Grade 10 Biology
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
Cell membrane
Separates inside of cell from external environment, and controls material flow
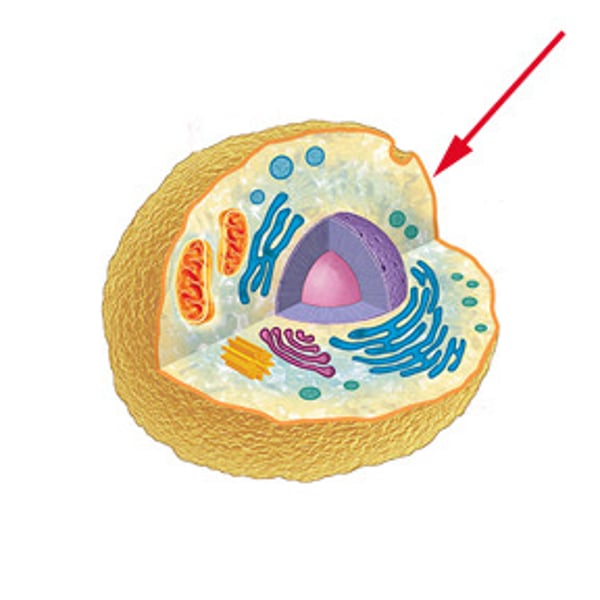
Cell Wall
Tough, rigid structure lying just outside plant cell membrane. Provides support.
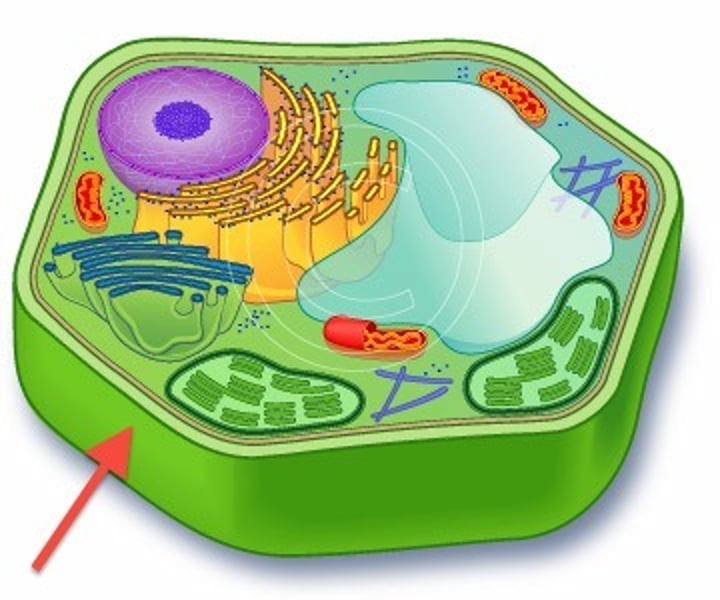
Centrioles
Help in mitosis by moving chromosomes
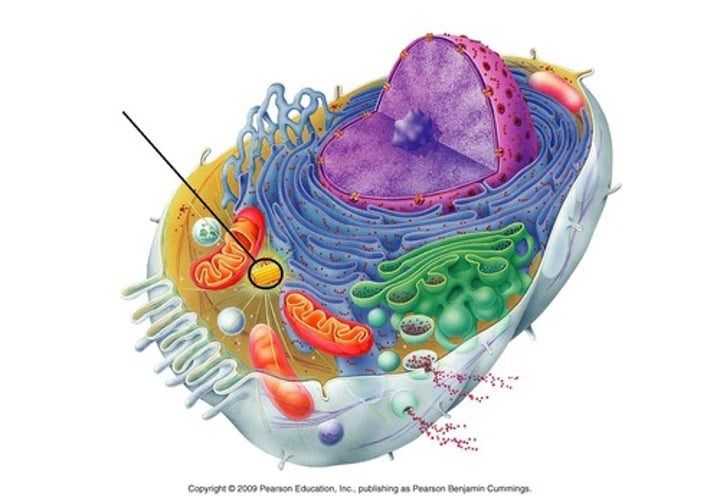
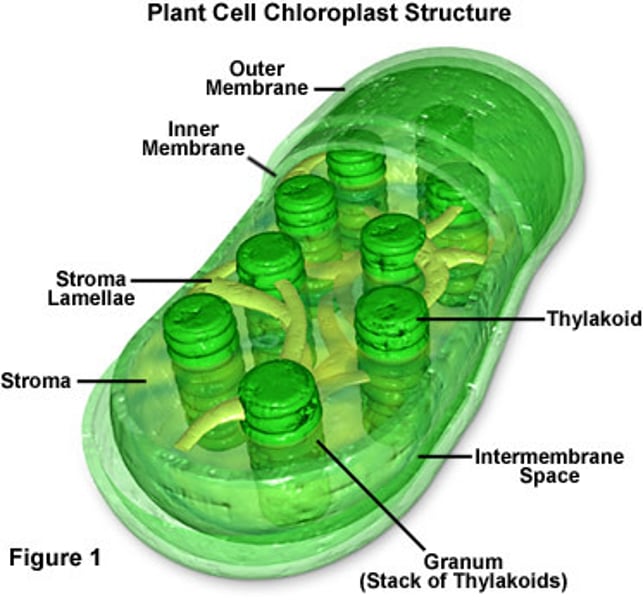
Chloroplast
Trap energy from sun to make glucose, which is broken down in mitochondria to power a plant cell
Cytoplasm
Includes Cytosol, organelles, and other life-supporting materials such as sugar and water. Contained in cell membrane.
