PSY333: Measurement & Testing (some level of finals)
0.0(0)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/130
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:38 PM on 5/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
1
New cards
Cattell
"First used the term ""mental tests"""
2
New cards
Binet
Associated with the first modern-day intelligence test (measure higher mental processes)
3
New cards
Wundt
First psychological laboratory that used experimental research
4
New cards
Terman
First use of the term intelligence quotient (IQ); revised Binet
5
New cards
Thorndike
Associated with the Stanford Achievement Test
6
New cards
WWI
What was the era that first widely used group testing?
7
New cards
Army Alpha
Group administation of intelligence test for the military; reading literacy
8
New cards
Army Beta
Used as an intelligence test, but is the language-free version
9
New cards
Thorndike
Research on vocational assessments
10
New cards
Miner
Person involved in occupation selection for large groups of high school students
11
New cards
Strong
First \-- much more general career counseling for the future aptitude tests
12
New cards
Woodworth's Personal Data Sheet
First modern personality inventory (WWI); measured suspectibility to mental health problems
13
New cards
aptitude
measure whether or not you're ready for something
14
New cards
Step 1: Determine the goals of your client
"Defines purpose of test; demographics are considered; what context the test is on
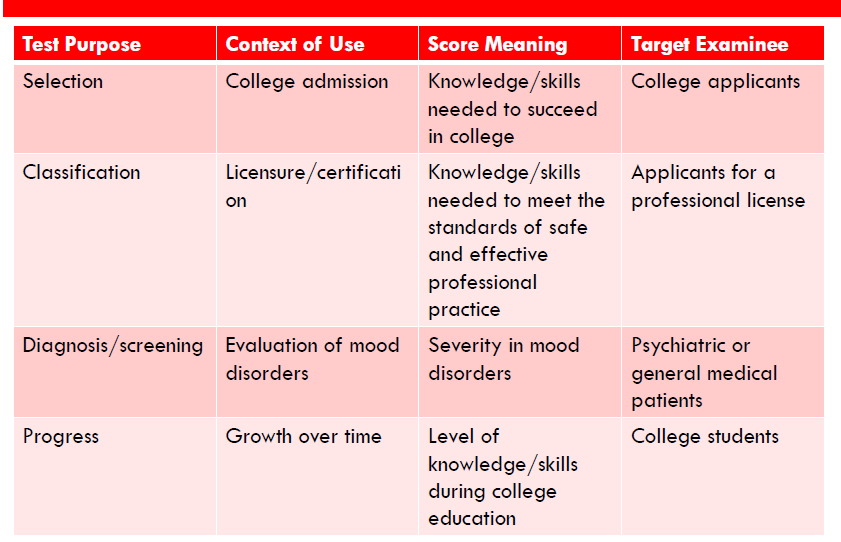
15
New cards
Step 2: Choose instrument types to reach client goals
Asks the questions: What behaviors, content, skills is it intended to measure? What is the that the trait is based on? What about subsets/domains it is based on? Operationalization of test forms.
16
New cards
Step 3: Access information about possible instruments
Item formats are determined; test is written and item reviewers make sure it measures what is intended to measure
17
New cards
Step 4: Examine validity, reliability, cross-cultural, fairness, and practicality of the possible instruments
Before this is done, a pilot test is done to make sure the items are valid, reliable, and fair, among other items. , this happens.
18
New cards
pilot test
Validation process
19
New cards
Step 5: Choose an Instrument Wisely
Determines test length, testing time, scoring approaches, and test procedures, administers test materials.
20
New cards
Level A
Tests which can be administered, scored, and interpreted by laypeople
21
New cards
Level B
Tests that require a psychology degree or coursework in testing
22
New cards
Level C
Tests that require an advanced psychology degree, a license and/or advanced training for that particular test
23
New cards
cognitive sources of construct-irrelevant variance
Knowledge or skill not related to the purpose of the test is required to answer an item correctly.
24
New cards
affective sources of construct-irrelevant variance
Language or images causes strong emotions that may interfere with the ability to respond to an item correctly (i.e. political opinions, beliefs)
25
New cards
physical sources of construct-irrelevant variance
aspects of tests interfere with the test takers' ability to attend to, see, hear, or sense the items or stimuli (consider disabled people!)
26
New cards
correlation coefficient
statistical relationship between two variables
27
New cards
scatter plot
"Used to visually examine data, especially to discover patterns (such as curvilinear relationships)
28
New cards
positive relationship
"an increase in one variable is related to an increase in the other variable
29
New cards
negative relationship
"an increase in one variable is related to a decrease in the other variable
30
New cards
no relationship
"two variables that are not related to each other
31
New cards
strong correlation
""
32
New cards
moderate strength
±0.30 ~ 0.69"
33
New cards
no strength
±.00 ~ 0.29"
34
New cards
scores from a test is a consistent measure of individuals’ true scores
reliability
35
New cards
correlation coefficient
To measure reliability, we use
36
New cards
method error
caused by test administrators or the testing environment
37
New cards
trait error
Error associated with test takers, subjects themselves
38
New cards
test-retest reliability
Relationship between scores on the same test administered twice with a time interval between the administration
39
New cards
practice effects
e.g., subjects may get better at second testing, subjects knowing how they answered in a similar test form
40
New cards
alternate-forms reliability
Coefficients of two equivalent tests are compared (time interval)
41
New cards
internal consistency
obtaining a reliability coefficient by assessing how items are correlated as a group
42
New cards
split-half reliability
internal consistency; correlation between scores from even-numbered items and scores from odd-numbered items
43
New cards
validity
whether a test measures what it is supposed to measure (
44
New cards
content validity
Does the \______ \______ cover a representative sample of behaviors to be measured in its entirety? Content experts
45
New cards
criterion validity
Does a test predict the target trait it is intended to measure?
