AP Biology Unit 5 - Heredity
1/72
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Genome
The genetic material of an organism or virus
Chromosomes
structures made of one DNA molecule and proteins
Somatic Cells
body cells
Gametes
reproductive cells
Chromatin
The complex of DNA and proteins that makes up eukaryotic chromosomes.
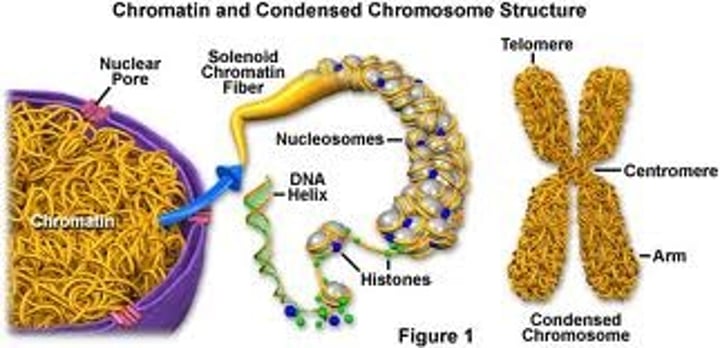
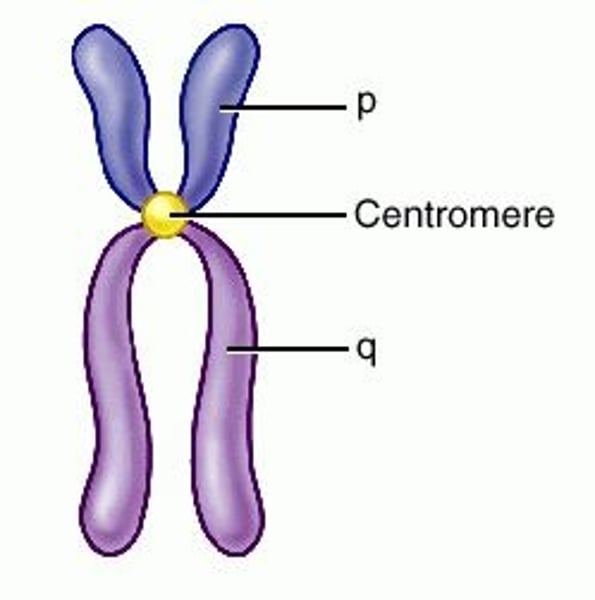
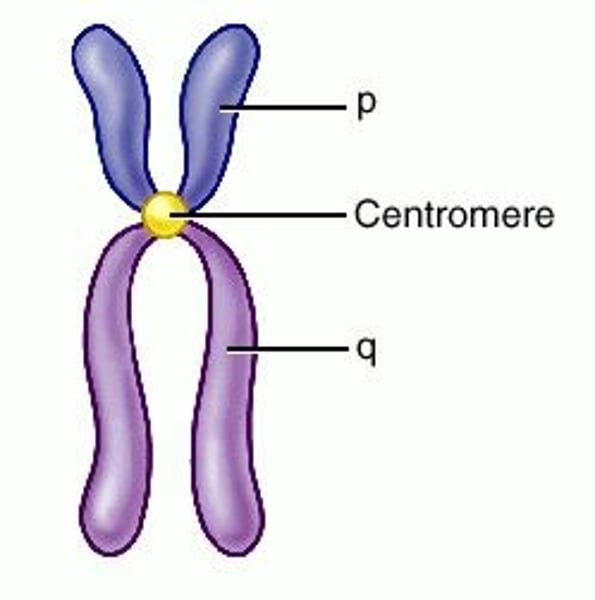
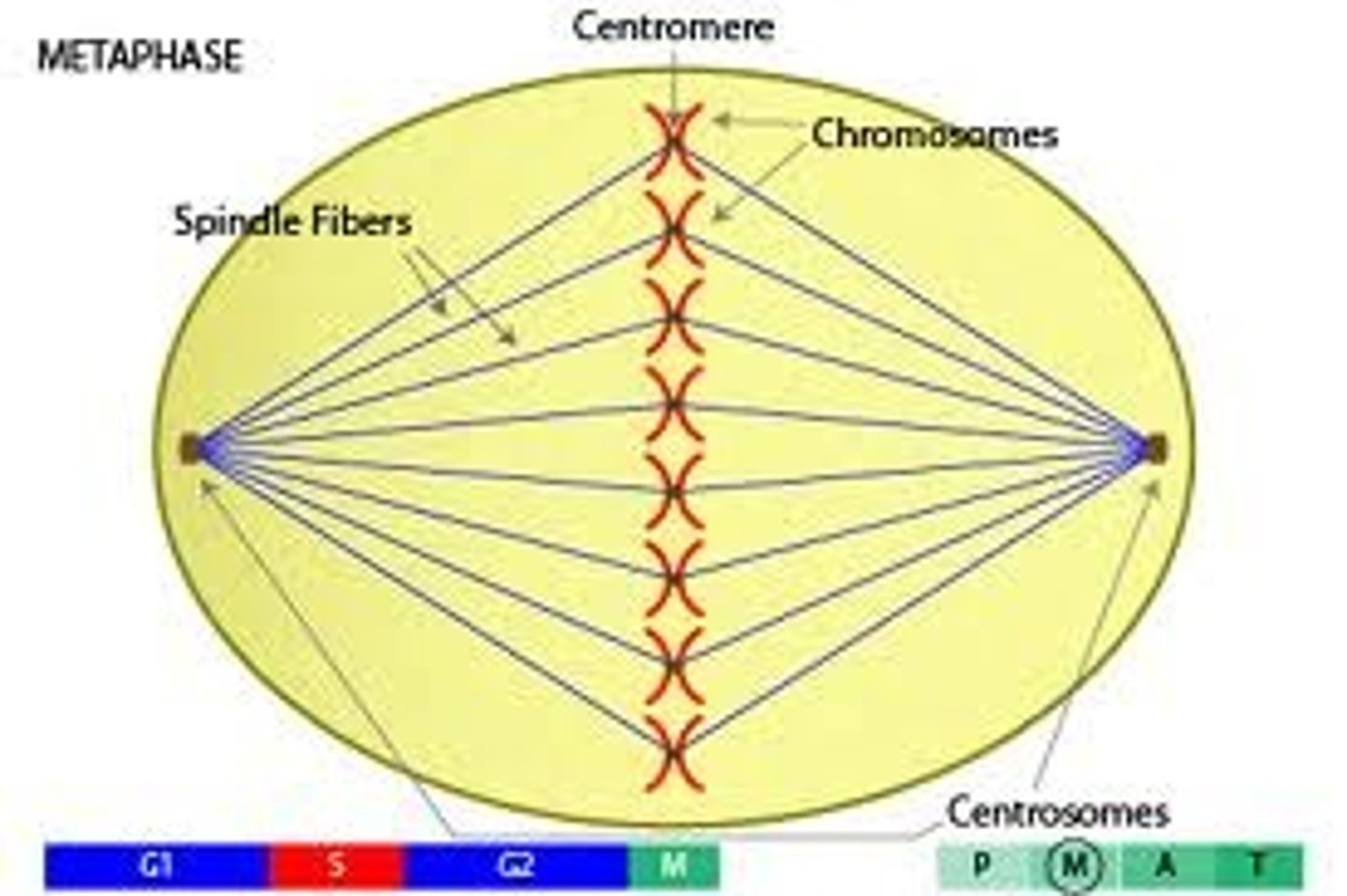
Centromere
Point on a chromosome by which it is attached to a spindle fiber during cell division.
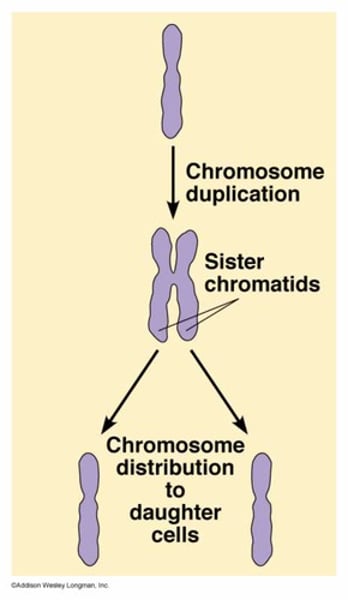
Sister Chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome; full sets of these are created during the S subphase of interphase.
Mitosis
division of the nucleus into two identical daughter nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells(immediately after mitosis, meiosis I, or meiosis II.)
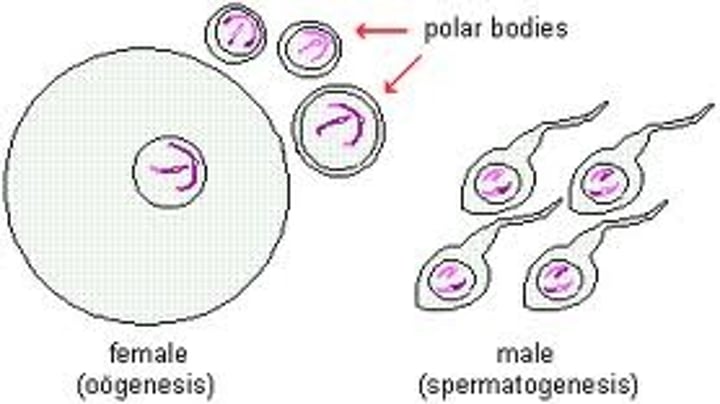
Meiosis
Cell division producing haploid gametes
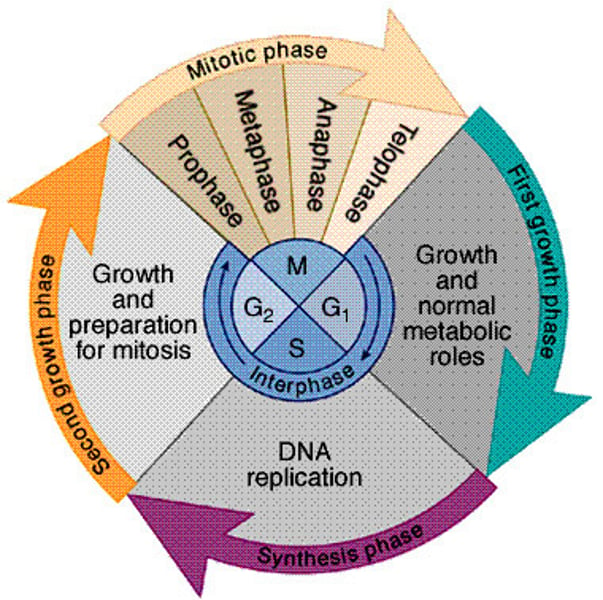
Mitotic (M) Phase
mitosis and cytokinesis
Mitosis: Cell separates and divides chromosomes
Cytokines: Cell divides cytoplasm and organelles.
