ANA 110 (Salmeron)-University of Kentucky-Exam 3
1/230
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
231 Terms
What enzymes are in the large intestine?
none
incisors anatomy
premolars anatomy
Path of fat absorption
- fat
- lipase
- micelles
- lacteals
- thoracic duct
What enzymes are in the small intestines?
- maltase
- sucrose
- lactase
- peptidase
- intestinal lipase
molars anatomy
canines (teeth) anatomy
Sympathetic division job in GI tract
decreases secretion and motility
Haustral churning
contract and squeeze contents into next haustra
Macronutrients
- carbohydrates
- proteins
- lipids
Micronutrients
- vitamins
- minerals
- phytochemicals
- antioxidants
- fiber
Phytochemicals
plant-based nutrient
Antioxidants
decrease production of free radicals that speed up aging process
Fiber
maintains digestive health
Digestive system definition
breaking down food into molecules small enough for absorption through cells lining its organs
Tubular system
- from mouth to anus
- provides extensive surface area in contact with the external environment of lumen
Digestive system is closely associated with the ________ _______ for transport of absorbed substances
cardiovascular system
Pathway of Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract
Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine
Accessory digestive organs
teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
Digestive system functions
- Ingestion
- secretion
- Digestion (Mechanical and Chemical)
- Absorption
- Defecation
What are the mucosal layers of the GI tract?
- serosa
- muscular layer
- submucosa
- mucosa
Serosa layer of GI tract
- Epithelium and connective tissue
- protection and lubrication
- outside layer
Muscular layer of GI tract
- smooth muscles
- Two layers: inner longitudinal and outer circular layer
- movement of tube and its contents
Submucosa layer of GI tract
- loose connective tissue, lymphatics, and nerves
- nourishes surrounding tissues and transports absorbed materials
Mucosa layer of GI tract
- epithelium and connective tissue
- protection, secretion, absorption
What is the peritoneum?
largest serous membrane in the body
- Two parts: visceral and parietal
parietal peritoneum