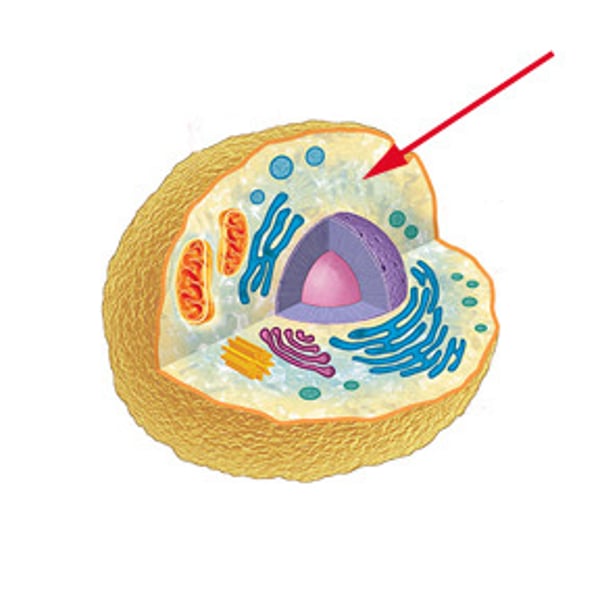
Cytoskeleton
Filaments and tubules that provide a framework for the cell, helping maintain structure and providing "tracks" for organelles and vesicles.
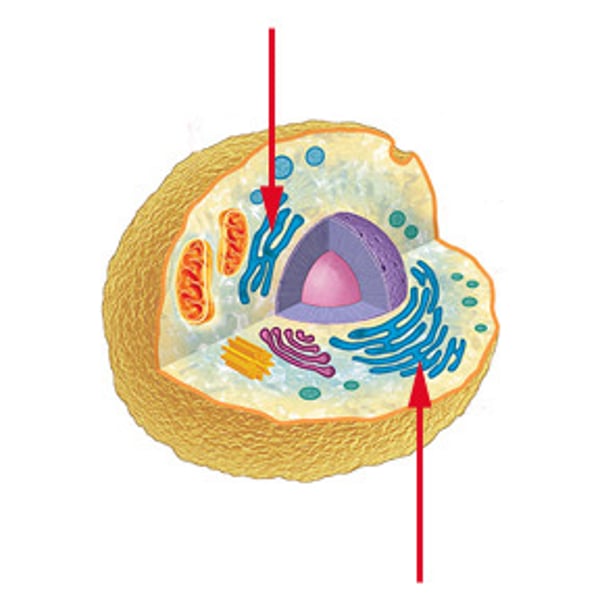
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Network of membrane-covered channels that transport materials, made in cell. Is connected to nucleus
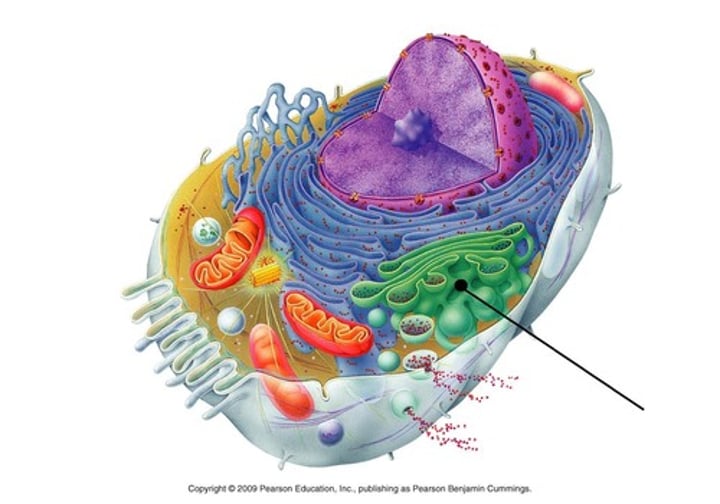
Golgi apparatus
Sorts and packages proteins and other molecules for transport out of cell
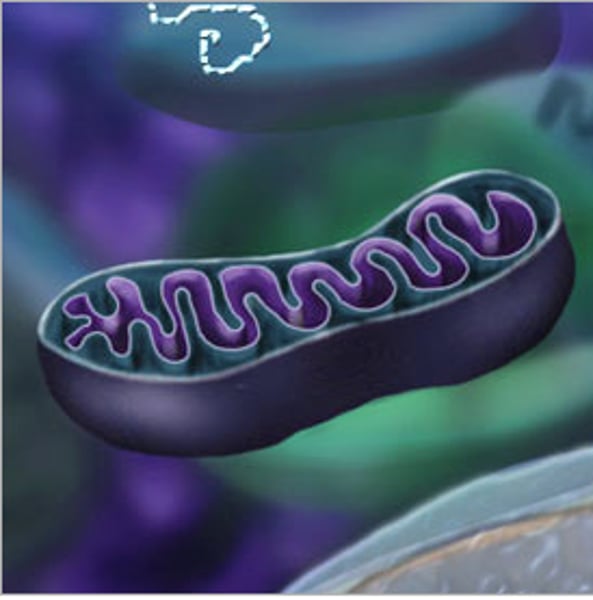
Mitochondria
Where energy is released from glucose to fuel cell activities
Lysosome
Produced by Golgi apparatus, breaks down dead organelles.
