Topic 1.1 - What Is A Business (SL/HL)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:10 AM on 5/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
1
New cards
Business
A decision-making organization that is involved in the process of using **inputs** to produce **goods** and/or provide **services**.
\
* Businesses can also provide goods and services to other businesses
\
* Businesses can also provide goods and services to other businesses
2
New cards
Inputs
The resources that a business uses in the production process
\
EXAMPLES:
\
* Labor
* Raw materials
\
EXAMPLES:
\
* Labor
* Raw materials
3
New cards
Outputs
The products generated using inputs
4
New cards
Product
Refers to both goods and services
5
New cards
Goods
Physical products
6
New cards
Services
Intangible products
7
New cards
Role of a business
The role of businesses is to combine human, physical, and financial resources to create goods and services in order to satisfy the **needs** and **wants** of people, organizations, and governments.
8
New cards
Needs
The basic necessities that a person must have to survive
9
New cards
Wants
People’s desires, i.e. the things they would like to have
10
New cards
Entrepreneur
* An individual who plans, organizes and manages a business, taking on financial risks in doing so.
* Entrepreneurs have the skills needed to oversee the whole production process, whilst having the ability and willingness to take potentially high risks
* They search for and exploit business opportunities by forecasting and/or responding to changes in the marketplace
* Entrepreneurs have the skills needed to oversee the whole production process, whilst having the ability and willingness to take potentially high risks
* They search for and exploit business opportunities by forecasting and/or responding to changes in the marketplace
11
New cards
Entrepreneurship
The collective knowledge, skills and experiences of entrepreneurs
12
New cards
Characteristics of successful entrepreneurs
* Creative
* Innovative
* Passionate
* Innovative
* Passionate
13
New cards
Purpose of business activity
The nature or purpose of a business is to generate **added value**. This occurs when there is a positive difference between the selling price of a product and the cost of producing the good or service.
14
New cards
Added value
Exists when products are appealing to customers, so they are willing to pay higher prices for such items
\
Added value =value of outputs (revenue received from the products sold) - the value of inputs (cost of production)
\
Added value =value of outputs (revenue received from the products sold) - the value of inputs (cost of production)
15
New cards
Customers
The people or organizations that purchase a product
16
New cards
Consumers
The people or organizations that actually use the product
17
New cards
Types of products
* Consumer goods
* Capital goods
* Services
* Capital goods
* Services
18
New cards
Consumer goods
Products sold to the general public, rather than to other businesses. They can be further split into;
\
* Consumer durables
* Consumer non-durables
\
* Consumer durables
* Consumer non-durables
19
New cards
Consumer Durables
Products that last a long time and can be used repeatedly
20
New cards
Consumer non-durables
Products that need to be consumed shortly after their purchase as they do not last or cannot be reused
21
New cards
Capital/producer goods
Physical products bought by businesses to produce other goods and/or services
22
New cards
Services
Intangible products provided by businesses, the service is not tangible, but the results are
23
New cards
Functional areas
For a business to operate effectively, tasks must be carried out by functional areas (departments). The nature of business requires these functional areas to work together in order to achieve the organization’s goal.
24
New cards
What are the functional areas
* Human resource management
* Finance & accounts
* Marketing
* Operations management
* Finance & accounts
* Marketing
* Operations management
25
New cards
Human resource management (HR)
Responsible for managing the personnel of the organization.
26
New cards
Roles of HR
* Human resource planning
* Organizational structures
* Management and leadership
* Motivation and demotivation
* Dealing with industrial/employee relations
* Organizational structures
* Management and leadership
* Motivation and demotivation
* Dealing with industrial/employee relations
27
New cards
Finance & accounts
In charge of;
* Managing the organization’s money
* Ensuring compliance with legal requirements (such as filing or corporate taxes)
* Informing those interested in the financial position of the business (such as shareholders and potential investors)
* The finance and accounts director must ensure that accurate recording and reporting of financial documentation takes place.
