Edexcel A Level Microeconomics
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Positive statement (def.)
Evidence based statement which can be proven true or false
Normative statement (def.)
Value judgment which cannot be tested
Scarcity (def.)
Lack of resources to fulfil everyone's wants and needs
Renewable resources (def.)
Resources which can be replenished over time
Non-renewable resources (def.)
Resources which cannot be replenished once they are used
PPF (def.)
Max potential output for two goods that an economy can produce, at a point time time, it it uses all of its factors of production to their full capacity.
Capital goods (def.)
Useful not in themselves but for goods and services they can help produce in future
Opportunity cost (def.)
next best alternative forgone
Pareto efficiency (def.)
State of allocation of resources in which it is impossible to make any one party better off without making at least one party worse off
Allocative efficiency (def.)
When value consumers place on good or service (reflected in price) = cost of resources used up in production
Specialisation (def.)
When individual/firm concentrates on performing specific task or narrow range of tasks in production process
Division of labour (def.)
Separation of production process into individual tasks
Advantages of specialisation (micro)
Workers skilled in narrow range of tasks/ cost efficient/ workers specialise in tasks they are good at/ not constantly changing tasks
Disadvantages of specialisation (micro)
Boredom/ Lack of diversification/ Less transferable skills/ Workers replaceable with machinery
