Week 1 - Osteology & Arthrology
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
What is Physiology?
A broad area of scientific inquiry that focuses on the biological function of living organisms.
What is Kinesiology?
Scientific study of human movement, performance and function
What is Osteology?
Is the scientific study of bones
What is Arthrology
is the science concerned with the anatomy, function, dysfunction and treatment of joints.
Functions of Skeleton
Supporting framework for the body
Attachment points for muscles
Provides protection of vital organs
Blood cell formation - red bone marrow produces red and white blood cells and platelets
Mineral storage - calcium and phosphorus
Bone is plastic
Relationship of Skeletal Muscle to Bones
Skeletal muscles create movements by pulling on bones
Bone serve as levers, and joints as fulcrums
Origins
The anchor
Belly
The meat
Insertion point
The end point of the muscle to bone
Fulcrum (F)
Elbow joint
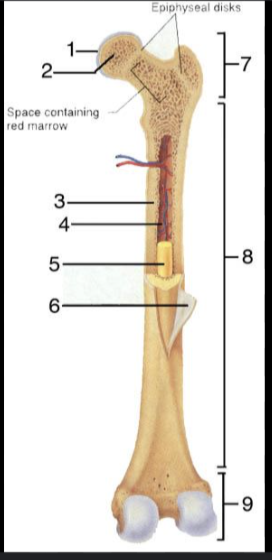
What is #1?
Articular Cartilage
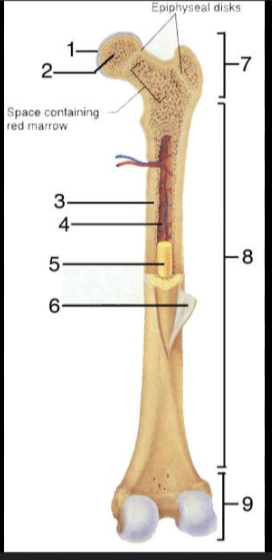
What is #2?
Spongy bone
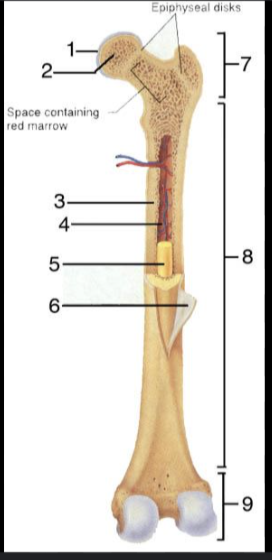
What is #3?
Medullary Cavity
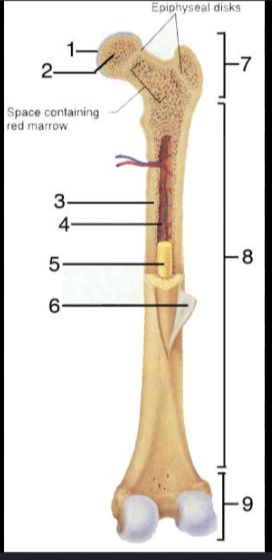
What is #4?
Nutrient Artery
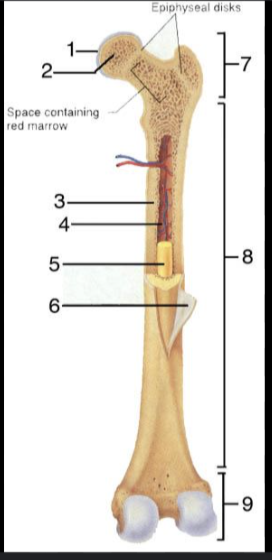
What is #5?
Yellow Bone Marrow
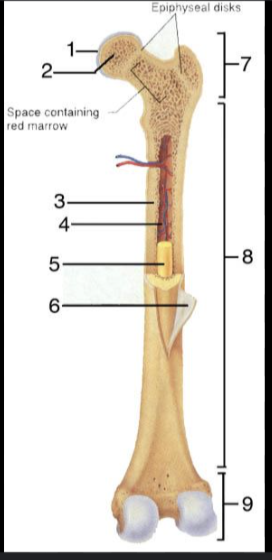
What is #6?
Periosteum
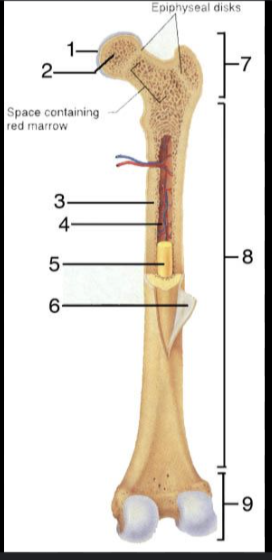
What is #7?
Proximal epiphysis
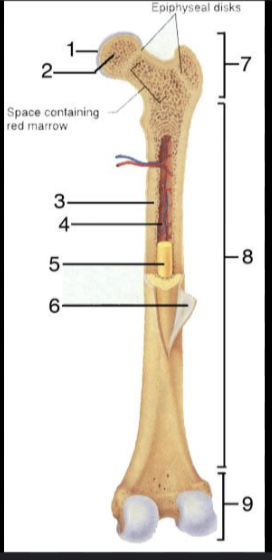
What is #8?
Diaphysis
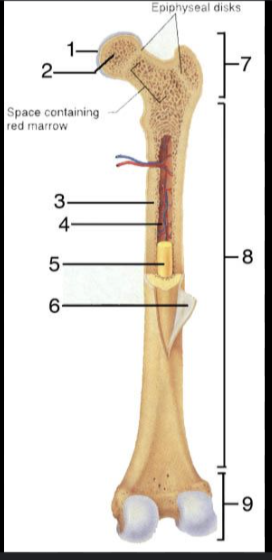
What is #9?
Distal epiphysis
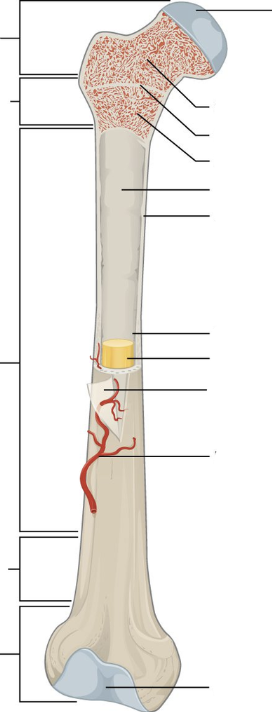
What is the outer layer of bone called?
