Chapter 27 - Electrolyte Balance - Part 2 - Final
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Essential Electrolytes
Sodium, chloride, potassium, calcium, magnesium, phosphate
Essential Electrolytes Functions
-Balance blood pH
-Facilitate waste excretion from cells
-Maintain fluid balance
-Promotes proper functioning of nerve, muscle, heart, and brain cells
-Transports nutrients into cells
Electrolytes
-Chemical compounds that dissociate into ions in water
-Due to the ions being charged particles they conduct electrical current -> electrolytes
Categories of Electrolyte
-Inorganic salts
-Inorganic/organic acids and bases
-Some proteins
Electrolyte - Increased Osmotic Pressure
-Due to dissociation into at least two ions -> NaCl or MgCl2
-Causes fluid shifts, influences movement of water from lesser osmolality to higher osmolality (osmosis)
Extracellular Ions
-Consumed in food/water we ingest
-Removed from the body by kidneys, liver, skin and lungs
Concentration of Electrolytes
Change when the individual is growing, or gaining/losing weight
Electrolyte Balance =
= Salt Balance
Electrolyte Roles
-Control fluid movements
-Provide minerals for excitability
-Secretory activity
-Membrane permeability
Sodium
Most abundant cation in the ECF
Sodium Role
Control ECF volume and water distribution in the body
-Exerts significant osmotic pressure
-Cellular plasma membranes = impermeable to sodium
What follows sodium?
Water follows sodium -> when change in plasma sodium, change in plasma, BP, ICF, and IF volumes
Content of Sodium
Total amount of sodium in the body determines ECF volume and BP
What increases sodium and ECF content?
Low BP activates renin-angiotensin-aldosterone -> increased sodium, and water volume in ECF
