Lab Practical
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/137
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
1
New cards
What is the purpose of the second stop when using a micropipette?
This is the appropriate ending position for completely dispensing liquid from a micropipette tip
2
New cards
What is the metric system prefix for 10^0
Base Unit
3
New cards
What is the metric system prefix for 10^-3
Milli
4
New cards
What is the metric system prefix for 10^-6
Micro
5
New cards
What is the metric system prefix for 10^-9
Nano
6
New cards
53 mg = How many grams?
0.053g
7
New cards
Calculate the amount of grams of NaCl (58.44 g/mol) to prepare 2000 mL of 3M NaCl solution
350.64Ho
8
New cards
How many moles are in 6L of a 1.5M KOH solution? (56.11 g/mol)
9
9
New cards
The density of 2M NaCl is 1.077 g/mol. How much should 8mL of 2M NaCl weigh (round to 3 decimal places)
8.616
10
New cards
How many moles are in 471 mL of a 2M KOH (56.11 g/mol) solution?
0.942
11
New cards
What is the correct equation for calculation total magnification?
(Ocular mag) * (Objective mag)
12
New cards
You are working with a microscope with 20x ocular lenses and the following objective lenses: 4x, 20x, 400x. Suppose the field of view on this micoscope is 0.5 mm at a total magnification of 400x. Calculate the field of view when using the 4x objective.
2.5
13
New cards
A buffer is made up of:
A weak acid and its conjugate base
14
New cards
Given a stock solution of 8M NaOH, calculate the milliliters of stock solution needed to prepare 1 mL of a 152 mM NaOH solution
0.019
15
New cards
Water has a higher pH of lemon juice. What must be true regarding Water's concentration of hydrogen ions relative to lemon juice?
Water has a lower concentration of hydrogen ions than does lemon juice
16
New cards
What property of water is the basis for the pH scale?
Water self ionizes
17
New cards
What chemical in the reaction is the weak acid?
Na₂HPO₄ + H₂O ⇌ NaH₂PO₄ + OH⁻ + Na⁺
Na₂HPO₄ + H₂O ⇌ NaH₂PO₄ + OH⁻ + Na⁺
NaH₂PO₄
18
New cards
What is the pH of a solution with a concentration of 0.00003871M hydrogen ions?
4.41
19
New cards
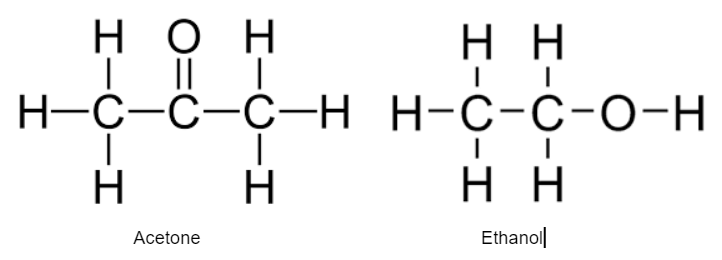
Which molecule is more nonpolar?
Acetone is more nonpolar than ethanol
20
New cards
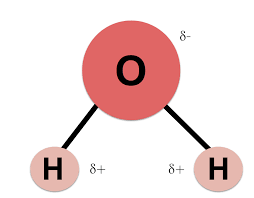
How many polar areas are present that allow water to interact with other polar molecules?
3
21
New cards
Given a stock solution of 9M NaOH, calculate the mL of stock solution needed to prepare 1 mL of a 168 mM NaOH
0.02 mL
22
New cards
Biuret reagent is used in a colorimetric test that can determine protein concentration by spectrophoteometry. Biuret regent specifically reacts with the presence of what?
Peptide bonds
23
New cards
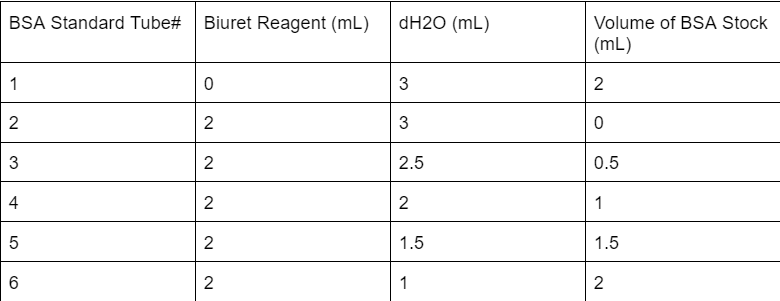
Which test tube is the appropriate blank for a Biuret protein assay?