Functions of money
Medium of exchange/ Store of value/ Unit of account/ Method of deferred payment
Free market economy (def.)
Economic system where resources are privately owned and allocated by price mechanism
Mixed economy (def.)
Where resources are partly allocated by market forces and partly by government
Conditions of demand
income/ willingness/ taste/ population/ substitute goods/ complementary goods
Veblen good (def.)
Good for which quantity demanded increases as price increases
PED > 0
Giffen good (def.)
Good for which higher price causes an increase in demand
Income effect > substitution effect
Law of diminishing marginal returns
After optimal level of capacity is reached, adding an additional factor of production results in smaller increases in output
Types of demand
Latent/ Effective/ Competitive/ Joint/ Derived/ Composite
Latent demand (def.)
Demand for something that consumers do not buy because they do not have enough money or it is not yet available
Effective demand (def.)
Quantity of good or service that consumers are willing and this willingness is backed up by ability to buy at given price in given time period
Competitive demand (def.)
When demand for one good increases or decreases, demand for another good does opposite

Joint demand (def.)
When demand for one good increases or decreases, demand for another good follows

Derived demand (def.)
Product is demanded only because of demand for final product it contributes to

Composite demand (def.)
When good is demanded for different purposes. Change in demand for one purpose affects others

Conditions of supply (PINTSWC)
productivity/ indirect tax/ no. firms/ technology/ subsidy/ weather/ costs of production
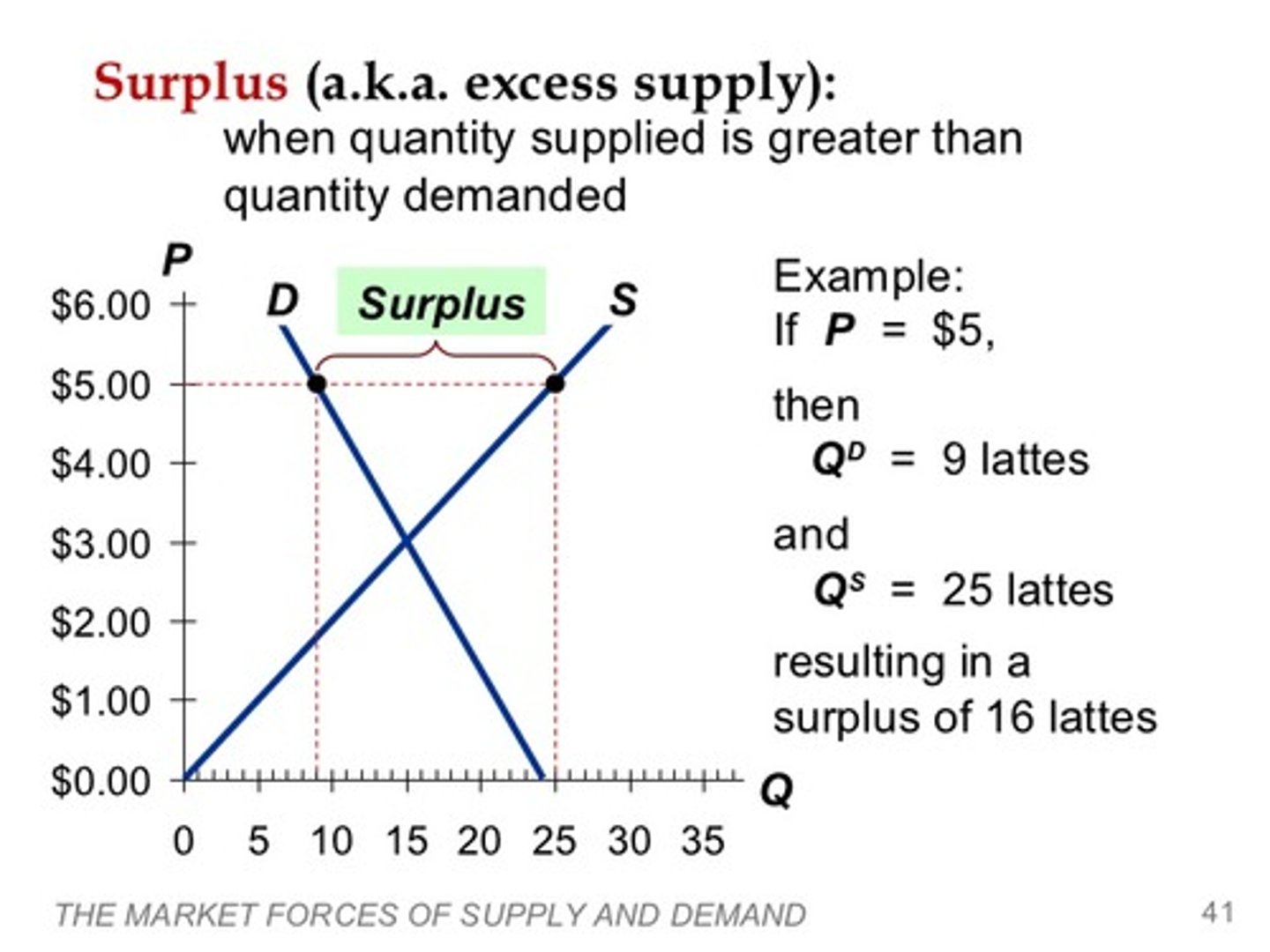
Excess supply
Quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded
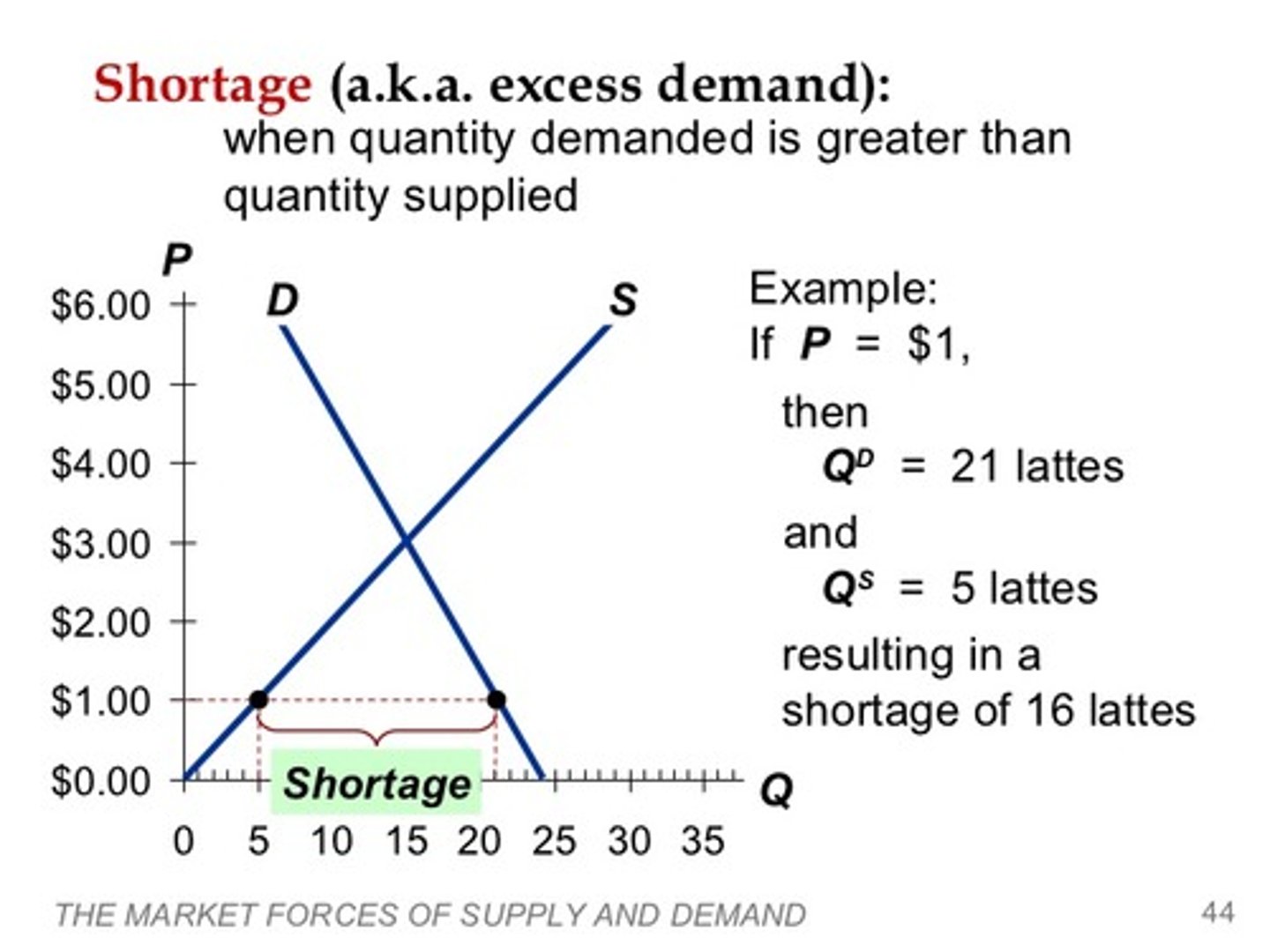
Excess demand
Quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied
Roles of price mechanism (R/I/S/A)
Rationing/ Incentivising/ Signalling/ Allocating
PED (eq.)
PED = percentage change QD / percentage change P
YED (eq.)
YED = percentage change QD / percentage change Y
XED (eq.)
XED = Percentage change QD A / percentage change P B
Unitary price elastic demand
PED = 1
Perfectly price elastic demand
PED = infinity
Relatively price elastic demand
PED > 1
Perfectly price inelastic demand
PED = 0
Relatively price inelastic demand
PED < 1
Inferior good
YED < 0
Normal good
YED > 0
Luxury good
YED > 1
Substitute goods
XED > 0
Complementary goods
XED < 0
Unrelated goods
XED = 0
Deterimants of PED (AS/ I / TP / BL / N / A)
Availability of substitutes/ % income spent/ Time period/ Brand loyalty/ Necessity/ Addictiveness
Relationship between P(elastic good) and TR
P(elastic good) ∝ TR
Relationship between P(inelastic good) and TR
P(inelastic good) ∝ TR
PES (eq.)
PES = Percentage change QS / percentage change P
Determinants of PES
Amount of spare capacity/ Factor mobility/ Time period/ Length of production process/ Availability of stocks/ Durability
Direct tax (def.)
Tax on income or wealth
Indirect tax (def.)