What decreases sodium and ECF content?
BP elevated -> increased sodium and water excretion -> ANF secretion -> inhibit sodium reabsorption and inhibit ADH effect of DCT/CD
ECF Sodium Content Increases
Rise in ECF osmolality -> ADH + thirst -> increased water retention and intake -> reduced sodium concentration and increased ECF volume
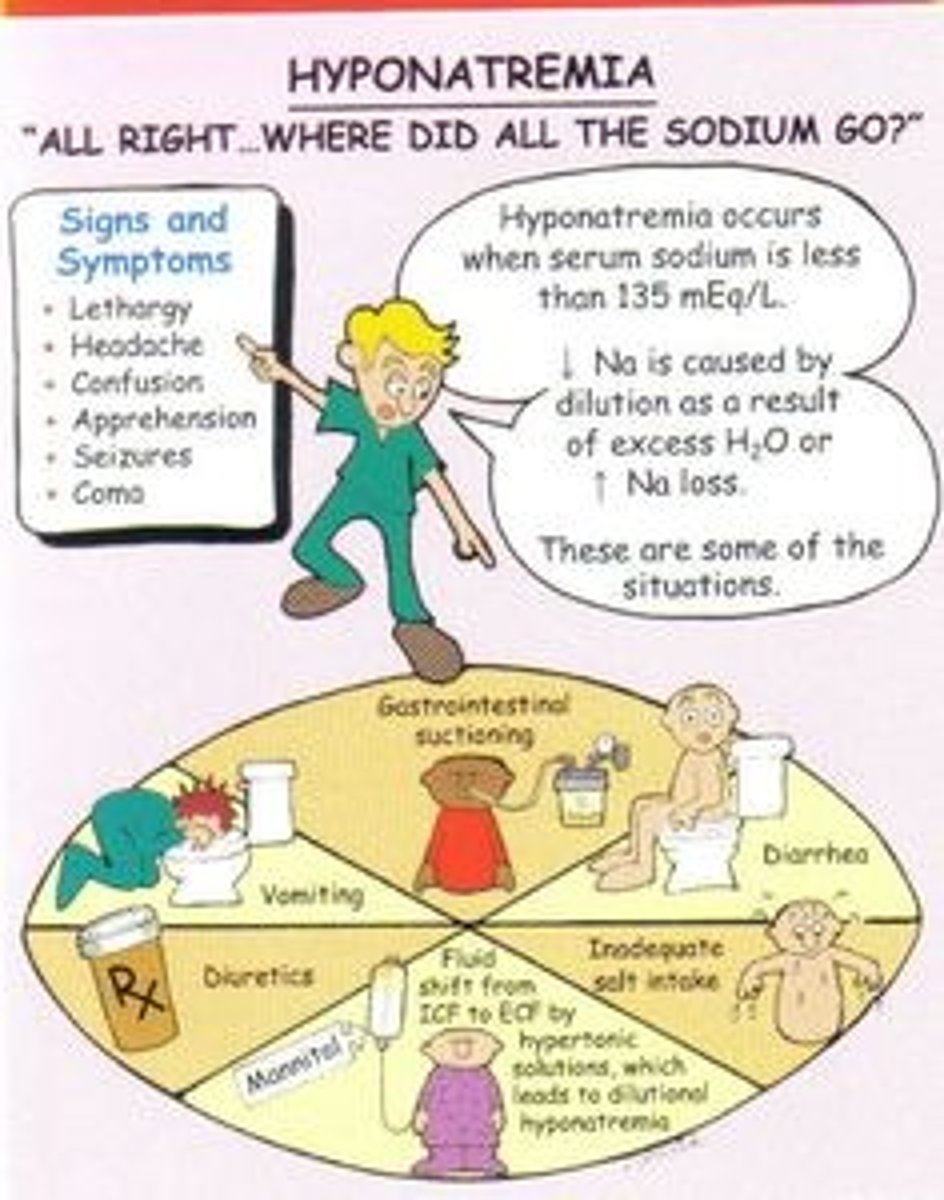
Hyponatremia
-Over dilution of blood due to excess water consumed post exercise -> mental confusion, seizures, coma
-Solute loss -> water retention, decreased BV and BP (circulatory shock)
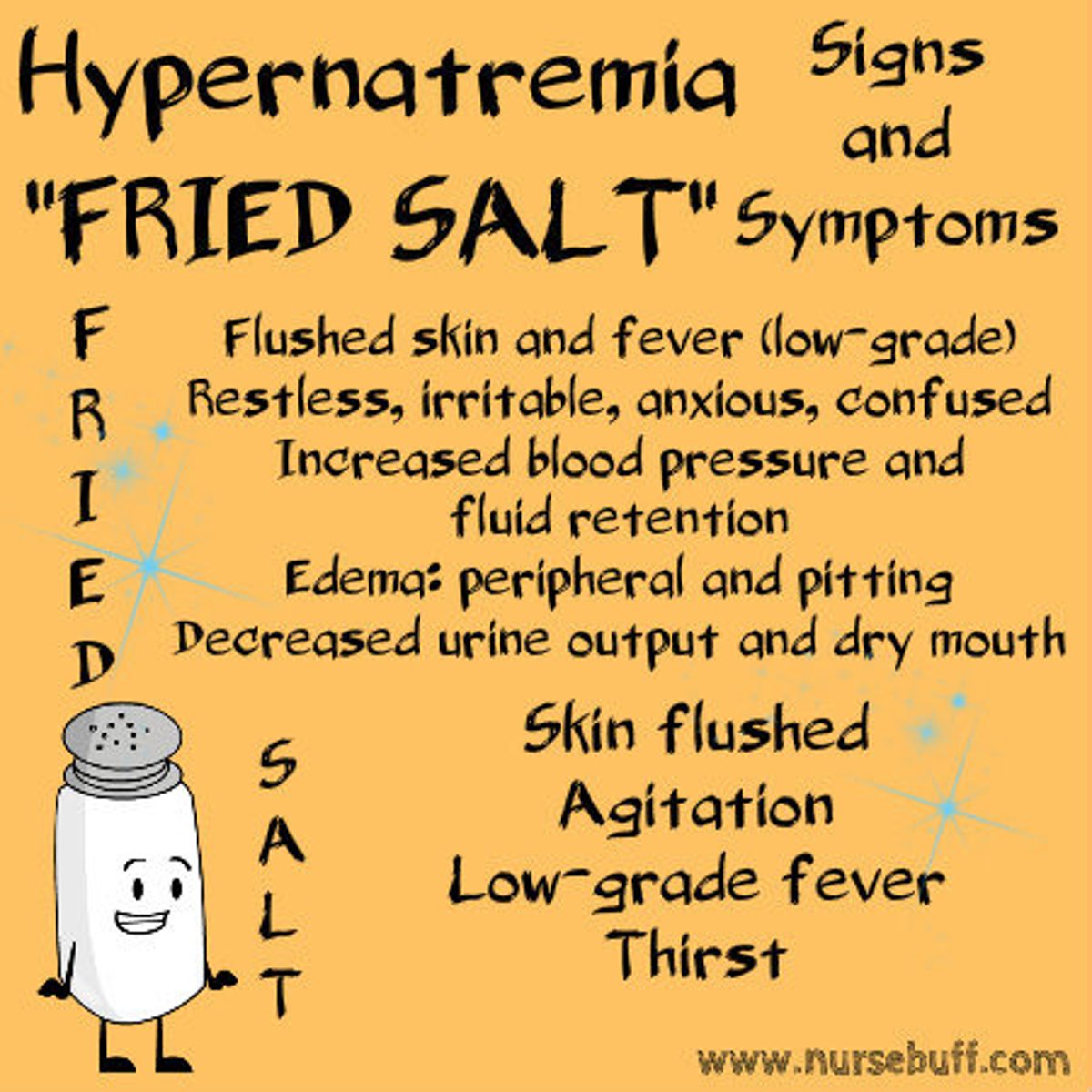
Hypernatremia
-Due to excess aldosterone secretion -> pulmonary edema and muscle convulsion
-May be caused by dehydration -> leads to thirst, confusion, lethargy, coma
Chloride
-Predominant anions of the ECF
-Accompanies sodium in ECF
Chloride Regulation
-Predominant cation sodium -> most important factor in regulation
-Acidosis -> less chloride accompanies sodium due to HCO3 reabsorption -> restore blood pH to normal
Hypochloremia
-Due to excess sweat, diuresis, vomiting, diarrhea,
-Low salt intake/SIADH
Hyperchloremia
-Dehydration
-High blood sodium (Cushing syndrome)
-Kidney disease
Potassium
-Chief intracellular cation
-Tightly regulated -> determine RMP for electrically excitable cells
Potassium Regulation
Regulated by aldosterone secretion
Elevated potassium -> aldosterone secretion -> increases sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion (depolarization and hyperpolarization)
Hypokalemia
-Excess potassium secretion -> due to excess elevation of aldosterone and insulin administration (activates sodium potassium pump)