Tube 2
24
New cards
What reagent was used as an indicator to detect the presence of lipids?
Sudan IV
25
New cards
What reagent was used as an indicator to detect the presence of carbs?
Benedict's Test
26
New cards
What reagent is used as an indicator to detect the presence of nucleic acids?
Ethidium Bromide
27
New cards
What reagent is used as an indicator to detect the presence of proteins?
Biuret reagent
28
New cards
All polysaccharides are this type of sugar
Non-reducing
29
New cards
What type of sugar is glucose?
Monosaccharide (reducing)
30
New cards
What type of sugar is glycogen?
Polysaccharide (non-reducing)
31
New cards
What type of sugar is starch?
Polysaccharide (non-reducing)
32
New cards
What type of sugar is lactose?
Disaccharide (reducing)
33
New cards
What type of sugar is galactose?
Monosaccharide (reducing)
34
New cards
What type of sugar is sucrose?
Disaccharide (non-reducing)
35
New cards
The only non-reducing disaccharide is?
Sucrose
36
New cards
What is bond for nucleic acids?
Phophodiester
37
New cards
What is bond for proteins
Peptide
38
New cards
What is bond for lipids?
Ester
39
New cards
What is bond for carbs?
Glycosidic
40
New cards
What type of sugar is cellulose
Polysaccharide (non-reducing)
41
New cards
Where will a noncompetitive inhibitor bind
Not to the active site
42
New cards
In the enzyme activity exercise, match each reagent to its role
Enzyme sodium diphosphate
Product phosphatase
Substrate p-nitrophenyl phosphate
Inhibitor p-nitrophenyl
Enzyme sodium diphosphate
Product phosphatase
Substrate p-nitrophenyl phosphate
Inhibitor p-nitrophenyl
Enzyme phosphatase
Product p-nitrophenyl
Substrate p-nitrophenyl phosphate
Inhibitor sodium diphosphate
Product p-nitrophenyl
Substrate p-nitrophenyl phosphate
Inhibitor sodium diphosphate
43
New cards
Select all the correct answers. pH can disrupt the structure of a protein by interfering with?
Primary structure
Secondary structure
Tertiary structure
Quaternary structure
Primary structure
Secondary structure
Tertiary structure
Quaternary structure
Secondary structure
Tertiary structure
Quaternary structure
Tertiary structure
Quaternary structure
44
New cards
T/F Enzymes work by adding energy to the reaction
False
45
New cards
The phosphatase enzyme used in lab consists of a single polypeptide chain. What is the highest level of organization displayed in this phosphatase enzyme?
Tertiary
46
New cards
T/F Phosphatases are a group of enzymes that add a phosphate group from the substrate
False
47
New cards
Why was the base sodium hydroxide added to the enzyme reaction mixture after incubation in the enzyme lab?
To ionize the product, producing a yellow solution
48
New cards
A patient sample was found to contain 0.110 U/mL of alkaline phosphatase. Normal levels of alkaline phosphatase are between 30 and 120 U/L. Is this patient sample within the normal range?
Yes
49
New cards
Digestion by pepsin will create:
Short peptides and amino acids
50
New cards
When swallowing what structure covers the trachea?
EpiglottisW
51
New cards
Food travels down what to the stomach?
Esophagus
52
New cards
This is one of the end products of the reaction catalyzed by lipase
Fatty acid
53
New cards
This reagent was used to detect the end product of the carbohydrate digestion reaction
Benedict-Q
54
New cards
What is the end product of the carbohydrate digestion reaction catalyzed by amylase?
maltose
55
New cards
Contractions of the longitudinal muscle layer in the intestines are responsible for moving food along the digestive tract. What is this process called?
Peristalsis
56
New cards
Enzymatic digestion begins in the mouth with the secretion of which enzyme?
