
Found in:
Large blood vessels
Elastic Connective Tissue
Amorphous matrix with large network of collagen fibers
Provides shape to structures that are not indented to deform
Found in:
The flexible portion of the nose
Hyaline Cartilage
Amorphous matrix with large network of elastin fibers
Provides shape to structures that must deform
Found in:
The external portion of the ear
Elastic Cartilage
Thick parallel bundles of collagen
Provides a large amount of strength in the direction of fibers
Populated primarily by chondrocytes
Found in:
The pubic symphysis
Fibrous Cartilage
Hard, calcified matrix built upon dense, parallel bundles of collagen fibers
Populated primarily by osteocytes
Found in:
Throughout the skeleton
Bone
Liquid matrix with few protein fibers
Composed of erythrocytes and leukocytes
Transports material throughout the body
Found in:
Blood vessels
Blood
Embryonic connective tissue
Found in:
The embryo
Mesenchyme
Muscular tissue containing long, branched, multinucleated cells
Cells are striated in appearance
Voluntary and neruogenic contraction
Found in:
Attached to the skeleton and skin (ex. biceps femoris muscle)
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Muscular tissue containing short, branched, generally uninucleate cells
Striated in appearance
Involuntary and myogenic contraction
Found in:
The walls of the heart
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Muscular tissue containing short, spindle-shaped cells
Non-striated in appearance
Involuntary in both myogenic and neurogenic contraction
Found in:
The walls of hollow organs (ex. small intestine)
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Transmits electrical signals throughout the body
Neuroglia cells/glial cells
Found in:
Spinal cord
Nervous Tissue
May be keratinized or non-keratinized, functions in protection from abrasion
Found in:
Epidermis
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Identify one location in the body where simple squamous epithelium can be found:
Lining the alveoli of the lungs
Identify one location in the body where simple cuboidal epithelium can be found:
Lining the kidney tubules
Identify one location in the body where simple columnar epithelium can be found:
Lining the inner surface of the small intestine
Identify one location in the body where pseudostratified columnar epithelium can be found:
Lining the inner surface of the trachea
Identify one location in the body where stratified squamous epithelium can be found:
Within the epidermis of the skin
Identify one location in the body where stratified cuboidal epithelium can be found:
Lining the largest ducts of the sweat glands