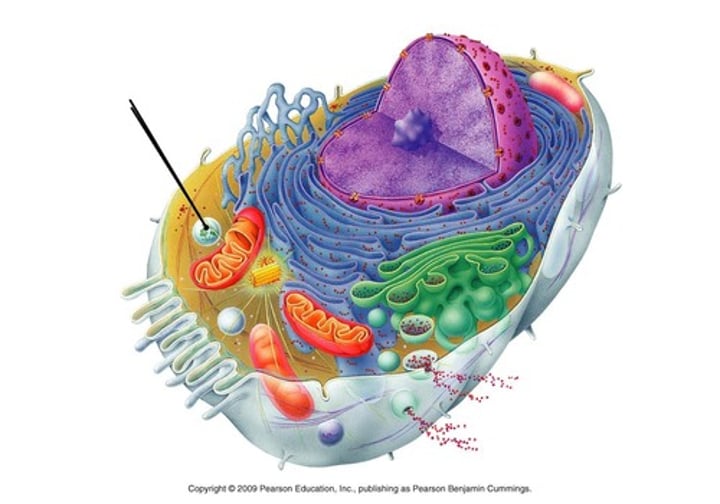
Nucleolus
Makes ribosomes which help make proteins
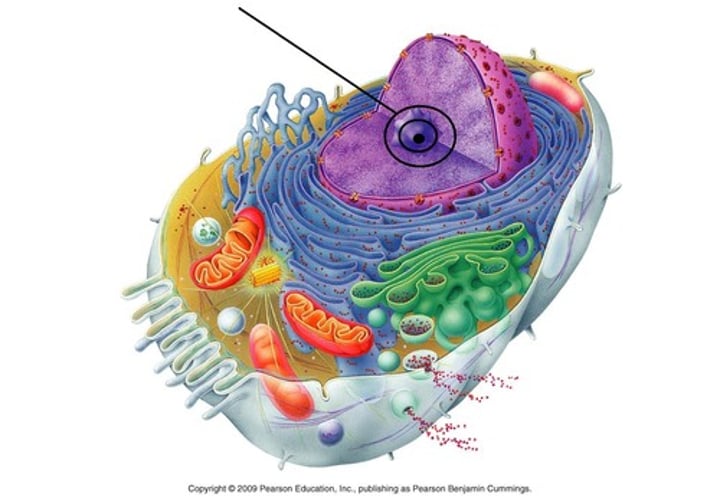
Nucleus
Controls cell activities
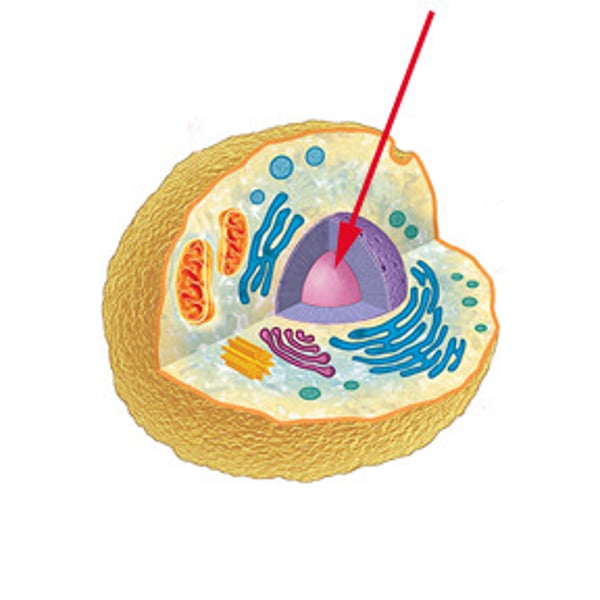
Ribosome
Helps produce proteins which make up much of a cell's structure, and required for vital activities. Some float in cytoplasm and others are attached to the ER
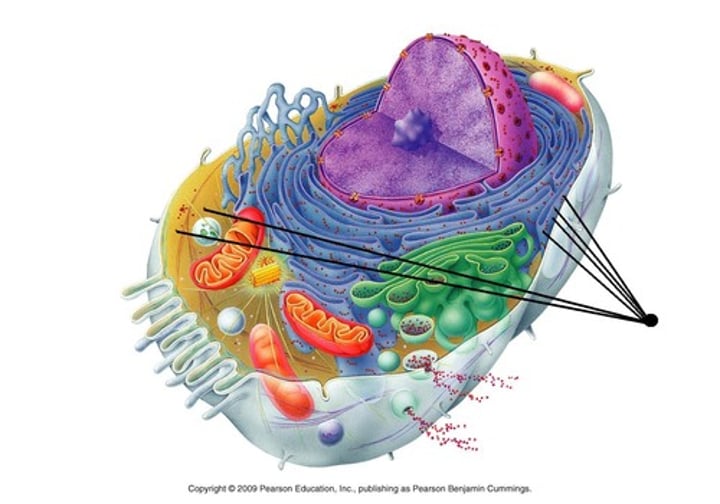
Vacuole
Contain water and materials used to store or transport small molecules
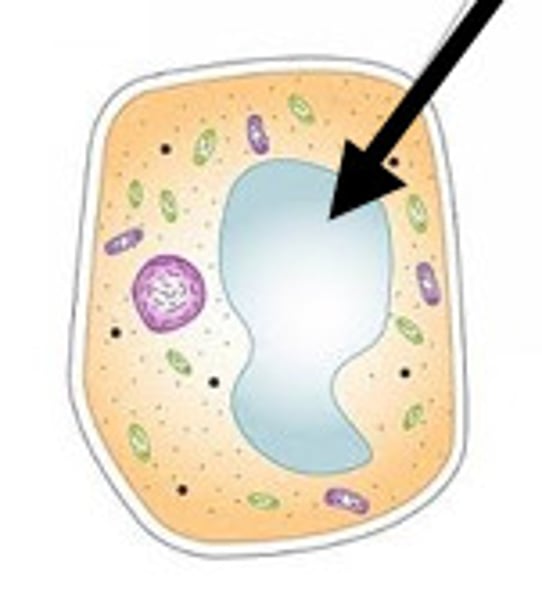
Vacuole
Plant cells contain one large ______, while animal cells contain many small ones.