Tax on expenditure (only taken when good is purchased)
Specific tax (def.)
Tax per unit
Ad valorem tax (def.)
Tax based on percentage of price of g/s
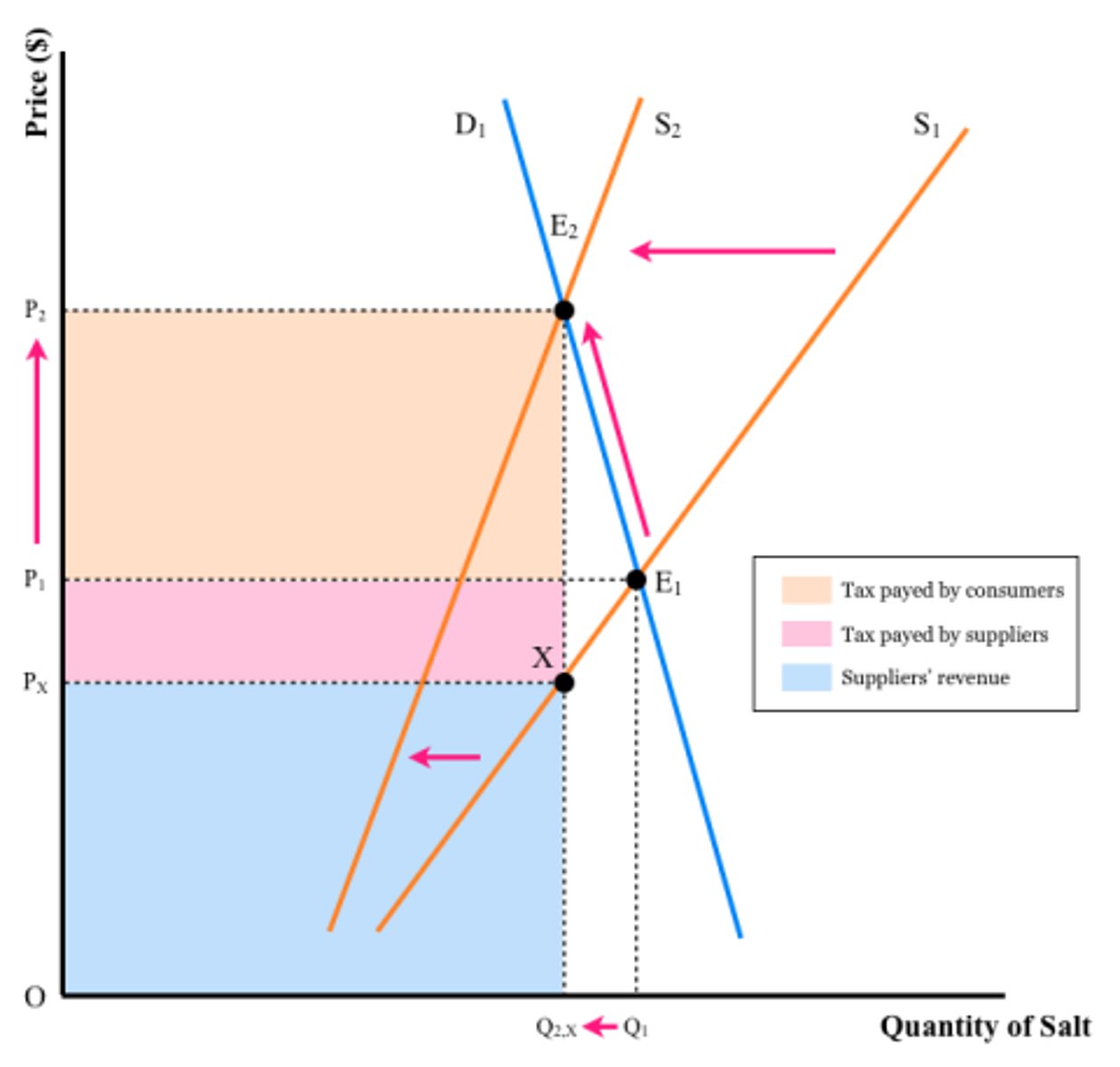
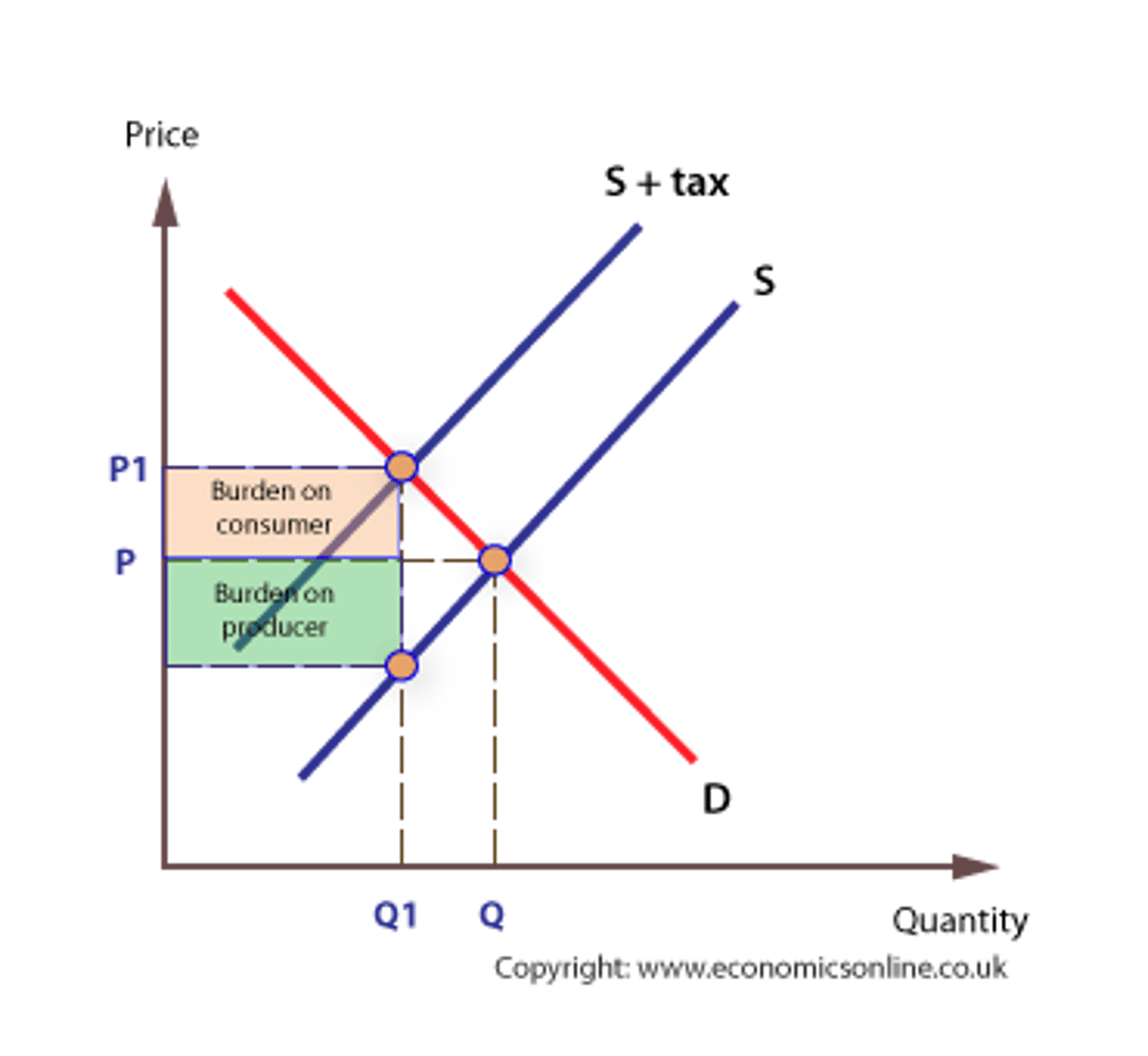
Impact of PED on producer and consumer share of tax
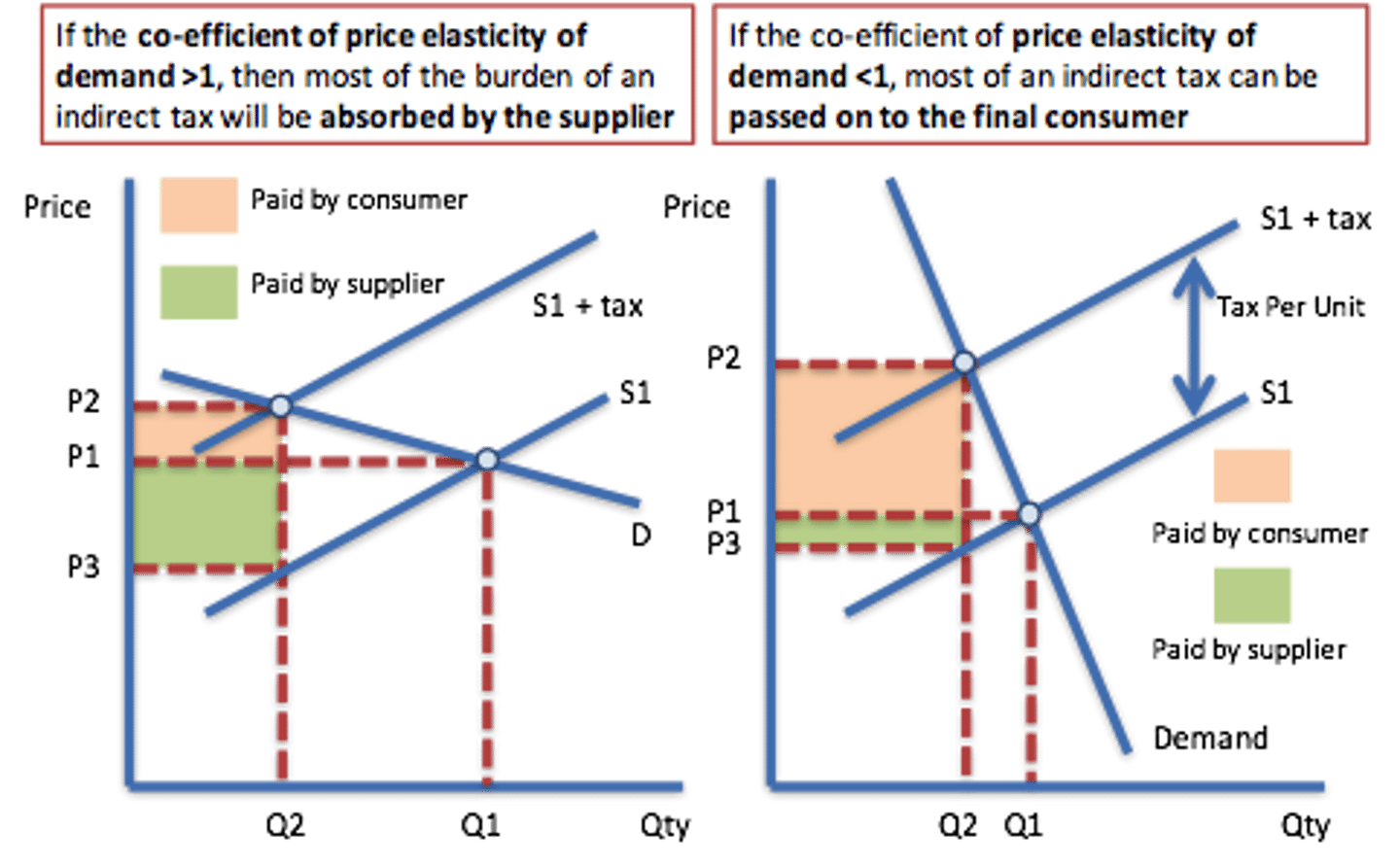
Subsidy (def.)
Grant paid by government to producers to increase supply
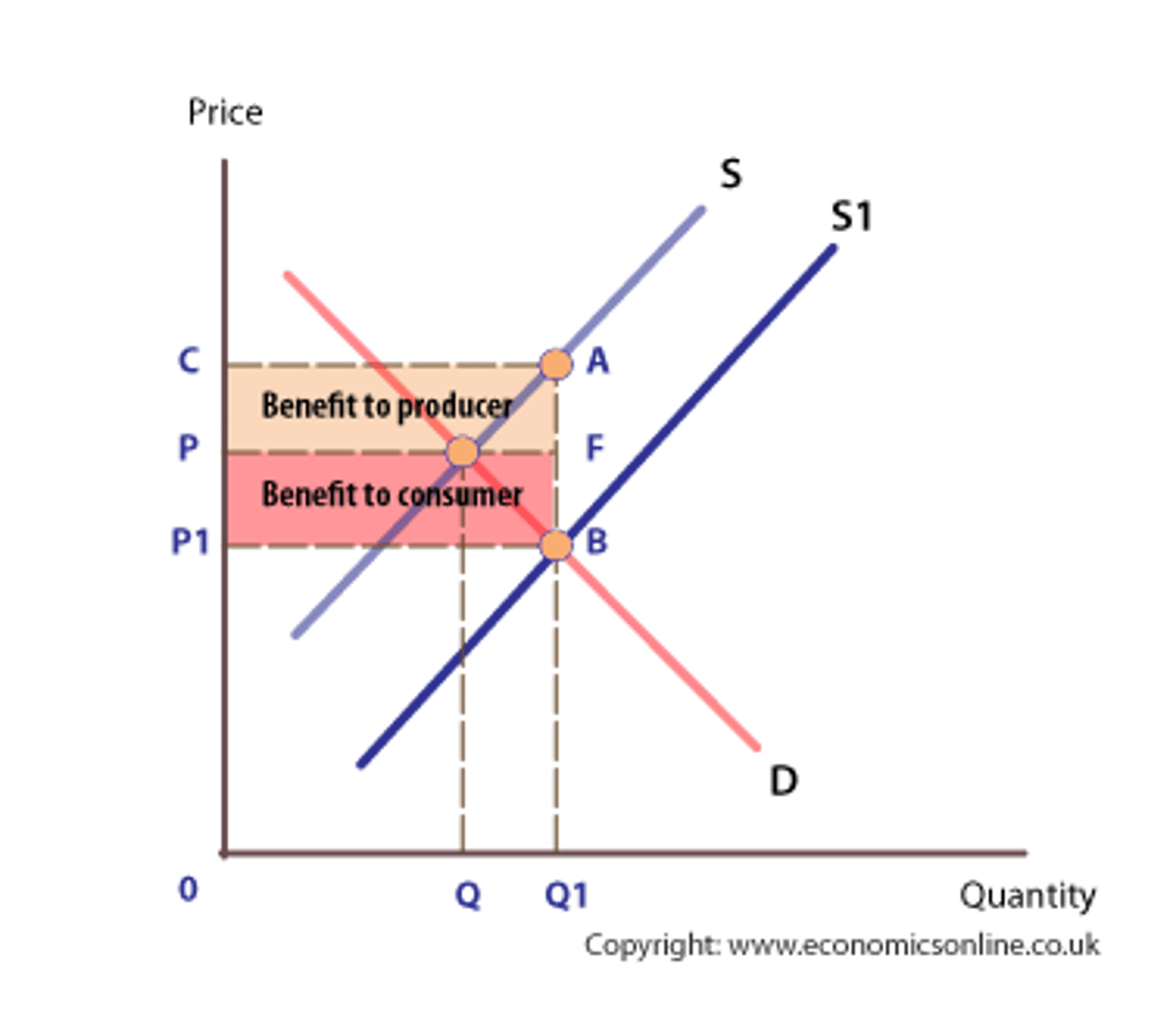
Market failure (def.)
When free market fails to allocate resources efficiently
Public good (def.)
Goods that are non-rival and non-excludable
Non-rival (def.)
Consumption of good by one person does not reduce amount available for others
Non-excludable (def.)
It is not possible to provide good or service to one person without it thereby being available for others to enjoy
Free-rider problem
Individuals benefit from resource/good/service without paying for them, which leads to underprovision of goods in free market and market failure.
Quasi-public good (def.)
Good that only has one characteristic of public good - either non-rival or non-excludable
Private cost (def.)
Costs experienced by two parties involved in transaction
External cost (def.)
Costs experienced by third parties not involved in transaction
Social cost (def.)
Private costs + external costs
Private benefit (def.)
Benefits experienced by two parties involved in transaction
External benefit (def.)
Benefits experienced by third parties not involved in transaction
Social benefit (def.)
Private benefits + external benefits
Deadweight loss (def.)