Identify one location in the body where stratified columnar epithelium can be found:
Lining the male urethra
Identify one location in the body where transitional epithelium can be found:
Lining the inner surface of the urinary bladder
Identify one location in the body where areolar connective tissue can be found:
In the lamina propria of mucous membranes
Identify one location in the body where adipose connective tissue can be found:
Around the kidneys
Identify one location in the body where reticular connective tissue can be found:
Within the lymph nodes
Identify one location in the body where dense regular connective tissue can be found:
Within the ligaments
Identify one location in the body where dense irregular connective tissue can be found:
Within the dermis of the skin
Identify one location in the body where elastic connective tissue can be found:
Large blood vessels
Identify one location in the body where hyaline cartilage can be found:
Within the flexible portion of the nose
Identify one location in the body where elastic cartilage can be found
Within the external portion of the ear
Identify one location in the body where fibrous cartilage can be found:
Within the pubic symphysis
Identify one location where mesenchyme can be found:
Within the embryo
Identify one location in the body where skeletal muscle tissue can be found:
Within the biceps femoris muscle
Identify one location in the body where cardiac muscle tissue can be found
Within the walls of the heart
Identify one location in the body where smooth muscle tissue can be found
Within the walls of the small intestine
Identify one location in the body where nervous tissue can be found:
Within the spinal cord
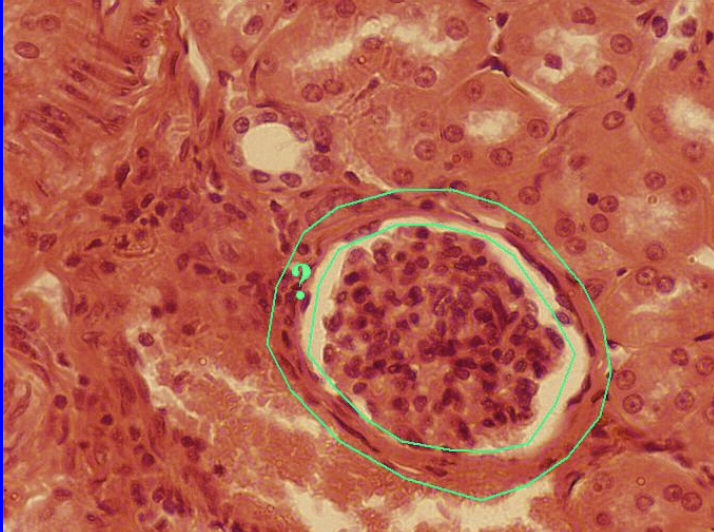
Simple Squamous Epithelium
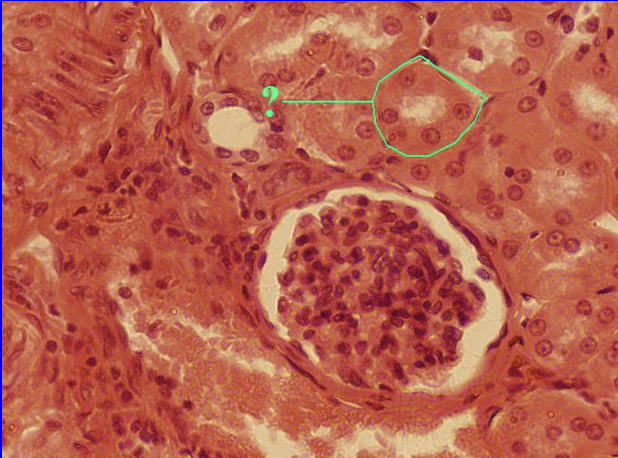
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
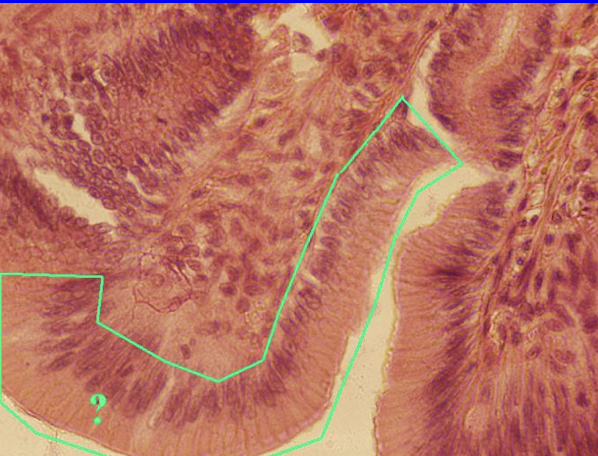
Simple Columnar Epithelium
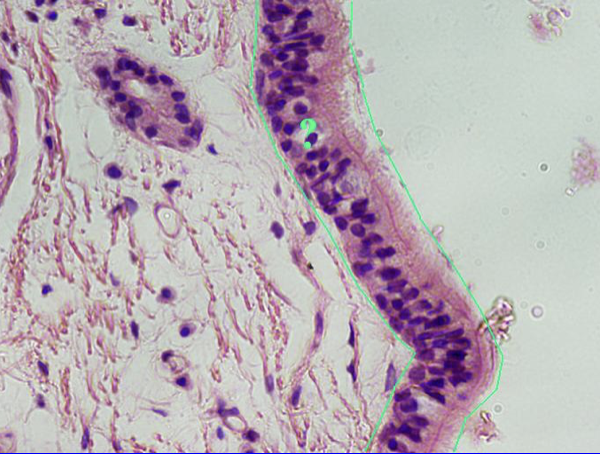
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
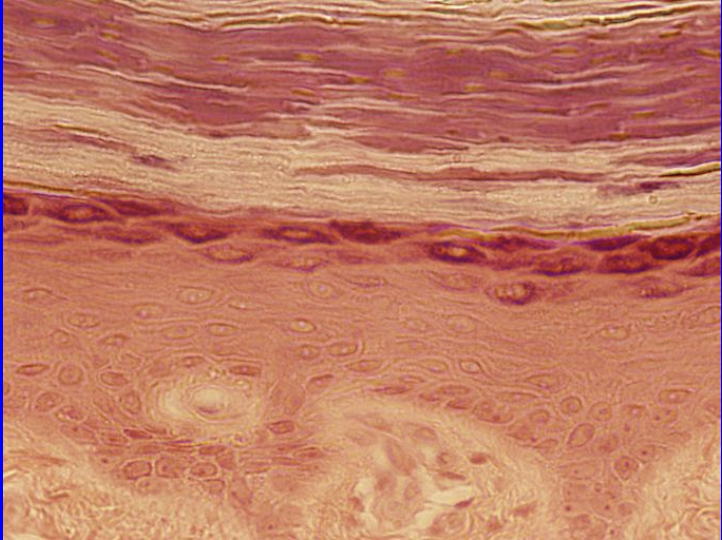
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
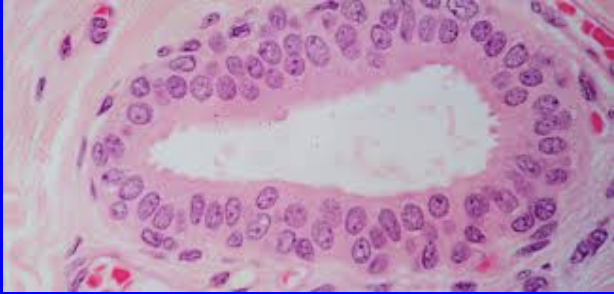
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
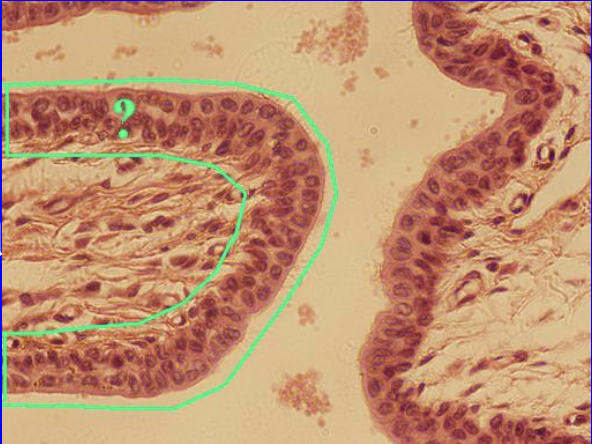
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
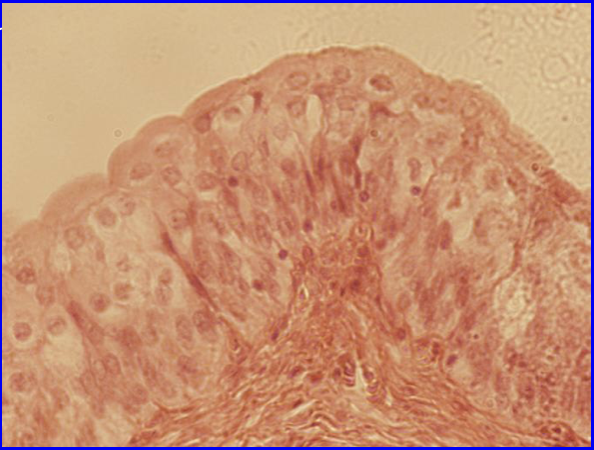
Transitional Epithelium
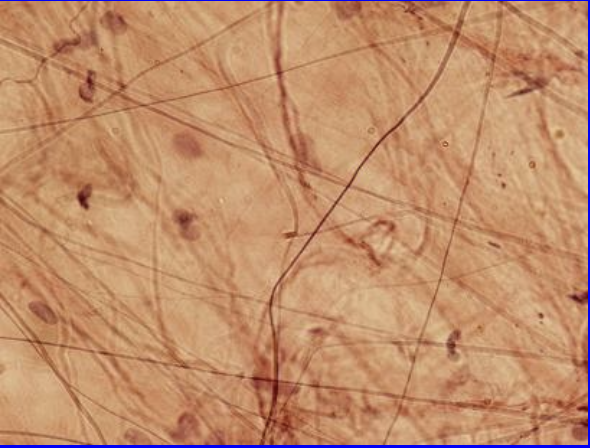
Areolar Connective Tissue
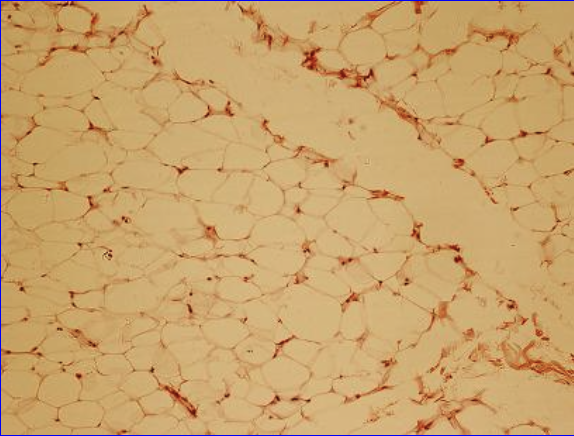
Adipose Connective Tissue
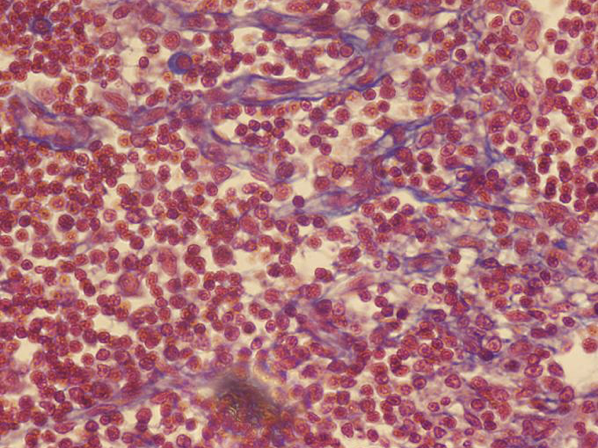
Reticular Connective Tissue
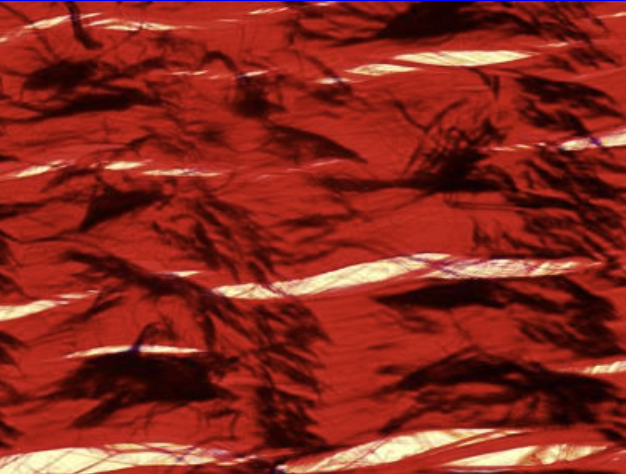
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