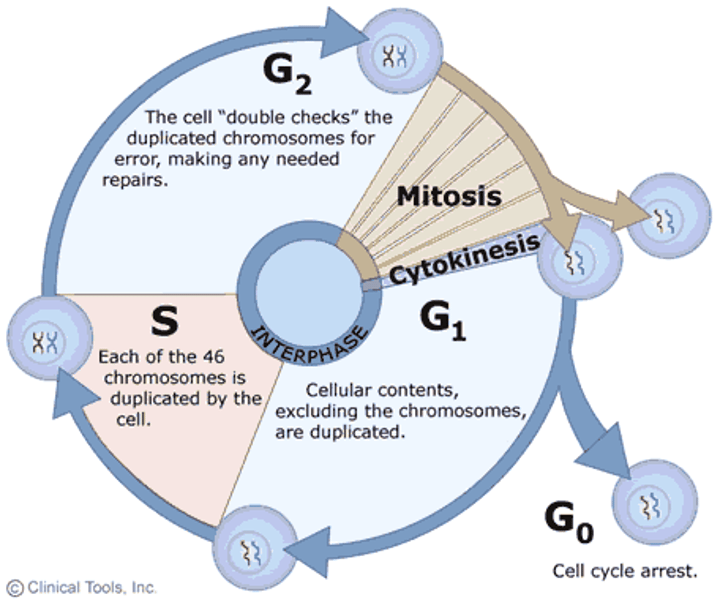
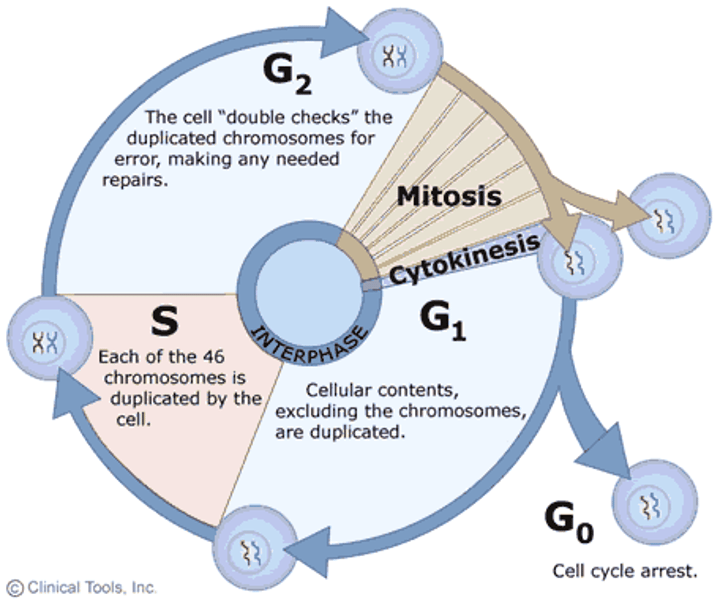
Interphase
Cell grows, replicates chromosomes, produces new organelles and cyclins.
G1 phase
Cell grows, duplicates organelles, and gathers materials for DNA replication.
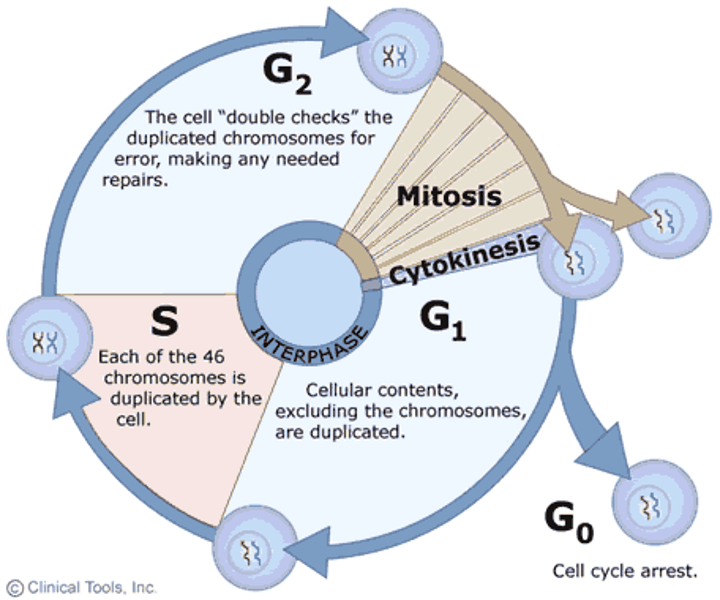
S phase
DNA replication occurs
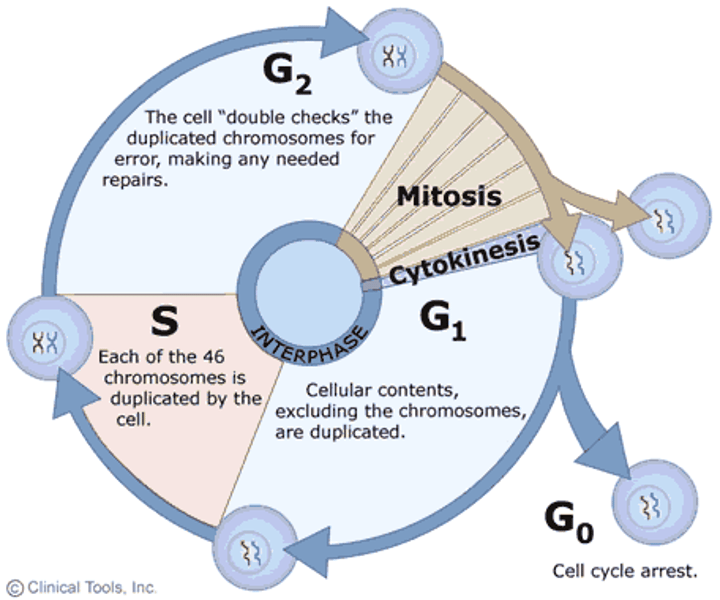
G2 Phase
growth and final preparation for division, nucleus well defined.
Mitotic Spindle
a structure made of microtubules that controls chromosome movement during mitosis
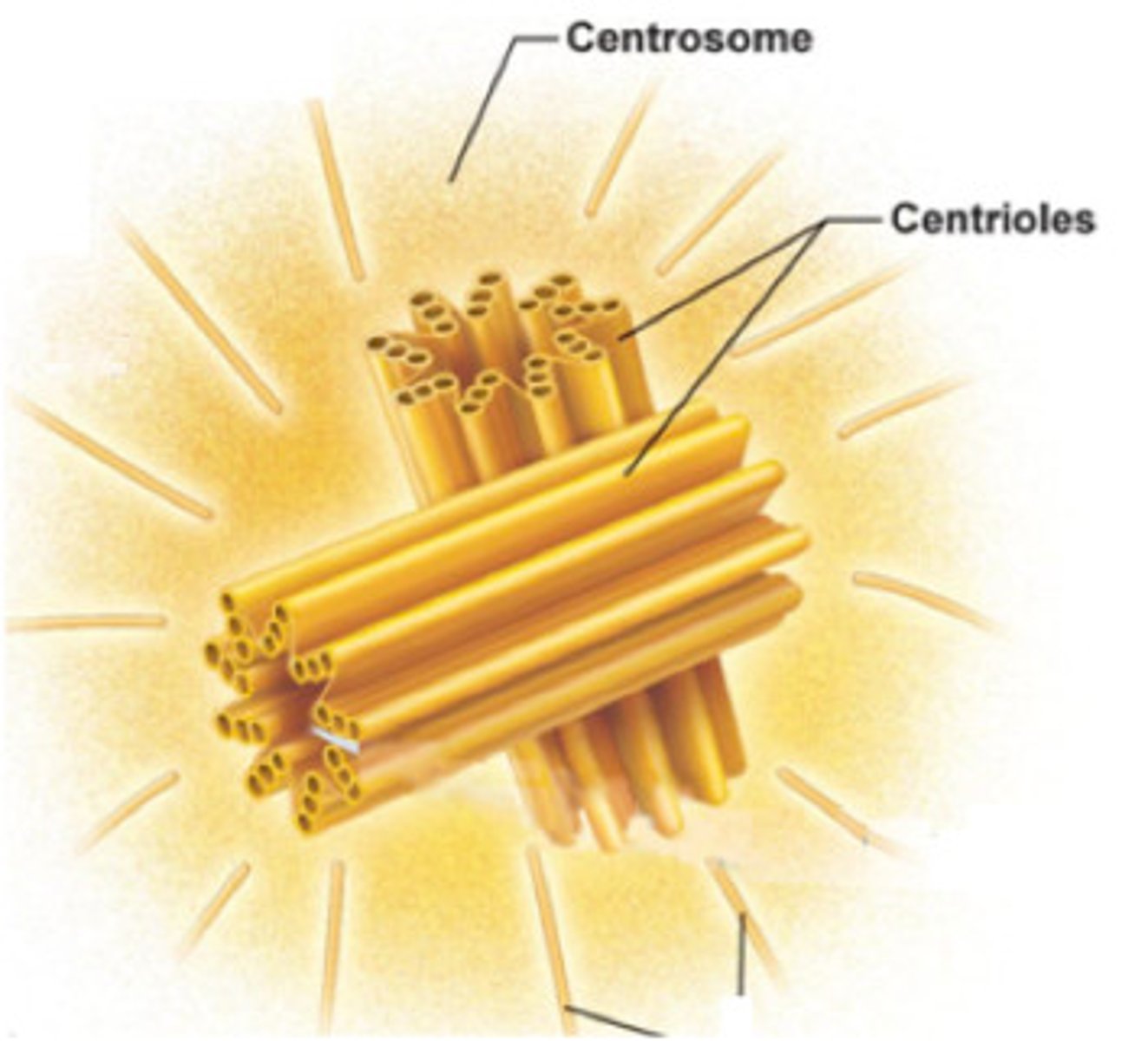
Centrosome
A structure that functions as the microtubule organizing center and is important during cell division, has two centrioles.