lines the abdominopelvic cavity
visceral peritoneum
covers organs
Peritoneal cavity contains _____ _____ between two serous membranes
serous fluid
retroperitoneal organs
- organs outside of peritoneal cavity
- kidneys and pancreas
Roof of peritoneum
diaphragm
Anterior of peritoneum
rectus abdominus and anterior abdomen wall
Are there organs in the peritoneal cavity?
no, only peritoneal fluid
Lesser Omentum
- from liver to stomach
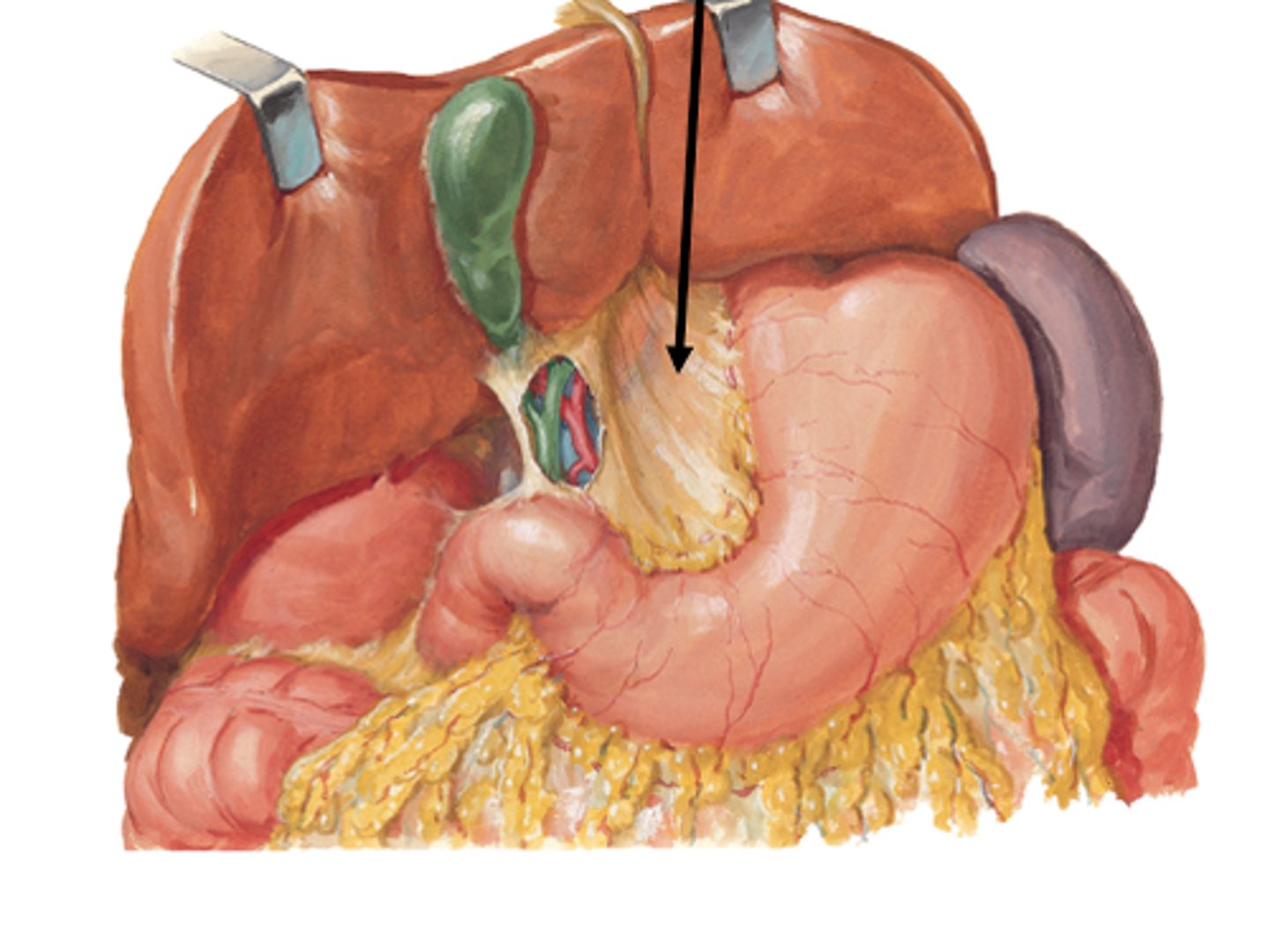
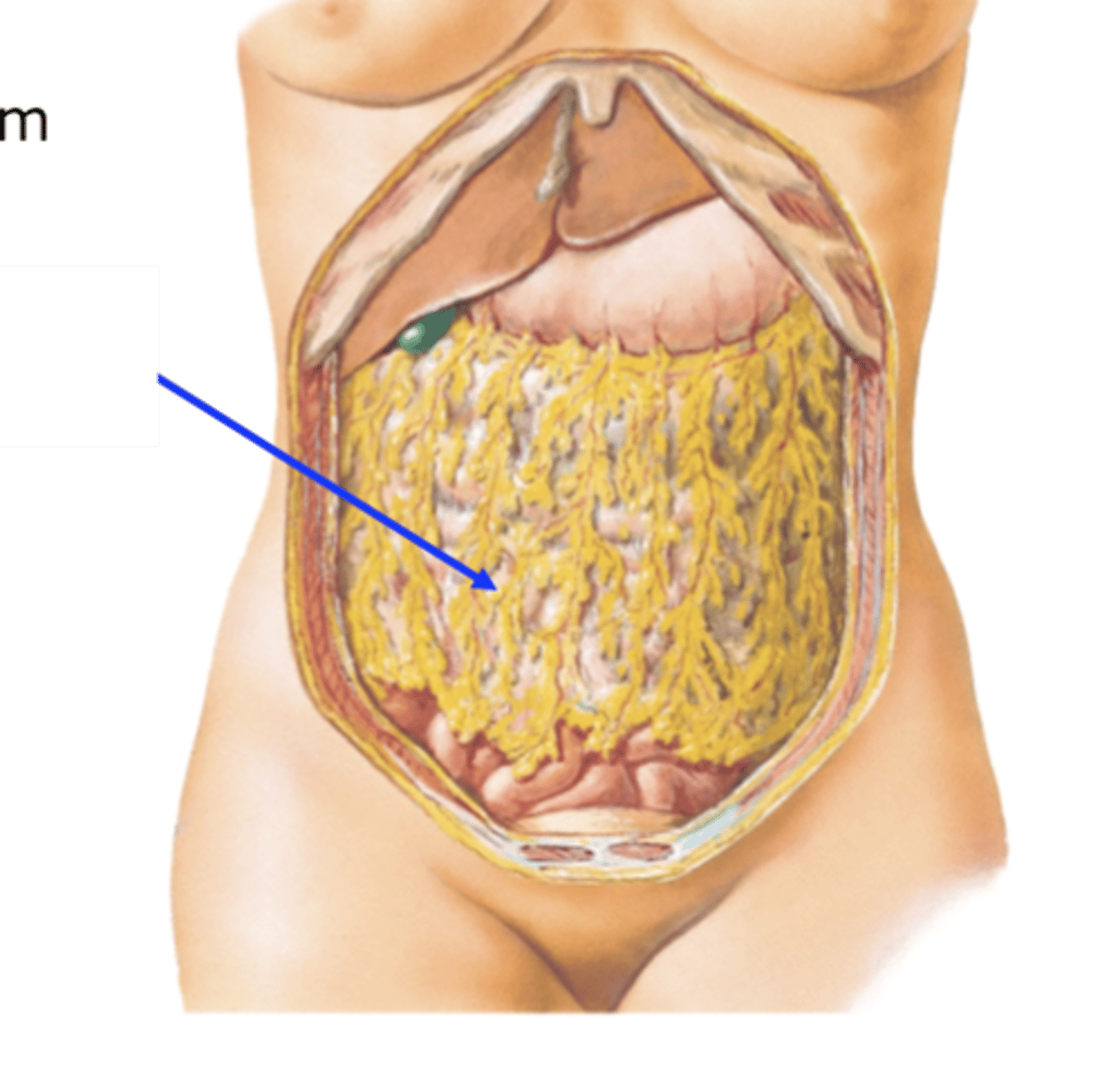
Greater omentum
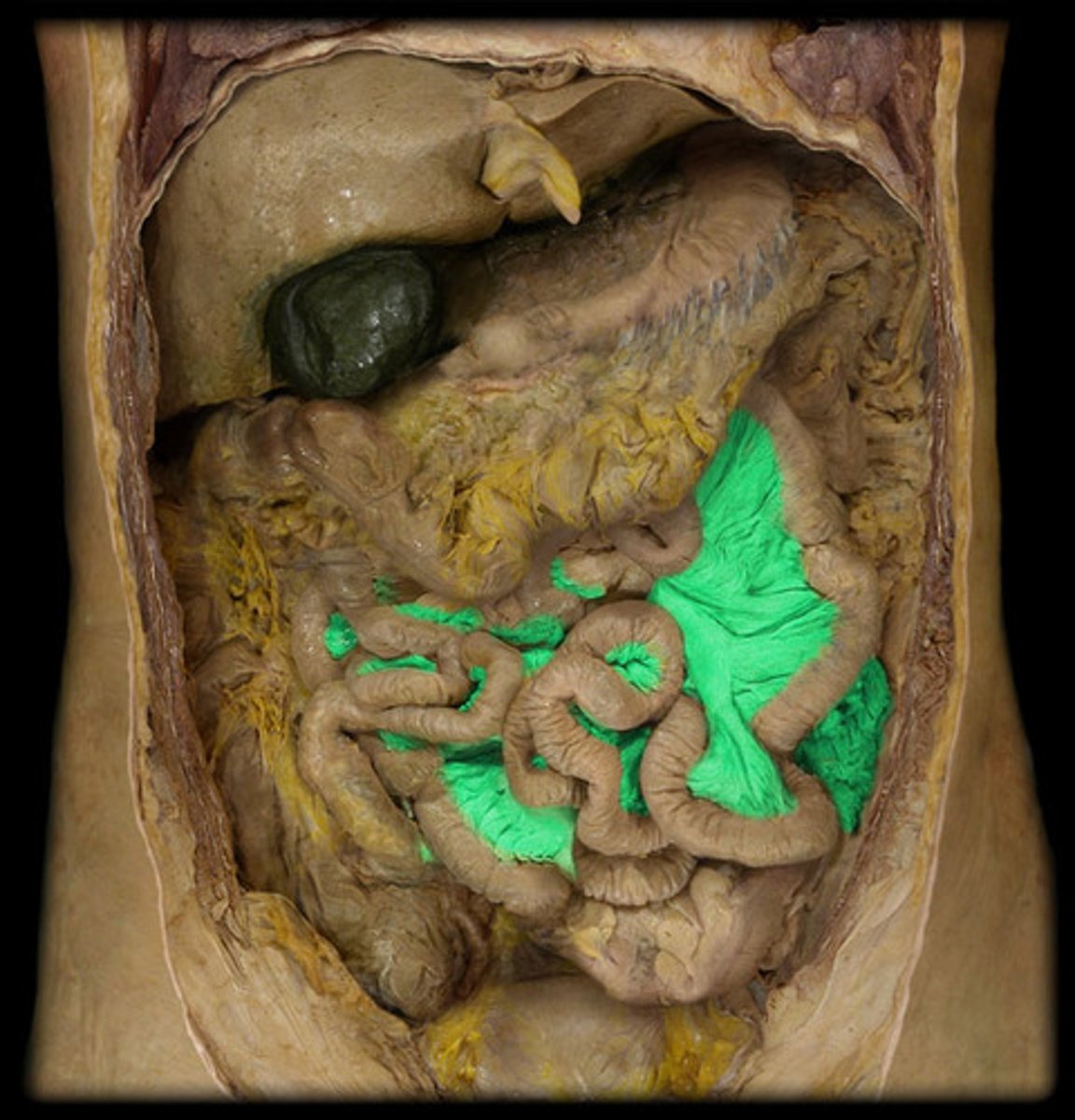
Mesentary
attaches intestines to the posterior abdominal wall and is formed by the double peritoneum
The ______ ______ holds food and is responsible for the first steps in digestion
oral cavity
Anterior oral cavity
- oral orifice
- lips
Orbicular oris
muscle inside lips
Posterior oral cavity
oropharynx (throat)
Superior oral cavity
- hard palate
- soft palate
Hard palate
forms rigid surface for the tongue to force food against during chewing
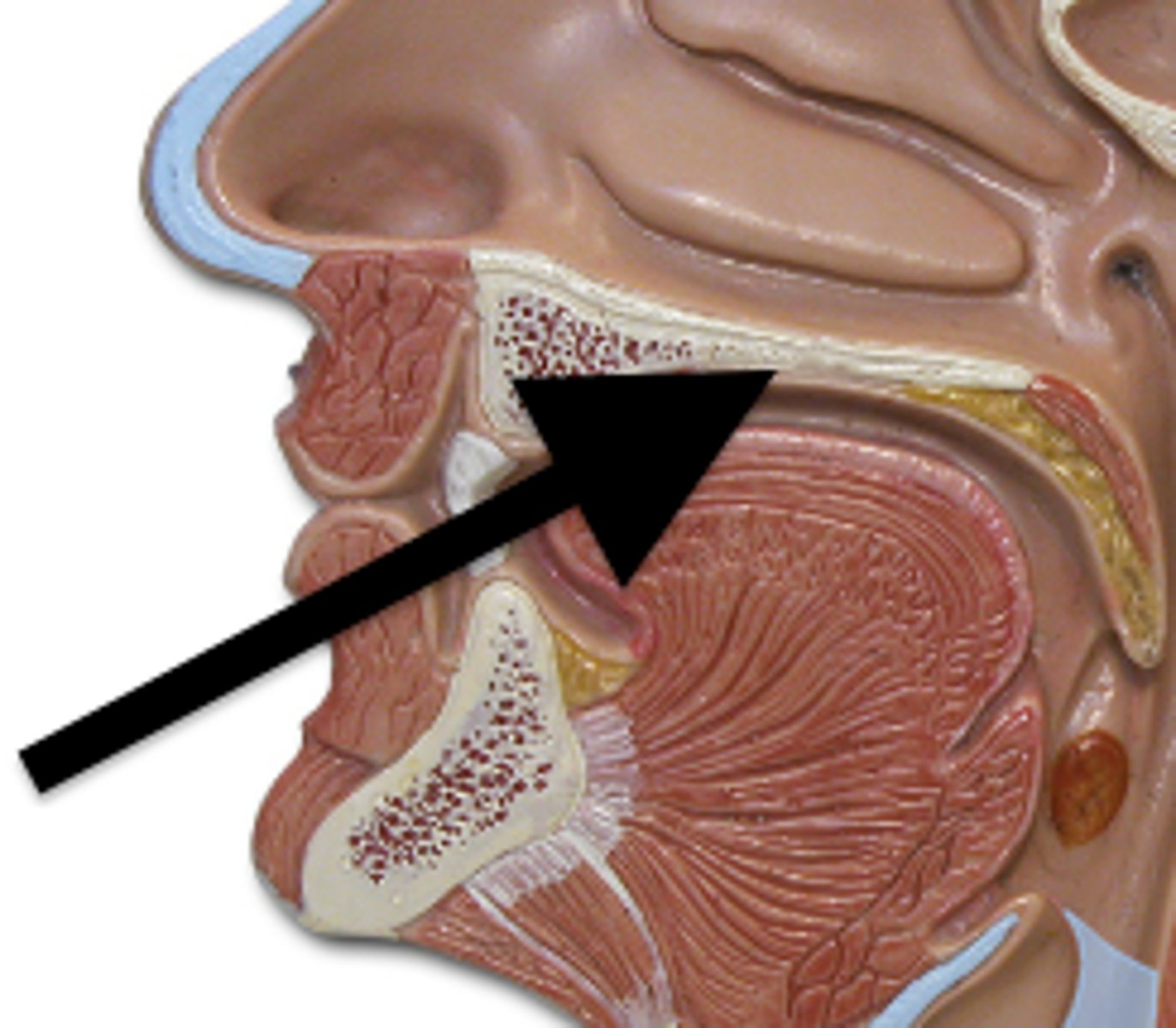
Soft palate
closes off nasopharynx during swallowing