* Managing the organization’s money
* Ensuring compliance with legal requirements (such as filing or corporate taxes)
* Informing those interested in the financial position of the business (such as shareholders and potential investors)
* The finance and accounts director must ensure that accurate recording and reporting of financial documentation takes place.
28
New cards
Marketing
Responsible for;
* Identifying and satisfying the needs and wants of customers
* It is ultimately in charge of ensuring that the firm’s products sell.
* Identifying and satisfying the needs and wants of customers
* It is ultimately in charge of ensuring that the firm’s products sell.
29
New cards
Marketing activities
* Market research
* Promotion
* Branding
* Pricing
* Distribution
* Promotion
* Branding
* Pricing
* Distribution
30
New cards
Operations management
Responsible for the process of converting raw materials and components into finished goods, ready for sale and delivery to customers
\
* Operations is also applied to the process of providing services to customers
\
* Operations is also applied to the process of providing services to customers
31
New cards
Functional areas in large businesses
A large organization is able to allocate resources to each of the four functional areas, making their roles easily identifiable
32
New cards
Functional areas in small businesses
In a small business owned by just one person, each function would need to be carried out by the same person
33
New cards
Business sectors
Businesses can be classified according to the stage of production (or chain of production) that they are engaged in
34
New cards
What are the business sectors
* Primary
* Secondary
* Tertiary
* Quaternary
* Secondary
* Tertiary
* Quaternary
35
New cards
Primary sector
Businesses operating in the primary sector are involved with the extraction, harvesting and conversion of natural resources
\
* Primary sector activities tend to account for a large percentage of output and employment in low income countries (LEDCs).
* Businesses operating in the primary sector in high income countries (MEDCs) use mechanization and automation, such as combine harvesters and automatic watering systems.
* As countries achieve sustained economic growth and development, there is less reliance on the primary sector in terms of employment and national output, partly because there is little value added in primary sector production
\
* Primary sector activities tend to account for a large percentage of output and employment in low income countries (LEDCs).
* Businesses operating in the primary sector in high income countries (MEDCs) use mechanization and automation, such as combine harvesters and automatic watering systems.
* As countries achieve sustained economic growth and development, there is less reliance on the primary sector in terms of employment and national output, partly because there is little value added in primary sector production
36
New cards
Secondary sector
Businesses that operate in the secondary sector are involved in the manufacturing or construction of products
\
* The output is then sold to customers, be they other businesses, governments, foreign buyers, or domestic customers
* Medium income countries (economically developing countries) tend to have a dominant secondary sector that accounts for a relatively large proportion of the country’s national output
* Economists argue that the secondary sector is a wealth-creating sector because manufactured goods can be exported worldwide to earn income for the country
* Value is added to the natural resources used during the production process
\
* The output is then sold to customers, be they other businesses, governments, foreign buyers, or domestic customers
* Medium income countries (economically developing countries) tend to have a dominant secondary sector that accounts for a relatively large proportion of the country’s national output
* Economists argue that the secondary sector is a wealth-creating sector because manufactured goods can be exported worldwide to earn income for the country
* Value is added to the natural resources used during the production process
37
New cards
Tertiary sector
Businesses in the tertiary sector specialize in providing services to the general population
\
* Physical goods can be transformed in the process of providing a service.
* In high income countries **(MEDCs)** such as Canada and Germany, the tertiary sector tends to be the most substantial sector in terms of both employment and as a percentage of gross domestic product
* The decline of the manufacturing/secondary sector in MEDCs also signifies their growing reliance on the tertiary sector
\
* Physical goods can be transformed in the process of providing a service.
* In high income countries **(MEDCs)** such as Canada and Germany, the tertiary sector tends to be the most substantial sector in terms of both employment and as a percentage of gross domestic product
* The decline of the manufacturing/secondary sector in MEDCs also signifies their growing reliance on the tertiary sector
38
New cards
Gross domestic product (GDP)
The value of the country’s output annually
39
New cards
Quaternary sector
A subcategory of the tertiary sector, businesses in the quaternary sector are involved in intellectual, knowledge-based activities that generate and share information
\
* The quaternary sector exists mainly in high income countries **(MEDCs)** as it requires a highly educated workforce.