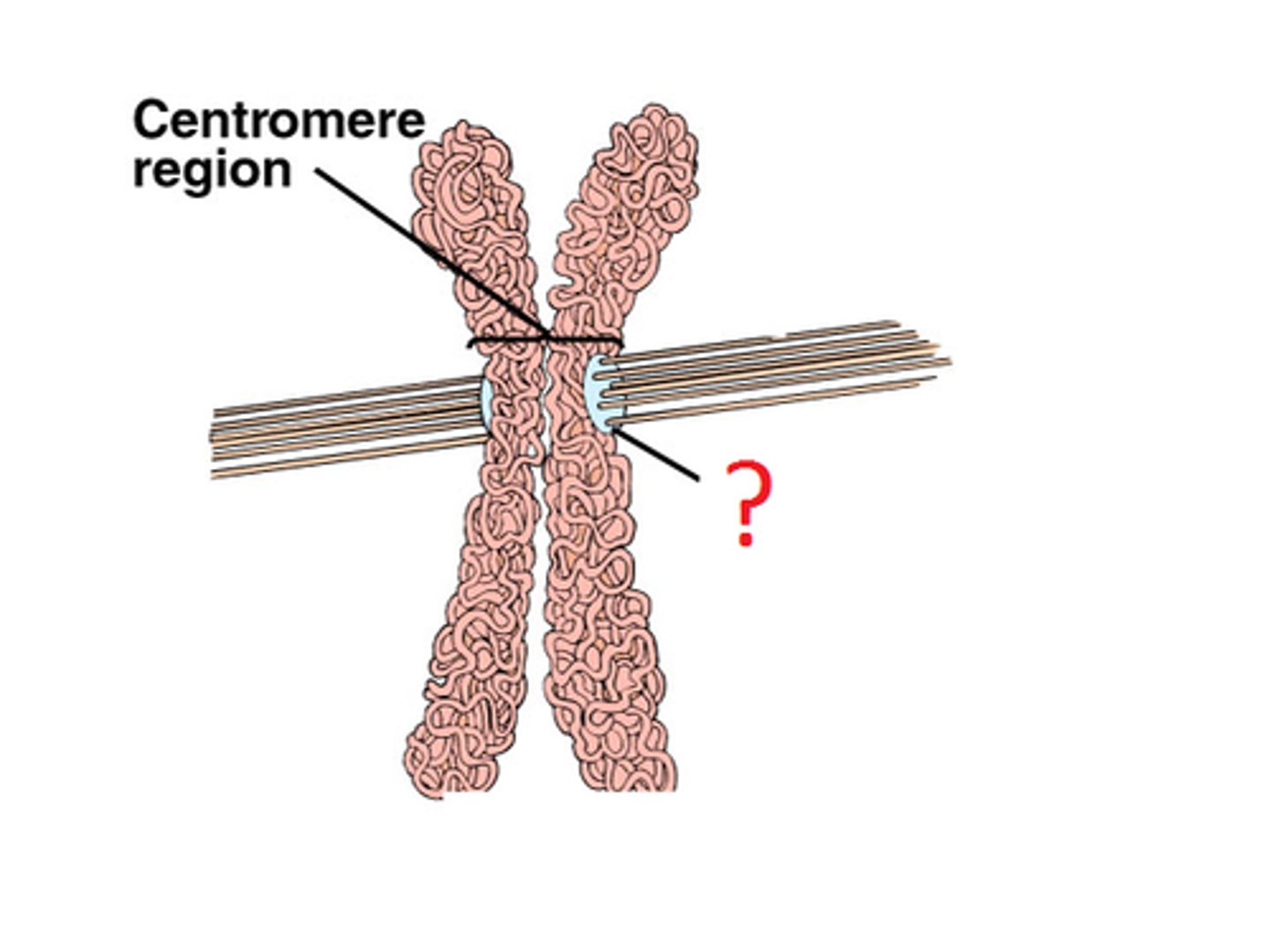
Kinetochore
A structure within the centromere containing the motor protein dynein. Moves the chromosomes apart during anaphase.
Cell Cycle Control System
A cyclically operating set of molecules in the eukaryotic cell that both triggers and coordinates key events in the cell cycle.
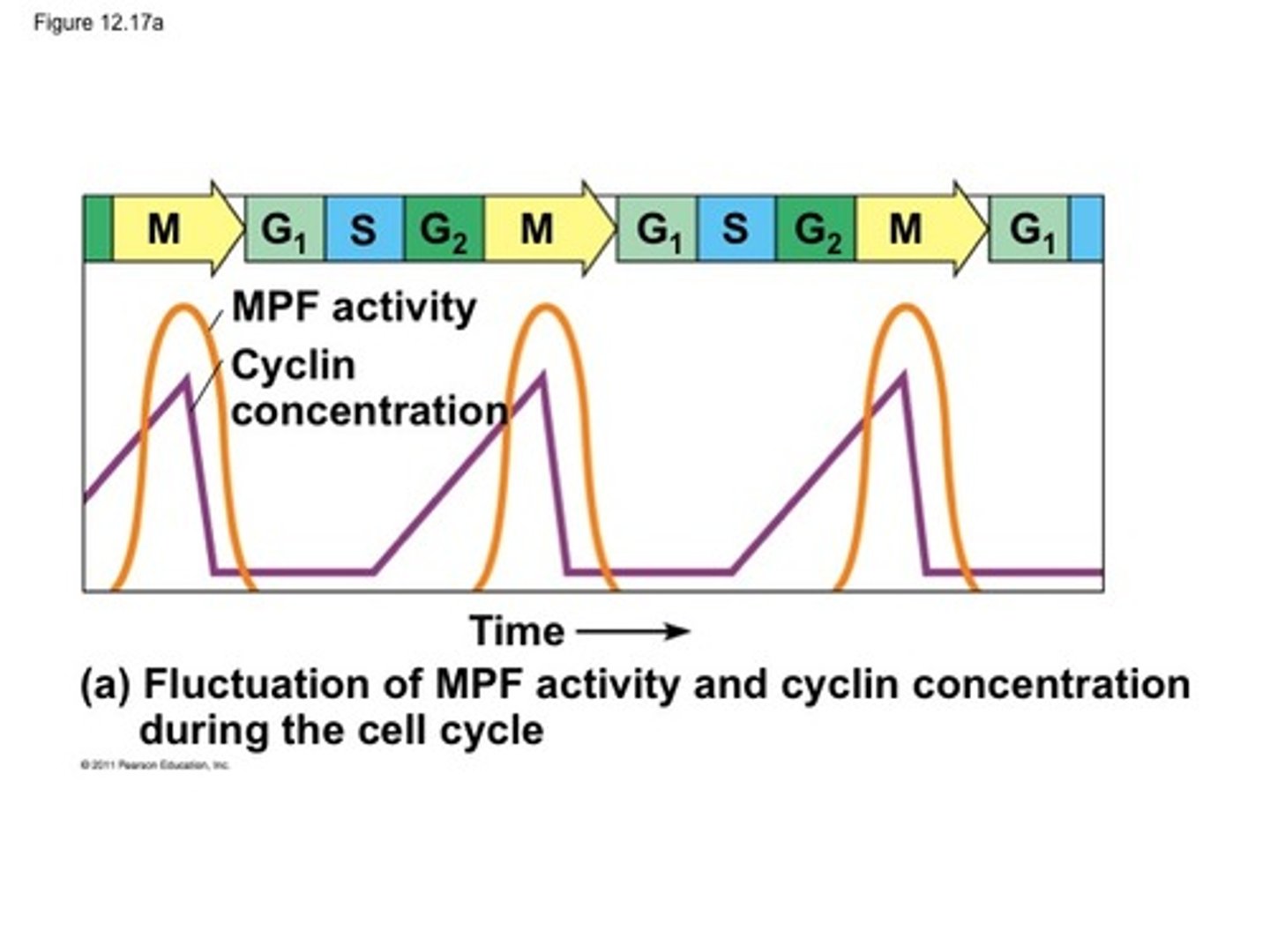
Cyclin
a protein that regulates the cell cycle
CDK
(Cyclin-dependent kinases) A protein kinase that is active only when attached to a particular cyclin. Activity rises and falls depending on the concentration of the cyclin partner.