Cell Wall, Chloroplast
Organelles only found in plant cells
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the Cell
Cytosol
Cytoplasm contains a liquid called _______
Arm
Supports tube and connects to base
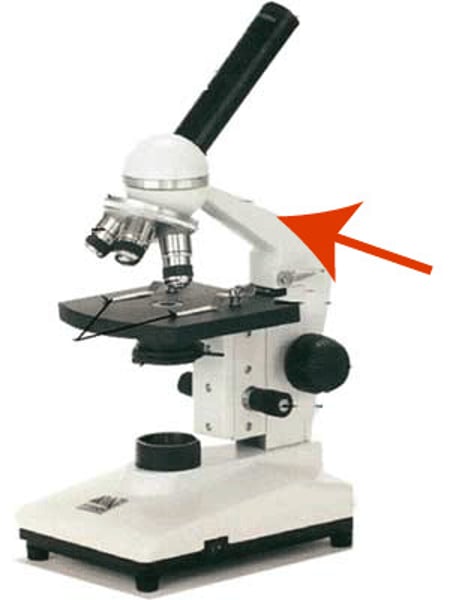
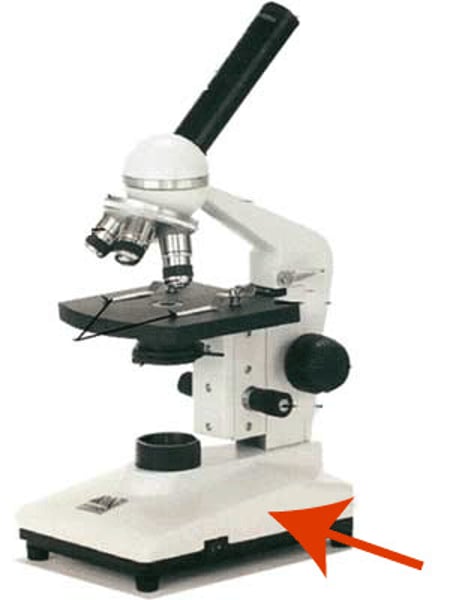
Base
Bottom of microscope for support

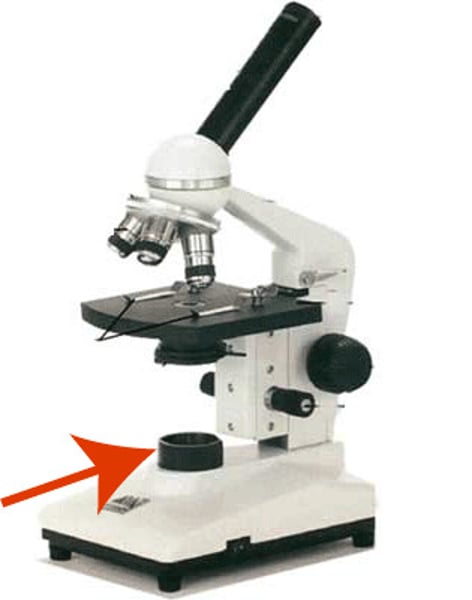
Lamp
Illuminates specimen

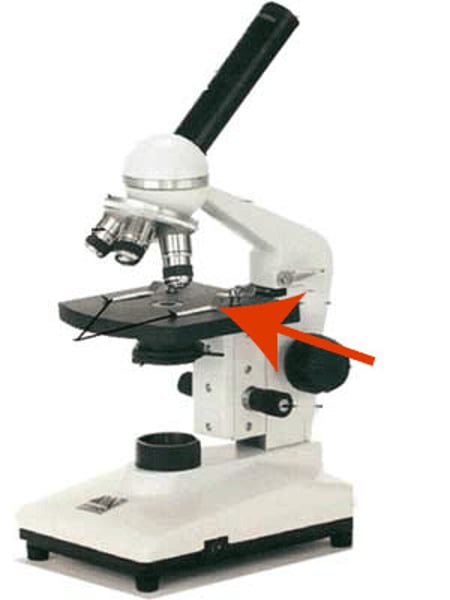
Stage
Flat platform to place slides

Diaphragm
Controls amount of light entering hole in stage
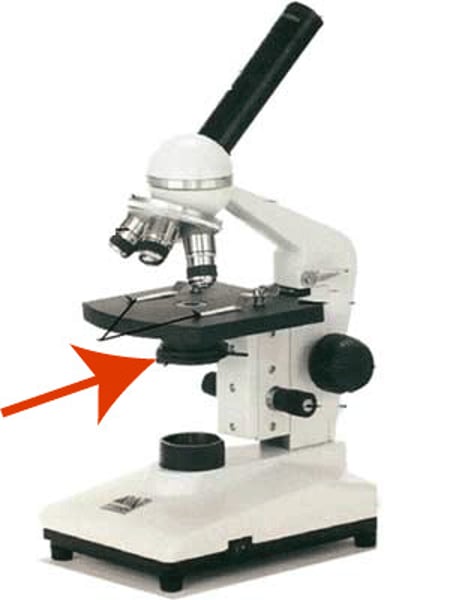
Stage opening
Opening in stage to let in light
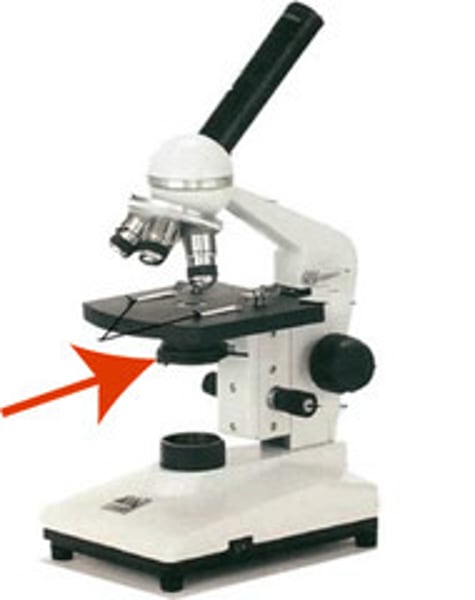
Clips
Hold slide in place
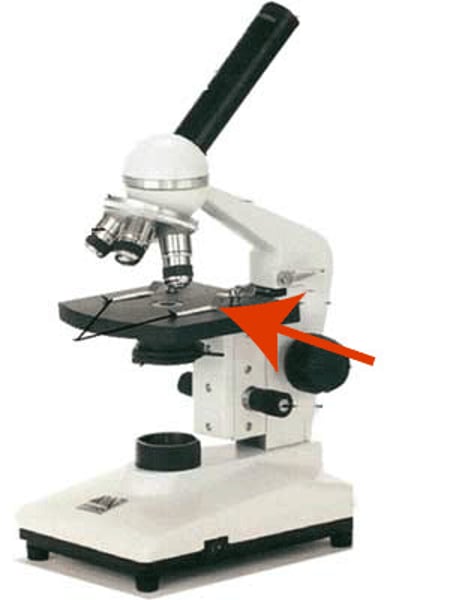

Objective lens
Lower lens which is magnified by eyepiece
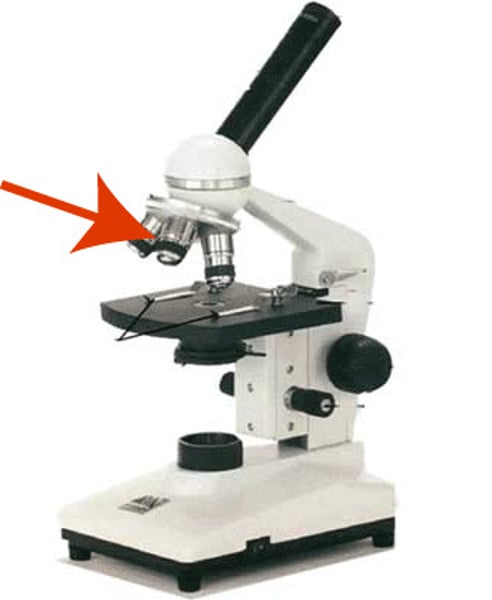

Revolving nosepiece
Rotating part of microscope below body tube to hold lenses
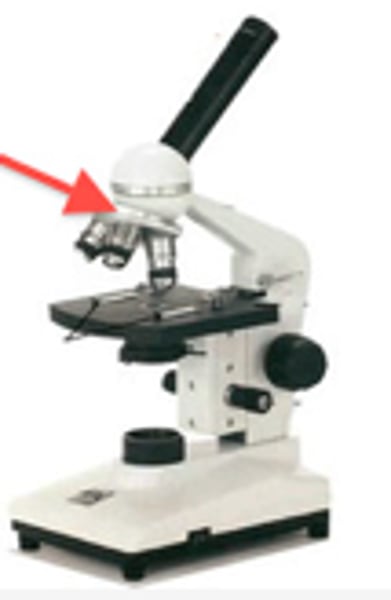
Body tube
Holds eyepiece, connects to objective lenses
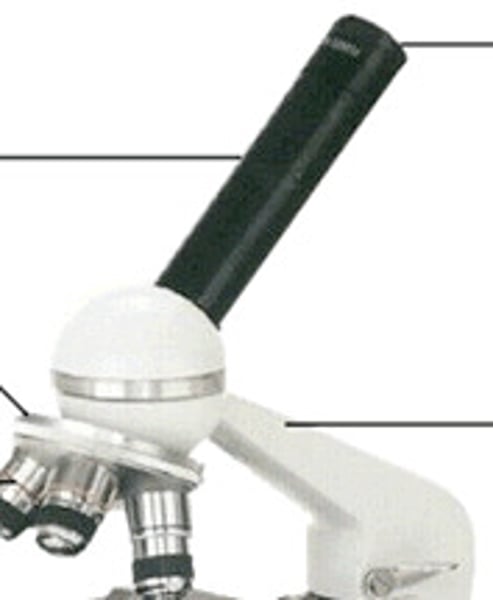

Eyepiece
Upper lens that you look through