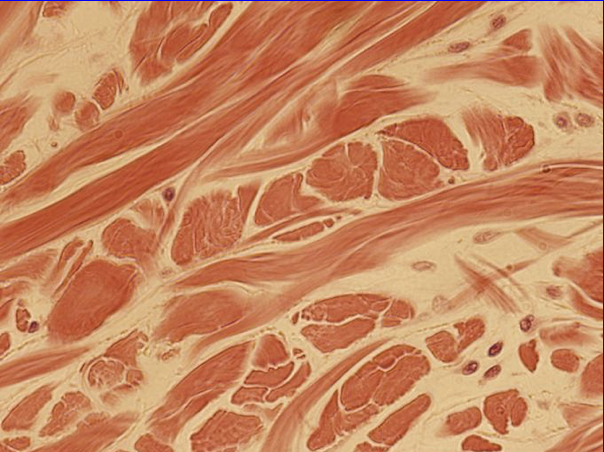
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
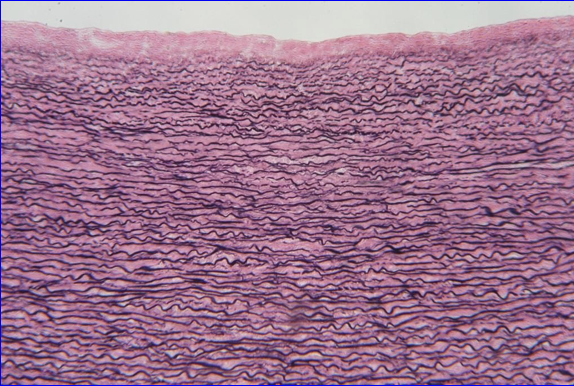
Elastic Connective Tissue
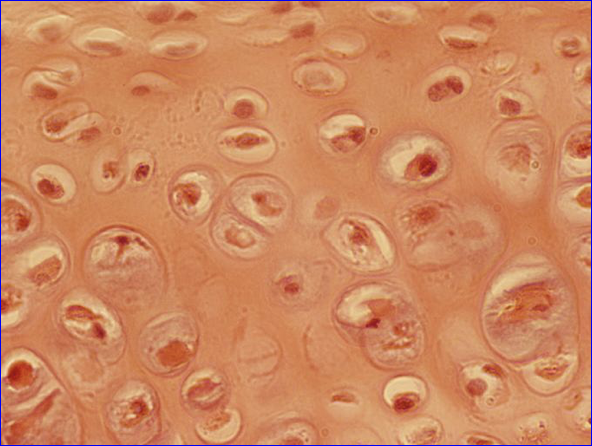
Hyaline Cartilage
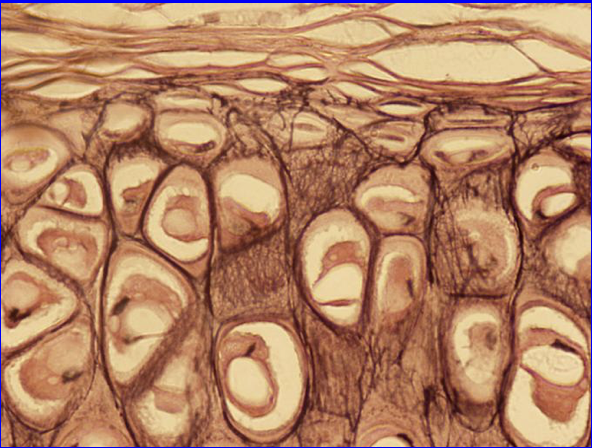
Elastic Cartilage
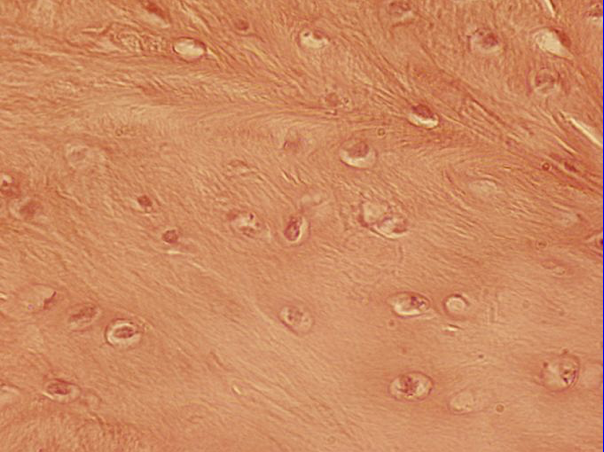
Fibrous Cartilage
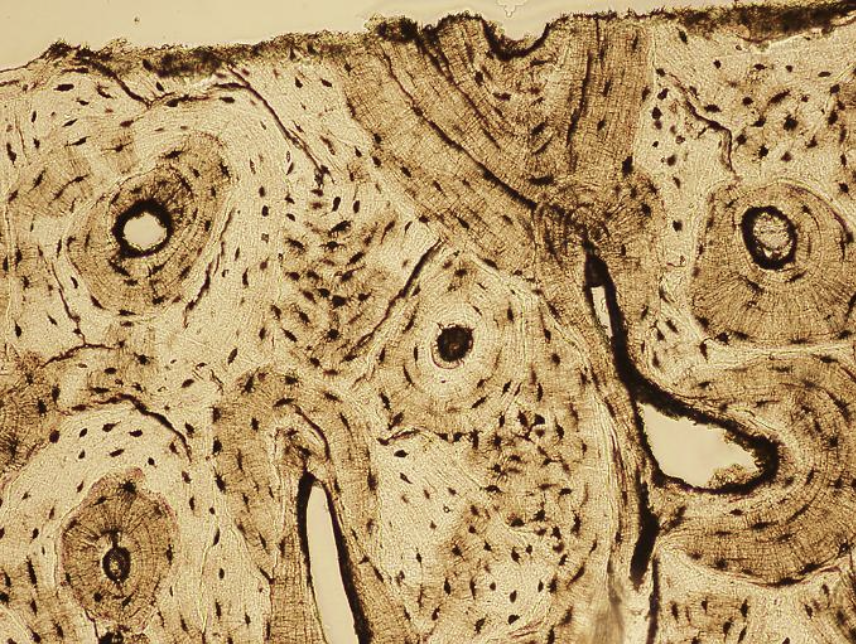
Bone
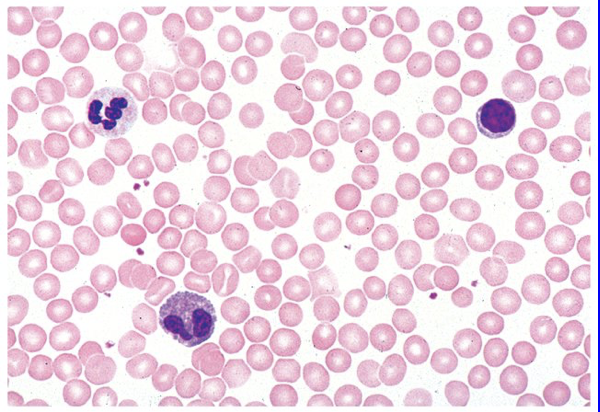
Blood
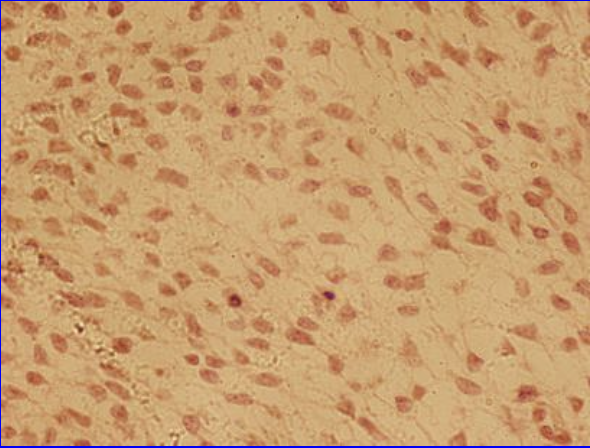
Mesenchyme
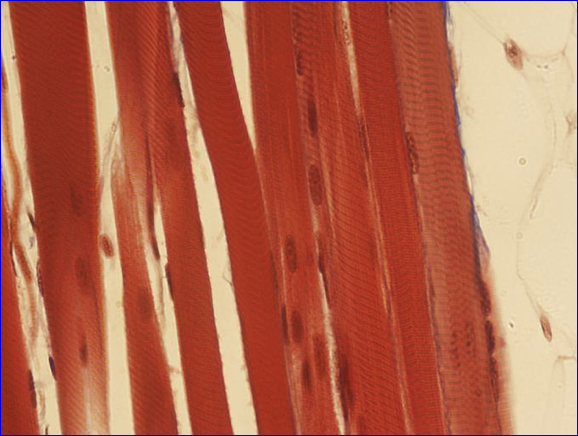

Skeletal Muscle Tissue
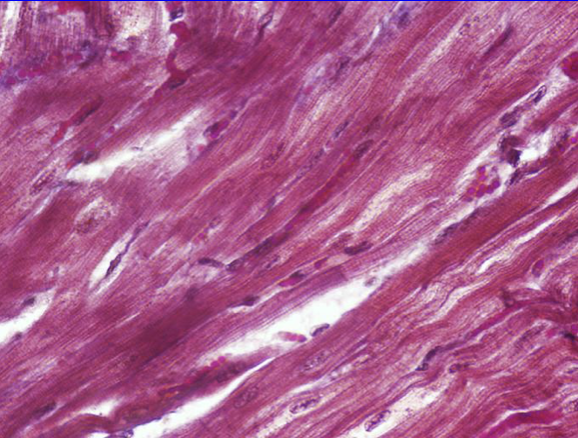
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
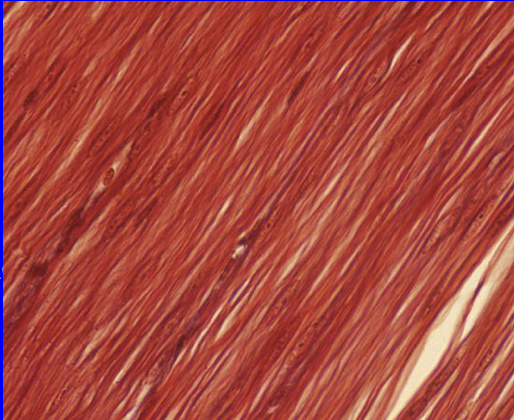
Smooth Muscle Tissue
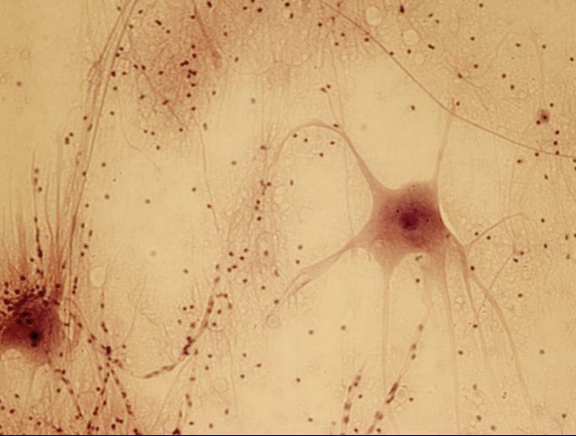
Nervous Tissue
________ tissues are sheets of cells that line body surfaces, either external or internal.
Epithelial
________ tissues are support tissues where is a specific cell type is imbedded within a non-living (acellular) matrix.
Connective
________ tissues are excitable tissues that are capable of contraction.
Muscle
________ tissues are excitable tissues that are capable of transferring and integrating signals from one part of the body to another.
Nervous
What are the cell junctions between cardiac muscle cells called?
Intercalated discs
What are the mucus producing cells in epithelial tissue called?