* It is also the sector in which high-tech and e-commerce businesses invest for further growth and evolution
\
* The quaternary sector exists mainly in high income countries **(MEDCs)** as it requires a highly educated workforce.
* It is also the sector in which high-tech and e-commerce businesses invest for further growth and evolution
40
New cards
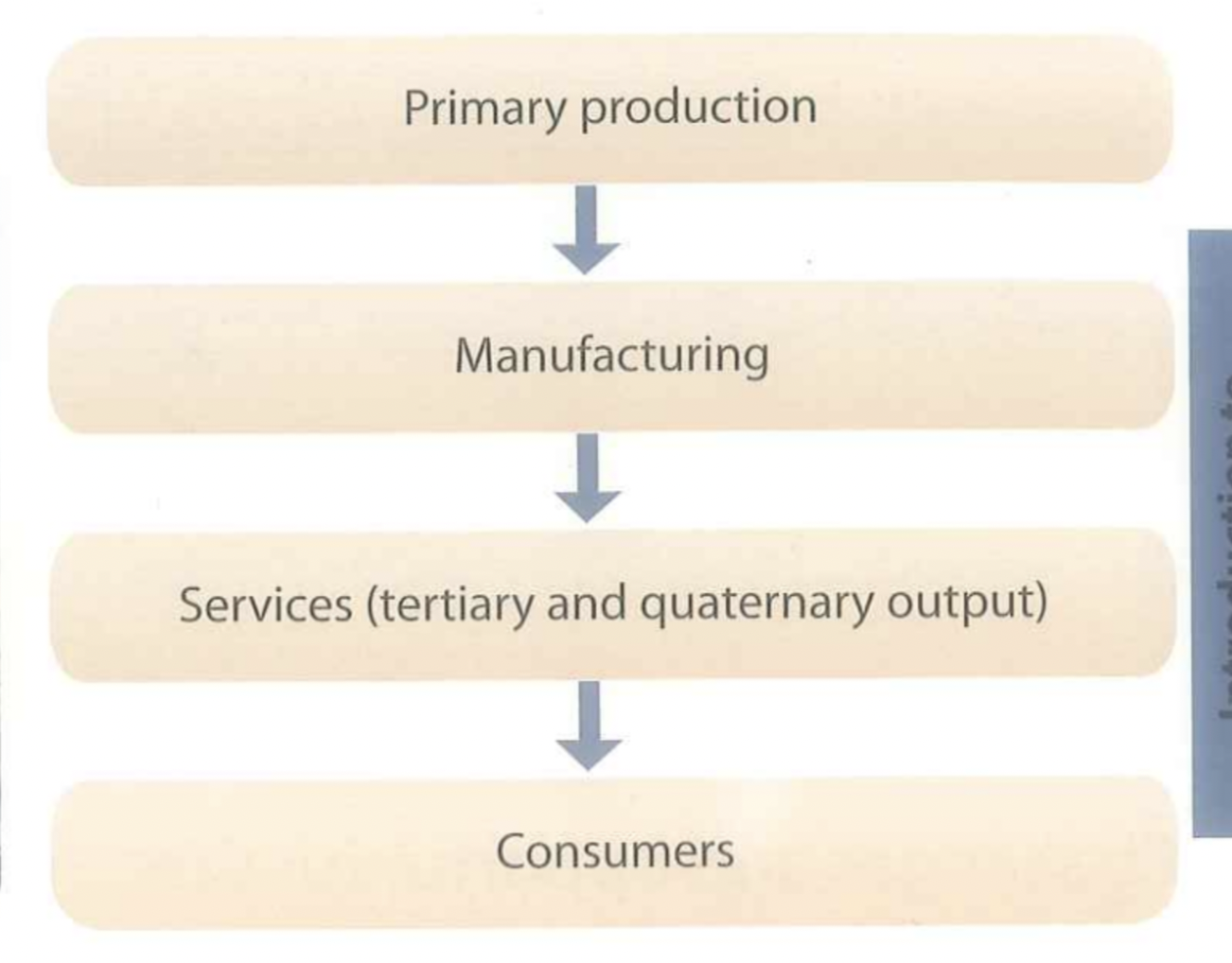
Chain of production
The four business sectors are linked through the chain of production, which tracks the stages of item’s production from the extraction or raw materials used to make the product all the way through being delivered to the customers.