-Fatigue, muscle cramps, temporary paralysis
-Due to water pills/diuretics
Hyperkalemia
Due to renal disease -> less renal excretion -> intestinal cramping, diarrhea, temporary paralysis
Calcium
-Role in exocytosis (including NT), muscle contraction
-Regulates AP in cardiac muscle, blood clotting
Sites for ECF Calcium Regulation
Kidneys, GI tract, and bones (majority)
Calcium Regulation
Deposit into and reabsorption from bone
Long term -> maintain balance between absorption across intestine wall and excretion by kidneys
Calcium Regulation Hormones
PTH, vitamin D, calcitonin
-PTH increases blood calcium via osteoclasts, renal tubules resorption
-Vitamin D absorbed in SI
-Calcitonin decreases blood calcium, inhibits osteoclasts preventing bone breakdown
Hypocalcemia
Affects PM permeability to sodium causing nerve and muscle tissue to spontaneous AP -> muscle tetany
Hypercalcemia
Prevents depolarization of nerve and muscle cells -> deposit CaCO3 salts in soft tissues -> irritation and inflammation
Can lead to cardiac arrhythmias
Phosphate
85% in the body in the form of CaPO4 salts in bone and teeth, the rest is in cells
Phosphate Roles
-Binds to lipids, proteins and carbs
-Component of DNA, RNA, ATP
-Regulate enzyme activity
-Act as buffer
Hypophosphatemia
Due to vitamin D deficiency
Alcohol abuse -> decreased blood clotting and WBC function
Hyperphosphatemia
Due to acute and chronic renal failure, decreased filtrate by kidneys, chronic laxative use
Magnesium
Stored in bones or ICF
Hypomagnesium
Due to alcohol abuse -> muscle convulsions and weakness
Hypermagnesemia
Rare
Due to renal failure -> nausea, hypotension, and low RR
Also due to chronic laxative use, excess ingestion of antacids, or magnesium intake