MPF
(Maturation-promoting factor) a protein complex required for a cell to progress from late interphase to mitosis. The active form consists of cyclin and a protein kinase.
growth factors
Regulatory proteins, ensure that cell division occurs properly
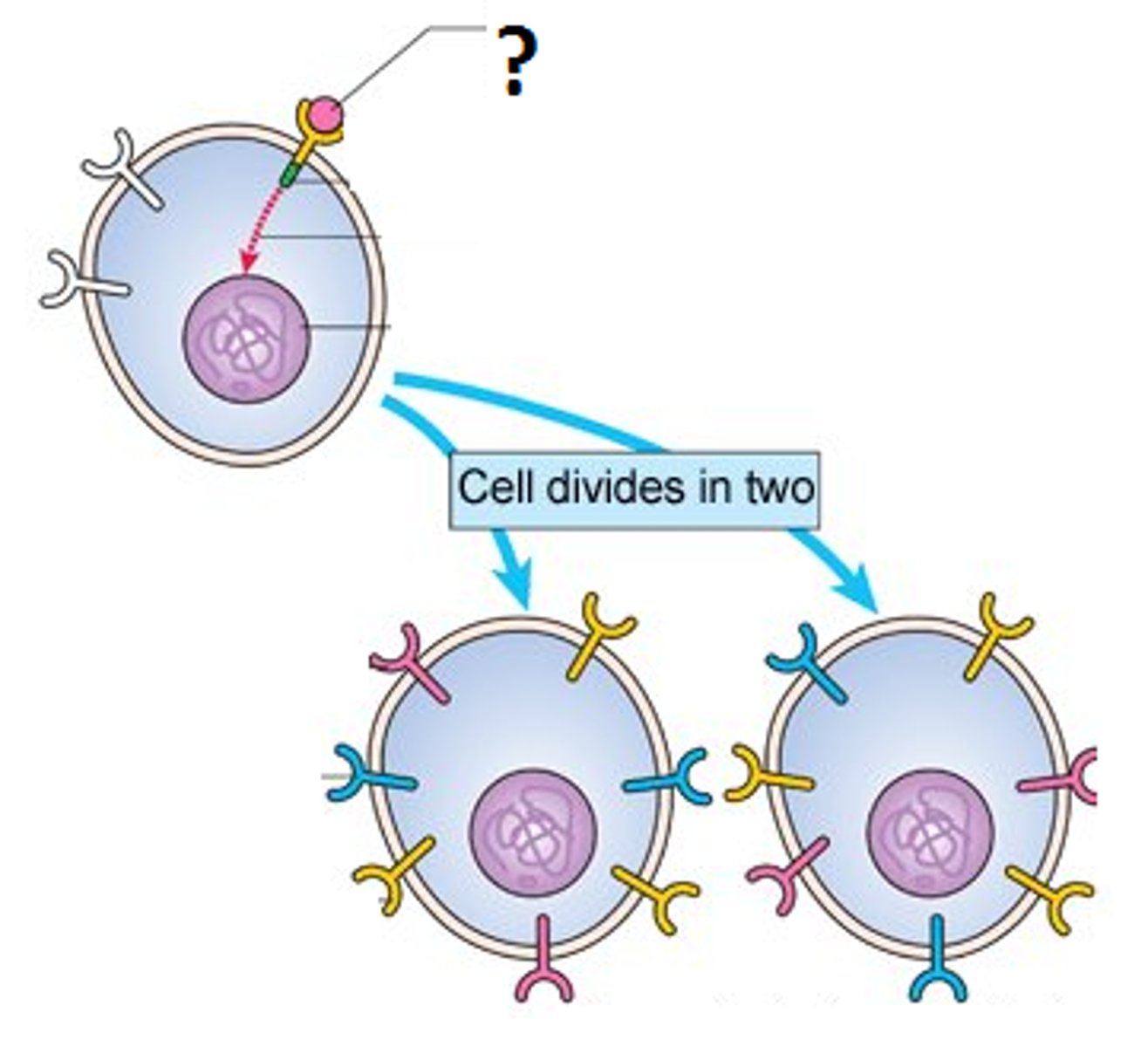
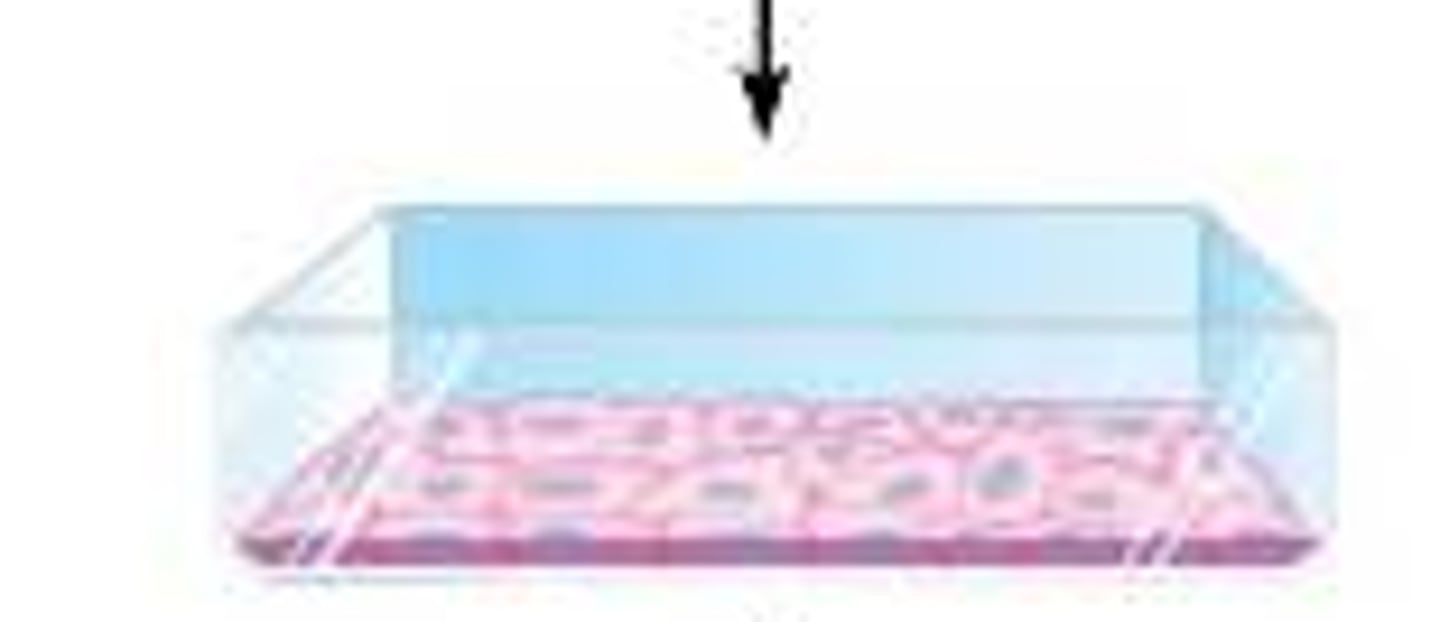
Density Dependent Inhibition
crowded cells stop dividing
Prophase
Chromosomes become visible, nuclear envelope dissolves, spindle forms
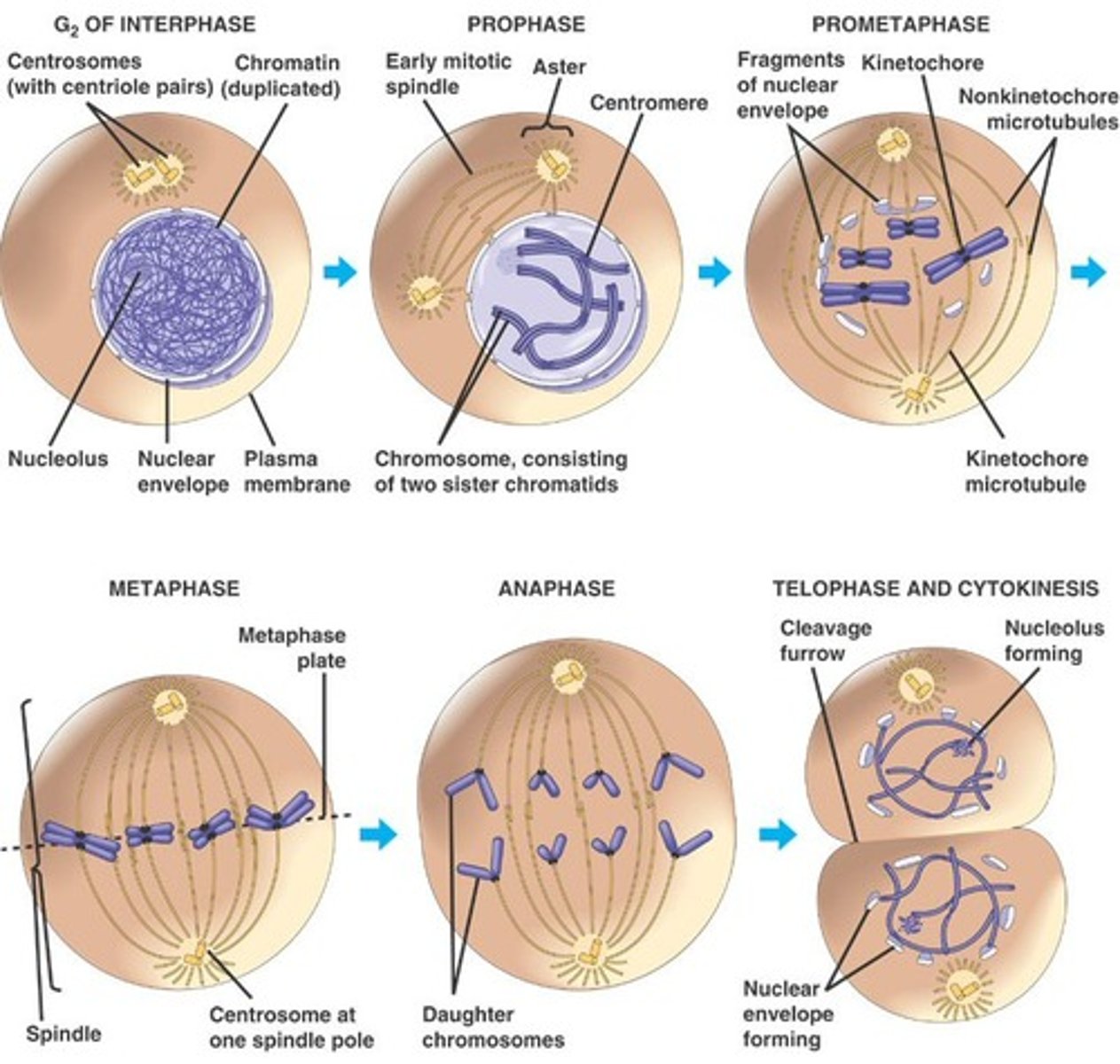
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase
the chromatids (Mitosis) or homologous chromosomes/chromatids (Meiosis) separate and move toward opposite poles
Telophase
The chromosomes begin to stretch out and lose their rodlike appearence. A new nuclear membrane forms around each region of chromosomes.