41
New cards
Challenges of starting a new business
* __Lack of finance__ **→** all businesses need finance for the purchase of fixed assets. However start-up firms and most owners of new or small businesses do not have the credentials to secure sufficient funding without major challenges. Even if entrepreneurs are able to borrow some money, the funds may be insufficient or the relatively high interest charges might seriously affect the cash flow position of the business. Hence, new sole traders often have to remortgage their own homes to raise finance needed, thereby offering the lender more collateral in case they fail to repay the loan.
* __Unestablished customer base__ **→** a major challenge facing new businesses is attracting customers, i.e building a broad and loyal customer base. The problem is intensified when there are well established competitors already in the market. Customer loyalty is built over a long period of time, which may require marketing know-how and large amounts of money.
* __Cashflow problems__ **→** financing working capital is a major challenge for many business start-ups. A business may have a lot of stock, such as raw material, semi-finished outputs, or finished goods that it cannot easily turn into cash. Customers might demand a lengthy credit period (30-60 days) enabling them to buy now and pay later, so the business will not receive the cash payment until the credit period is over. However, during this time, the business still needs to pay for its on-going costs such a swages, rent, utility bills, taxes, and interest payments on bank loans.
* __Marketing problems__ **→** marketing challenges arise when businesses fail to meet customer needs, thereby resulting in poor sales and lack of profitability. Supplying the right products to the right customers at the right price is especially crucial for new businesses. However, small and new businesses might lack the expertise to do this. Quite often, the key to small business success is to identify a niche in the market and then fill it.
* __People management problems__ **→** business start-ups may lack experience in hiring the right staff with all the necessary skills. This can lead to poor levels of labor productivity and the need to retrain staff or to rehire people, all of which can be very expensive and time consuming. Moreover, new businesses might not know the ideal organizational structure or the most practical methods of staff motivation that best suits their organizational needs.
* __Production problems__ **→** it can be challenging for business start-ups to accurately forecast levels of demand so they are more likely to either over produce or under produce. Overproduction tends to lead to stockpiling, wastage, and increased costs. By contrast, underproduction leads to dissatisfied customers and a loss of potential sales.
* __Legalities__ **→** it is necessary for businesses to comply with all necessary legislation, including business registration procedures, insurance cover for staff and buildings, consumer protection laws and rules about intellectual property such as copyrights, patents, an trademarks. The paperwork and legal requirements of setting up a new business can be cumbersome, confusing, time consuming and expensive. Any oversight could result in the business having to pay compensation or financial penalties. This would obviously damage the already vulnerable cash flow position of business start-ups.
* __High production costs__ **→** new businesses are likely to have high set-up costs and running costs due to the large amount of money needed to purchase or pay for capital equipment, machinery, stocks, rent, advertising, insurance, and so forth. Smaller businesses will also be at a cost disadvantage as they cannot benefit from economies of scale. By contrast, economies of scale allow larger and more established businesses to benefit from lower average costs of production due to the size of operations, such as being able to get discounts from their suppliers for large bulk purchases or being able to borrow money at a lower interest rate because of their larger size and financial collateral.
* __Poor location__ **→** businesses face a dilemma in the location decision; busy areas offer the highest potential number of customers, but the premises in these area will also cost the most. Fixed costs, such as rent or mortgage payments account for a large percentage of total costs for many businesses. An aim for any new business is to reach. break-even as soon as possible, by keeping fixed costs down. This is one reason why many entrepreneurs set up small businesses that operate initially from their own homes (which also has a tax advantage). Ofcourse this is not suitable for businesses where location plays a key factor in business survival.