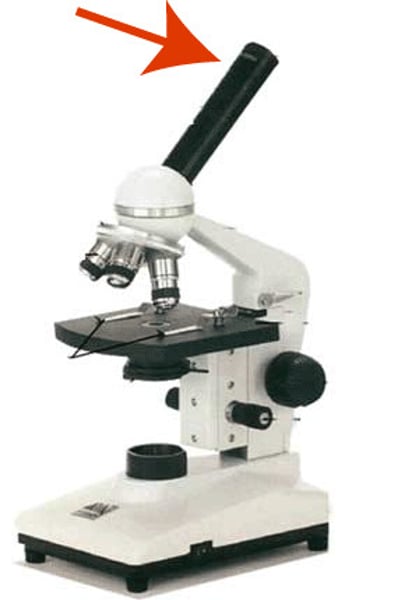
Coarse adjustment knob
Knob to move stage or top of microscope up or down
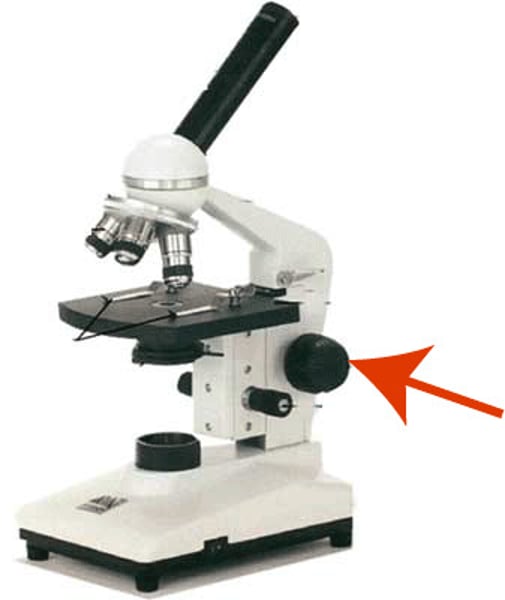

Fine adjustment knob
Knob to fine tune focus after moving coarse knob
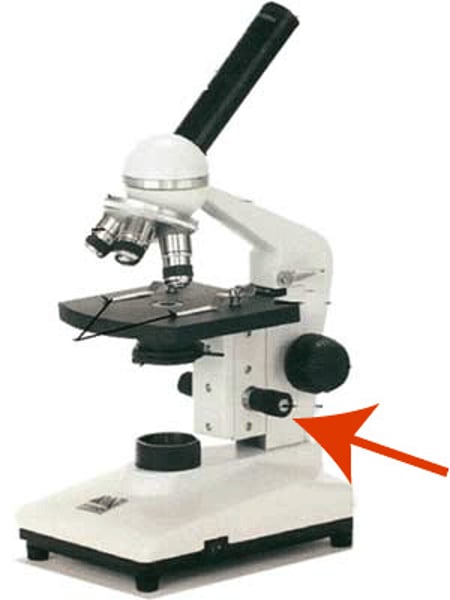
Coarse
The _______ knob is moved first
10
Magnification factor of medium power objective lens
40
Magnification factor of high power objective lens
4
Magnification factor of low power objective lens
10
Magnification factor of eyepiece
40
Total magnification with a low (4x) power objective lens
400
Total magnification with a high (40x) power objective lens lens
100
Total magnification with a medium (10x) power objective lens
Nuclear Membrane
Surrounds nucleus
Nuclear pores
Openings in nuclear membrane
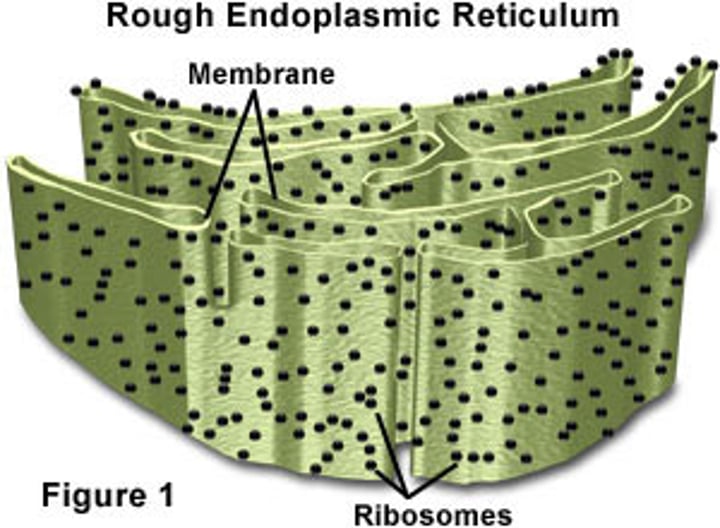
Ribosomes
Rough ER has _______ around it
Spontaneous Generation
Aristotle believed in ________
cells, fundamental unit, cells
Cell theory:
All living things composed of one or more ______,
Cell is the _________ _____ of life,
All cells come from pre-existing _____
