Inorganic chemistry
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
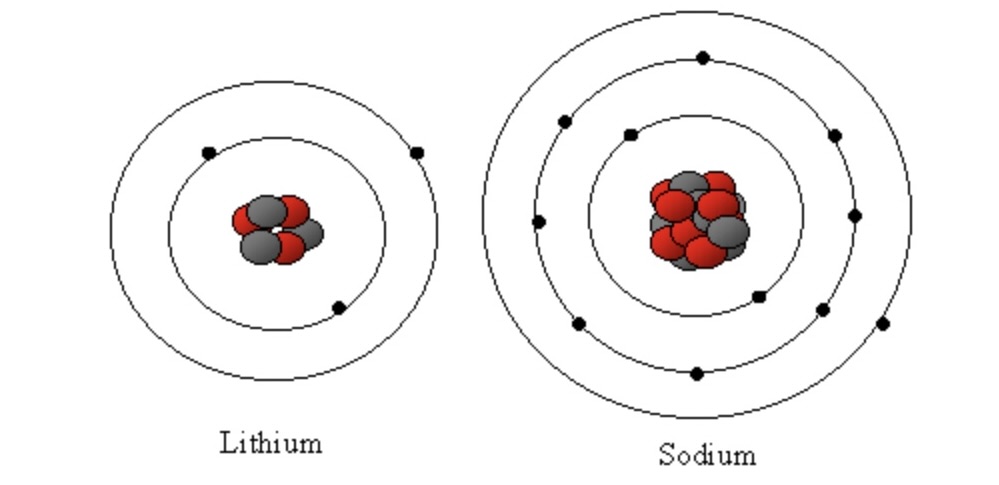
What are Group 1 elements?
Alkali metals.
What are the most important alkali metals?
Lithium
Sodium
Potassium
Rubidium
Caesium
Francium
What do all alkali metals have in common?
They all have one electron on the outer shell.
What are the properties of alkali metals?
Soft.
Low density.
Low melting point.
Highly reactive → lose one electron and become unstable.
What is the reaction between Group 1 metals and water?
Group 1 metal + water → metal hydroxide + hydrogen
2M(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2MOH(aq) + H2(g)
What are the two features of the metal hydroxide produced?
Colourless aqueous solution.
pH 7-14 → alkaline solution.
Reaction with alkali metal and water as you descend Group 1
Lithium → slow, fizzing.
Sodium → vigorous fizzing, dissolves quick.
Potassium → lilac flame.
What is the reaction between a Group 1 metal and oxygen?
Oxygen + metal → metal oxide
Physical trends as you descend Group 1
Softer as you descend.
Melting point decreases as you descend.
What is the reactivity of Group 1 metals as you descend the group?
Reactivity increases as you descend.
More electron shells between nucleus and outer most electron.
Less force of attraction, easier to lose the electron.
What are Group 7 elements known as?
Halogens (diatomic molecules).
What are the main halogens?
Fluorine
Chlorine
Bromine
Iodine
Astatine
What is the appearance of the halogens at room temperature?
The colour gets darker as you descend the group.
Fluorine → yellow gas
Chlorine → plane green gas
Bromine → orange/brown liquid (brown gas)
Iodine → grey solid (purple vapour)
Astatine → dark grey solid
What is the appearance of the halogens in and aqueous solution?
Fluorine → dosen’t form a stable solution
Chlorine → pale green solution
Bromine → orange solution
Iodine → brown solution
What are physical trends in Group 7?
Melting and boiling points increase as you descend due to stronger intermolecular forces.
Density increases as you descend.
How does reactivity change as you descend Group 7?
Reactivity decreases as you descend the group.
The are more election shells between the outermost electron and the nucleus.
Weaker forces of attraction to gain an electron.
What are metal halides?
Ionic compounds.
Formed when halogens react with Group 1 and 2 elements.
Form ionic salts.
What charge do halide ions carry?
-1
Non-metal halides
Covalent compounds.
Former when halogens react with hydrogen.
Form hydrogen halides.
What happens when hydrogen halides dissolve in water?
An acidic solution is formed.
What is a displacement reaction?
When a more reactive halogen or element displaces a less reactive one from a halide solution.
Which halogens displace each other?
Chlorine displaces both bromine and iodine.
Bromine displaces iodine.
What do all Group 7 elements have in common?
7 electrons on the outer electron.
Gain 1 electron to become a halide ion.
What’s the composition of air?
Nitrogen → 78%
Oxygen → 21%
Carbon dioxide → 0.04%
Argon → 0.9%
What method do you use to find the percentage of oxygen in the air?
Burning phosphorus in a bell jar.
What’s the method of finding oxygen percentage?
Small amount of phosphorus placed on dish on water in bell jar (water in and out checked).
Phosphorus is ignited using a hot wire, reacted with oxygen to form phosphorus oxides.
Once all oxygen is used up water begins to rise to replace oxygen.
Record water level.
Why is phosphorus used?