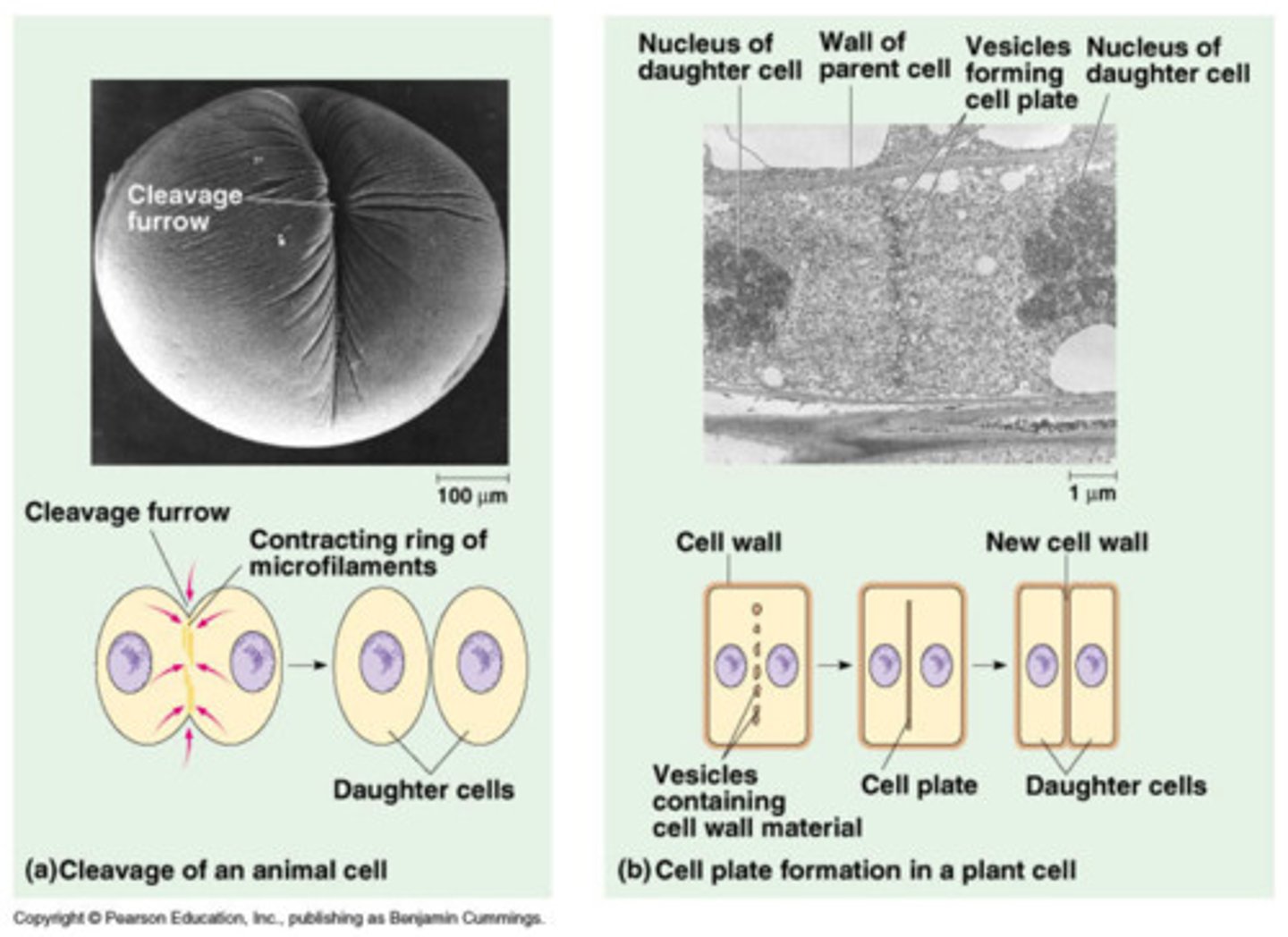
Cytokinesis in plants
cell plate forms
Cytokinesis in animals
Cleavage furrow forms
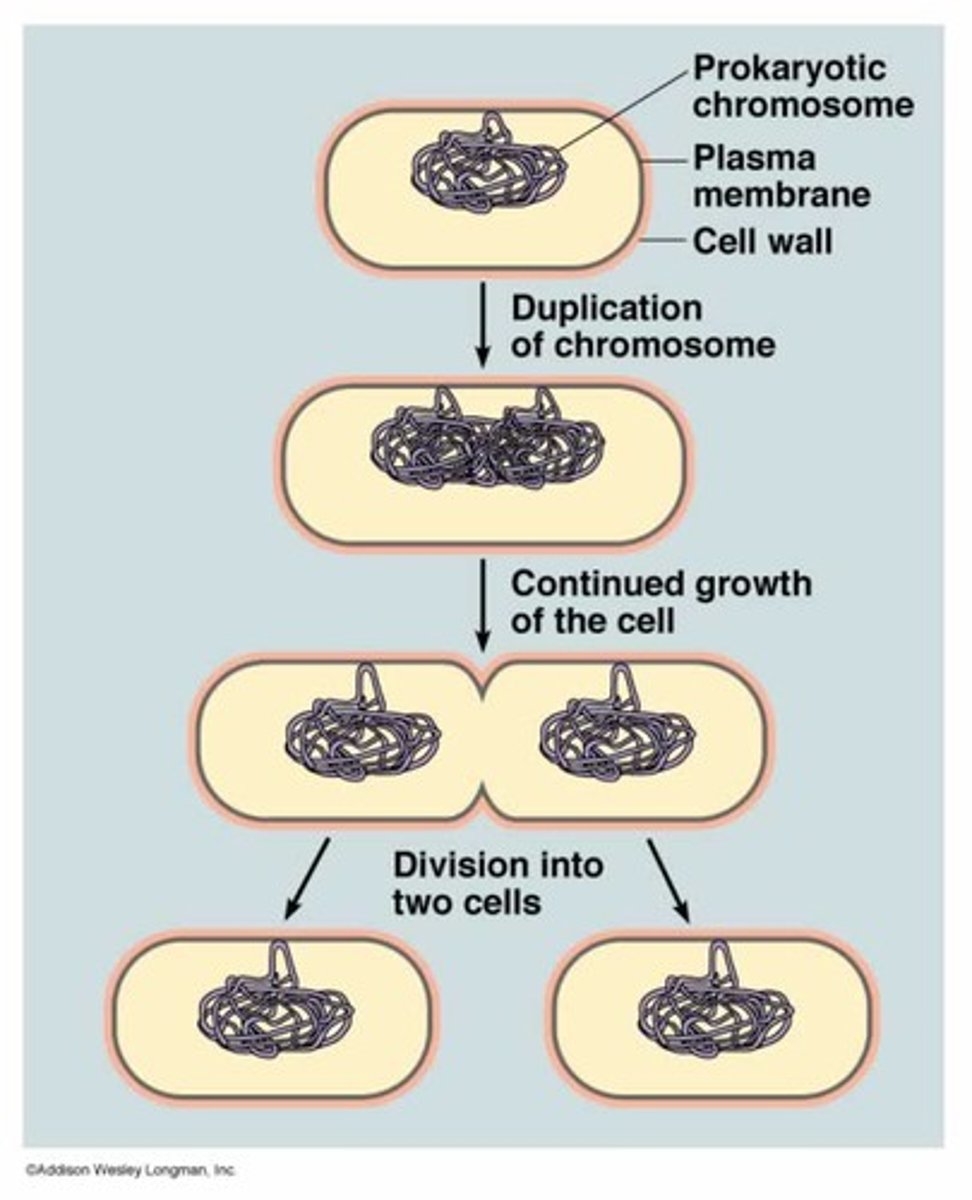
Binary Fission
one cell divides to form two identical cells
Karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape.
homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes that have the same sequence of genes, though may have different alleles (versions) of those genes. Maternal/Paternal
Sex Chromosomes
X and Y chromosomes.