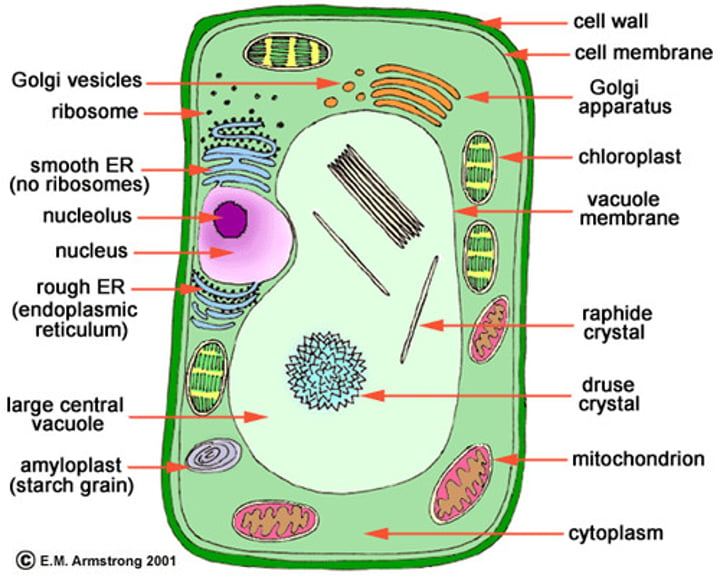
Plant cell
Type of cell
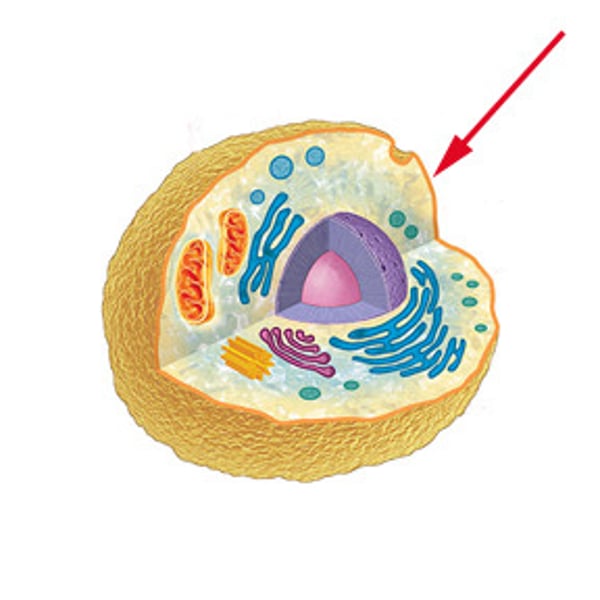
Animal cell
Type of cell
Chloroplast
Cell structure that converts light into energy
DNA
Genetic information in nucleus
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Mailing system of the cell
Golgi apparatus
Packaging department of cell
Growth, repair, reproduction
3 reasons cells divide
Cell cycle
All stages of cell's life
Interphase
First part of cell cycle
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
Second part of cell cycle
Interphase
Longest stage of cell cycle
First Gap Phase
First stage of Interphase
Synthesis Phase
Second stage of Interphase
Second Gap Phase
Third stage of Interphase
G1
Stage of interphase where cells grow in size
S
Stage of interphase where DNA is replicated
G2
Stage of interphase where cells prepare for division
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
Stages of Mitosis
Nucleus
Location of chromosomes
46
Number of chromosomes in a human cell
true
True or false: when dividing, each daughter cell receives the same genetic material