Compact bone
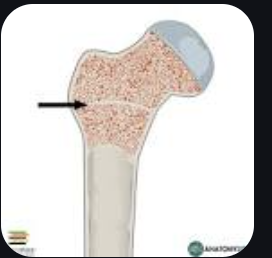
Epiphyseal Plate
A layer of cartilage where proliferating cells are gradually replaced by bone
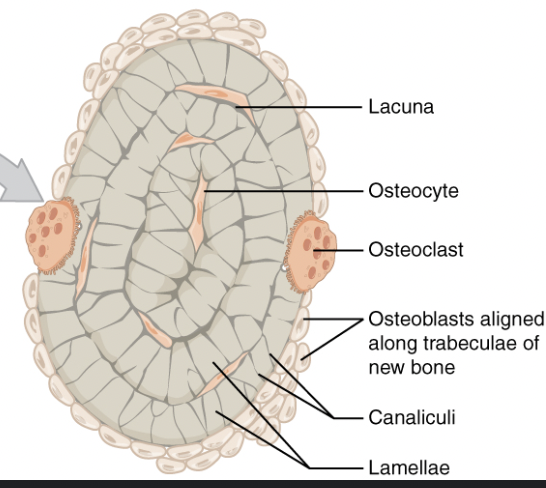
Osteocytes
Widely separated cells & maintains bone tissue, surrounded by matrix
Matrix is about:
25% water
25% protein
mainly Collagen
50% minerals salts
Calcium carbonate
Calcium phosphate
How do bone remodel itself?
It changes due to response to mechanical stress or the absence of stress. i.e. bone is plastic
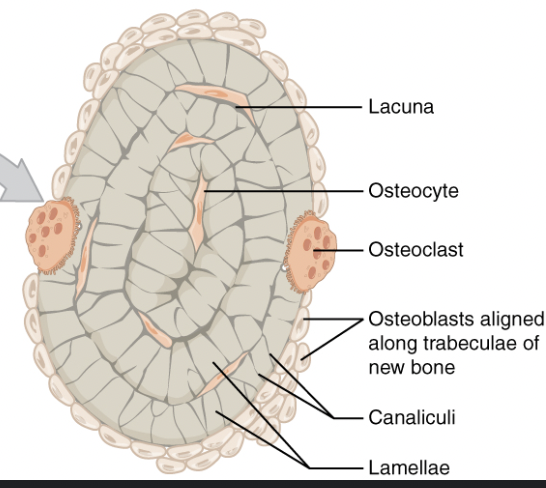
Osteoblasts
Forms bone matrix
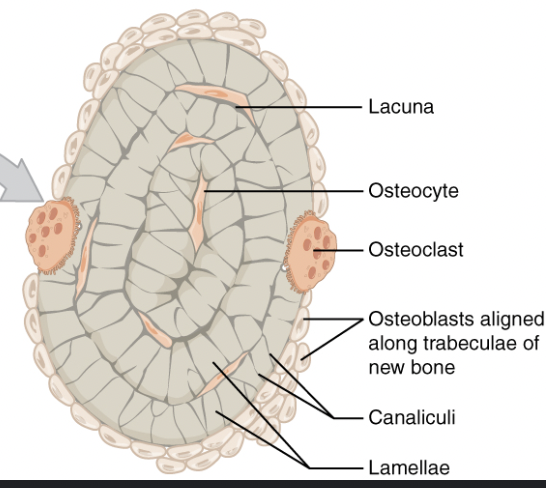
Osteoclasts
Reabsorbs bone
Response to Activity
Bones of physically active individuals tend to be denser and therefore more mineralized than those of sedentary individuals of the same age and gender
How many bones in the body
206 bones
Long bones
Longer than they are wide. Ex: Femur, Humerus
Short bones
Wider than they are long. Ex: Carpals, Tarsals
Flat bones
Flat and broad surface. Ex: Sternum
Irregular bones
Bones that do not fit into any of the categories. More complex shapes. Ex: Vertebrae
Sesamoid bones
Small bone that forms in tendon. Ex: Patella
Adult Skull vs Baby Skull
Adult Skulls are more developed and has less cartilage in the skull.
More prominent than baby as well as longer chin and head
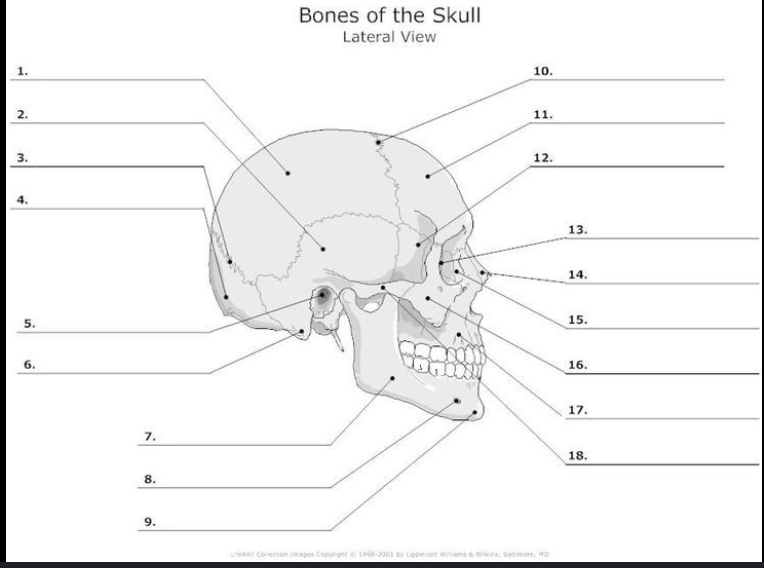
What is #1?
Parietal bone
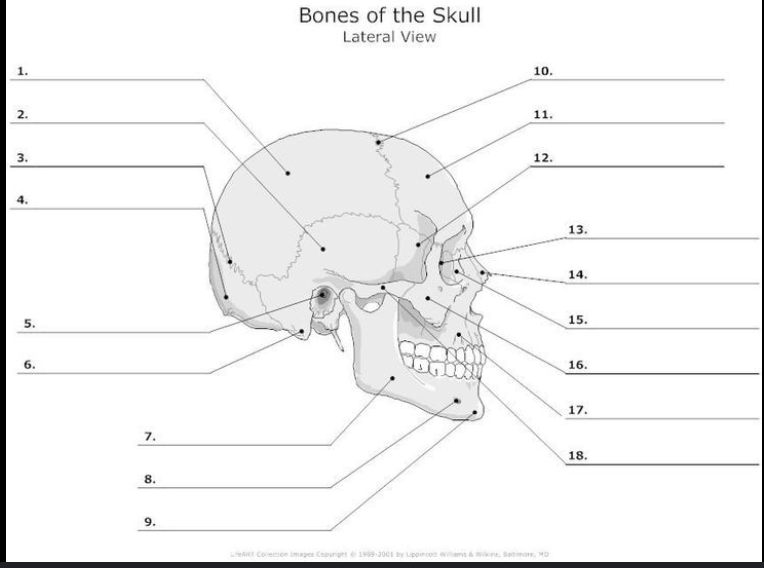
What is #2?