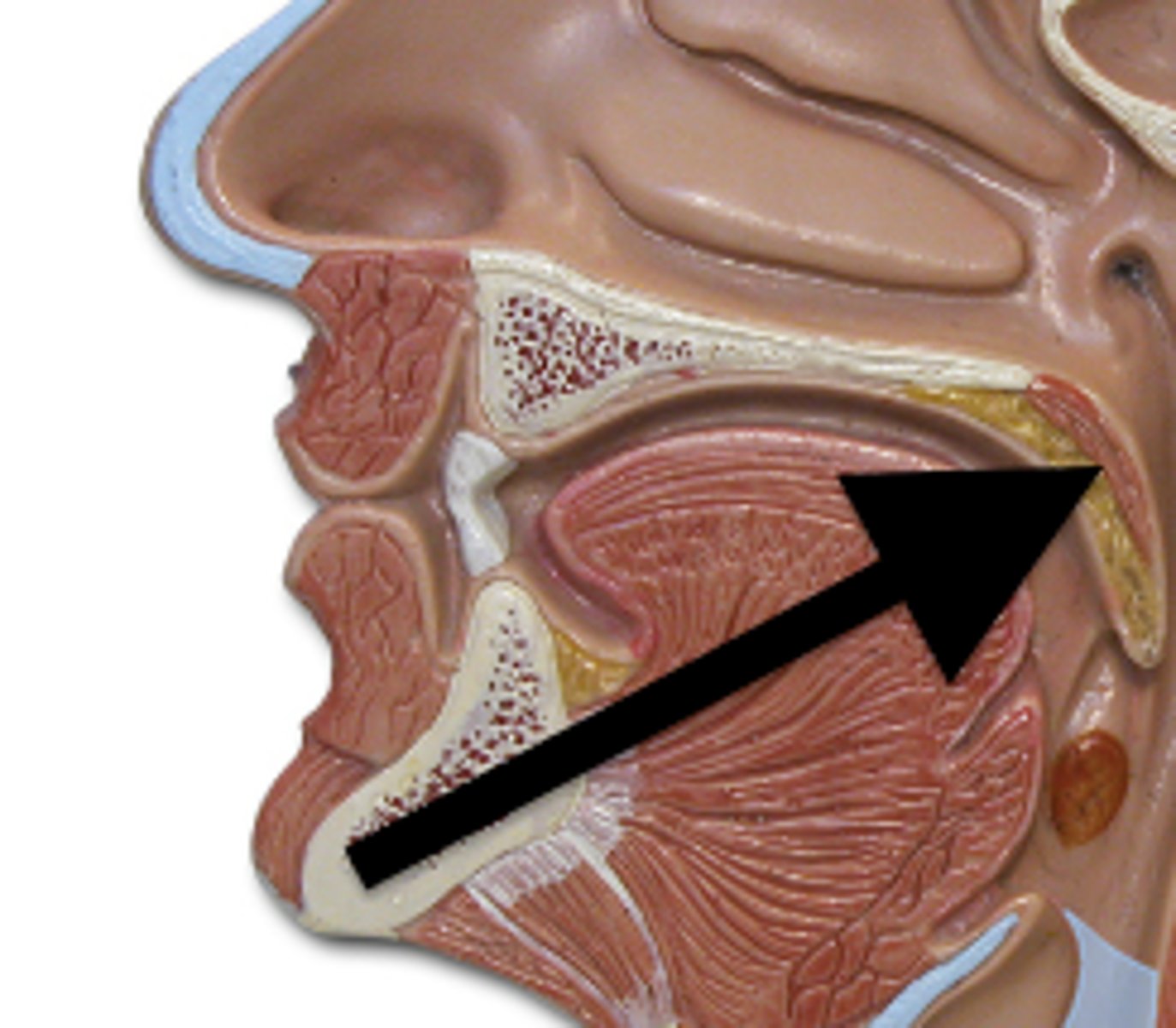
Inferior oral cavity
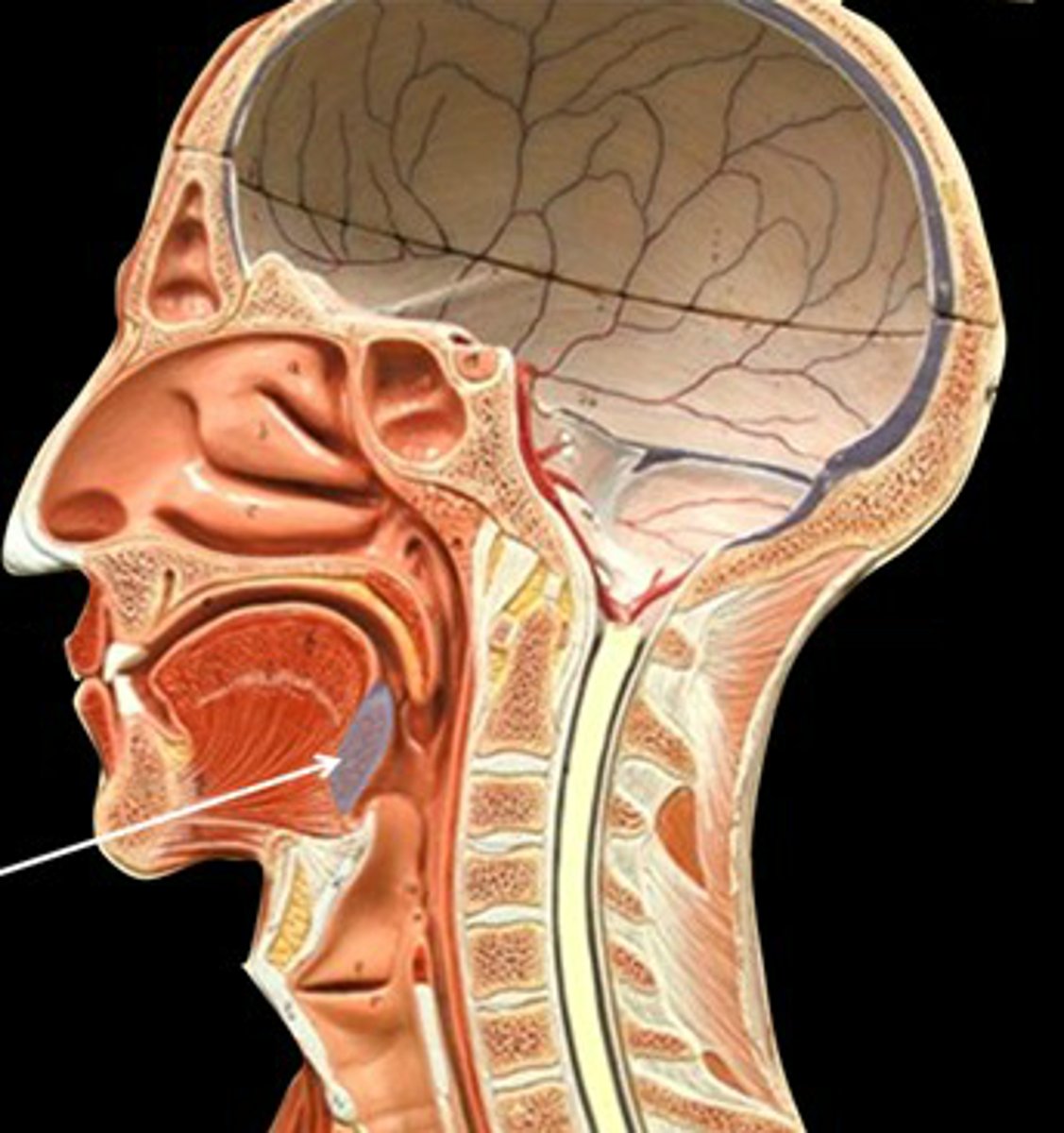
tongue
lingual frenulum
anchors tongue to floor of mouth
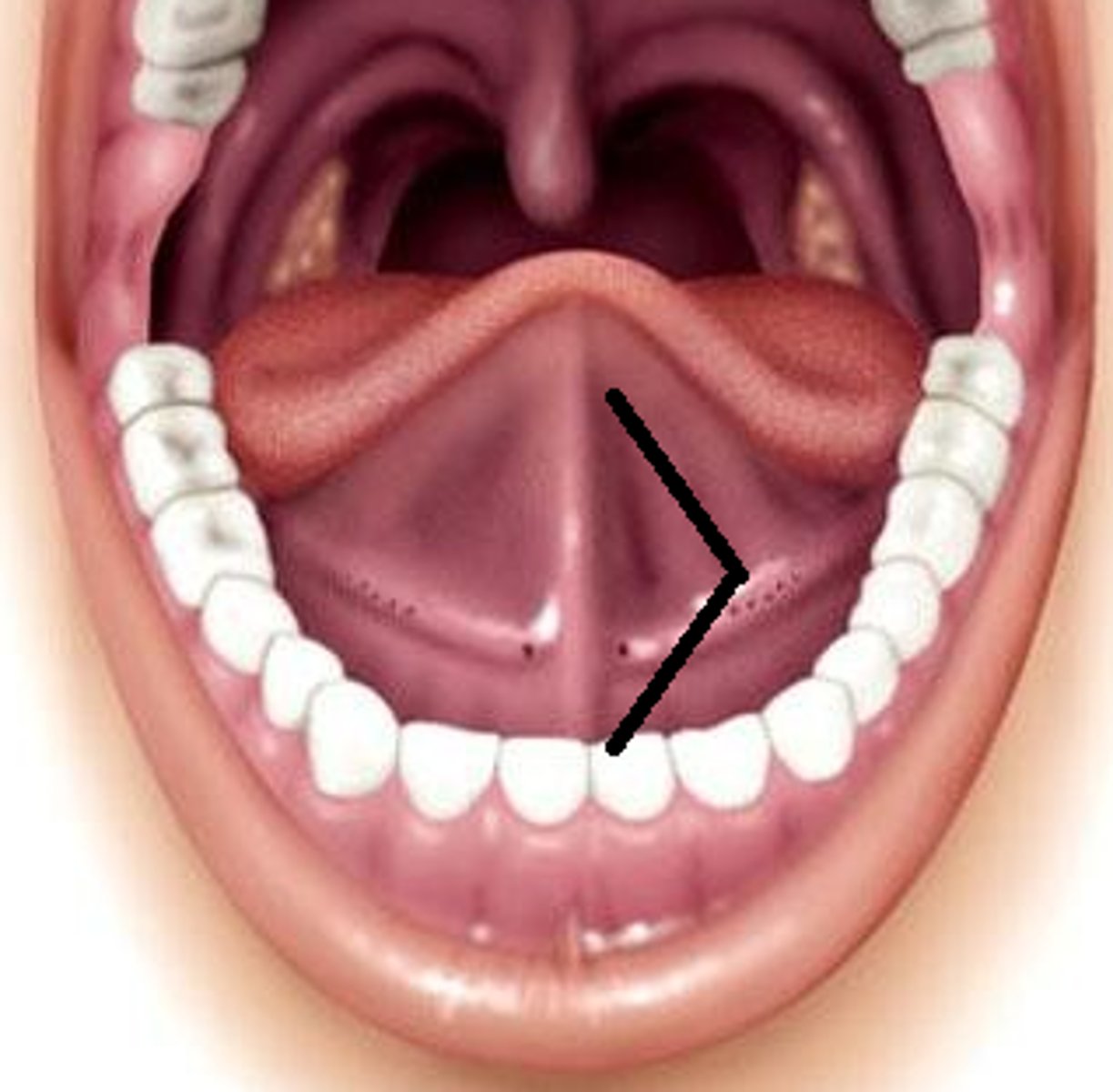
Uvula
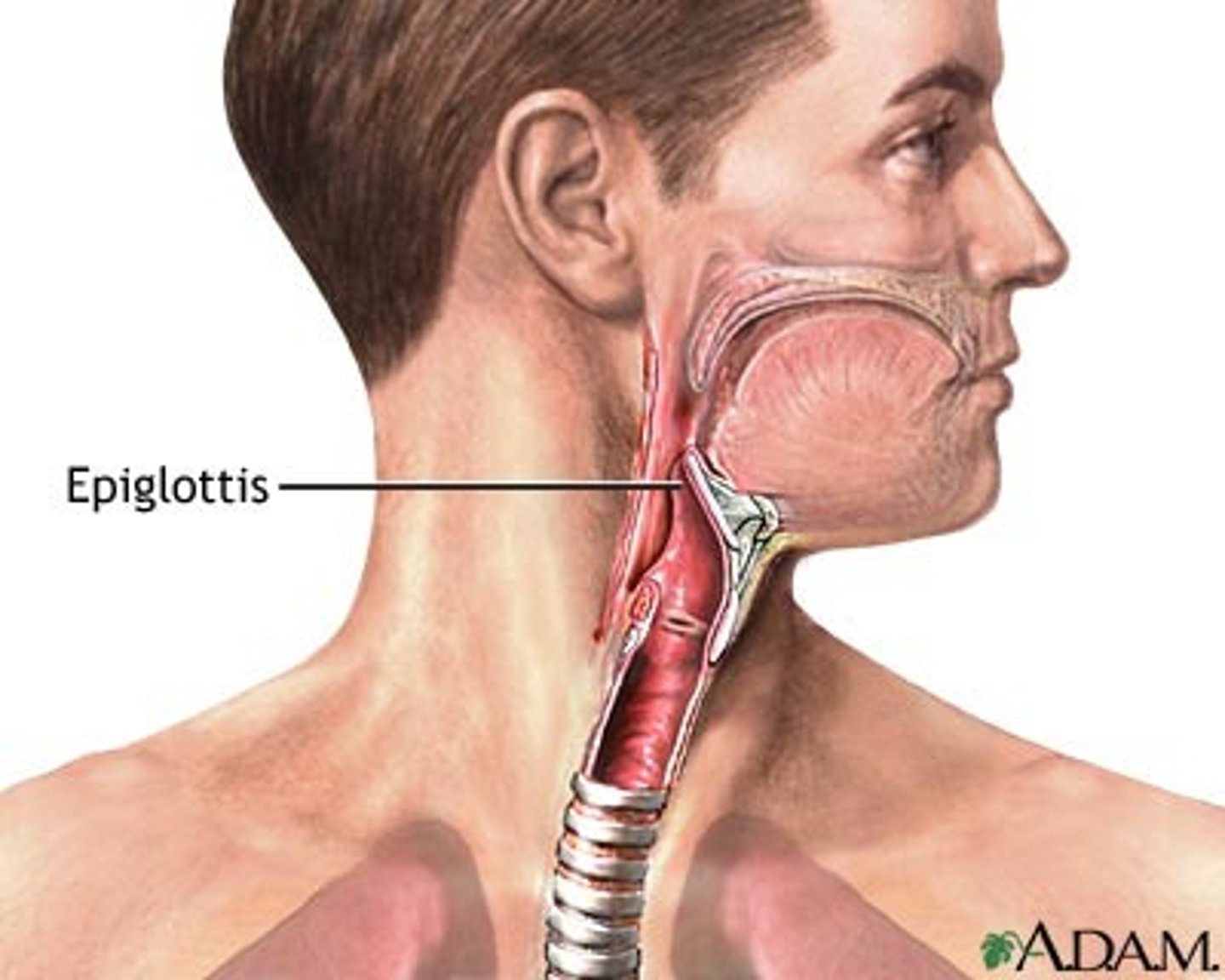
Epiglottis
covers larynx during swallowing
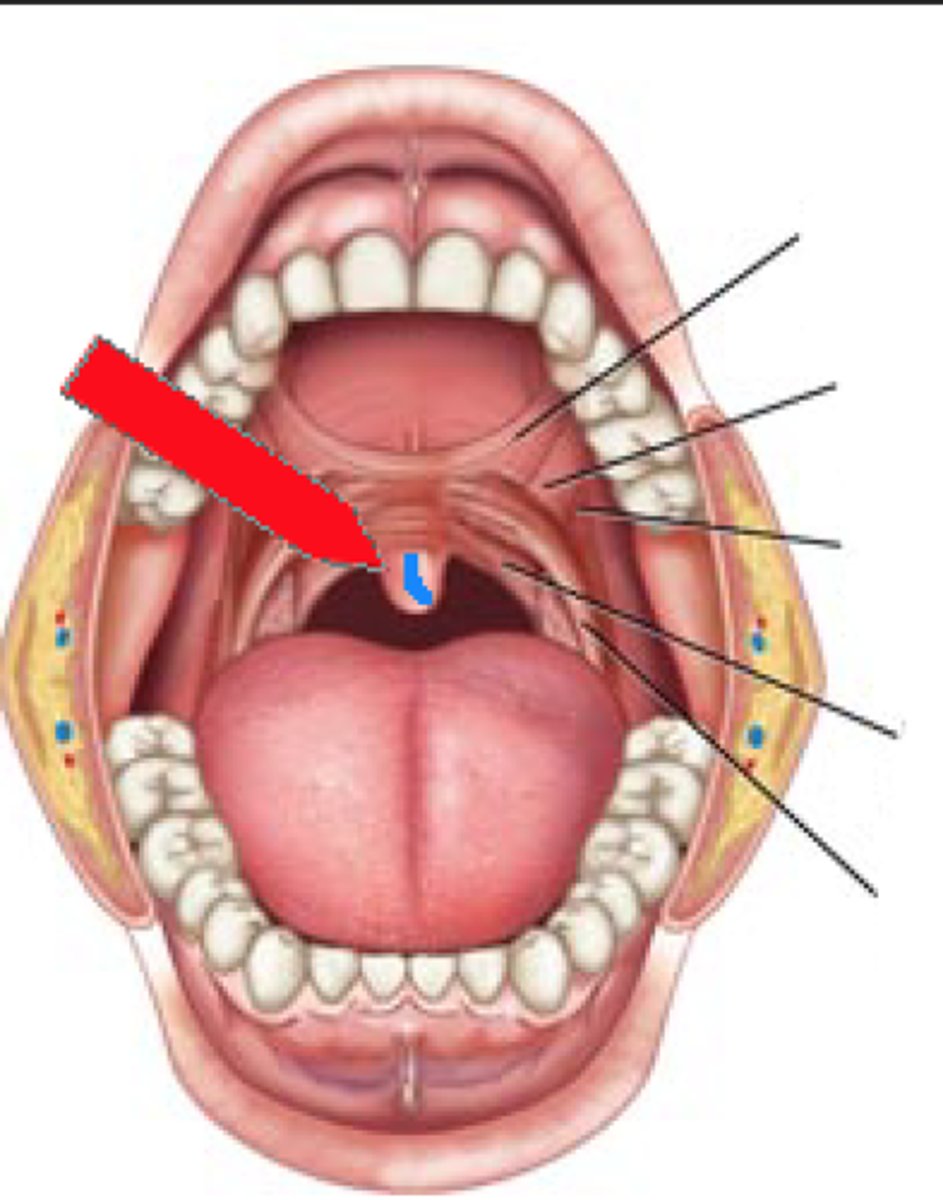
Lingual tonsil anatomy
(Circum)vallate papillae anatomy
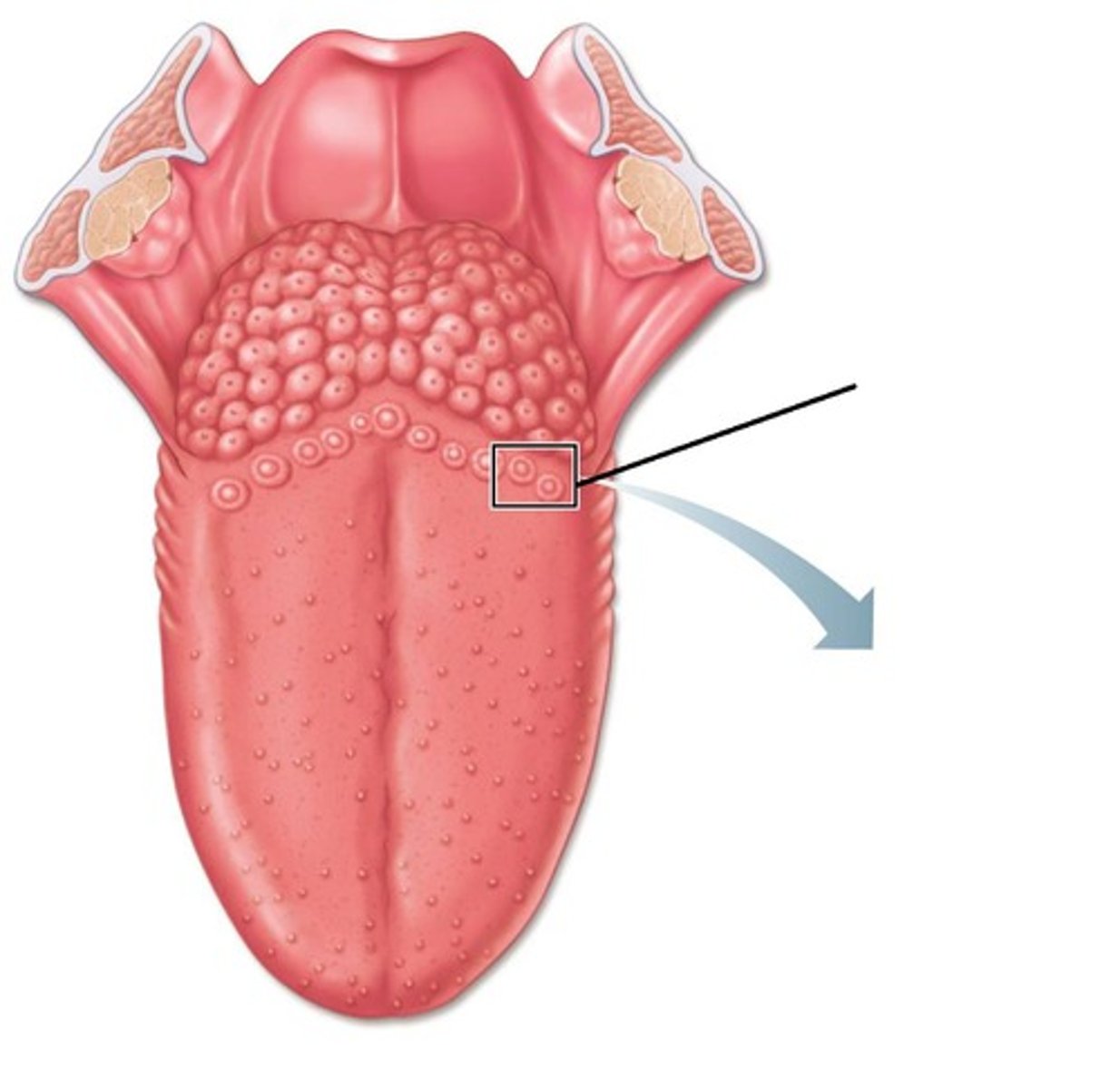
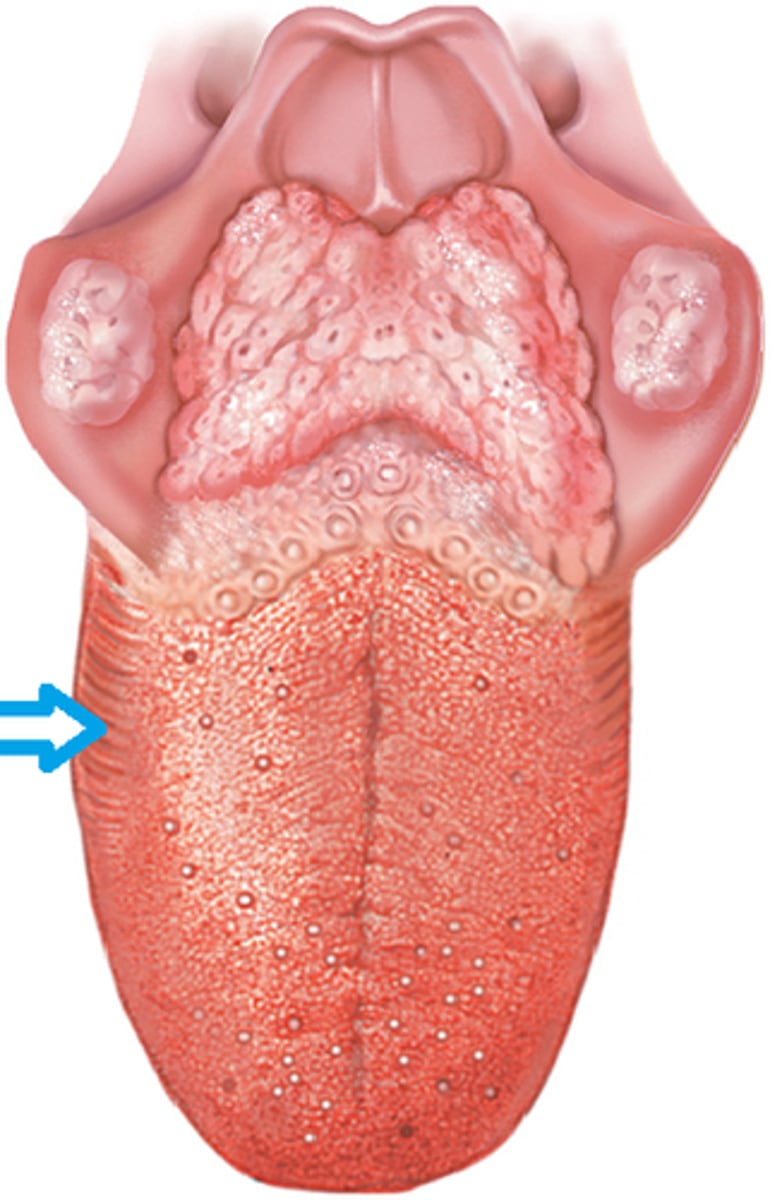
Filiform papillae anatomy
Foliate papillae anatomy
"leaf like"
fungiform papillae
"mushrooms"
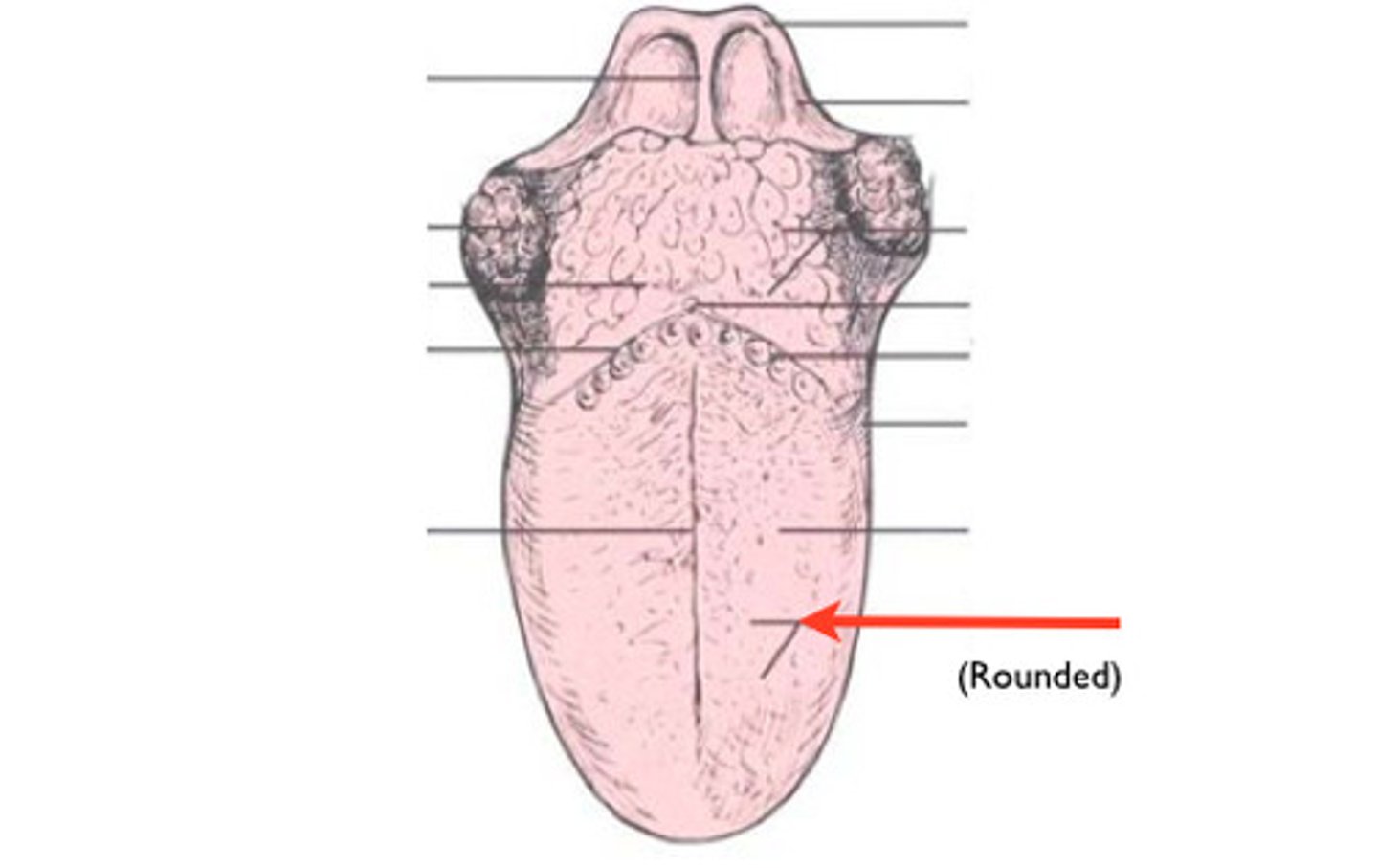
Traditional ideas of a taste map are _________
incorrect
What are the names of teeth?
incisors, canines, premolars, molars
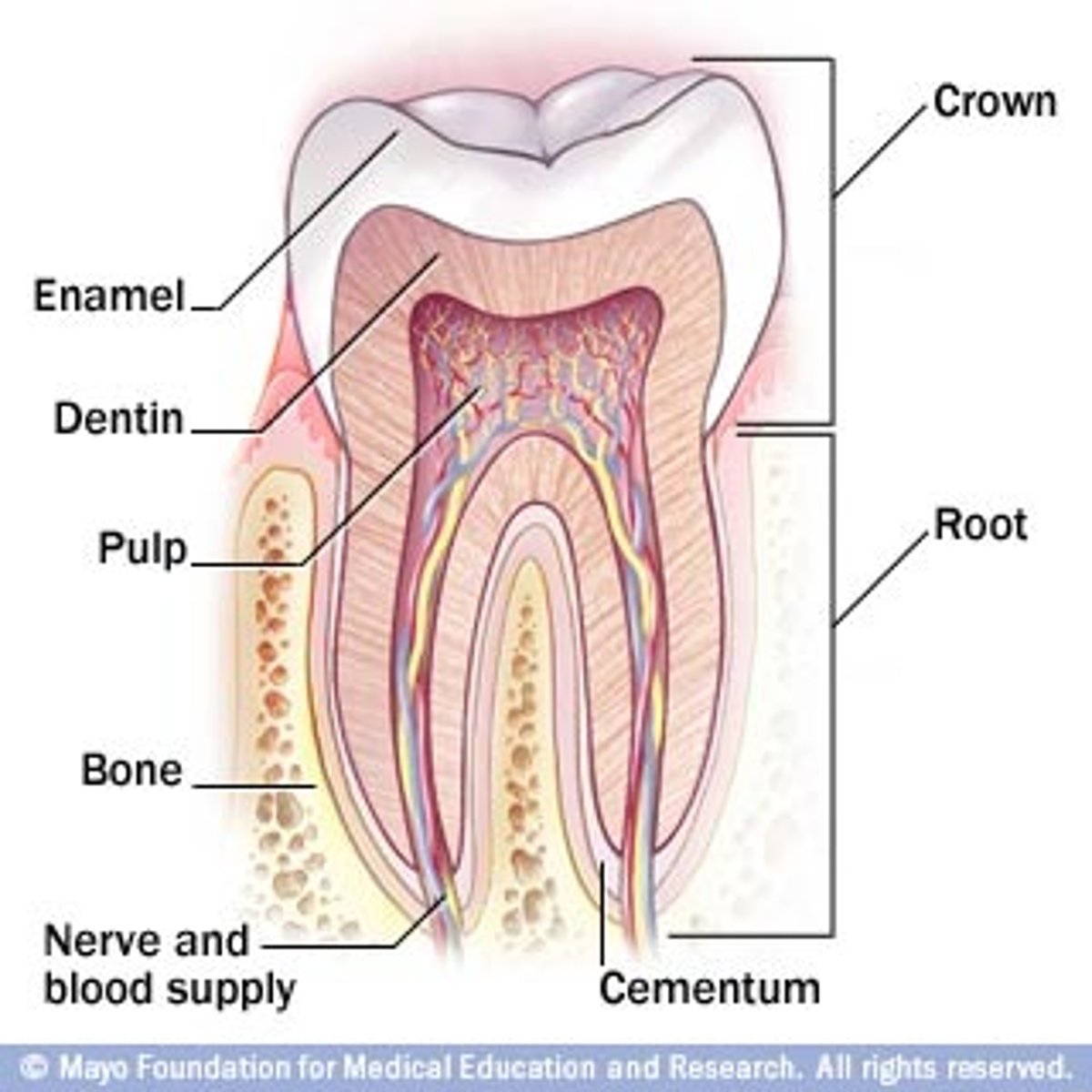
Tooth Anatomy
enamel, dentin, pulp, Root canal, and cementum
How many teeth do adults have?
- 32
- 2 incisors, 1 canine, 2 premolars, 3 molars
How many teeth do children have?
- 20
- 2 incisors, 1 canine, 0 premolars, 2 molars
Function of salivary glands
produce saliva through ducts (exocrine) autonomically
What are the salivary glands?