* __External influences__ **→** all businesses, irrespective of size or how long they have been in operation, are prone to exogenous socks that create a challenging trading environment, such as global financial crisis or the outbreak of a pandemic. However, larger and more established firms tend to be better resourced to handle these external influenced. Hence, new businesses face the added challenge of being more vulnerable to external shocks which also means the potential for business failure is great.
* __Unestablished customer base__ **→** a major challenge facing new businesses is attracting customers, i.e building a broad and loyal customer base. The problem is intensified when there are well established competitors already in the market. Customer loyalty is built over a long period of time, which may require marketing know-how and large amounts of money.
* __Cashflow problems__ **→** financing working capital is a major challenge for many business start-ups. A business may have a lot of stock, such as raw material, semi-finished outputs, or finished goods that it cannot easily turn into cash. Customers might demand a lengthy credit period (30-60 days) enabling them to buy now and pay later, so the business will not receive the cash payment until the credit period is over. However, during this time, the business still needs to pay for its on-going costs such a swages, rent, utility bills, taxes, and interest payments on bank loans.
* __Marketing problems__ **→** marketing challenges arise when businesses fail to meet customer needs, thereby resulting in poor sales and lack of profitability. Supplying the right products to the right customers at the right price is especially crucial for new businesses. However, small and new businesses might lack the expertise to do this. Quite often, the key to small business success is to identify a niche in the market and then fill it.
* __People management problems__ **→** business start-ups may lack experience in hiring the right staff with all the necessary skills. This can lead to poor levels of labor productivity and the need to retrain staff or to rehire people, all of which can be very expensive and time consuming. Moreover, new businesses might not know the ideal organizational structure or the most practical methods of staff motivation that best suits their organizational needs.
* __Production problems__ **→** it can be challenging for business start-ups to accurately forecast levels of demand so they are more likely to either over produce or under produce. Overproduction tends to lead to stockpiling, wastage, and increased costs. By contrast, underproduction leads to dissatisfied customers and a loss of potential sales.
* __Legalities__ **→** it is necessary for businesses to comply with all necessary legislation, including business registration procedures, insurance cover for staff and buildings, consumer protection laws and rules about intellectual property such as copyrights, patents, an trademarks. The paperwork and legal requirements of setting up a new business can be cumbersome, confusing, time consuming and expensive. Any oversight could result in the business having to pay compensation or financial penalties. This would obviously damage the already vulnerable cash flow position of business start-ups.
* __High production costs__ **→** new businesses are likely to have high set-up costs and running costs due to the large amount of money needed to purchase or pay for capital equipment, machinery, stocks, rent, advertising, insurance, and so forth. Smaller businesses will also be at a cost disadvantage as they cannot benefit from economies of scale. By contrast, economies of scale allow larger and more established businesses to benefit from lower average costs of production due to the size of operations, such as being able to get discounts from their suppliers for large bulk purchases or being able to borrow money at a lower interest rate because of their larger size and financial collateral.
* __Poor location__ **→** businesses face a dilemma in the location decision; busy areas offer the highest potential number of customers, but the premises in these area will also cost the most. Fixed costs, such as rent or mortgage payments account for a large percentage of total costs for many businesses. An aim for any new business is to reach. break-even as soon as possible, by keeping fixed costs down. This is one reason why many entrepreneurs set up small businesses that operate initially from their own homes (which also has a tax advantage). Ofcourse this is not suitable for businesses where location plays a key factor in business survival.
* __External influences__ **→** all businesses, irrespective of size or how long they have been in operation, are prone to exogenous socks that create a challenging trading environment, such as global financial crisis or the outbreak of a pandemic. However, larger and more established firms tend to be better resourced to handle these external influenced. Hence, new businesses face the added challenge of being more vulnerable to external shocks which also means the potential for business failure is great.
42
New cards
Collateral
Financial guarantee for securing external loan capital to finance investment expenditure for business growth
43
New cards
Working capital
The money available for the daily runnings of a business
44
New cards
Niche
Segment of a larger market that can be defined by its own unique needs, preferences, or identity that makes it different from the market at large
45
New cards
Opportunities of starting a new business (GET CASH)
* Growth → entrepreneurship tend to benefit personally when there is ana ppreciartion in the value of their businesses, especially as property and land tend to increase in value over time. This is called capital growth. it is quite common for the capital growht of a business to be worth more than the value of the owener’s salaries.