Loss of eocnomic efficiency that occurs when socially optimal quantity of good/service isn’t produced or consumed
Negative externality diagram
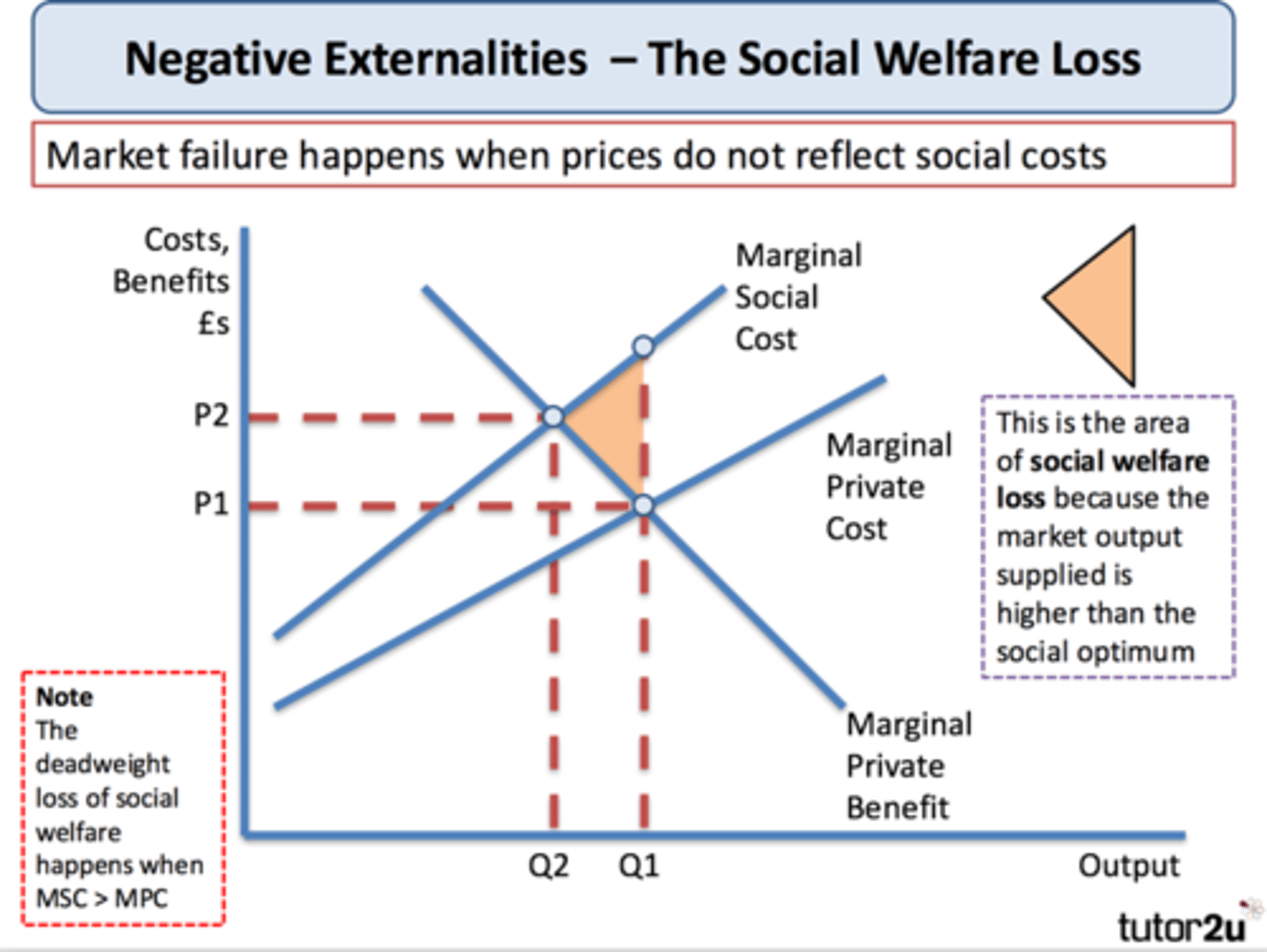
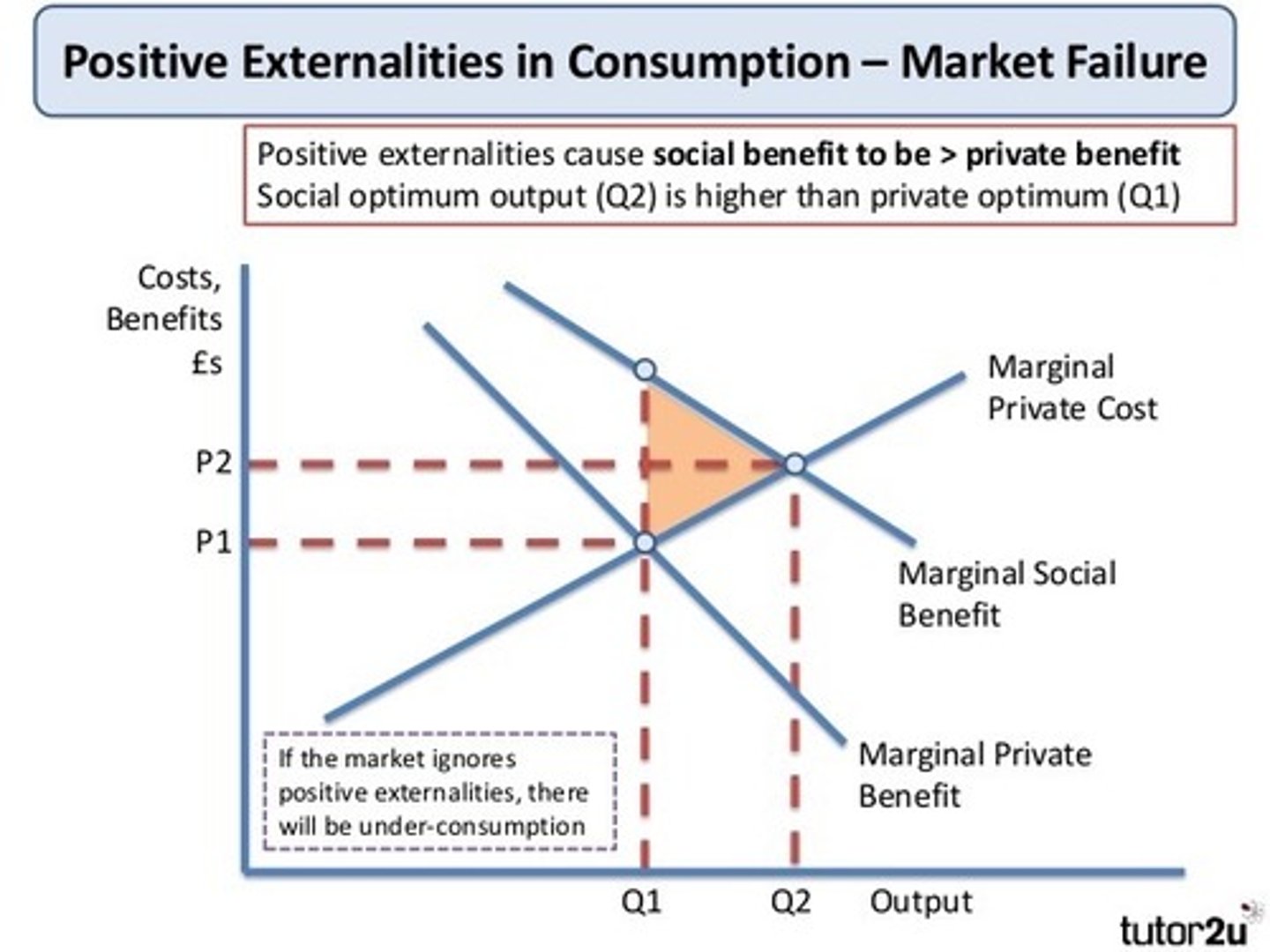
Positive externality diagram
Benefits of monopoly
significant profits/ higher prices/ lower wages
Imperfect information (def.)