Its highly reactive and ensures that all the oxygen has been consumed and reacted.
What precautions should be taken when finding oxygen percentage?
Phosphorus is toxic and should be handles with care.
Ventilation.
Goggles and gloves.
What is a metal displacement reaction?
When a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal.
What are the forms of displacement reactions?
Metal + metal oxide (Heating)
Metal + aqueous metal solution
What occurs when the second metal is less reactive?
No reaction occurs.
What is the order of reactivity of elements.
K
Na
Li
Ca
Mg
Al
C
Zn
Fe
H
Cu
Ag
Au
What happens when Fe reacts with water and oxygen?
Rusting.
Experiment to check the conditions of rusting
Nail in test tube exposed to air + water = rust.
Nail in test tube with boiled water and oil on top = not rust.
Nail in test tube with calcium chloride = no rust.
What are the ways of rust prevention?
Barrier methods.
Galvanising.
Sacrificial protection.
What are some barrier methods?
Paint or grease prevents iron from getting in contact with water.
Coating could be damaged and iron could be exposed.
What is sacrificial protection?
A more reactive metal is put above the iron → it will corrode first.
Zinc is put above iron as it will oxide before iron.
What is galvanising?
Coating iron with zinc.
Zinc reacts with air to form ZnCO3 that forms a barrier.
What is electroplating?
When iron is dipped in molten zinc.
What is combustion?
Burning or heating something in oxygen to form oxides.
magnesium + oxygen → magnesium oxide (white flame + powder)
hydrogen + oxygen → water
sulphur + oxygen → sulphur dioxide (blue flame + colourless poisonous gas)
What is thermal decomposition?
When a substance brakes down when heat is applied.
Example of thermal decomposition
metal carbonate → metal oxide + carbon dioxide
copper (II) carbonate → copper (II) oxide + carbon dioxide
green solid → black solid (test for CO2 with limewater)
What is the greenhouse effect?
Maintaining global temperatures.
Ultraviolet radiation emitted from the sun.
Some radiation is absorbed while other is re-emitted from the earth surface as infrared radiation.
Infrared radiation is trapped by the green house gases that stop and absorb the energy.
What are the green house gases and their sources?
Carbon dioxide → burning fossil fuels + respiration.
Methane → cattle + decomposing landfill waste.
Water vapour → evaporation.
What is the enhanced greenhouse effect?
Increased greenhouse gases trap more heat and increase earth temperatures leading to global warming.
How do metals reactive water?
More active metals react violently with water.
Less reactive metal react slow and form metal hydroxides and hydrogen.
How do metals react with acids?
Only metals above hydrogen react with dilute acids.
What is the word equation for metals reacting with acids?
metals + acids → salt + hydrogen

What is oxidation?
Gain oxygen.
Loss of electrons.
What is reduction?
Loss of oxygen.
Gain of electrons.
What is a redox reaction?
When oxidation and reduction occur at the same time.
Example of a redox reaction
Mg +Cu → Mg + Cu
Oxidation:
Mg → Mg²⁺ + 2e⁻Reduction:
Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu
What are the two different agents?
Reduction agents → gets oxidised
Oxidation agents → get reduced
What mnemonic is used for redox?

How are metals found in the earth?
Metals are found on the earths crust as pure elements or combined in ores.
What is an ore?
Rocks that have enough metals that are worth being extracted.
What are the processes of metal extraction?
Electrolysis - more reactive than carbon
Blast furnace
Displacement
Heating with carbon
Why is extraction usually a reduction process?
Most metal ores are found as oxides and the extraction removed oxygen.
e.g iron oxide and aluminium oxide
What is the iron ore?
Hematite → Fe2O3
What is the aluminium ore?
Bauxite → Al2O3
What is correlation between reactivity and extraction?
More reactive metals at the tops → oxides easily.
Less reactive metals at the bottom → resistant to oxidation.
What is needed for the extraction of iron?
Hematite → iron source.
Coke → source of carbon for reduction.
Lime stone (CaCO3) → removed impurities.
What is the process of iron extraction?
Blast furnace:
Zone 1 → Carbon burns in oxygen (exothermic) → C + O2 → CO2
Zone 2 → Carbon dioxide reacts with coke to form carbon monoxide → C02 + C → 2CO
Zone 3 → Carbon monoxide reacts with iron (II) oxide to form iron → Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO3
Limestone decomposes = CCO3 → CaO + CO2
Calcium oxide neutralises silicon dioxide to form slag.
Th extraction of aluminium
Bauxite is dissolved in molten cryolite to lower the melting point.
→ Al3++3e−→Al cathode
→ 2O2−→O2+4e− anode
Carbon in graphite reacts with the oxygen (CO2) and has to be replaced.
Electricity used is expensive.
What is aluminium used for?
Aircraft bodies → high strength to weight ratio + low density
Saucepans → unreactive + good heat conductor
Food cans → non-toxic + corrosion and acid resistant
What is copper used for?