Autosomes
non-sex chromosomes
Diploid
2 sets of chromosomes
Haploid
having a single set of unpaired chromosomes
Fertilization
Fusion of an egg and sperm cell
Zygote
diploid fertilized egg
Crossing Over
exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during prophase I of meiosis
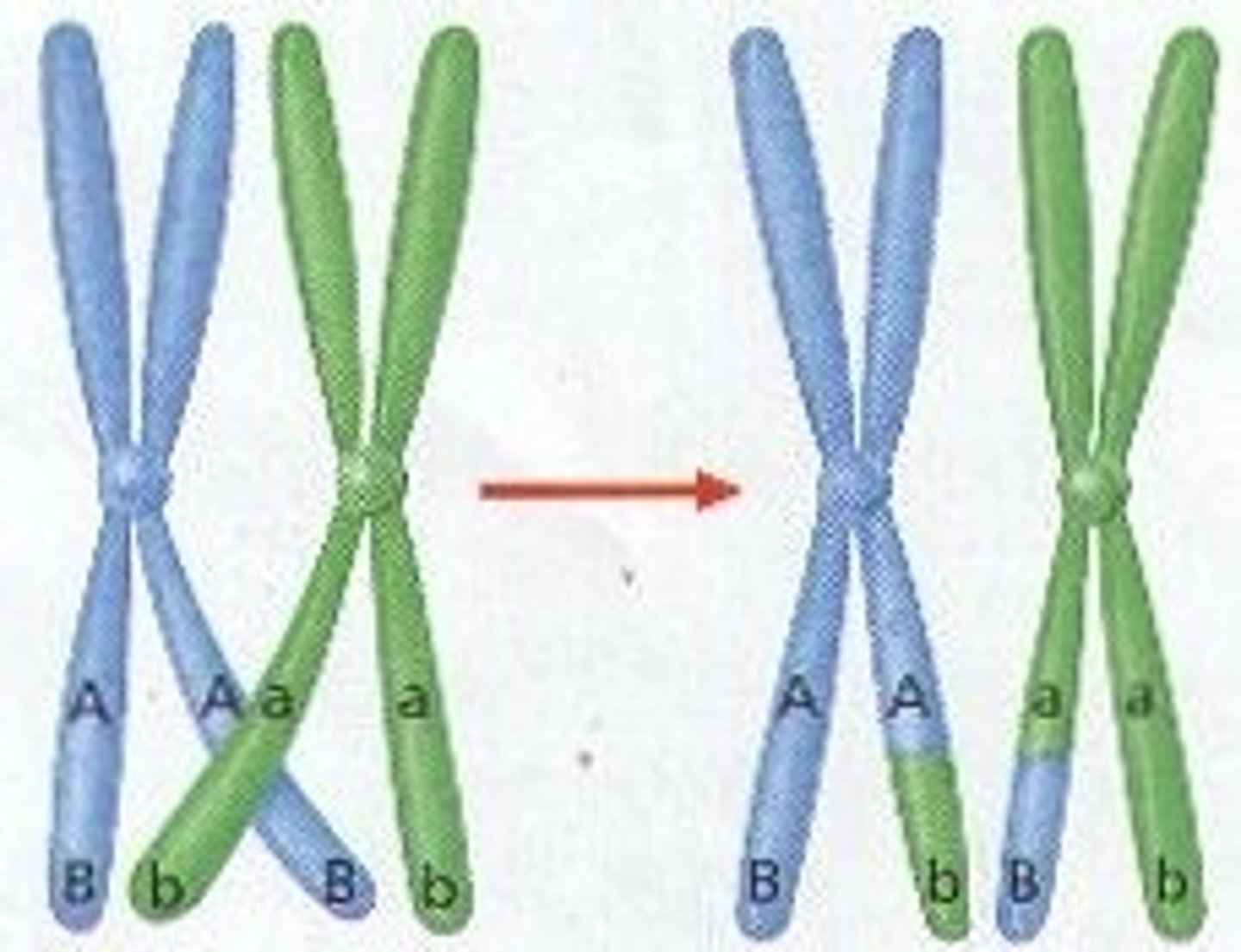
Tetrad
structure containing 4 chromatids that forms when homologs pair during meiosis
True Breeding
have identical alleles of a given gene/ homozygous
Hybridization
The cross of two true-breeding parents. (BB x bb)
P generation
Parental Generation
F1 generation
offspring of the P generation
F2 generation
offspring of the F1 generation
Alleles
Different forms of a gene
Punnet Square
A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross
Homozygous
having two identical alleles for a trait. BB or bb
Heterozygous
having two different alleles for a trait. Bb
Phenotype
physical characteristics of an organism (blue eyes)
Genotype
genetic makeup of an organism (bb)
Mendel's Law of Segregation
Alleles segregate from one another during the formation of gametes. (due to independent assortment)