46
New cards
concurrent validity
Focuses on the prediction of current performance or psychological behavior
47
New cards
predictive validity
Focuses on the prediction of future performance or psychological behavior
48
New cards
construct validity
Does an assessment measure a theoretical construct that it is designed to measure (e.g., intelligence)?
49
New cards
convergent validity
Are two assessments measuring the construct related?
50
New cards
discriminant validity
Are two asssessments measuring different constructs ?
51
New cards
factor analysis
Found construct you want to measure from the test scores
52
New cards
fairness
whether an individual's score is not affected by potential bias inherent in a test, test procedure and interpretation
53
New cards
the 1960s (civil rights movement)
Fairness did not get much attention until
54
New cards
fairness in testing process
Equal testing condition + proctors
55
New cards
fairness as lack of measurement bias
Idea that all items should behave equally across all examinees
56
New cards
fairness in access to the construct as measured
accessibility in testing; showing their status on target without being advantaged or disadvantaged by their individual characteristics or opportunity to learn
57
New cards
differential item functioning
Statistical approach to examine test fairness by identifying items that perform differentially across subgroups of test takers while controlling for test takers' ability
58
New cards
cognitive interview
examining response processes through probing questions
59
New cards
achievement testing
tests that measure what one has learned
60
New cards
aptitude testing
measure what one is capable of learning
61
New cards
personality assessment
used to assess habits, temperament, likes and dislikes, character, and similar behaviors
62
New cards
diagnostic tests
tests that assess problem areas of learning; often used to assess learning disabilities
63
New cards
cognitive ability tests
tests that measure a broad range of cognitive ability
64
New cards
intellectual and cognitive functioning
tests that measure a broad range of cognitive functioning in general intelligence, intellectual disabilities, giftedness, changes in overall cognitive functioning
65
New cards
special aptitude tests
tests that measure one aspect of ability; likelihood of success in a vocation
66
New cards
multiple aptitude tests
tests that measure many aspects of ability; likelihood of success in multiple vocations
67
New cards
interest inventories
tests that measure likes and dislikes as well as one's personality orientation toward the world of work; career counseling
68
New cards
classification methods
a tool whereby an individual identifies whether he or she has, or does not have, specific attributes or characteristics
69
New cards
readiness tests
tests that measure one's readiness for moving ahead in school. used to assess readiness to enter first grade
70
New cards
mental age/chronological age x 100
How do you calculate IQ (use / as a division sign)?
71
New cards
Spearman-Brown formula
What formula is used for split-half reliability due to the test being cut in half?
72
New cards
"bar graph
"visual for a categorical, discrete variable"
73
New cards
"histogram
visual for continuous variables
74
New cards
"frequency polygon
used to see the distributional shape of data
75
New cards
positively skewed
"(Type of curve)
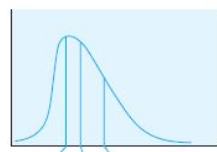
76
New cards
negatively skewed
"(Type of curve)
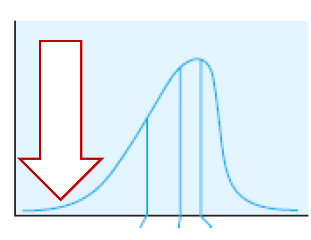
77
New cards
Mode < Median < Mean
"Left to right, how are measures of central tendency distributed in positively skewed distributions?
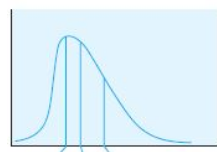
78
New cards
Mode > Median > Mean
"Left to right, how are measures of central tendency distributed in negatively skewed distributions?
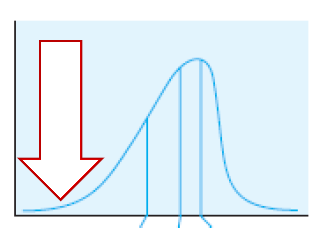
79
New cards
variance
avg of squared distance from the mean
80
New cards
deviation score
the difference between an individual score and the mean
81
New cards
norm referenced
scores that are compared to a set of test scores called the norm group
82
New cards
criterion-referenced scores
scores are compared to a predetermined standard; i.e. mastering a certain level of knowledge, used for diagnoses
83
New cards
percentile
proportion of people falling at and below a score in a standard normal distribution
84
New cards
T-scores
µ \= 50, σ \= 10; used for personality tests
85
New cards
deviation IQ
µ \= 100, σ \= 15; used for tests of intelligence
86
New cards
Stanines
µ \= 5, σ \= 2, round to nearest whole number; used for achievement testing
87
New cards
Sten scores
µ \= 5.5, σ \= 2, round to nearest whole number; used for personality inventories and questionnaires
88
New cards
NCE scores
µ \= 50, σ \= 21.06; used for educational tests
89
New cards
SAT scores
µ \= 500, σ \= 100
90
New cards
ACT scores
µ \= 21, σ \= 5
91
New cards
Publisher type scores
µ and σ are artbitrarily set by publisher
92
New cards
SEM
σ of test scores x √1 - reliability of a test
93
New cards
standard error of measurement
Tells us how much error there is in the test and ultimately how much any individual's score might fluctuate due to this error
94
New cards
comprehension
problems with the \_____ of questions
95
New cards
information retrieval
failure in the information retrieving to answer (related to background characteristics)
96
New cards
decision process
low motivation/intention of faking or impression enhancement
97
New cards
response process
mismatch in the choice of response option; difference in interpretation of option meanings
98
New cards
interquartile range formula
\

99
New cards
Deviation score
X (raw score) - M (mean score)
100
New cards
Variance
Deviation score squared