Amylase
57
New cards
What secrets amylase?
Salivary glands
58
New cards
A synthetic cell is made of semi-permeable dialysis tubing and is filled with 10% sucrose. It is placed into a beaker containing 5% sucrose solution. What will happen to the cell?
The cell will gain weight as it takes on water
59
New cards
Diffusion is:
Movement of a molecule from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
60
New cards
Urea is able to cross the cell membrane and therefore is a penetrating solute. What are the osmolarity and tonicity of solution with 0.5M Osm Urea? The osmolarity of a cell is 0.3 Osm.
Hyperosmotic, hypotonic
61
New cards
Membranes are made up of many different compounds, like phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, etc. The ability of these components to move around one another is known as:
Fluid mosaic model
62
New cards
How many grams of solute would you need to make 200mL of 19% (w/v) CaCO3 (100.09 g/mol)?
38
63
New cards
Under the microscope, what did the cells who experienced lysis look like?
They were not there, they burst
64
New cards
Spiky red blood cells are in what state of tonicity?
Crenation
65
New cards
Neutral red is red under acidic conditions and yellow under basic conditions. In the positive control of the membrane integrity experiment, neutral red was added to a solution of yeast suspended in 1% sodium hydroxide. If you were to measure the pH of a solution, it would be basic and yet the solution turns red. Why?
The solution will turn red because neutral red is able to penetrate the cell membrane and the inside of the cell is acidic, even though the cell is in a basic solvent
66
New cards
T/F The maltose transporter is an example of active transport, in which ATP is hydrolyzed in order to move maltose into the cell.
TrueW
67
New cards
What is the substrate in the maltose transporter assay?
pNPalphaG
68
New cards
The maltose transporter protein is what kind of carrier protein?
Symporter
69
New cards
A molecule enters the cell through a transmembrane protein. The cell does not use ATP to import this molecule. What kind of transport is this?
Facilitated diffusion
70
New cards
What are the 3 processes carried out by the nephron?
Filtration, secretion, reabsorption
71
New cards
Smallest functional unit of the lung is called the: and is where gas exchange occurs
Alveoli
72
New cards
The lungs expand when there is an increase or decrease in thoraric cavity?
Increase
73
New cards
The lungs expand when this contracts
Diaphragm
74
New cards
In the aerobic respiration experiment, the dependent variable is best described as?
The amount of light transmitted through DCPIP solution
75
New cards
Where does glycolysis occur in the cell?
Cytoplasm
76
New cards
DCPIP is clear in its _____ state?
Reduced
77
New cards
Sequence the following structures to reflect the branching path of blood through the body beginning with air being taken in (Trachea, bronchi, Alveoli, Larynx, bronchioles, nares)
Nares
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchi
Bronchioles
Alveoli
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchi
Bronchioles
Alveoli
78
New cards
Breathing in humans is the result of?
Negative pressure
79
New cards
Where does fermentation occur in the cell?
Cytoplasm
80
New cards
In the fermentation experiments the dependent variable is best described as?