Monohybrid
A cross between individuals that involves one pair of contrasting traits
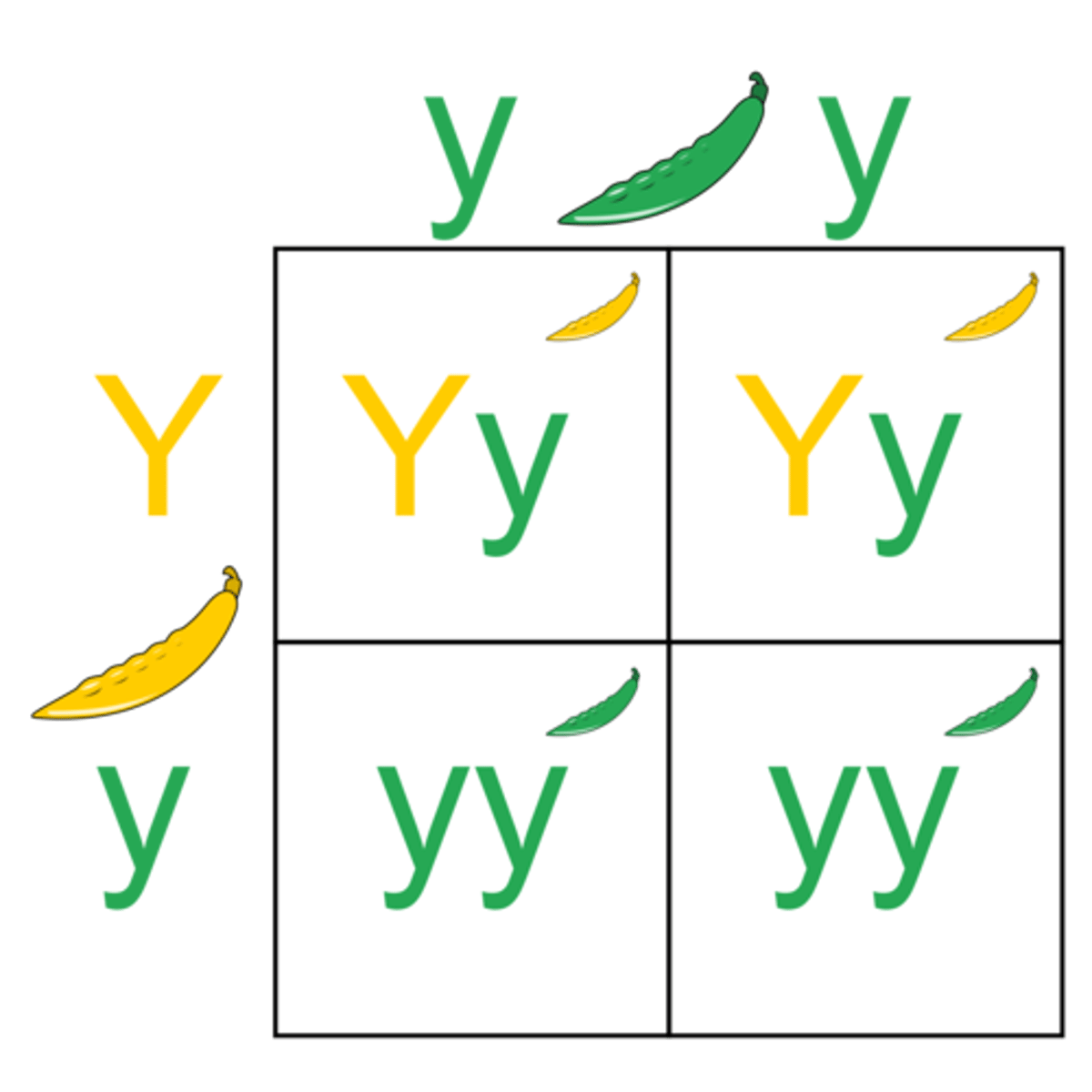
Dihybrid Cross
a cross between individuals that involves two pairs of contrasting traits
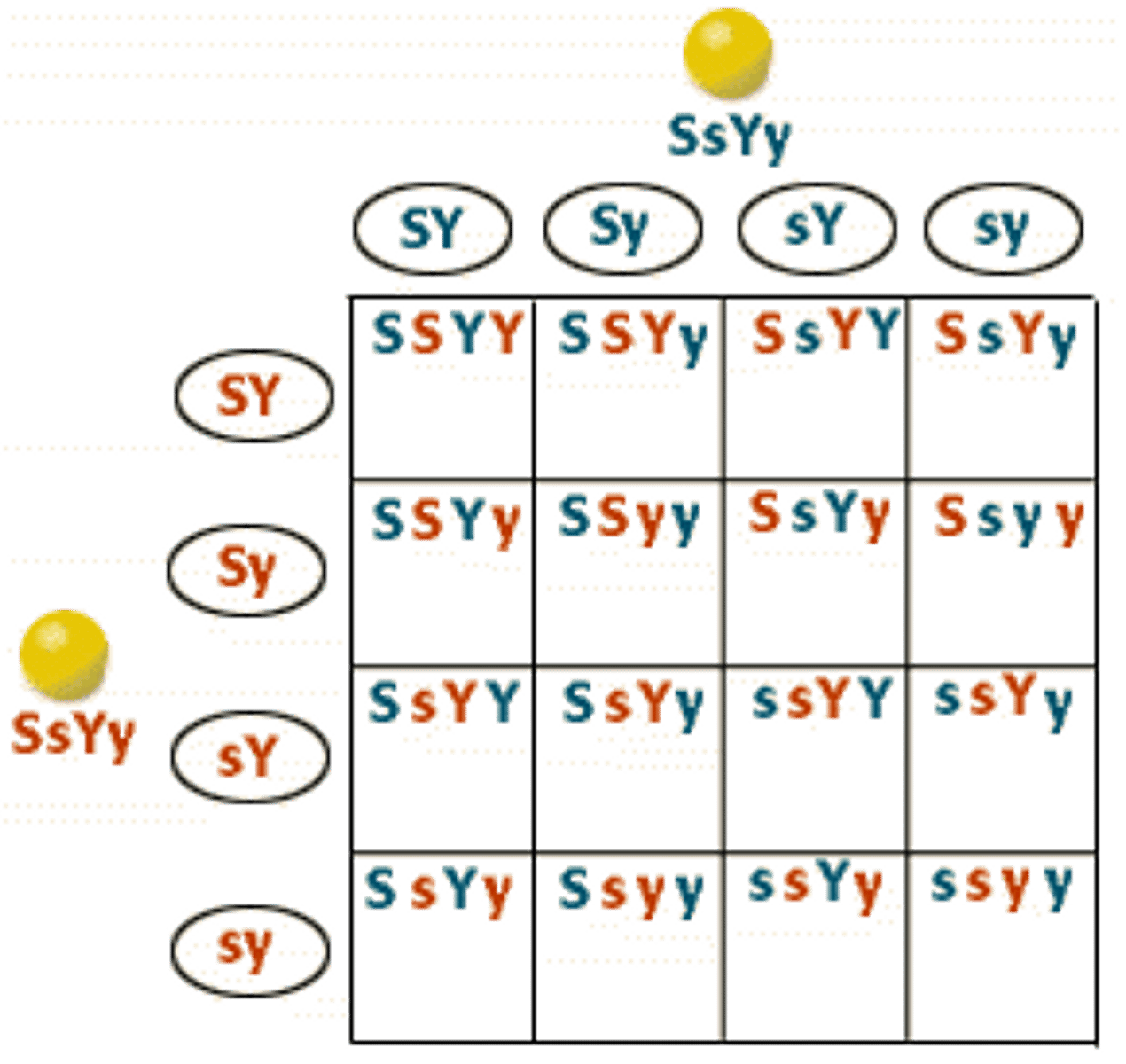
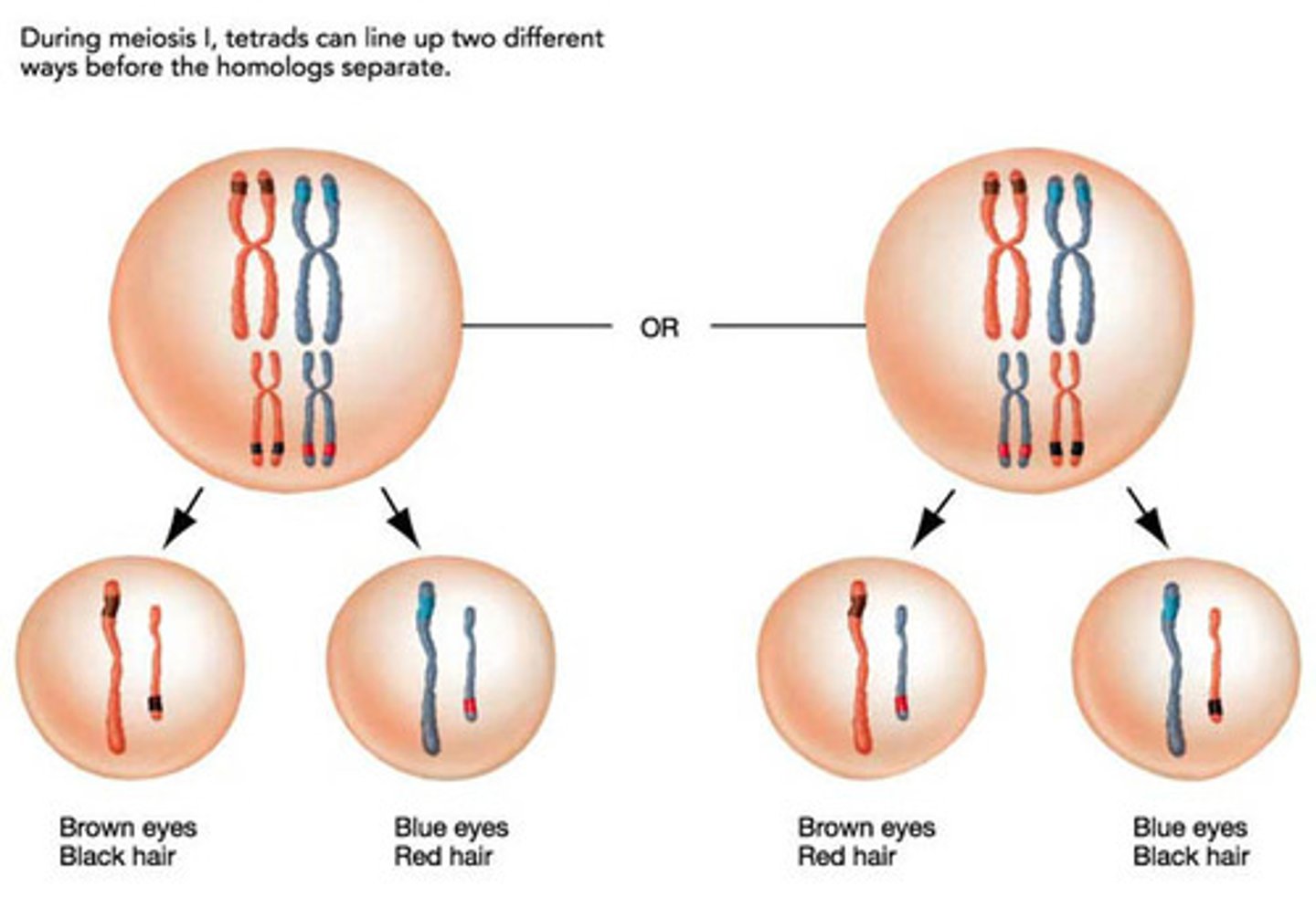
law of Independent Assortment
non-linked genes separate into gametes independent of one another in meiosis
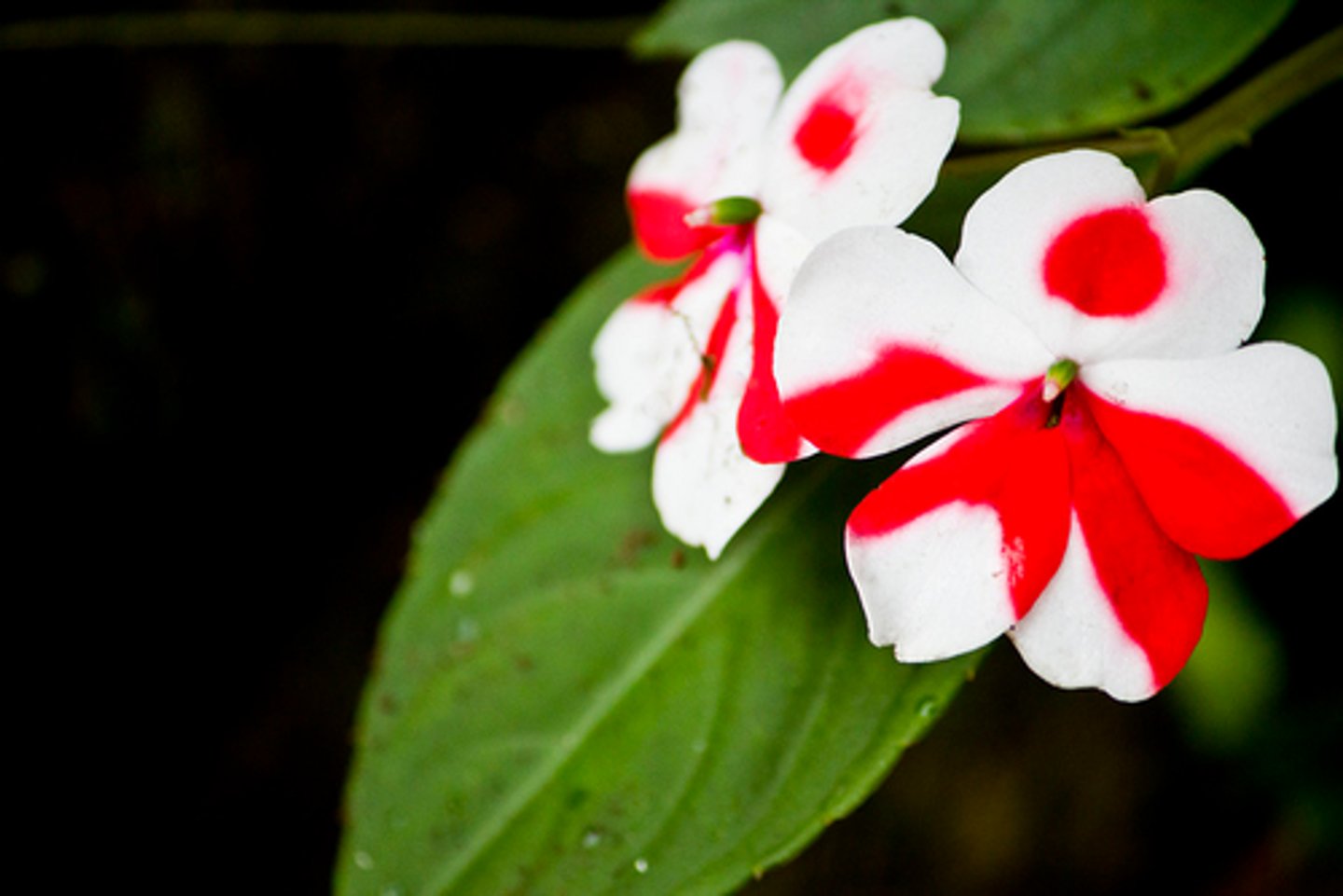
Codominance
A condition in which both proteins produced by the alleles for a gene are fully expressed. (spots/stripes)

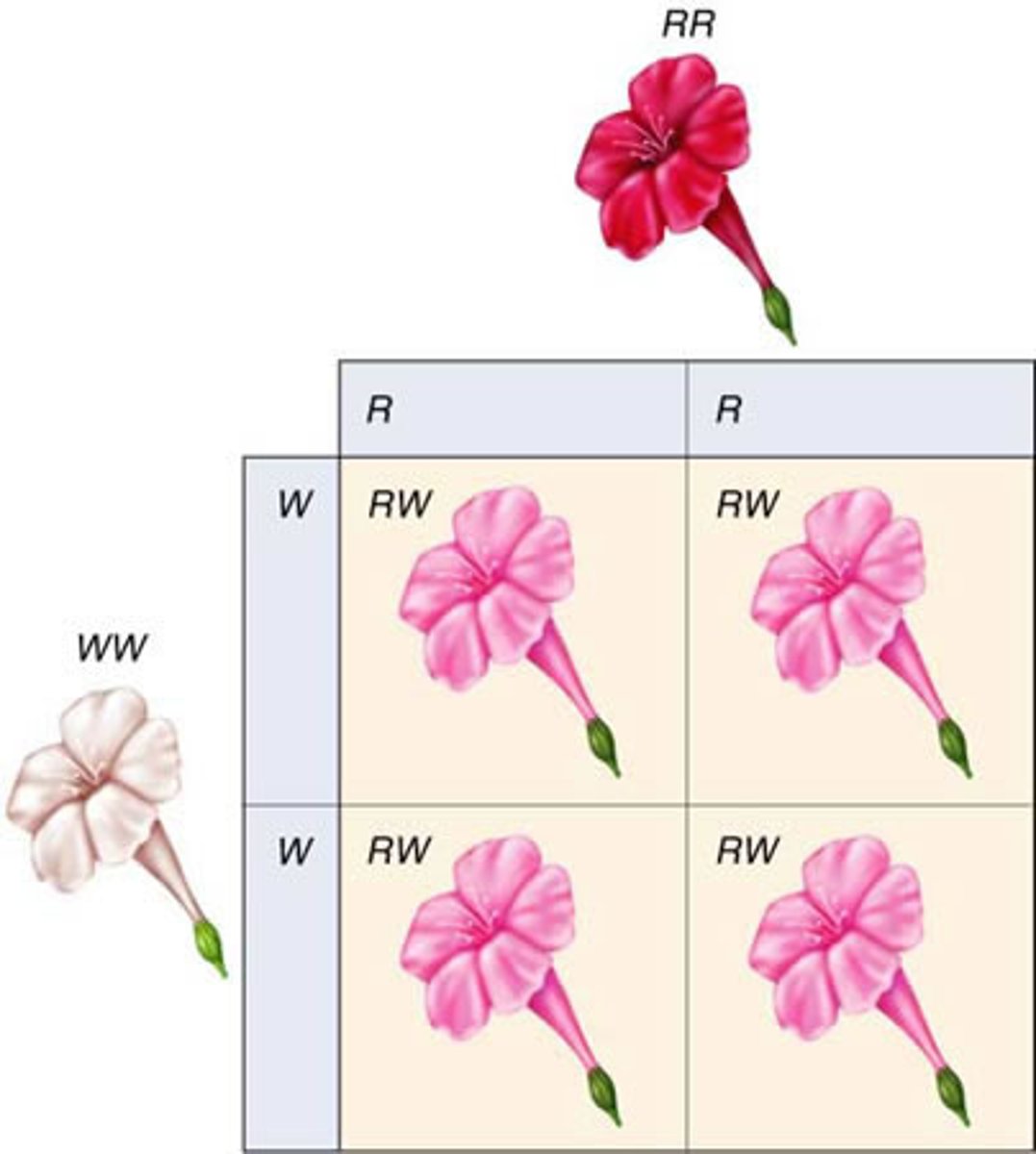
Incomplete Dominance
Cases in which one allele is not completely dominant over another. The two proteins produced by the alleles mix. (blended colors)
Multiple Alleles
A gene that has more than two alleles, like blood type (A,B,O)
polygenetic inheritance
many genes are involved in specifying traits that exhibit continuous variation (ie. a normal/bell-shaped curve). Ex: Human height, skin color
Pedigree
A diagram that shows the occurrence of a genetic trait in several generations of a family.