Temporal Bone
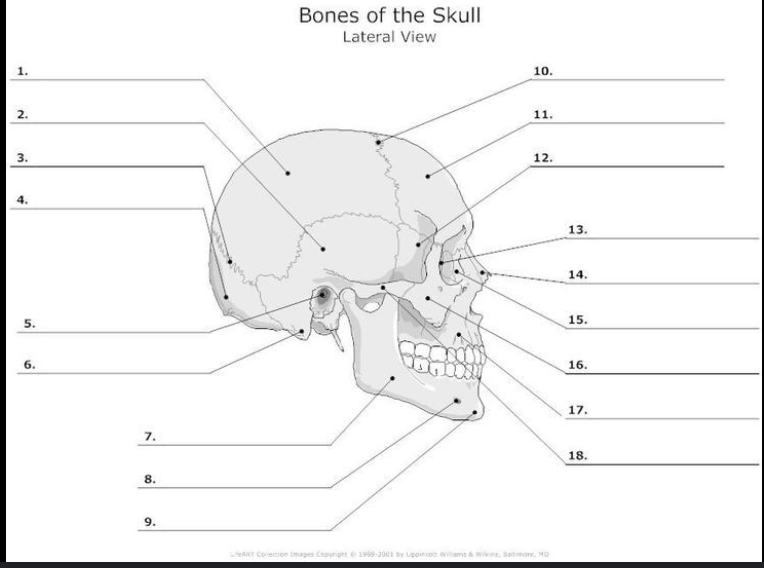
What is #4?
Occipital Bone
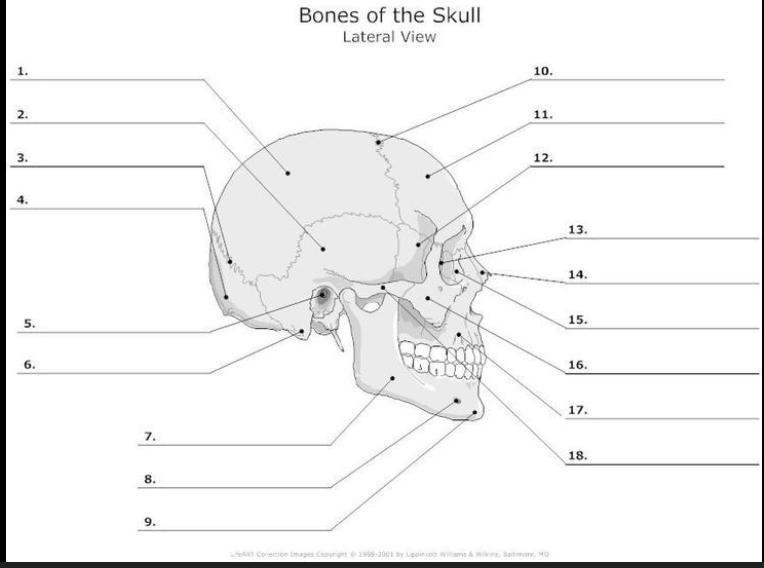
What is #11?
Frontal bone
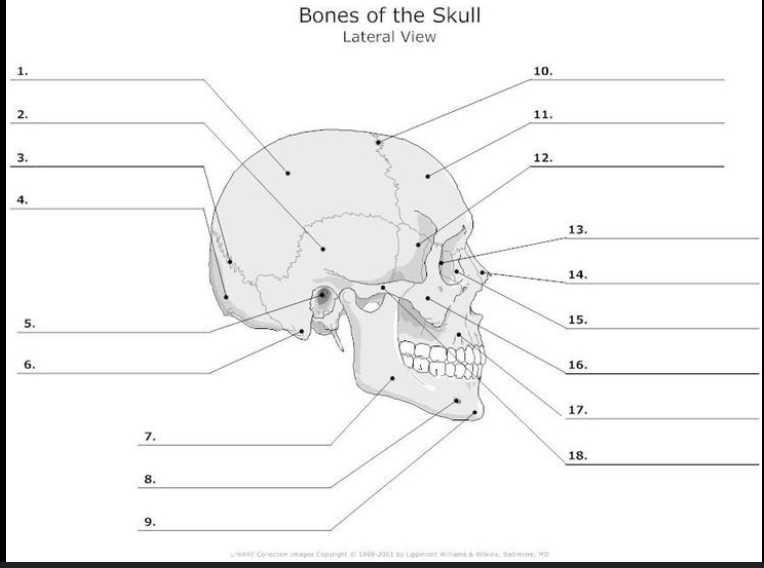
What is #16?
Zygomatic Bone
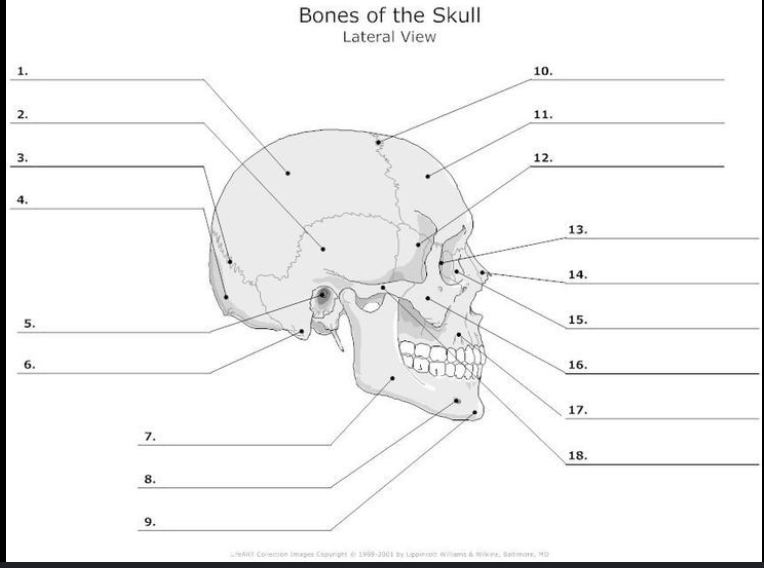
What is #17?