* Earnings → The potential returns from setting up your own business can easily outweigh the costs, even though the risks are hight. It is common that entrepreneurs earn far in excess of salaries from any other occupation that they might otherwise pursue.
* Transference & inheritance → in many societies, it is the cultural norm to pass on assets, including businesses, to the next generations. Many self-employed entrepreneurs view thier business as something that they are able to pass on (transferance) to their children (inheritence) to give them a sense of financial security that might not be possible if they chose to work for someone else.
* Challenge → some people might view setting up and running a business as a personal challenge. It is this challneg that dirves them to perform and what gives them particular satisfaction. Being successful in business boosts self-esteem.
* Autonomy → wokring for someone else means that employees have to follow the instructions and rules set by the organizationt hat they work for, such as conditions of employment, working hours, employment benefits and holiday entitlments. Conversely, being self employed means that there is autotnommy in how things are done within the organization. Essentially, this opportunity refers to the benefits of being your own boss.
* Security → there could be a greater sense of job security for someone who is their own boss. By contrast, employees can be dismissed, made redundant or even rpelcaed by technology. Although the risks are great, being self-employes also makes it potentially easier to accumulate personal wealth (financial security) to provide higher funds for retiremment.
* Hobbies → some people might want to purusr etheir passion or to turn their hobby and interests into a business opportunity. Succesful entrepreneurshave a passion for what they do and this is mde easier if the nature of the work is directly related to their personal interests.
* Earnings → The potential returns from setting up your own business can easily outweigh the costs, even though the risks are hight. It is common that entrepreneurs earn far in excess of salaries from any other occupation that they might otherwise pursue.
* Transference & inheritance → in many societies, it is the cultural norm to pass on assets, including businesses, to the next generations. Many self-employed entrepreneurs view thier business as something that they are able to pass on (transferance) to their children (inheritence) to give them a sense of financial security that might not be possible if they chose to work for someone else.
* Challenge → some people might view setting up and running a business as a personal challenge. It is this challneg that dirves them to perform and what gives them particular satisfaction. Being successful in business boosts self-esteem.
* Autonomy → wokring for someone else means that employees have to follow the instructions and rules set by the organizationt hat they work for, such as conditions of employment, working hours, employment benefits and holiday entitlments. Conversely, being self employed means that there is autotnommy in how things are done within the organization. Essentially, this opportunity refers to the benefits of being your own boss.
* Security → there could be a greater sense of job security for someone who is their own boss. By contrast, employees can be dismissed, made redundant or even rpelcaed by technology. Although the risks are great, being self-employes also makes it potentially easier to accumulate personal wealth (financial security) to provide higher funds for retiremment.
* Hobbies → some people might want to purusr etheir passion or to turn their hobby and interests into a business opportunity. Succesful entrepreneurshave a passion for what they do and this is mde easier if the nature of the work is directly related to their personal interests.
46
New cards
Capital growth
Capital growth is your property increasing in value over time.
47
New cards
Autonomy
Independence, freedom of choice and flexibility
48
New cards
Reasons for setting up a business
People set up their own businesses due to the opportunities to satisfy their personal desires, such as to fulfill a personal vision, to have the opportunity to achieve success, to be their own boss, or live a more extravagant lifestyle (if and when the business becomes successful). However, a significant number of new businesses fail to survive. There are three inter-related reasons or challenges behind this, a lack of cash in the business, poor cost control, substandard or weak management and leadership.
49
New cards
Reasons for start-up business failure
A significant number of new businesses fail to survive. There are three inter-related reasons or challenges behind this;
1. A lack of cash in the business
2. Poor cost control
3. Substandard or weak managament and leadership.
1. A lack of cash in the business
2. Poor cost control
3. Substandard or weak managament and leadership.