parotid, sublingual, submandibular
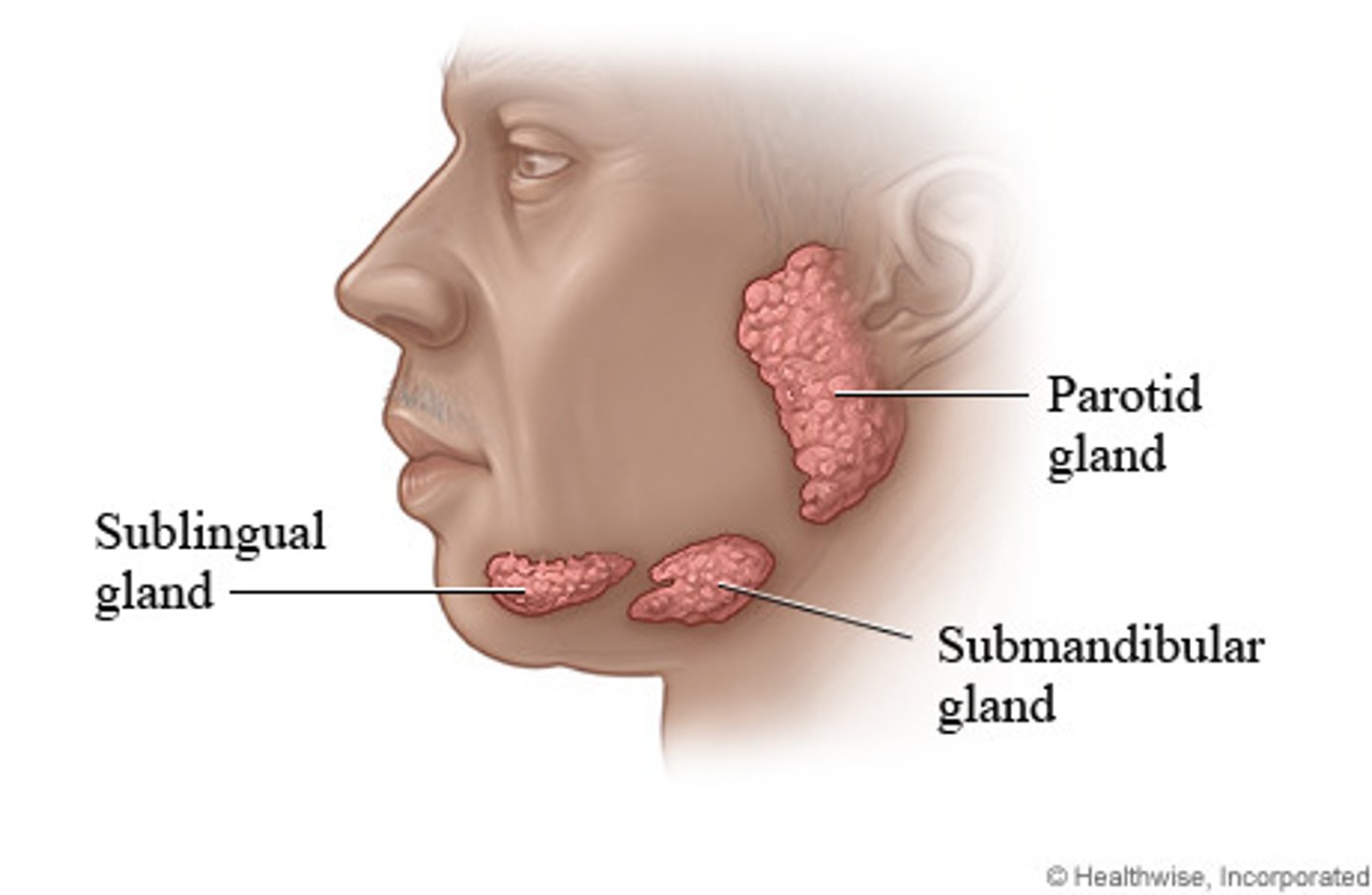
Functions of saliva
- moisten food
- dissolve food
- begin chemical digestion of carbohydrates with salivary amylase
- pH, antibodies, and lysozymes are also important
Salivary amylase
- critical for dissolving sugar
- digestion of starches to disaccharides
mechanical digestion
- mastication
- forming bolus, portions easy to follow
Chemical digestion
salivary amylase and lingual lipase
Lingual lipase
triglycerides into fatty acids and diglycerides once it reaches acidic environment of stomach
Does oropharynx have smooth muscle?
no, only skeletal muscle
Does laryngopharynx have smooth muscle?
inferior part is smooth
deglutition
swallowing
Skeletal muscle contractions in the oral cavity help do what?
help propel food to the esophagus
Peristalsis