DNA, Proteins
Chromosomes are made of
Prophase
Mitosis stage in which:
- chromatin condenses
- sister chromatids are formed
- centrioles move to each pole
- nucleolus disappears
- nuclear membrane breaks down
Metaphase
Mitosis stage in which:
- Spindle fibres attach to centromere
- Chromosomes line up at metaphase plate
Centrioles
Centrosomes contain:
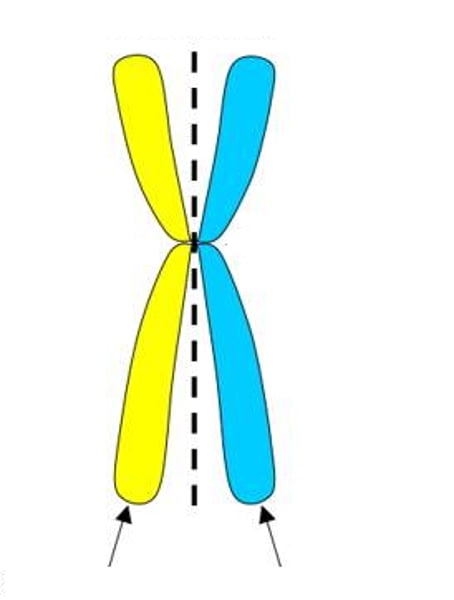
Centromere
Point of intersection of sister chromatids
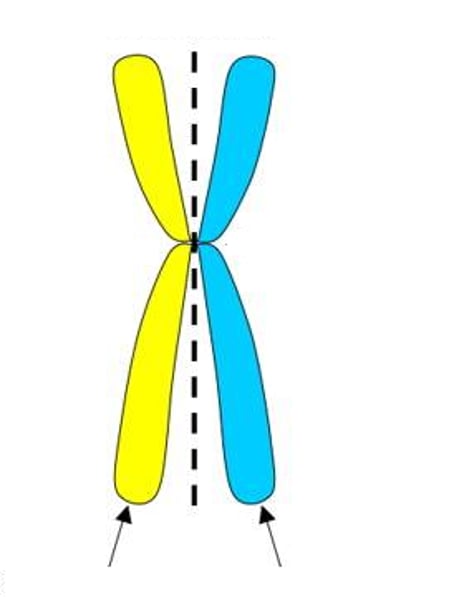
Sister Chromatids
This chromosome is made up of two:
Anaphase
Mitosis stage in which:
- Spindle fibres shorten
- Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles
- Cell starts to pinch
g0
Phase during which cells can no longer divide
Telophase
Mitosis stage in which:
- Cell membrane pinches inwards fully
- Nuclear membrane re-forms
Plant
After division of ______ cells, the cell size is halved
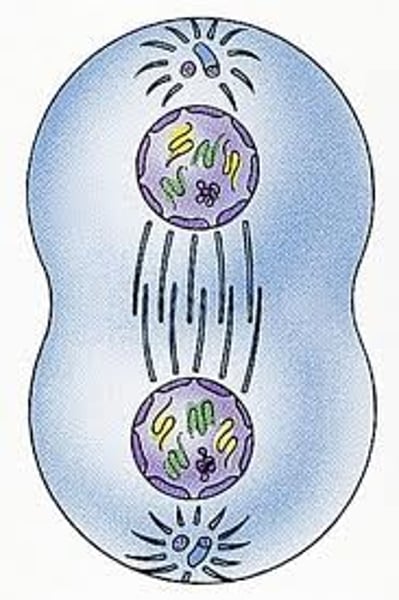
Cytokinesis
Cytoplasm splitting in half and moving to two daughter cells
Anaphase, telophase
Cytokinesis lasts during which phases of mitosis?