Maxilla
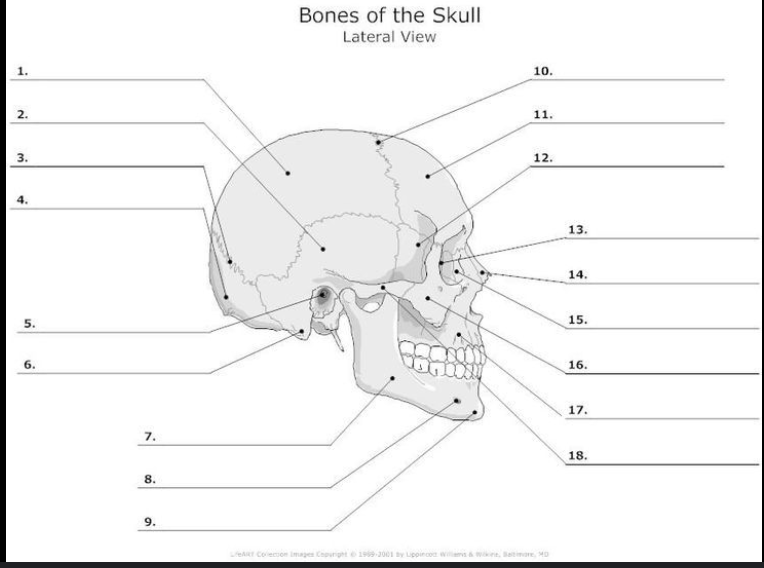
What is #9?
Mandible
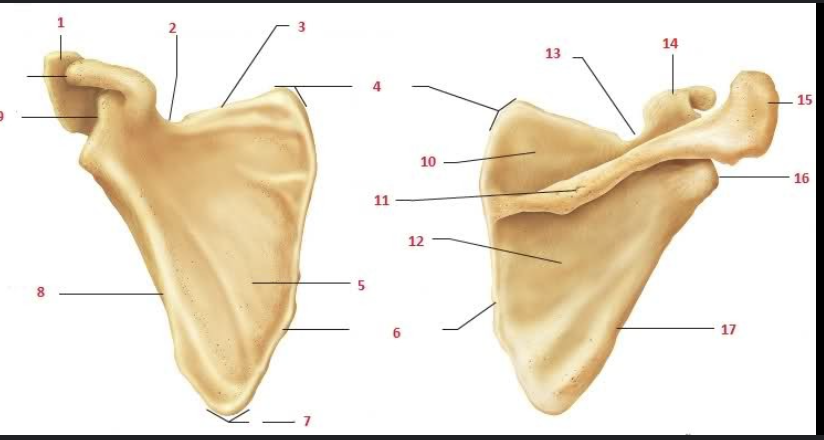
What is #1 and #15?
Acromion
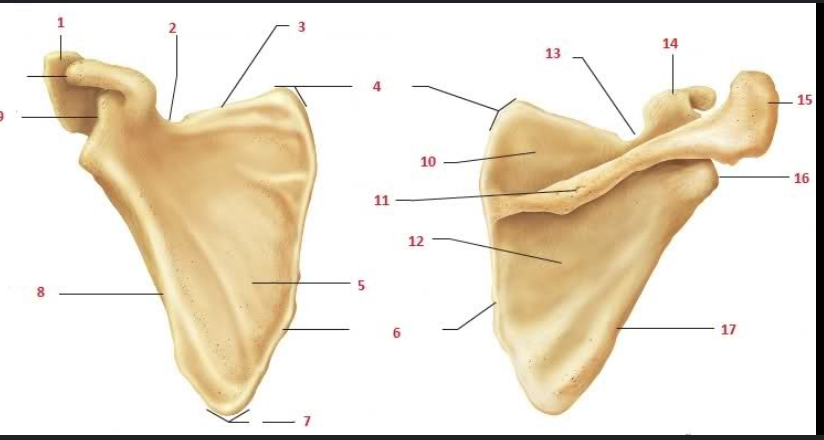
What is #9 and #14?
Coracoid process
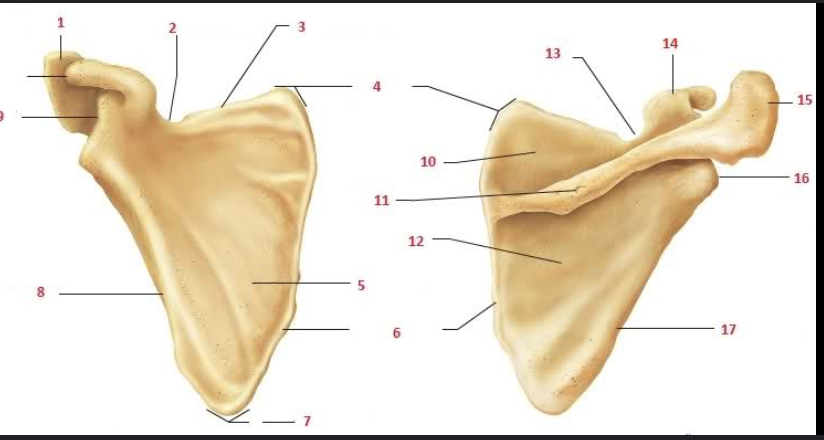
What is #2 and #13?
Suprascapular notch
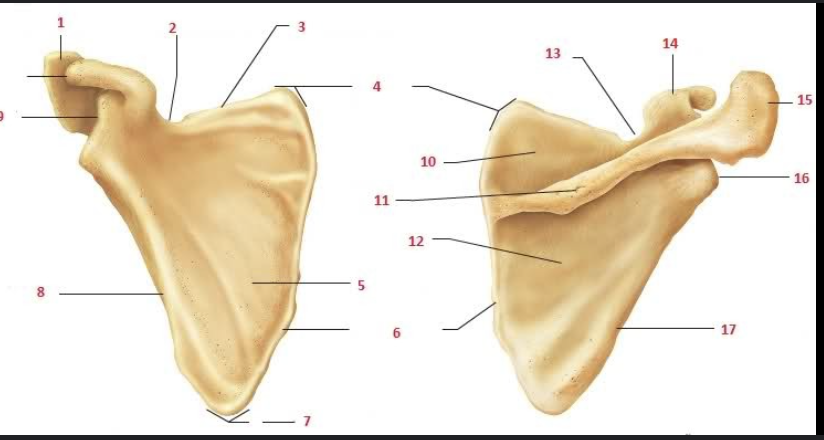
What is #5?
Subscapular fossa
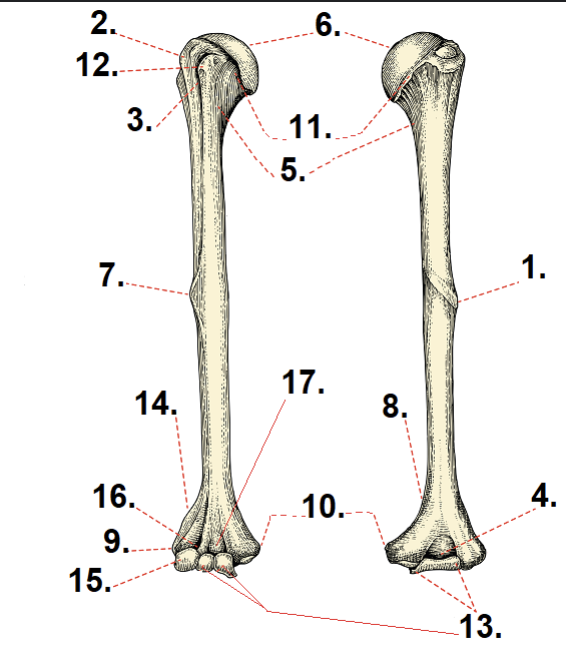
What is #1 and #7?