contraction of smooth muscles
What is the esophagus?
smooth muscle tube that connects the pharynx to the stomach
upper esophageal sphincter
food movement from pharynx to esophagus
lower esophageal sphincter
- food movement from esophagus to stomach
- prevents regurgitation of acidic stomach contents
Esophageal hiatus
opening in the diaphragm
Why is mucus secreted in the esophagus?
lubrication
stages of deglutition
oral, pharyngeal, esophageal
oral stage of deglutition
movement of bolus by tongue, upward and backwards against palate
pharyngeal stage of deglutition
- uvula and soft palate move upward
- epiglottis covers larync
- upper esophageal sphincter relaxes
esophageal stage of deglutition
- peristalis contractions of smooth muscle
- lower esophageal sphincter relaxes
I 8
10 E
A 12
- I 8 10 Eggs At 12
- Inferior vena cana (T8)
- Esophagus (T10)
- Aorta (T12)
What is the junction between the esophagus and stomach?
- esophageal hiatus
- gastroesophageal junction
What does the gastroesophageal junction do?
keeps the esophagus closed until swallowing occurs
The _______ connects the esophagus to duodenum
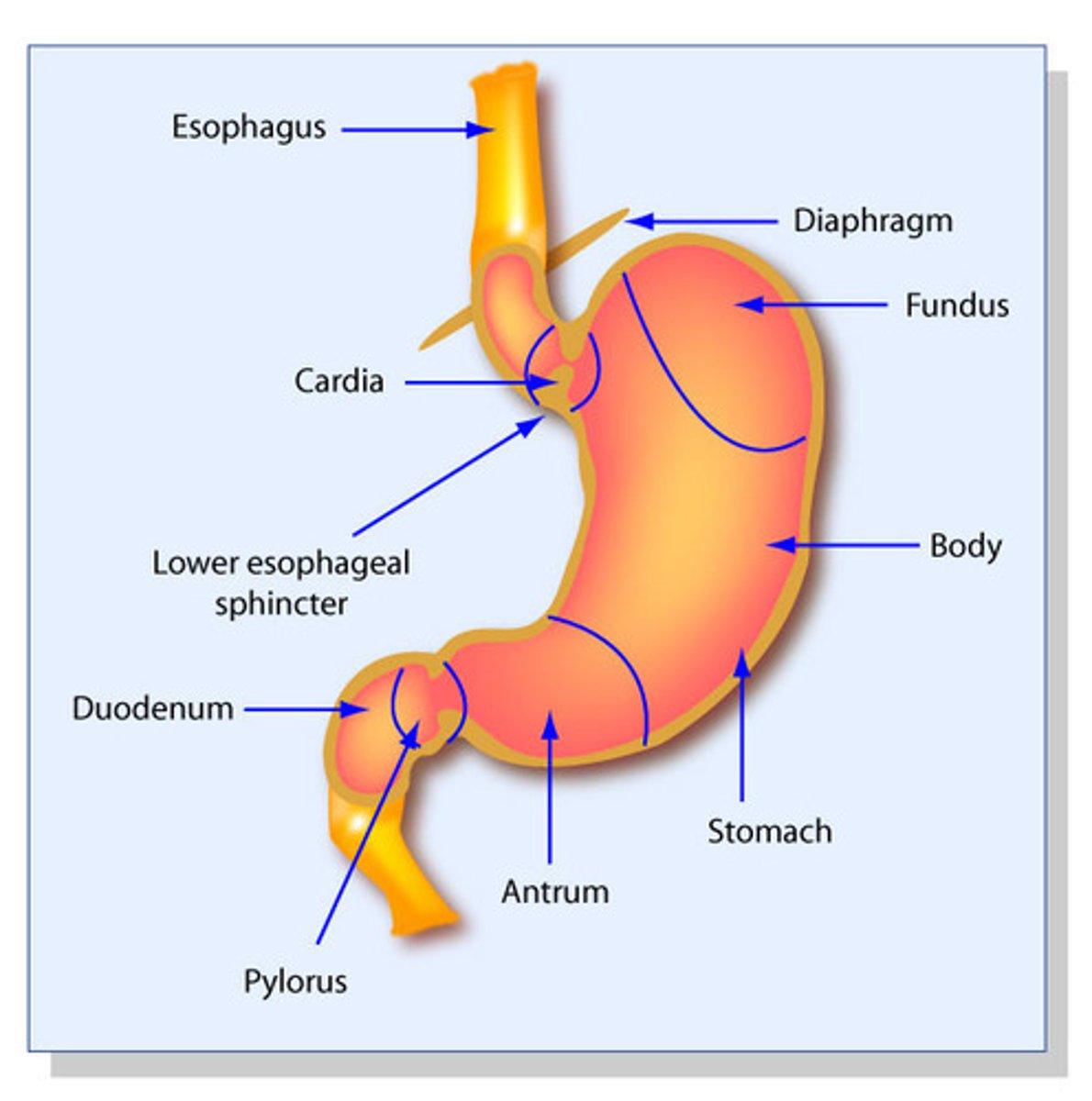
stomach
Duodenum
first part of the small intestine
fundus anatomy
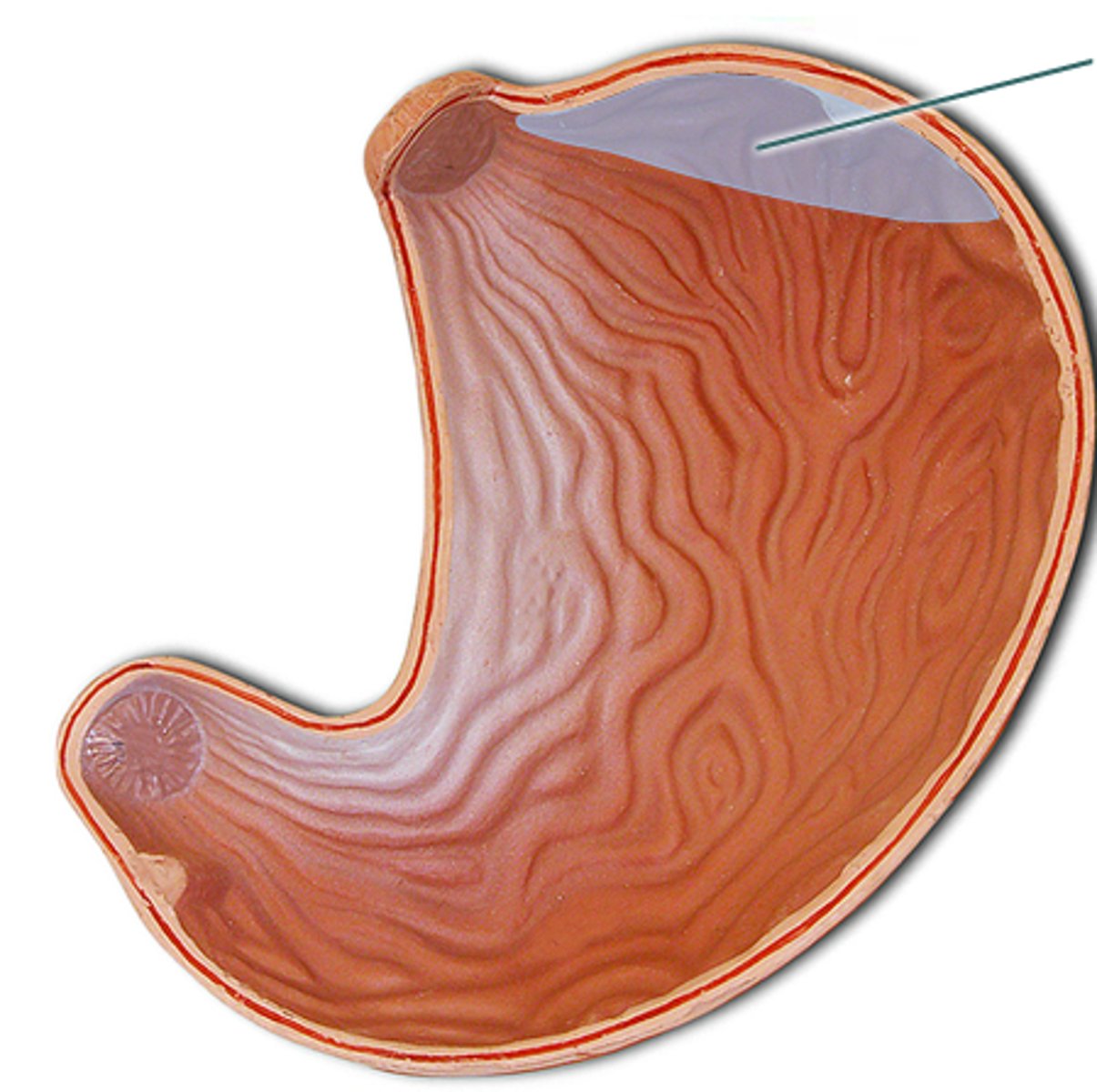
lesser curvature anatomy
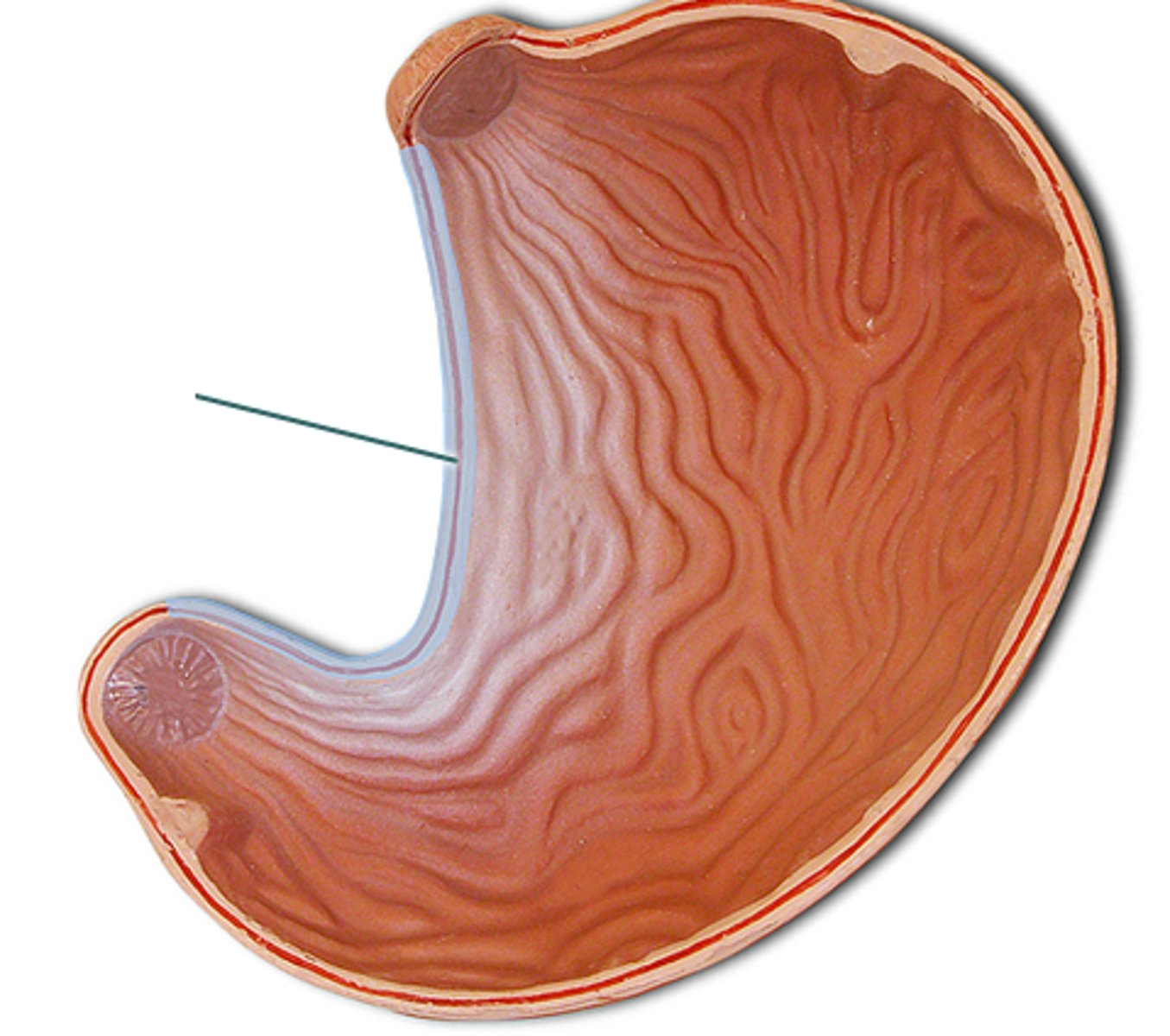
greater curvature anatomy
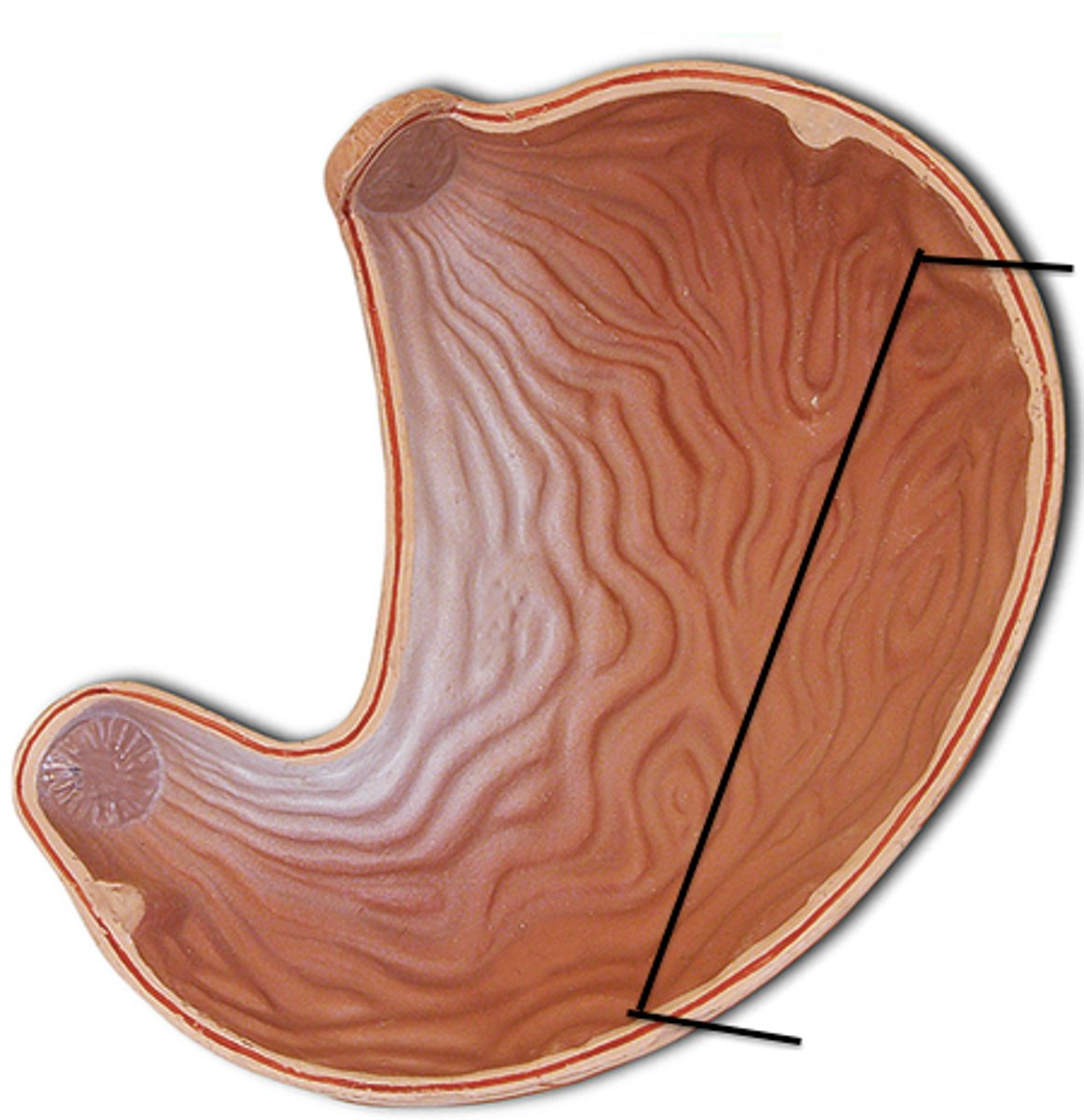
pylorus anatomy
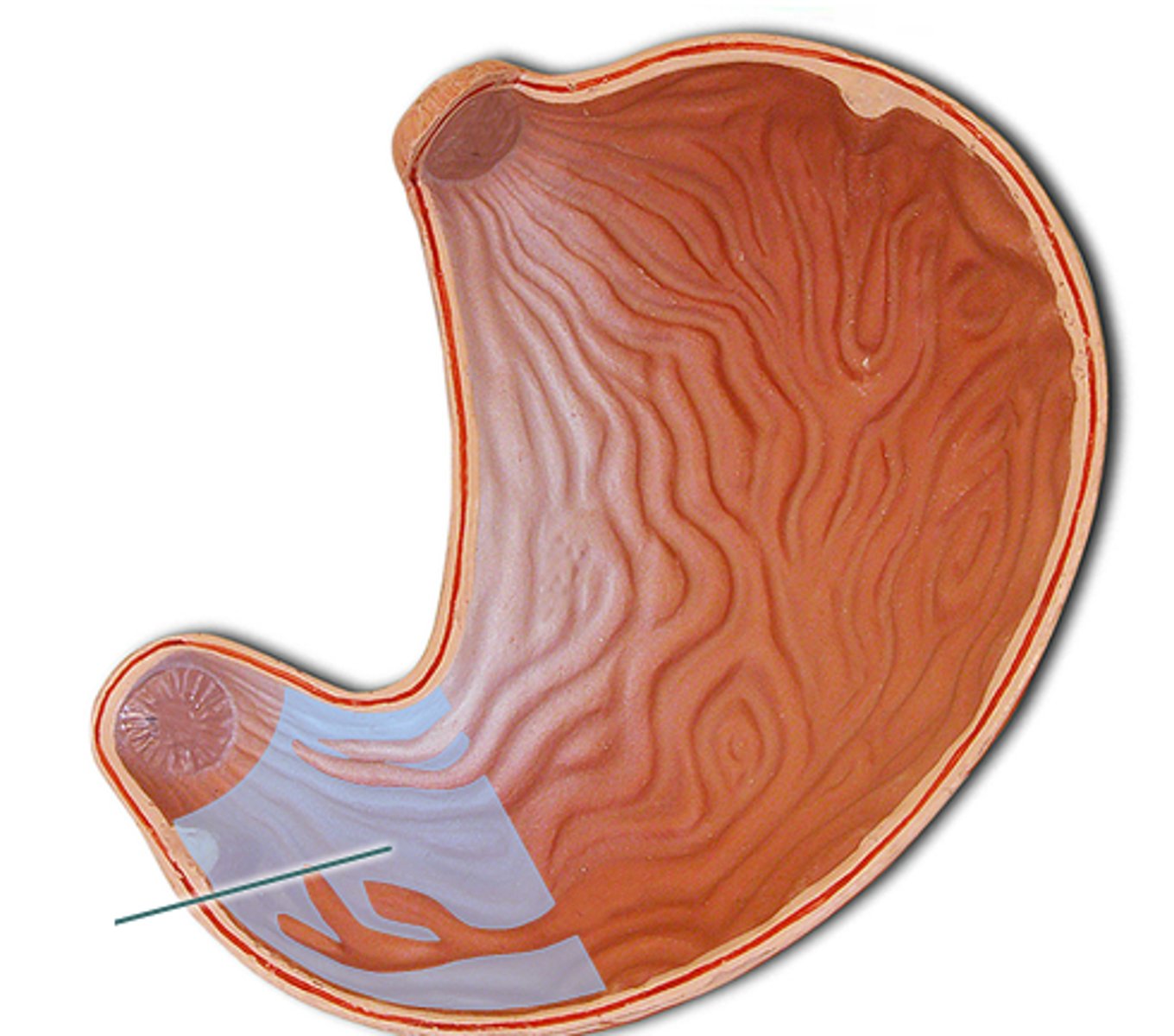
pyloric sphincter anatomy
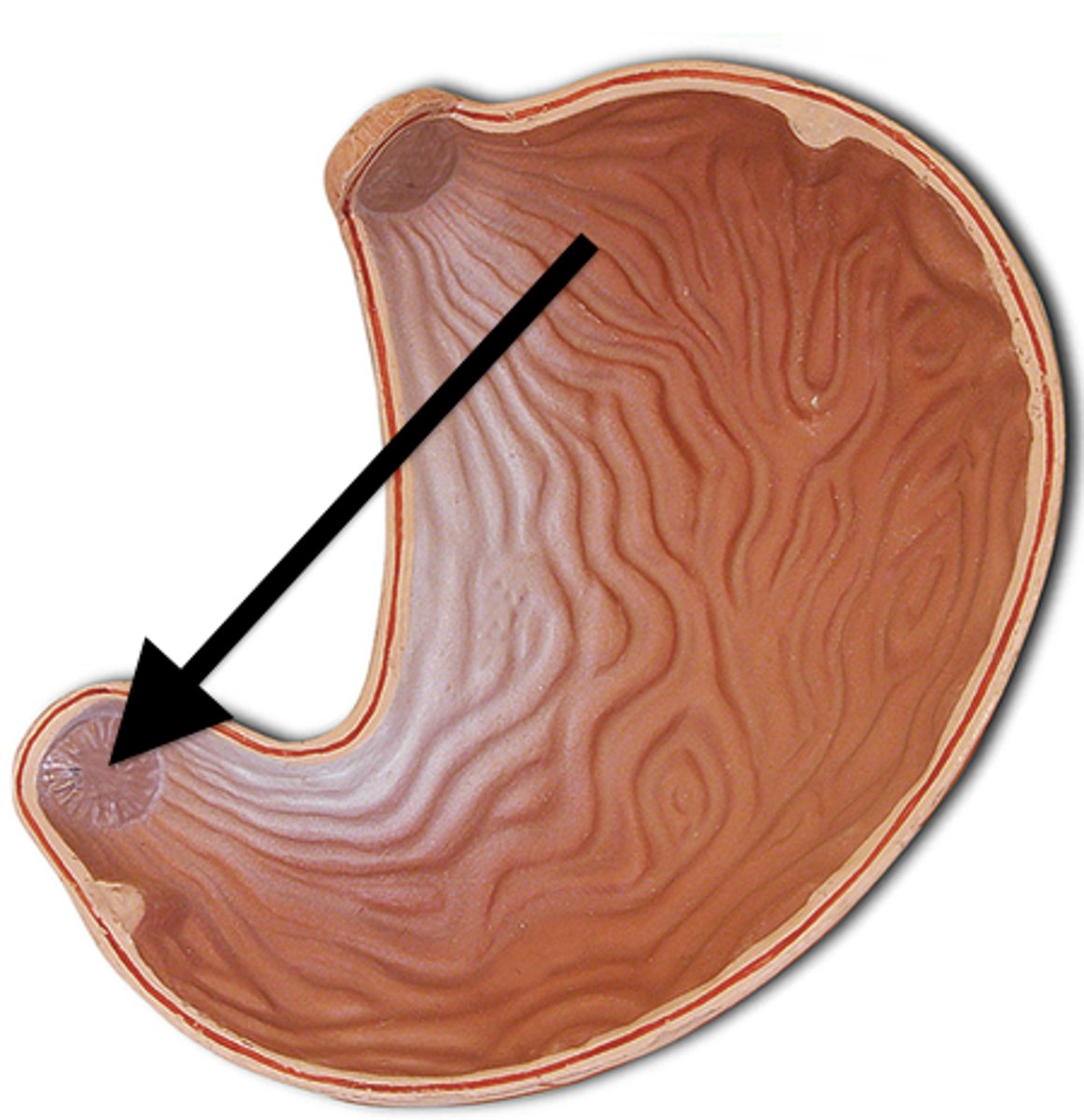
body of stomach anatomy
Longitudinal muscles of stomach
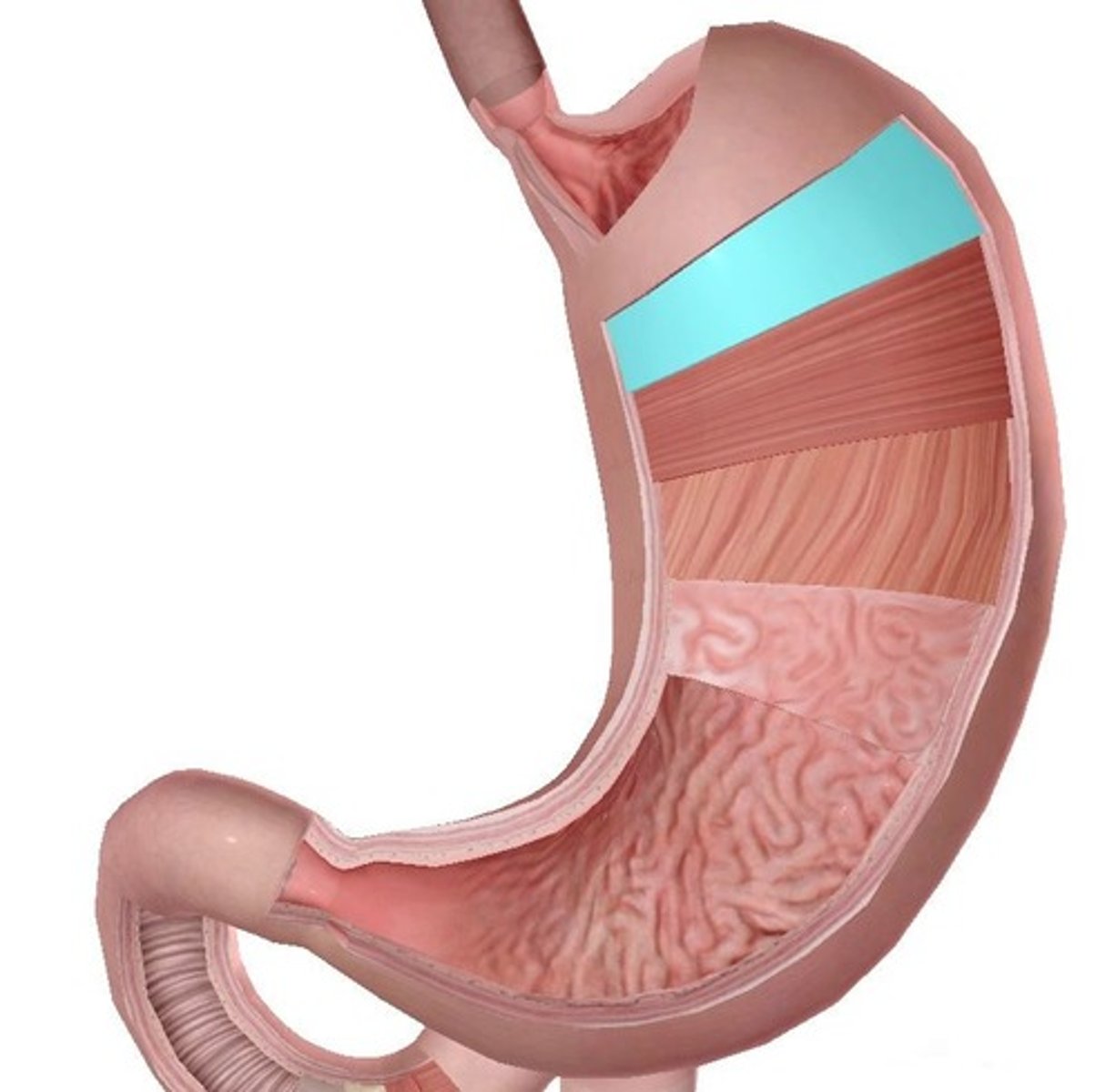
circular muscles of stomach