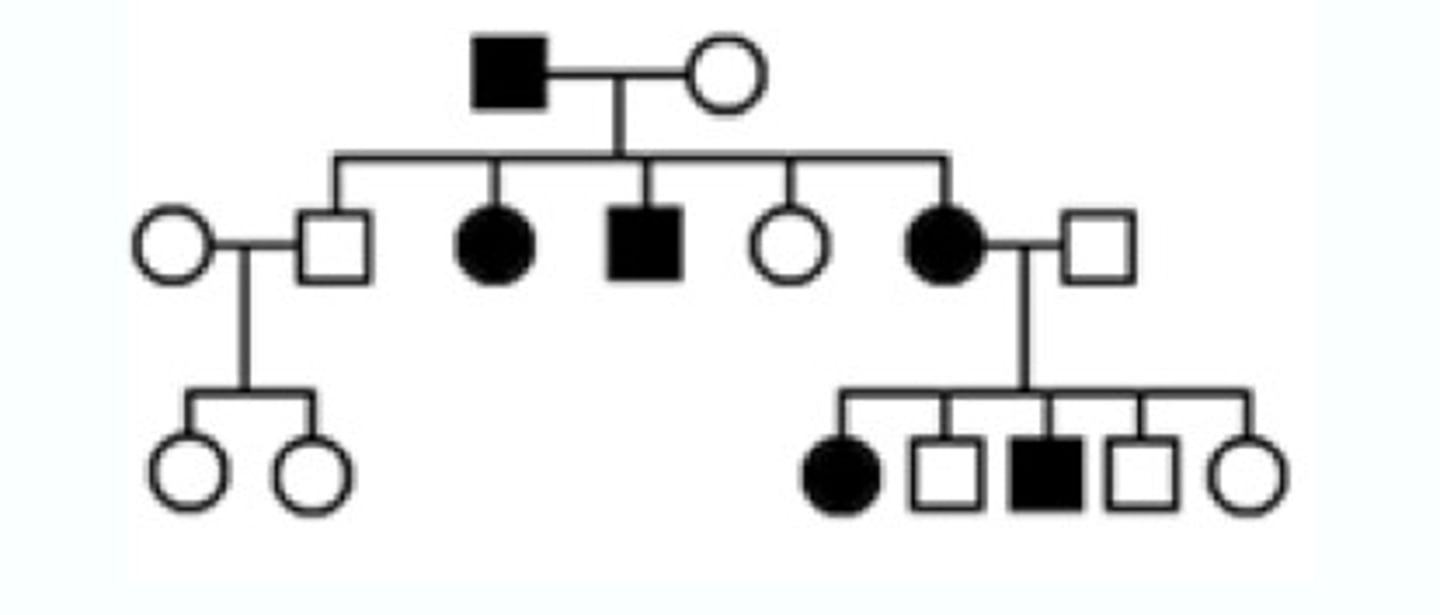
Sickle Cell Disease
autosomal recessive disorder resulting in mutated hemoglobin molecules that polymerize and cause misshapen red blood cells.
Huntington's disease
autosomal dominant disorder resulting in neurodegeneration, leading to dementia and death.
Wild Type
An individual with the normal (most common in nature) phenotype. Ex: red eyes in fruit flies
Mutant
An individual with a mutated form of an allele, not common in nature. Ex: white eyes in fruit flies
Linked genes
Genes located adjacent on the same chromosome that tend to be inherited together in genetic crosses.
X inactivation
one of two X chromosomes in a female is randomly inactivated and remains coiled as a Barr body
Nondisjunction
Error in meiosis in which homologous chromosomes fail to separate.
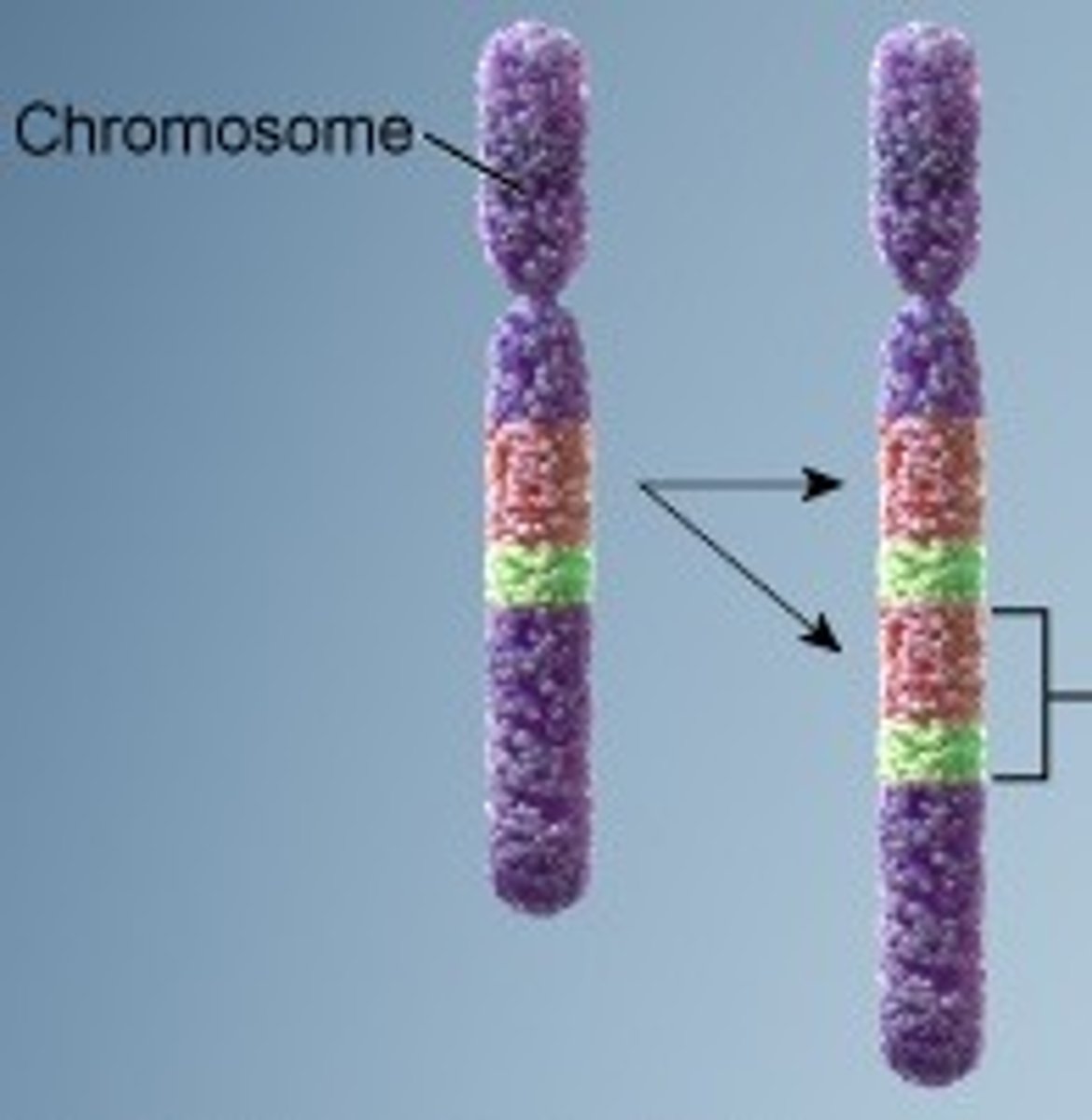
Duplication
repeats a segment
Down Syndrome
(Trisomy 21) Occurs when an individual has 3 chromosomes of the 21st pair instead of 2; caused by NONDISJUNCTION
Turner Syndrome
A chromosomal disorder in females in which either an X chromosome is missing ( making the person XO instead of XX) or part of one X chromosome is deleted.
Extranuclear Genes
genes found in organelles in the cytoplasm; inherited maternally (mitochondria in the egg)
locus
Location of a gene on a chromosome