Deltoid tuberosity
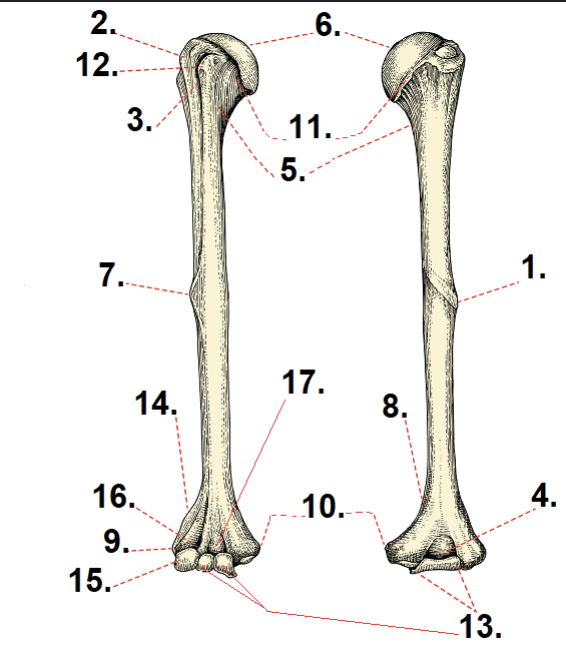
What is #2?
Greater tubercle
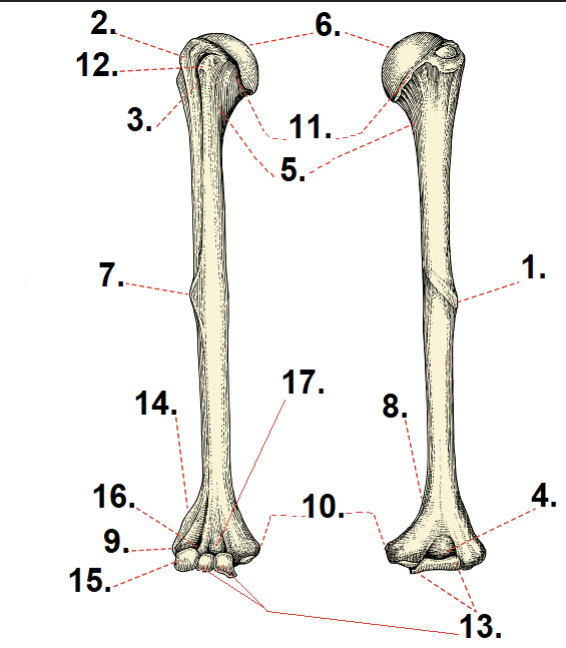
What is #3?
Lesser tubercle
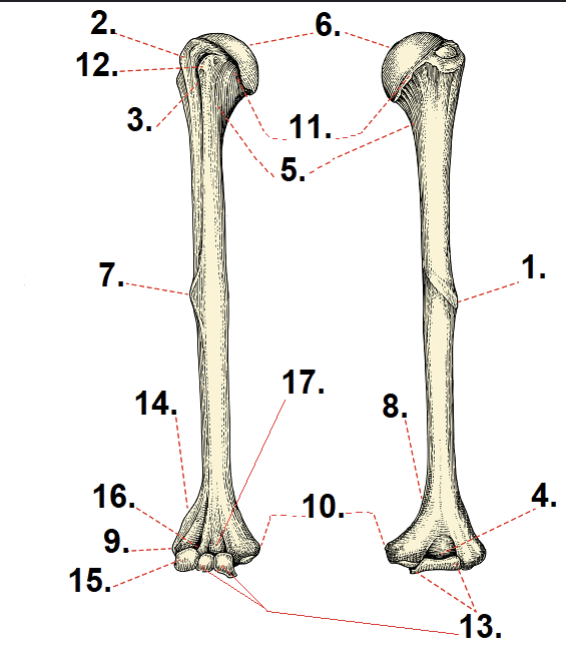
What is #6?
Anatomical neck
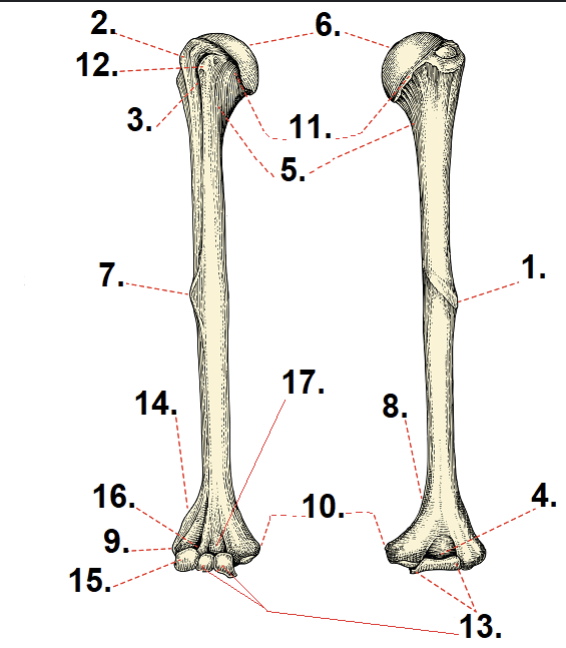
What is #11?
Head
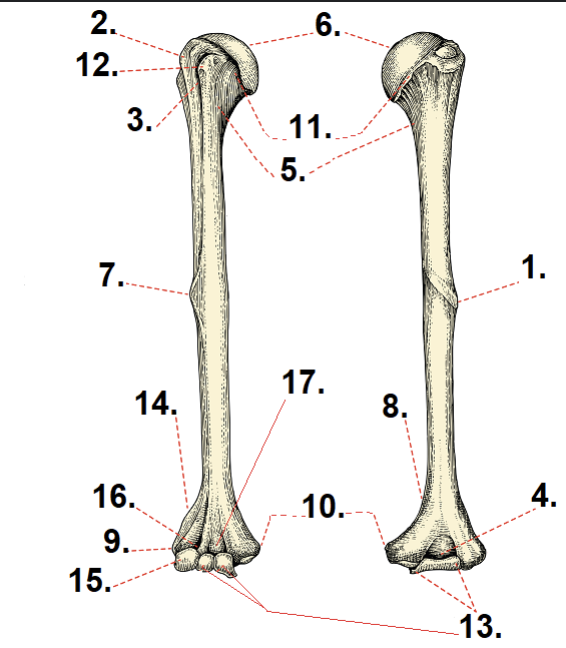
What is #5?