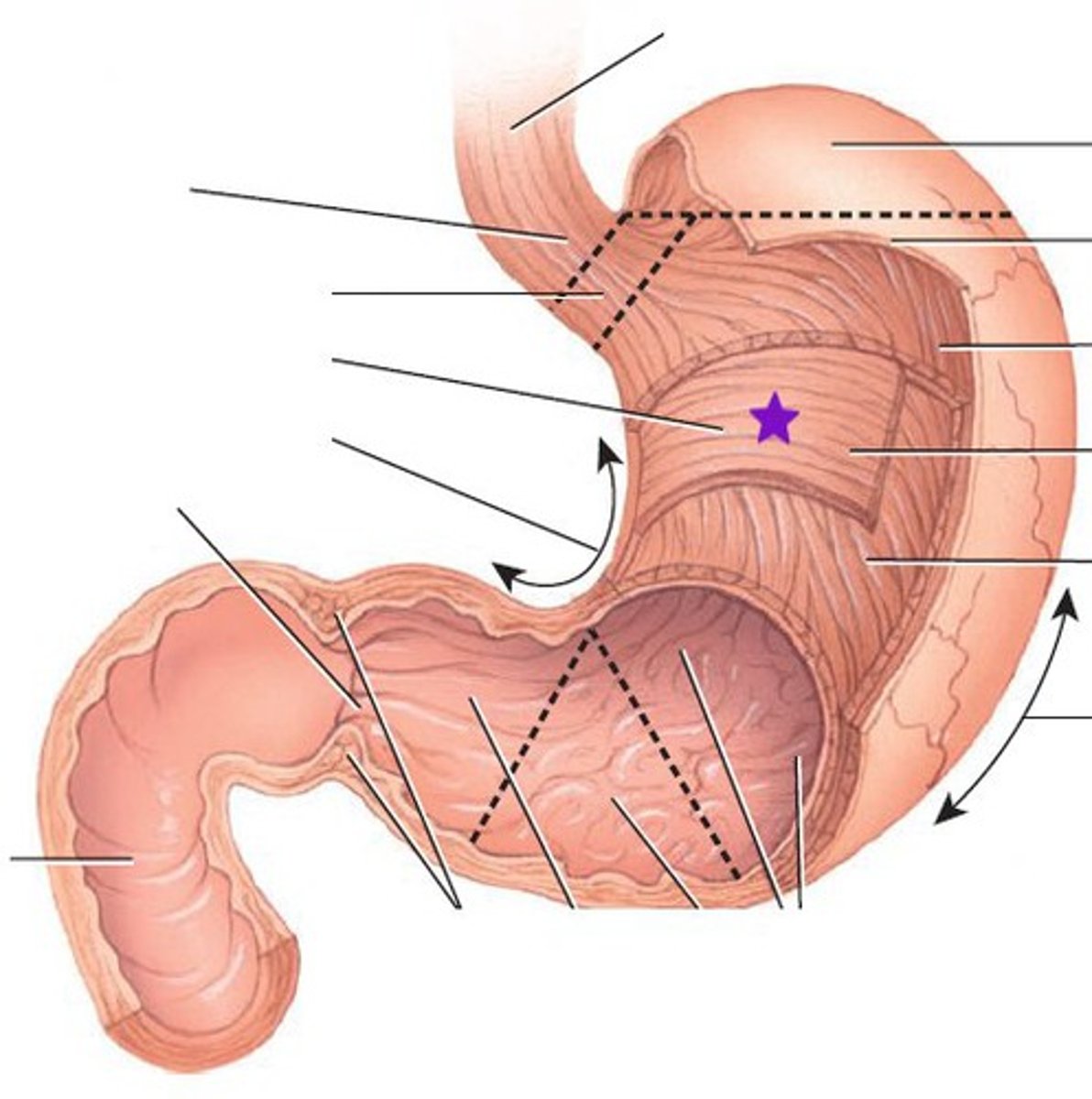
oblique muscles of stomach
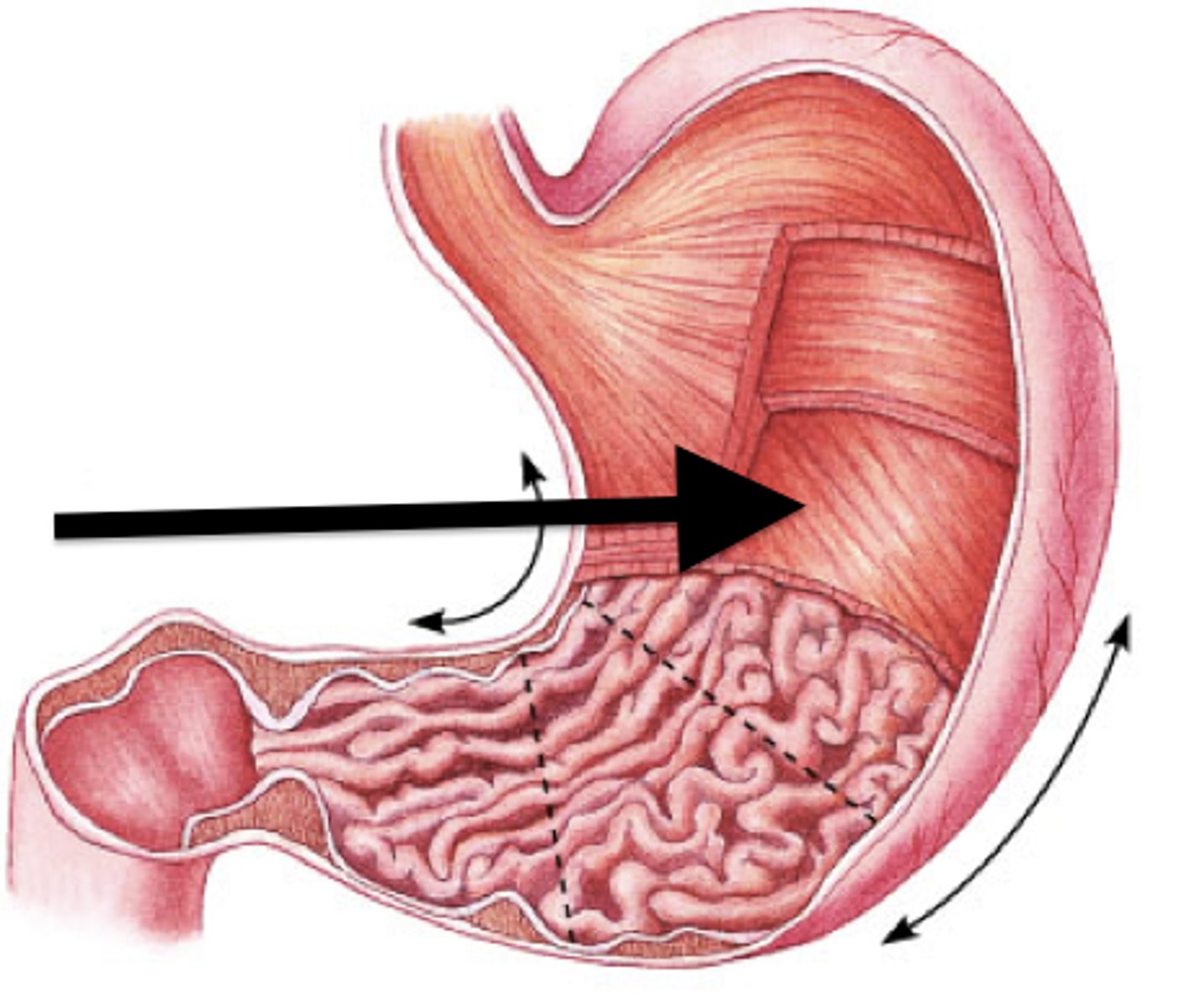
Main function of stomach
- enzymatic digestion of food
- mechanical digestion (rugae)
- immune defense (ph)
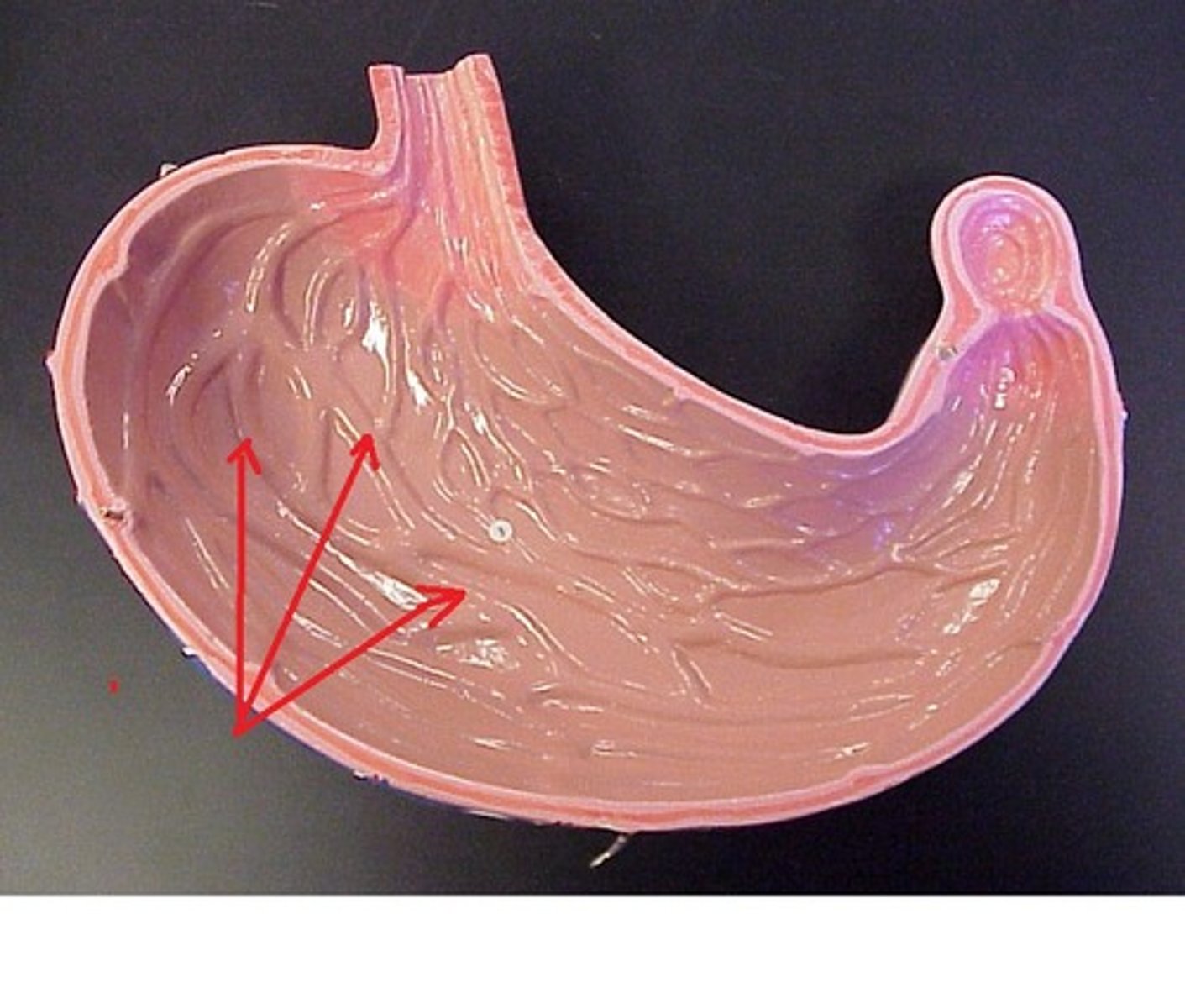
Rugae anatomy
waves of stomach
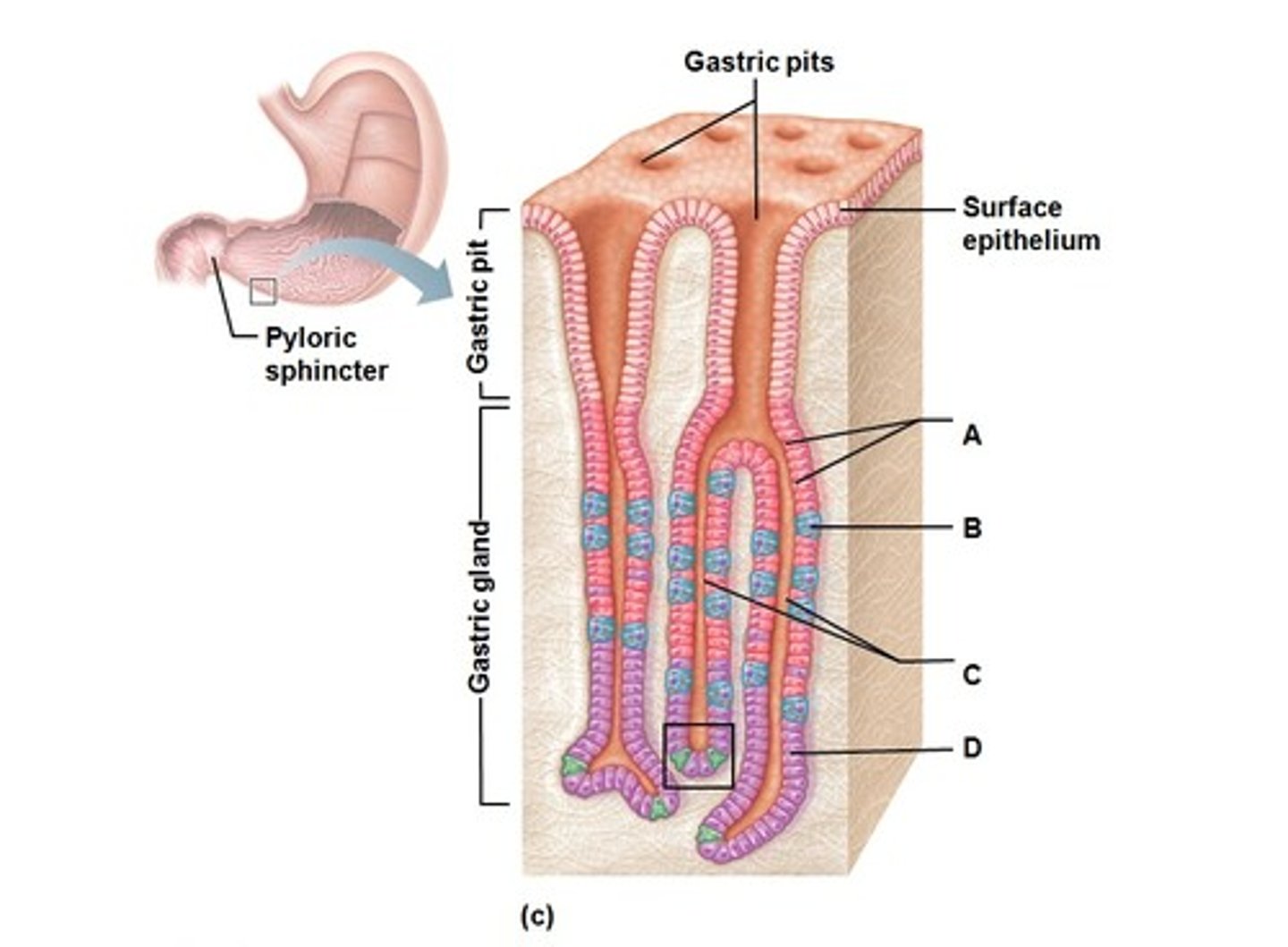
gastric pits of stomach
exocrine ducts from gastric glands that lead to the stomach lumen
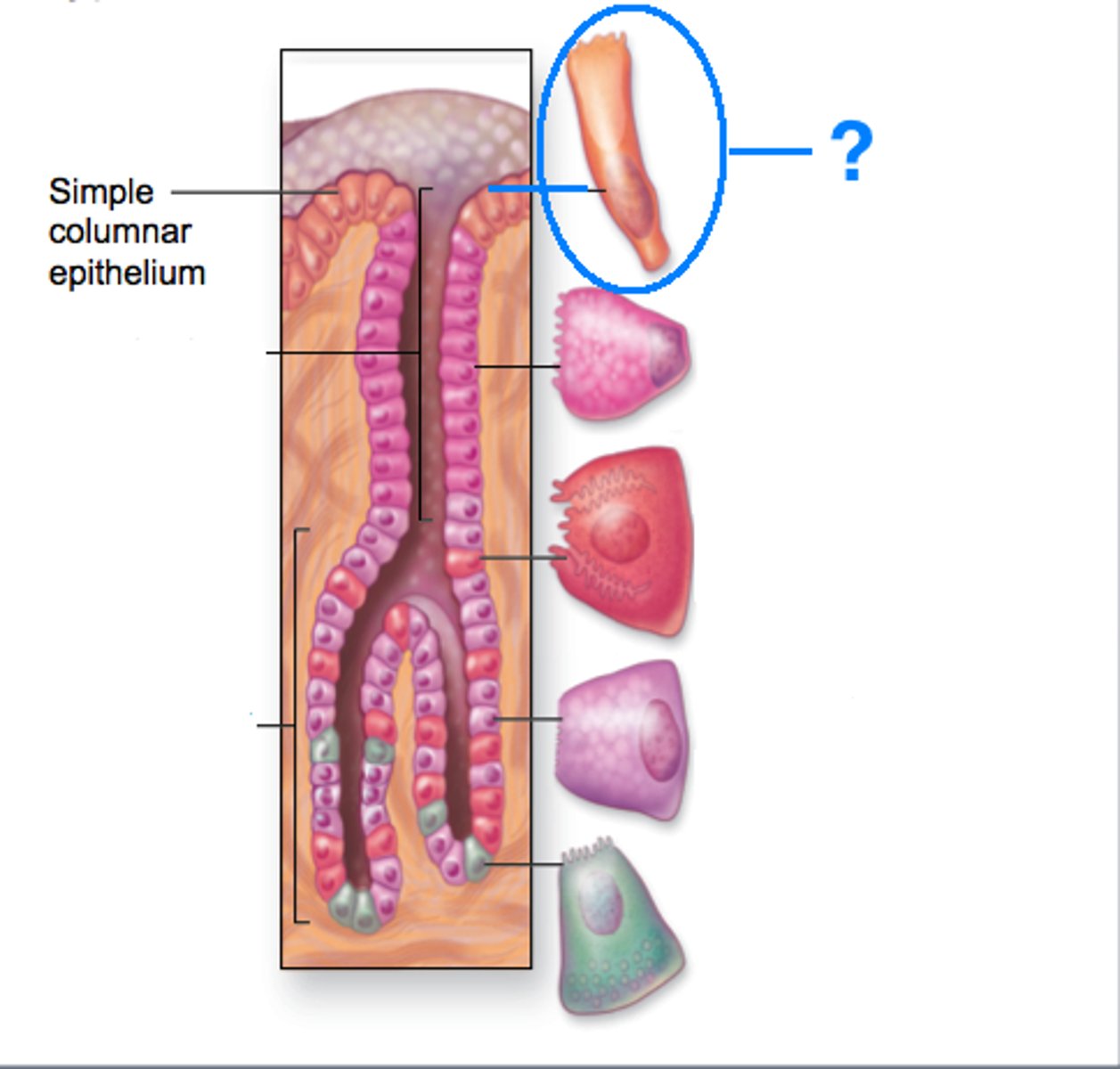
Surface mucous cell
secrete bicarbonate rich mucus
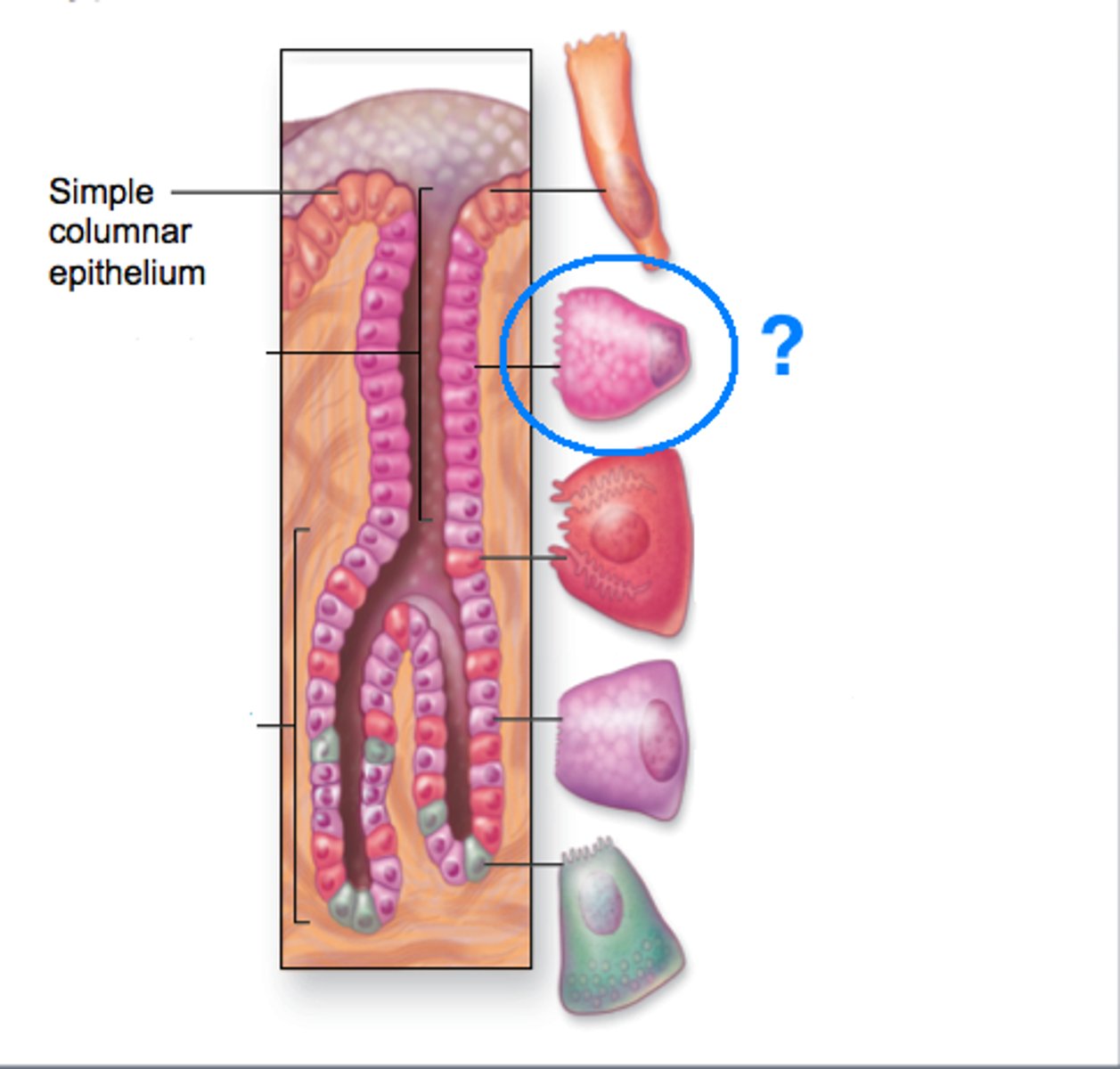
Mucous neck cell
secretes mucus
Parietal cells of stomach
- secretes hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor
- absorbs B12
- "peach like cells"
Chief cells of stomach
secrete pepsinogen and gastric lipase
- pink with dots towards inner stomach
Pepsinogen
protein digestion