When at least one party has incomplete information
Asymmetric information (def.)
When one party in transaction has more information than other
Merit good (def.)
Good which is under-consumed by consumers if left to free market
MPB(perceived) < MPB(actual)
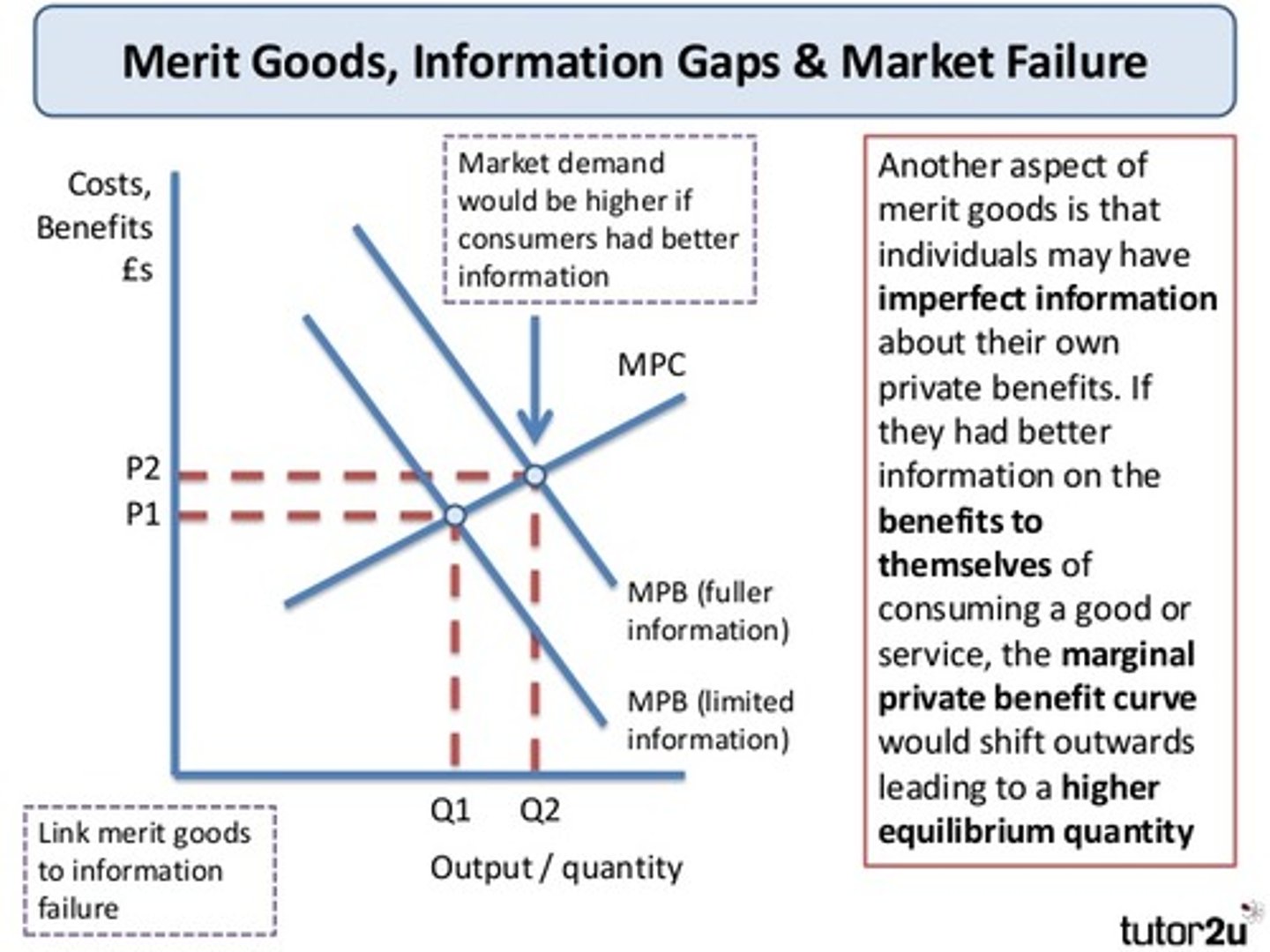
Demerit good (def.)
Good which is over-consumed by consumers if left to free market
MPB(perceived) > MPB(actual)
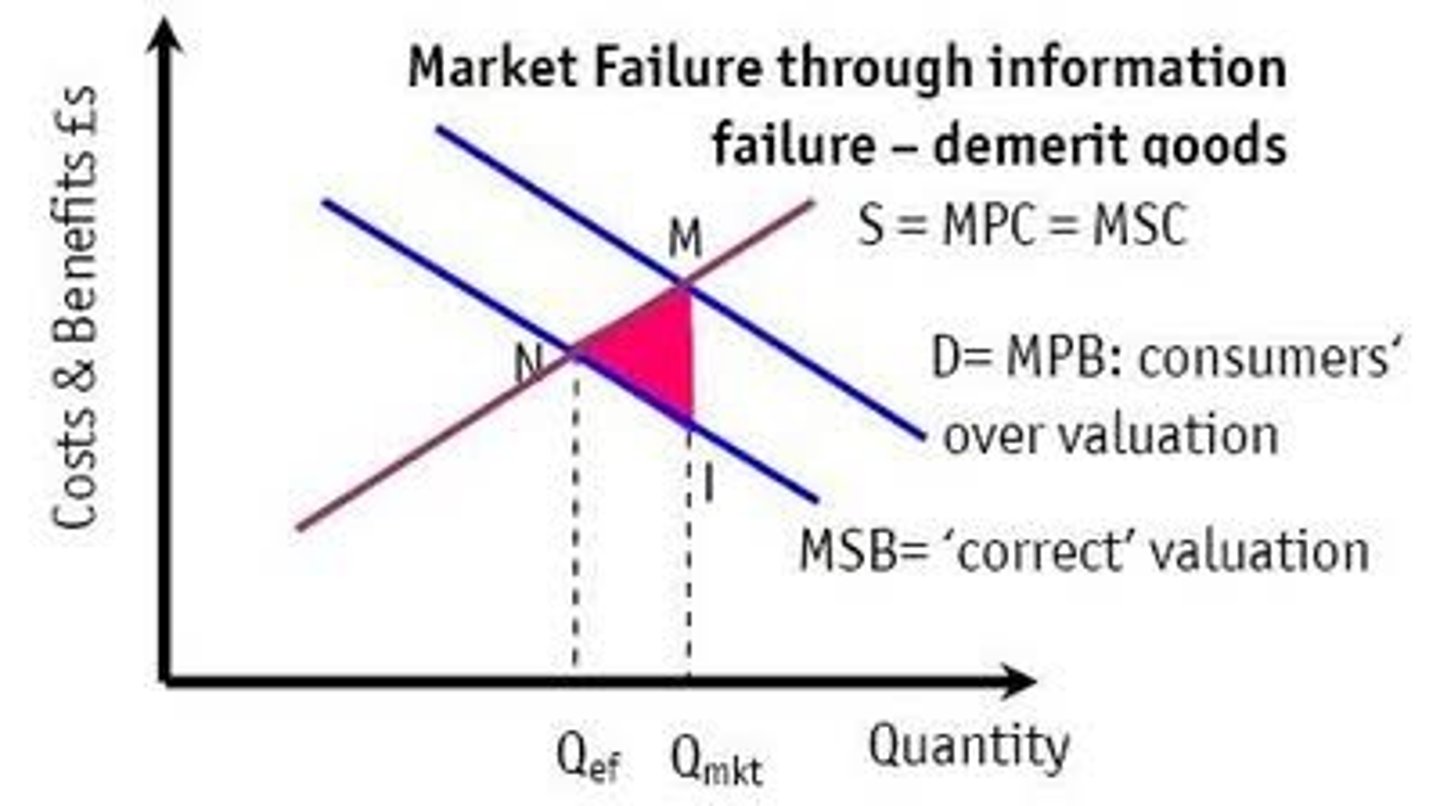
Market failures (TC/FR/II/AI/MG/DG/NE/PE/CM/LM)
Tragedy of the Commons/ Free rider problem/ Imperfect information/ Asymmetric information/ Merit good/ Demerit good/ Negative externality/ Positive externality/ Commodity markets/ Labour markets
Organic growth (def.)