Surgical neck
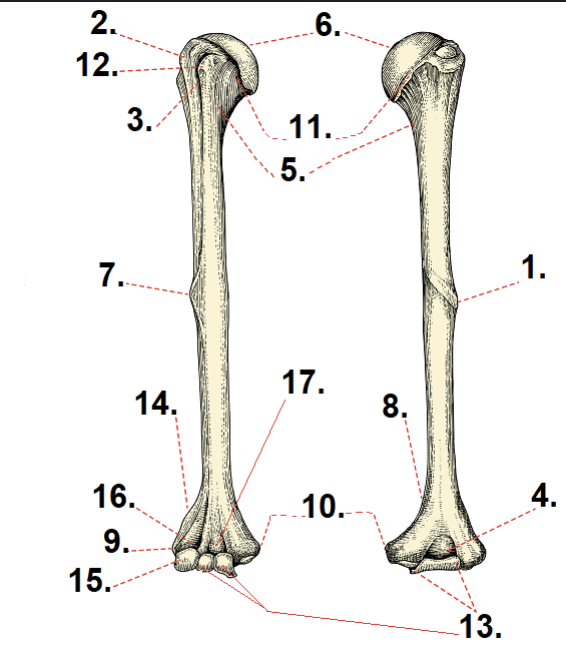
What is #10?
Medial epicondyle
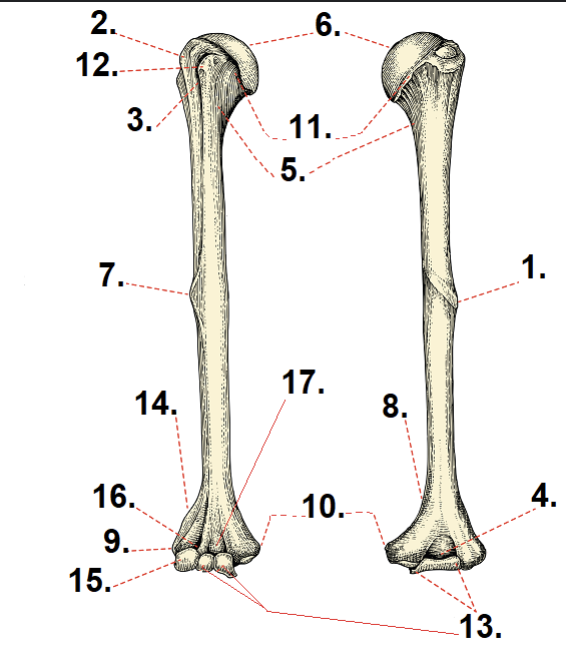
What is #9?
Lateral epicondyle
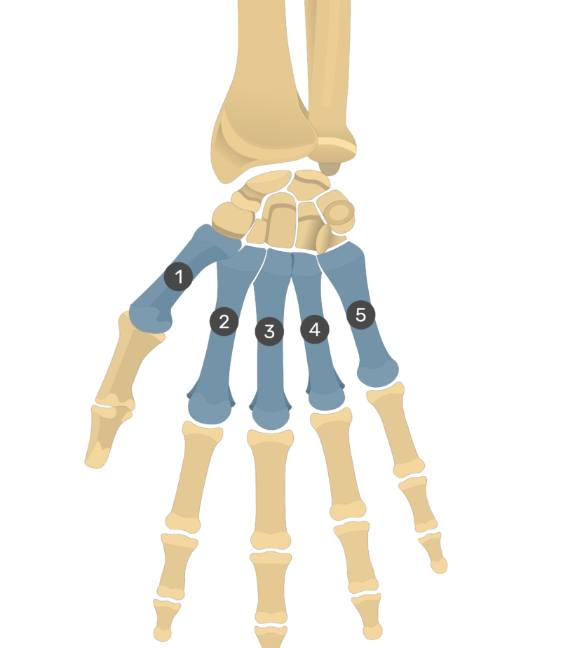
What are the bones of the hand/wrist?
Carpals
Metacarpals
Phalanges
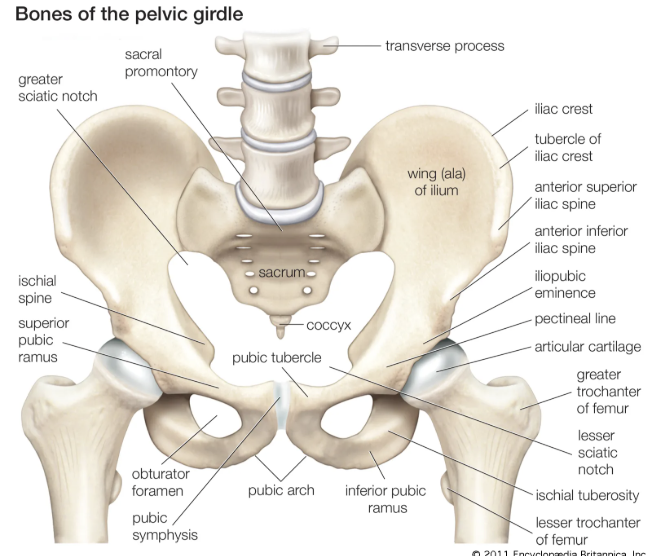
What are the main bones of the pelvic girdle
Ilium
Iliac fossa
Acetabulum
Ischium
Iliac crest
Anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS)
Pubic symphysis
Pubis
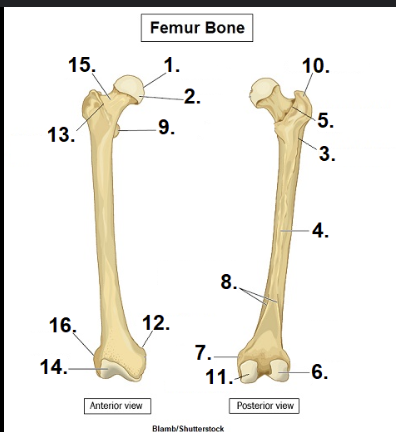
What is #1?
Head
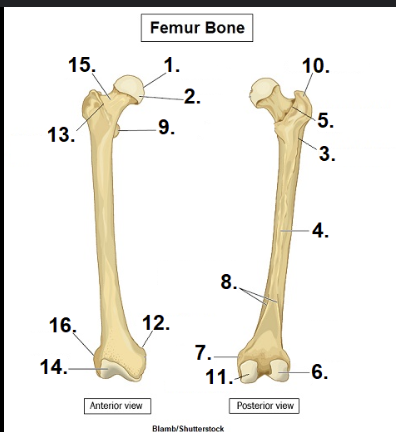
What is #15?