Goblet cells
What are the spaces in which chondrocytes reside called?
Lacunae
This epidermal layer consists of many layers of flattened keratinized dead cells:
Stratum Corneum
This epidermal layer contains a large percentage of actively mitotic cells:
Stratum Basale
This epidermal layer consists of a very thin transparent layer of flattened keratinized cells:
Stratum Lucidum
This epidermal layer consists of flattened but still living cells that contain keratin granules:
Stratum Granulosum
This hardened structure protects and supports the dorsal side of the distal phalangeal region:
Nail
This structure produces an oily secretion to lubricate the shaft of a hair or the surface of the skin:
Sebaceous gland
This structure produces a thin, watery secretion that carries heat away from the body as it evaporates:
Eccrine sweat gland
This structure produces a milky, protein- and lipid-rich secretion and is limited to the axillary and pubic regions:
Apocrine sweat gland
This structure produces a shaft of keratinized cells that extend from the surface of the skin:
Hair follicle
What is the membrane that surrounds the internal contents of the cell and provides a boundary between the external environment and the internal cell environment?
Plasma membrane
What paired, cylindrical bodies direct the formation of the mitotic spindle during cell division?
Centrioles
What minute, finger-like projections of the cell membrane serve to increase the surface area of the cell for absorption?
Microvilli
What membrane bound organelle contains the genetic material that controls the functioning of the cell?
Nucleus
What cytoskeletal element is primarily composed of actin?
Microfilament
What tiny spherical bodies, composed of RNA and protein, are the actual sites of protein synthesis?
Ribosomes
What membranous vesicles contain oxidase enzymes that detoxify alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, and other harmful chemicals?
Peroxisomes
What membranous system of tubules serves to either store and transport proteins or to synthesize steroids and lipids?
Endoplasmic Reticulum
What cytoskeletal element is primarily composed of tubulins and helps determine the shape of the cell?
Microtubule
What cytoskeletal elements are stable and resist mechanical forces acting on the cell?
Intermediate filaments
DNA replication occurs during which phase of the cell cycle?
Interphase
The chromosomes line up along the midline of the cell during which phase of mitosis?
Metaphase
The daughter chromosomes separate during which phase of mitosis?
Anaphase
The nuclear membrane disappears during which phase of mitosis?
Late prophase