Mitosis
Duplication of nuclei
Necrosis
Cells dying due to external factors
Apoptosis
Controlled death of old cells
Prophase
Phase of mitosis

Metaphase
Phase of mitosis
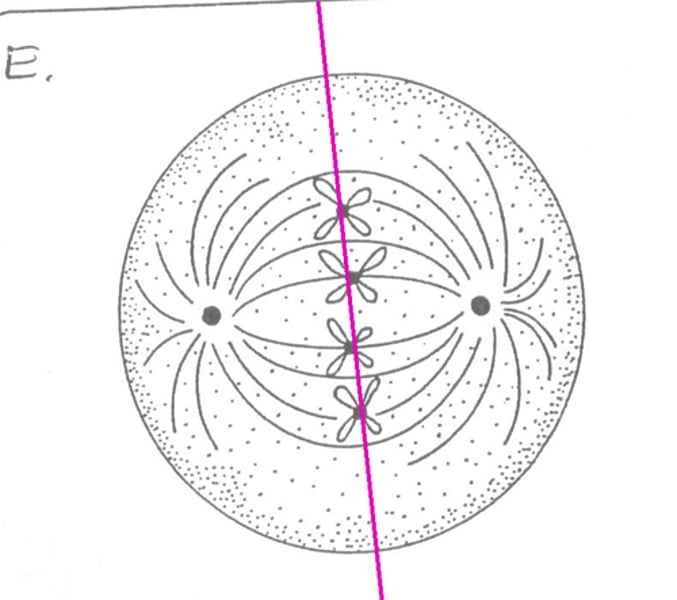
Anaphase
Phase of mitosis
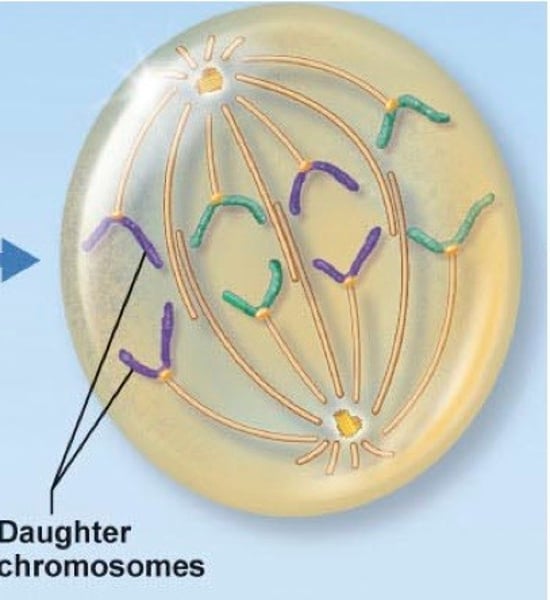
Telophase
Phase of mitosis
Epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
4 types of tissue in human body
Tissue
Group of cells similar in shape that work together to perform a specialized function
Epithelial
Tissue that lines surfaces of body, like skin or intestine lining
Nervous
Tissue that carries signals through neurons
Muscle
Tissue that changes shape by relaxing and contracting to affect body movement
Connective
Tissue that strengthens, supports, binds, or connects cell tissues (in animals)
Connective
Type of tissue made up often by bone, fat, or blood cells
Nervous
Type of tissue made up by neurons
Muscle
Type of tissue made up by myocytes (muscle cells)
Epithelial
Type of tissue made up often by skin/epidermal cells
Dermal, ground, vascular, meristematic
4 types of tissue systems in plants
Dermal
Tissue that protects plants from injury and water loss (often made up by epidermal and guard cells)
Ground
Tissue that stores produced carbohydrates in plants, and photosyntesizes (made up by cells such as parencyma and sclerenchyma)
Vascular
Tissue that transports water, minerals, and nutrients in plants (made up by cells such as Xylem and Phloem)
Cancer
Group of diseases that results in uncontrolled cell division that leads to the formation of a tumor
Tumor
Lump of cells that continues to divide without a purpose