Neck
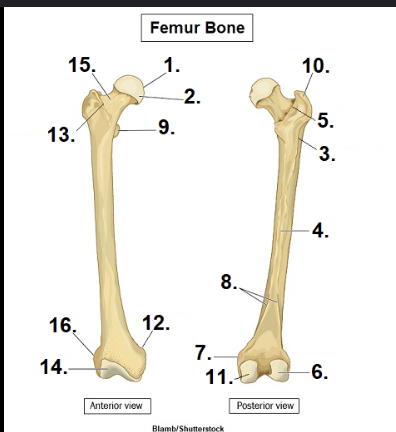
What is #10?
Greater Trochanter
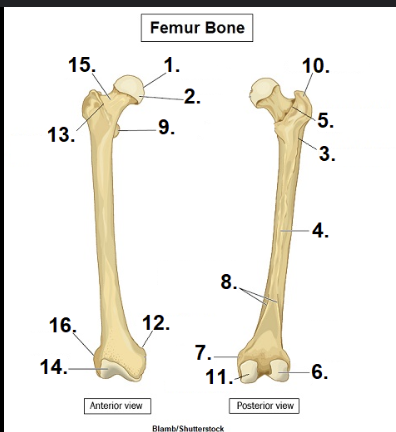
What is #11?
Medial condyle
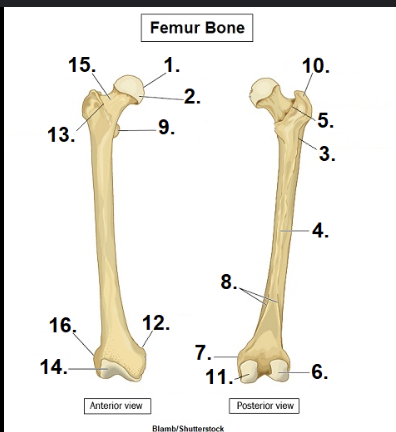
What is #6?
Lateral condyle
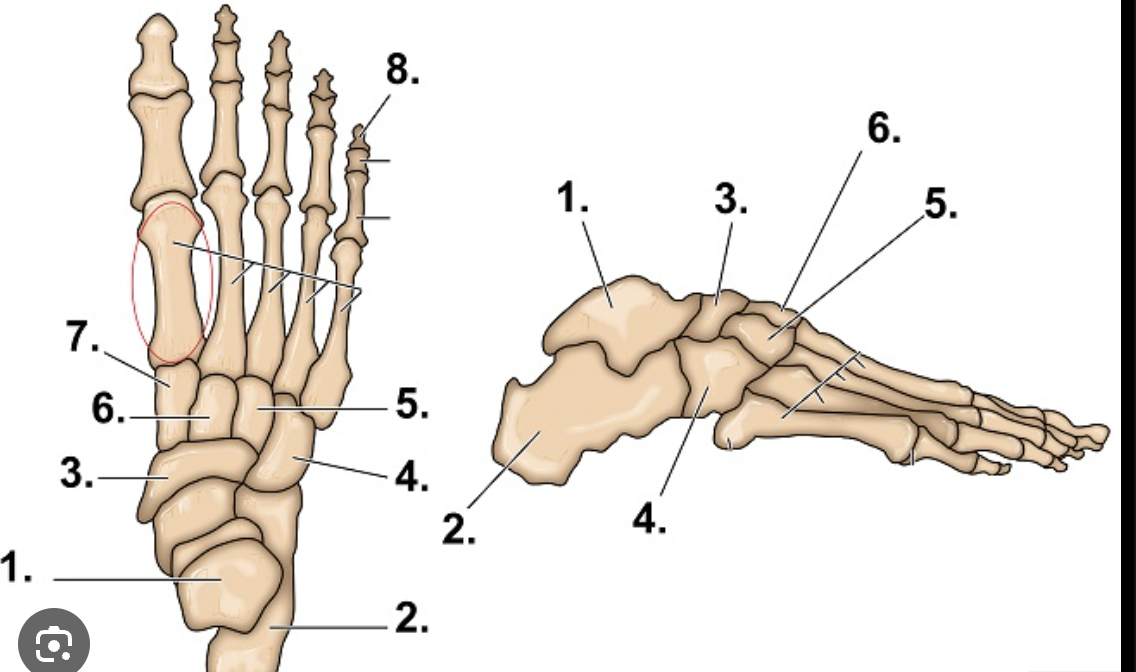
What is #1?
Talus
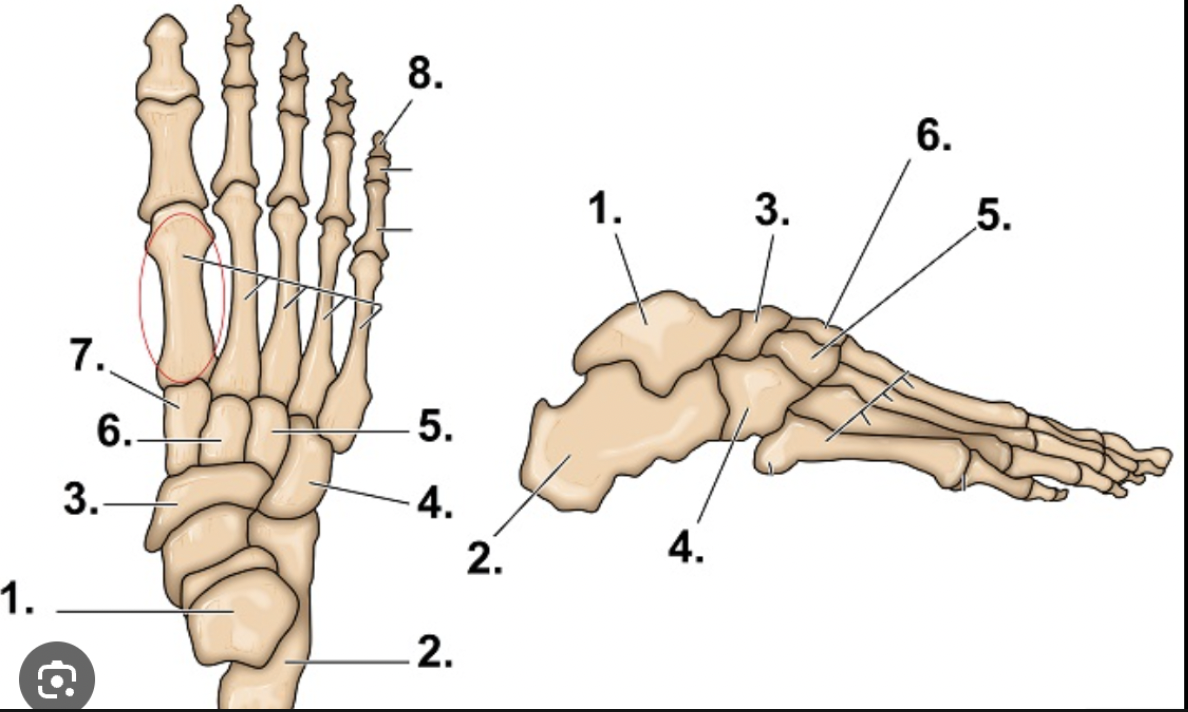
What is #2?