Electric wiring → ductile and good electricity conductor
Water pipes → unreactive and non toxic
What is iron used for?
Building material → strong malleable and cheap
Catalyst
What are the forms of steal used for?
0.25% carbon - car body and wiring → soft and malleable
0.5-1.4% carbon - tools → hard
20% chromium + 10% nickel - cutlery, sinks + chemical plants → strong + corrosion resistant
What is an alloy?
Mixture of two or more metals or non metals.
Benefits of alloys
Different sized atoms, prevents layers from sliding over each other easily.
Stronger and harder
Higher melting point + corrosion resistant
What are the solubility rule?
Soluble:
All sodium, potassium, ammoniums and nitrates.
Chlorides (except Ag + Pb)
Sulfates (except Ca, Pb + Ba)
Insoluble:
Carbonates (except Na, K and NH4)
Hydroxides (except Na, K and NH4)
Acids + protons
Proton donors as they ionise and produce H+ ions.
H+ makes solutions acidic.
Bases + protons
Bases are proton acceptors aa they ionise and produce OH- ions that accept protons.
OH- ions make solution alkaline.
What is the word equation for the reaction between an acid and base?
acid + base → salt + water
What is the word equation for the reaction between an acid and metal carbonate?
metal carbonate + acid → salt + carbon dioxide + water
What is the process of making an insoluble salt?
Mix two soluble salt solution in a beaker with a glass rod.
Precipitate will for → filter it to separate the solid from the solution and keep the insoluble salty on the filter paper.
Wash the insoluble salt with distilled water to remove impurities.
Leave to dry in oven to evaporate remaining water and then leave to dry.
What are the indication and the pH scale + examples?
Strongly acidic → pH 0-3 (hydrochloric acid)
Weakly acidic → pH 3-6 (ethenoic acid)
Neutral → 7 (sodium chloride)
Weakly alkaline → 8-10 (ammonia)
Strongly alkaline → 11-14 (sodium hydroxide)
What is the appearance of the phenolphthalein indicator in acid and alkaline solutions?
Acid → colourless
Alkali → pink
What is the appearance of the methyl orange indicator in acid and alkaline solutions?
Acid → red
Alkali → yellow
What is the appearance of the universal indicator in acid and alkaline solutions?
Acid → red
Alkali → blue
What is the appearance of the litmus paper in acid and alkaline solutions?
Acid → red
Alkali → blue
Features of acids
Source oh H+ ion
Disassociate from H+ ions in water
Acidity = concentration H+ ions
Features of bases
Source of OH- ions
Alkalis that are not soluble in water
What is a neutralisation reaction?
A reaction between an acid and alkali
All have the same ionic equation → OH- + H+ → H2O
What is the method titration?
Measure 25cm3 of Hal using a pipette.
Add it to a conical flash on top of a white tile with few drops of phenolphthalein indicator.
Fill burette with NaOH and record the initial vol. to 2 dp.
Open tap carefully and allow drops of the NaOH into the conical flask.
Close tap when solution turns pink.
Record the final volume and subtract it from the initial volume.
Repeat it 3 times and collect concordant results to calculate and average.
How do you make a soluble salt?
Add acid to a burette.
Add 25cm3 of alkali to a conical flask onto of a white tile and add a few f=drops of phenolphthalein indicator.
Open the tap and add drops of the acid into the conical flask and swirl.
Stop the. colour changes and record volume needed to neutralise the alkali.
Repeat without the recoded amount of acid, same amount of alkali and without the indicator.
Heat solution to evaporate most of the water + until crystals for around glass rod (saturated).
Cool the solution allowing crystals to form, filter remaining liquid.
Leave crystals to dry in oven.
How do you test for hydrogen?
Hold lit splint to mouth of test tube.
Should burn with squeaky pop.
How to test for oxygen?
Hold glowing splint to mouth test tube.
Splint should relight.
How to test for chlorine gas?
Hold blue litmus paper to mouth of test tube.
Should turn red then bleach white.
How to test for ammonia gas?
Hold red litmus paper to the mouth of the test tube.
Should turn blue.
How to test for carbon dioxide?
Bubble through limewater.
Should turn cloudy.
How to test for water?
Anhydrous copper sulfate + water → hydrated copper sulfate
White → blue.
Boils → 100°C
Freezes → 0°C
Test for cation?
Flame test:
Clean platinum/nichrome wire with HCl then dip into solid.
Place wire in the non luminous bunsen flame.
Flame test colours
Na+ → yellow
Li+ → red
K+ → lilac
Cu+ → green/blue
Ca+ → orange/red
Test for cation: NaOH
Cu2+ → blue precipitate (copper hydroxide)
Fe2+ → green (iron (II) hydroxide)
Fe3+ → orange/brown (iron (III) hydroxide)
NH4+ → ammonia gas
Test for anions
CO32+ + HCl → limewater cloudy
SO4- + HCl + BaCl → white precipitate
All add nitric acid and silver nitrate:
Cl- → white
Br- → cream
I- → yellow