Volume of CO2 gas produced
81
New cards
For the yeast fermentation experiment, a mixture of yeast + glucose + water was incubated in the temperatures listed below. Match temperatures with expected outcome
0 C
22 C
45 C
100C
Maximum CO2 produced, optimal temperature
No Co2 produced, limited free energy
Small amount of CO2 produced, limited free energy
No CO2 produced, proteins denatured
0 C
22 C
45 C
100C
Maximum CO2 produced, optimal temperature
No Co2 produced, limited free energy
Small amount of CO2 produced, limited free energy
No CO2 produced, proteins denatured
0: No Co2 produced, limited free energy
22: Small amount of CO2 produced, limited free energy
45: Maximum CO2 produced, optimal temperature
100: No CO2 produced, proteins denatured
22: Small amount of CO2 produced, limited free energy
45: Maximum CO2 produced, optimal temperature
100: No CO2 produced, proteins denatured
82
New cards
Based on glycolysis and lactose intolerance, speculate what might cause trehalose intolerance. Lactaid is brand name product which contains the enzyme lactase. Trehalose is a disaccharide produced in some insects as energy storage
The experiments showed glycolysis does not occur significantly without lactase which breaks down lactose. Trehalose intolerance could occur if insects do not posess the proper enzyme to break down trehalose. There is nothing that cleaves the bonds of trehalose. However just like how lactase can be obtained in the form of lactaid, the enzyme that breaks down trehalose can likely be obtained in other ways
83
New cards
Blood is sent from heart to body when muscles of the:
Ventricles contract
84
New cards
Select all answers that are monosaccharides
Glucose
Fructose
Galactose
Sucrose
Glucose
Fructose
Galactose
Sucrose
Glucose, Fructose, Galactose
85
New cards
Oxygenated blood travels from lungs to the heart via the:
Pulmonary vein
86
New cards
During PCR, thermal cycler switches between three different temperatures. Match what occurs in the PCR reaction with the appropriate temperature
45C, 60C, 72C, 95C
Taq olymerase adds nucleotides to growing chain of replicated DNA
Double stranded DNA molecules come apart
Primers base pair and bind to their target sequence on DNA template
This is not a temperature used in PCR reaction
45C, 60C, 72C, 95C
Taq olymerase adds nucleotides to growing chain of replicated DNA
Double stranded DNA molecules come apart
Primers base pair and bind to their target sequence on DNA template
This is not a temperature used in PCR reaction
45C: Not used
60C: Primers base pair and bind to target sequence
72C: Taq polumerse adds nucleotides...
95C: Double stranded DNA comes apart
60C: Primers base pair and bind to target sequence
72C: Taq polumerse adds nucleotides...
95C: Double stranded DNA comes apart
87
New cards
Determine correct DNA sequence from the mRNA sequence:
3'-GGA-UAC-AGC-AGA-AAU-GCU-UUA-5'
3'-GGA-UAC-AGC-AGA-AAU-GCU-UUA-5'
5'-CCT-ATG-TCG-TCT-TTA-CGA-AAT-3'
88
New cards
Transcribe the following DNA sequence to its corresponding mRNA:
AAATGCGCTA
AAATGCGCTA
UUUACGCGAU
89
New cards
Where does translation occur?
At the ribosomes in the cytoplasm
90
New cards
Gene is performing a DNA extraction but did not recover any DNA. He forgot the step where he was supposed to add the lysis buffer solution. How would this misstep result in a poor recovery of DNA?
Without the lysis buffer, the cells would be intact and the DNA will not be free in solution to be precipitated.
91
New cards
Using mRNA sequence and codon chart pictured below, determine the first amino acid to be produced. You can assume the ribosome attaches directly before the shown nucleotide sequence begins.
mRNA sequence:
5'-UCA-AAG-AUG-CUC-GUA-UGA-AGA-CCA-3'
mRNA sequence:
5'-UCA-AAG-AUG-CUC-GUA-UGA-AGA-CCA-3'
Met
92
New cards
Assuming perfect efficiency, the number of PCR products present in solution doubles after each cycle of a PCR reaction. Given that 2⁵=32, explain why there will be more than 32 copies of PCR product after 5 cycles of PCR.
The PCR begins with multiple copies of the template DNA, so more than one PCR product is produced by the first cycle
93
New cards
What is the function of the lacY gene?
Transports lactose into the cell
94
New cards
Describe how negative regulation of the lac operon is relieved when lactose is encountered. Specifically mention key molecules involved.
Negative regulation is when the repressor Lacl binds to the operator preventing lac expression. Lactose interacts with LacZ (beta-galactosidase) to create allolactose which binds to the repressor causing the repressor not to be able to bind to the operator.
95
New cards
T/F Large DNA molecules travel further than small DNA molecules during electrophoresis
False
96
New cards
In an electrolytic cell type, the anode has a ___ charge?
Positive
97
New cards
What is function of loading dye?
Binds to DNA sample, increasing density
98
New cards
T/F Operons are units of linked genes and their regulatory elements
99
New cards
An induced enzyme produced by cells only in the presence of a specific chemical, called the ___
Inducer
100
New cards
What does the Lacl protein (repressor) physically do to prevent expression of the lac operon?
Binds to the operator, preventing the ribosome from binding or progressing past the promoter.