Calcaneus
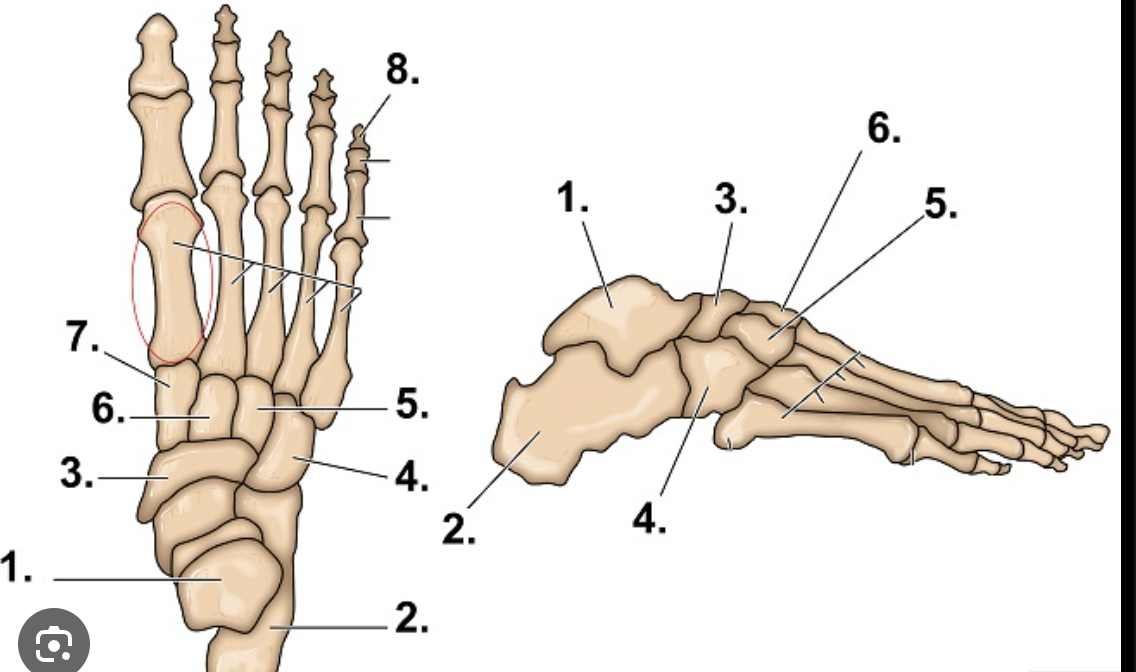
What are the main bones of the foot/ankle
Tarsals
Metatarsals
Phalanges
Vertebral Column
Provides support for the trunk and protects the spinal cord
33 vertebrae (26 distinct bones0
5 segments
What makes up the spine?
7 Cervical
12 Thoracic
5 Lumbar
Sacrum and coccyx
Facets (flat areas)
Located on the processes of the neural arches (synovial joint)
Intervertebral discs
Between the vertebral bodies (cartilaginous joint)
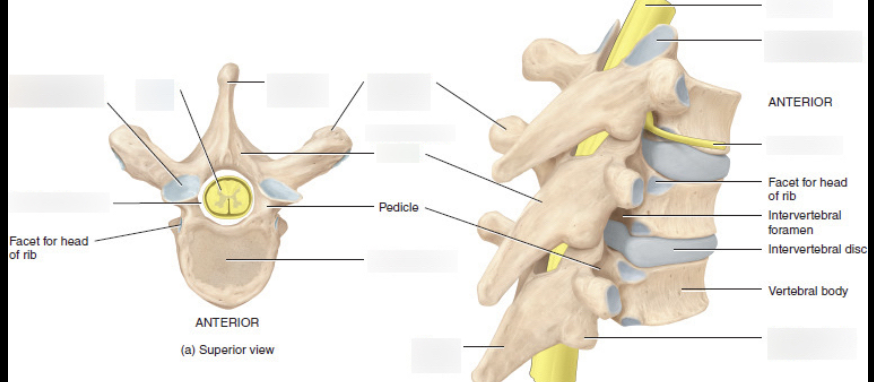
Main areas for intervertebral joints
Pedicle
Facet for head of rib
Intervertebral discs
Work as shock absorbers and allow slight movement so that the column is flexible and resilient
Scoliosis
Lateral curvature of vertebral column
Kyphosis
Hump back - exaggerated posterior thoracic curve
Lordosis
Sway back - exaggerated anterior lumbar curve
Fibrous joint
Immovable
Cartilaginous joint
slightly moveable
Synovial joint
Freely movable
Synovial Joint Functions
Lubricates the joint surfaces as they slide over each other during joint movement to reduce friction
Supplies nutrients to, and removes waste products from, the cartilage cells which have no direct blood supply
Pivot Joint
Uniaxial joint, allows rotation. Ex: C1-C2 vertebrae
Hinge joint
Uniaxial joint, allows flexion/extension. Ex: Knee, elbow, ankle
Condyloid joint
biaxial joint, allows flexion, extension, abduction/ adduction and circumduction. Ex: Knuckle joints
Saddle joint
Biaxial joint, flexion/extension, abduction/ adduction and circumduction. Ex: Thumb
Plane joint
Multiaxial joint, inversion, eversion, flexion/extension. Ex: Vertebrae
Ball-and-socket joint
Multiaxial joint, flexion/extension, abduction/ adduction, circumduction and medial/ lateral. Ex: Shoulder and hip joints
Ligament
Fibrous connective tissue that connects bone together
Tendon
Fibrous connective tissue that joins muscle to bone
Bursa
small sac or cavity filled with synovial fluid and located at friction points, especially joints
Sprain
Overstretching of ligaments
1st degree: fibers are stretched
2nd degree: partial tear of ligament
3rd degree: rupture of the ligament
Dislocation
Bones are displaced
Ligaments are sprained and may even be torn in several cases. Blood vessels are often ruptured and nerves may be compressed
Subluxation
Partial dislocation
Bursitis
Inflamed bursae
Arthritis
Joint inflammation
Structural Limits to Flexibility
Bony structure of the joint
Ligaments
Joint capsule
Muscle tendon unit - muscle and its fascial sheaths (the elongation of this tissue)