Increase factors of production in its own industry
Behavioural biases (HE/HA/WC/LA)
Herd mentality/ Habitual behaviour/ Weakness at computation/ Loss aversion
Tragedy of the commons
Individuals have access to a shared resource and act in their own interest, at the expense of other indviduals
Allocative efficiency
When value consumers place on good or service = cost of resources used up in production
P = MC
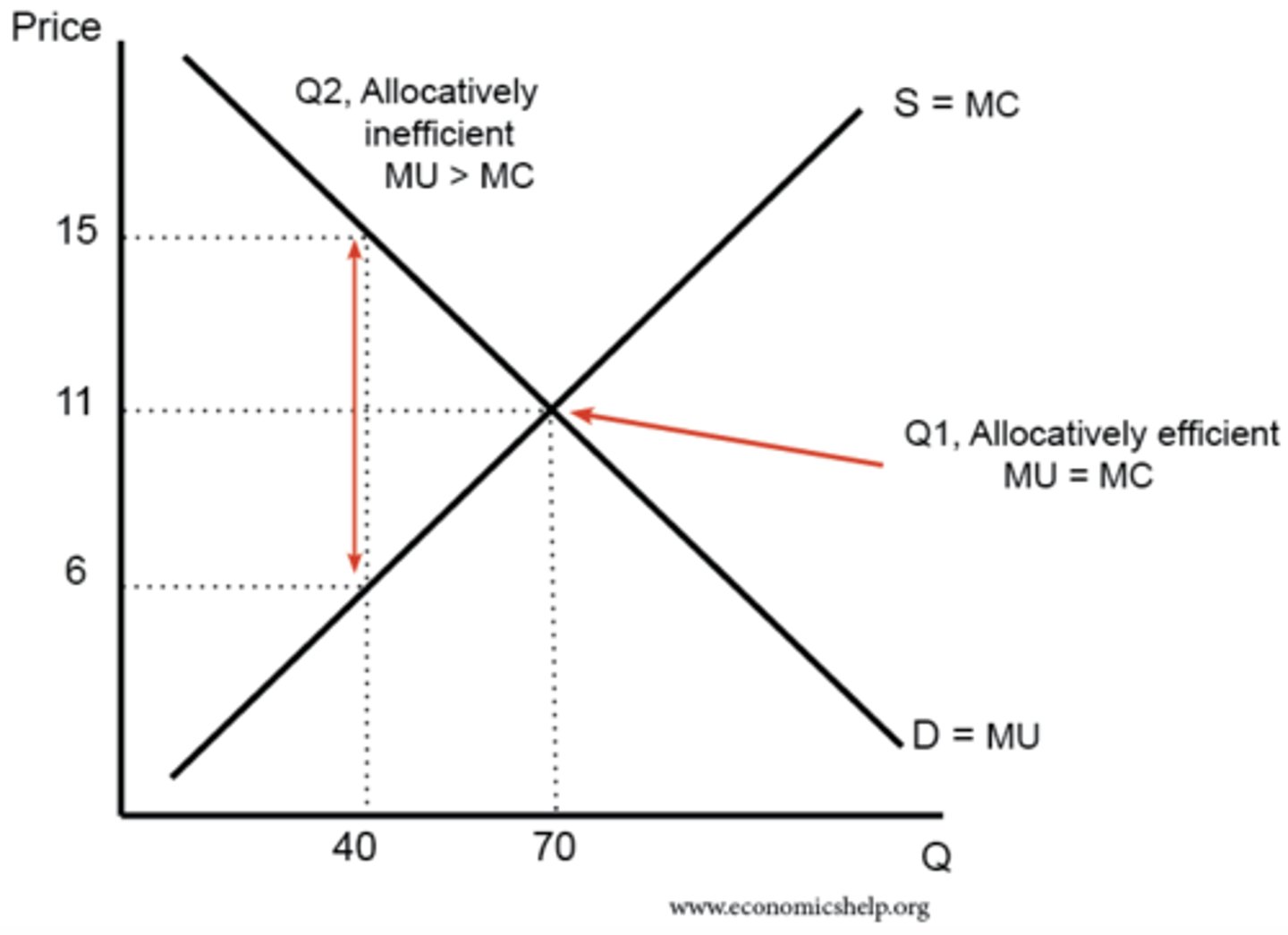
Productive efficiency
When output is being produced with minimum of combination of factor inputs
MC = AC
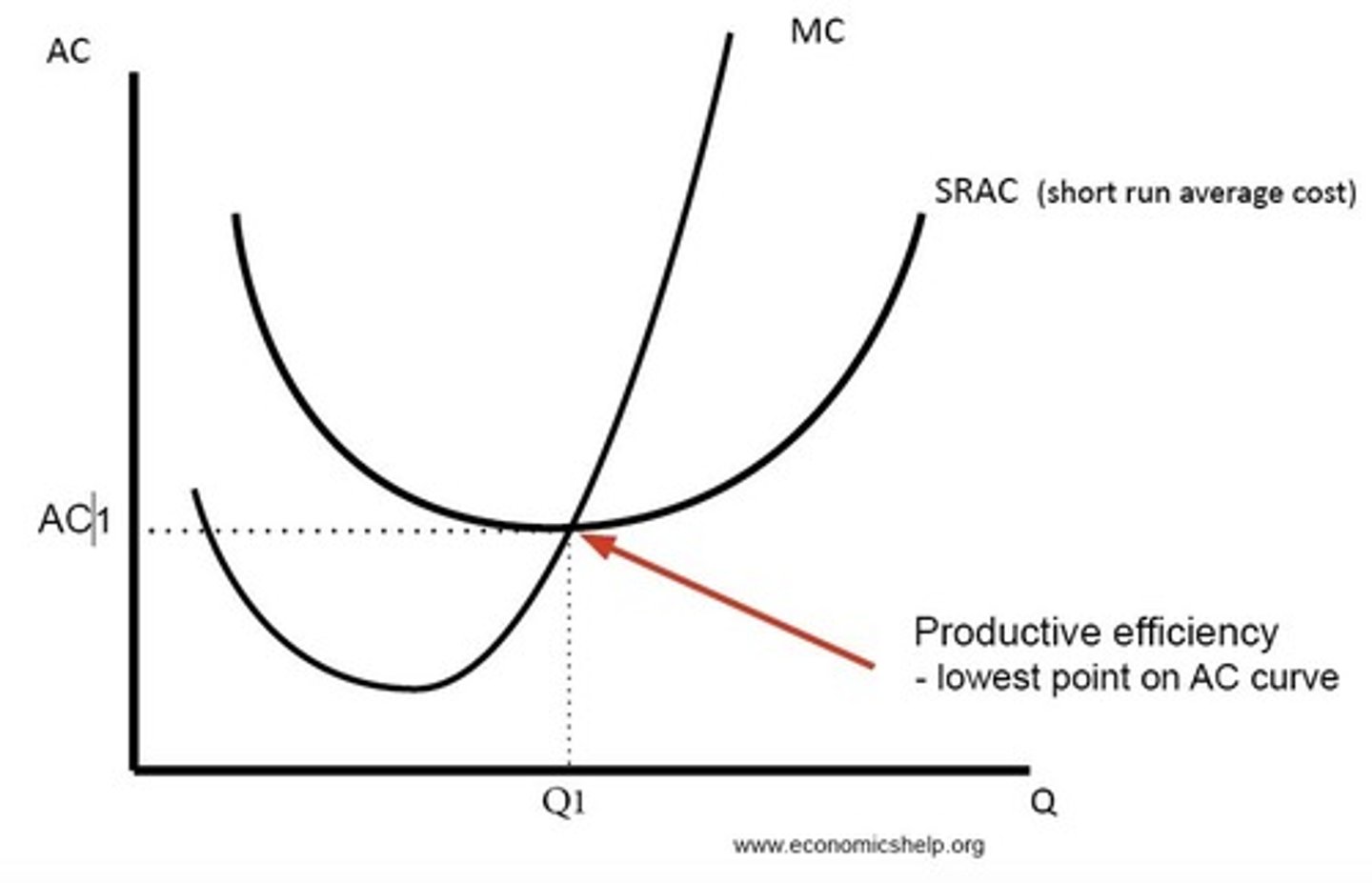
Technical efficiency
When maximum output that can be obtained from given input
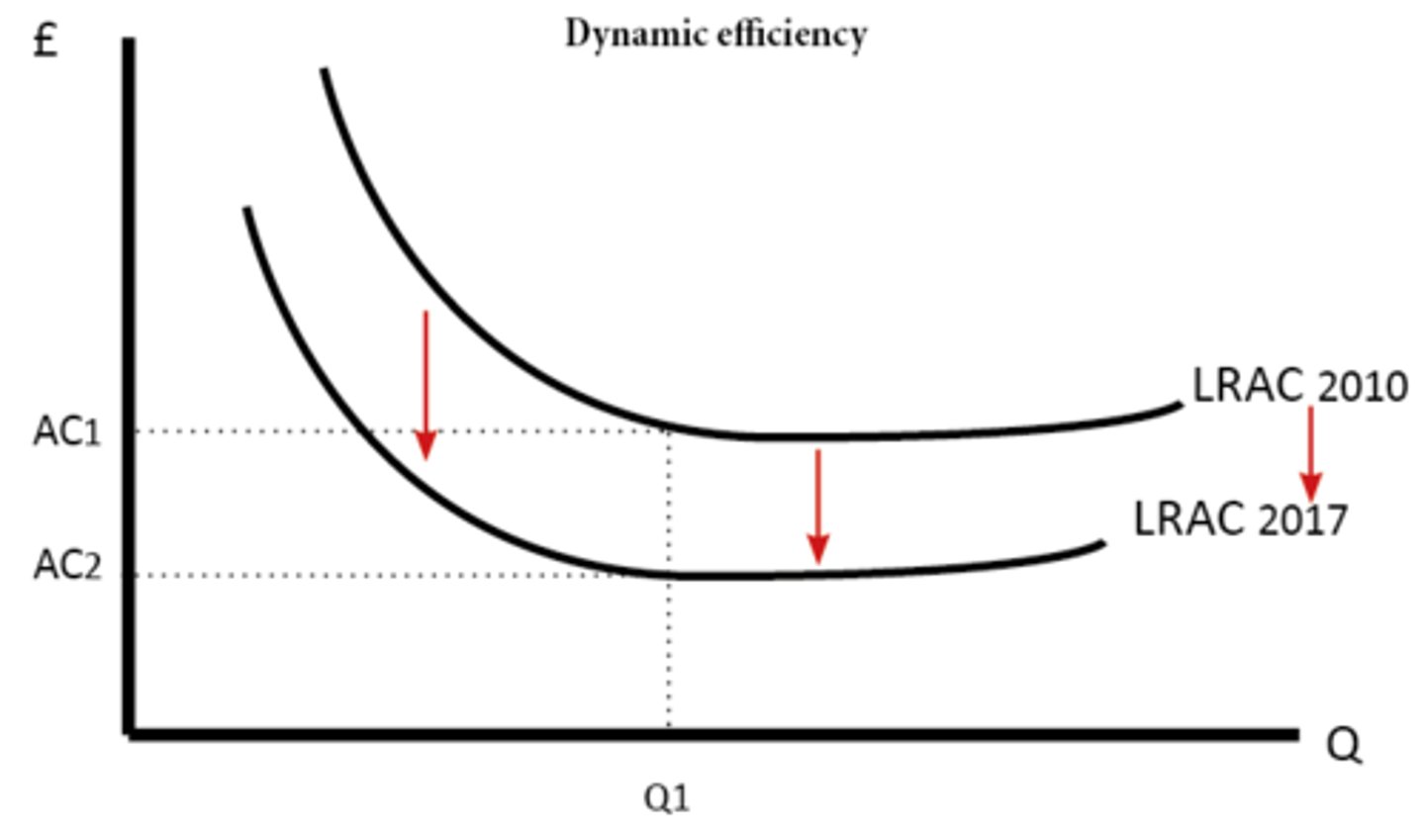
Dynamic efficiency
Productive efficiency of firm over extended period of time