Lecture 5 - Midterm 1
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
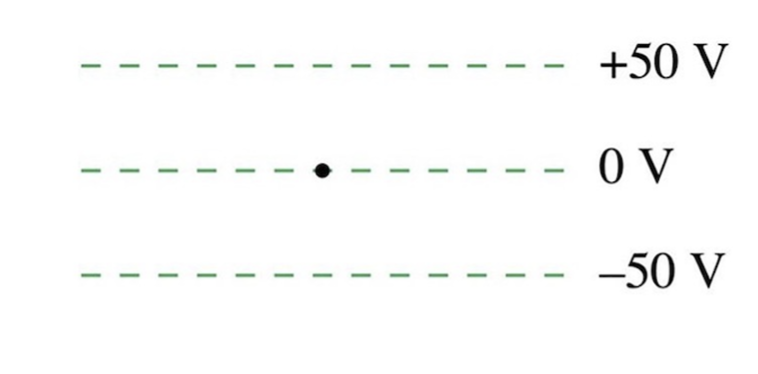
A proton is released from rest at the dot. Afterward, the proton
A. Remains at the dot.
B. Moves upward with steady speed.
C. Moves upward with an increasing speed.
D. Moves downward with a steady speed.
E. Moves downward with an increasing speed.
Moves downward with an increasing speed.
The electric potential, like the electric field,obeys the principle of superposition.
A. True
B. False
True
What is the relation between speed and potential based on charge?
Both slow down
A positive charge slows down as it moves to higher potential, a negative charge speeds up
A positive charge speeds up as it moves to higher potential, a negative charge slows down
Both speed up
A positive charge slows down as it moves to higher potential, a negative charge speeds up
Describe the interaction between charges:
electric force (F) and electric field (E)
electric force (F) and potential energy (U)
electric field (E) and kinetic energy (k)
electric field (E) and electric potential (V)
electric force (F) and potential energy (U)
Describe space modified by a charge (no interactions here):
electric force (F) and potential energy (U)
electric force (F) and electric field (E)
electric field (E) and kinetic energy (k)
electric field (E) and electric potential (V)
electric field (E) and electric potential (V)
The potential of a point charge is:
positive for (-) charge, negative for (+) charge
positive for (+) charge, negative for (-) charge
neutral for either charge
none of the above
positive for (+) charge, negative for (-) charge