Biology: B1: Cell structure and transport
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Magnification =
Size of image / Size of real object

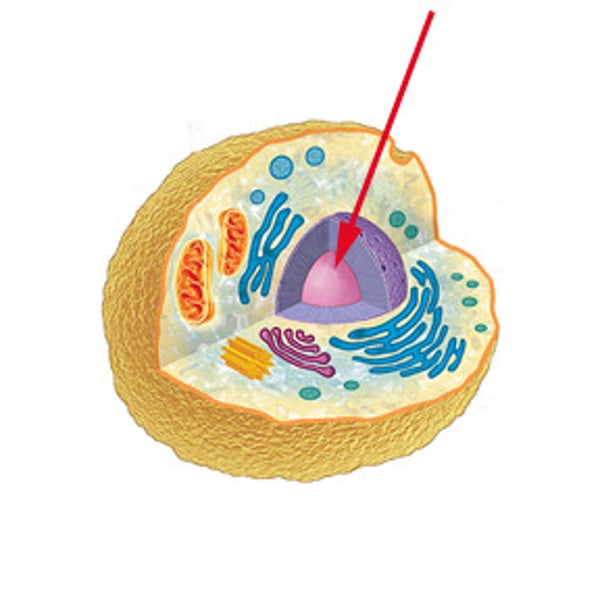
Nucleus
Controls all of the activities of the cell
Also includes the DNA or genes on the chromosomes, along with the instructions for making proteins for new cells
Ribosomes
Where protein synthesis takes place, making all of the proteins needed in the cell
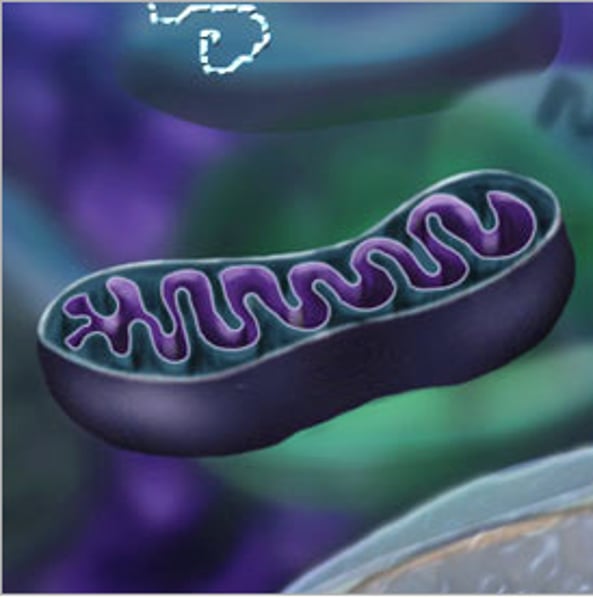
Mitochondria
Where aerobic respiration takes place for releasing energy for the cell.
The folded membranes inside it increase the surface area for respiration to take place
Chloroplasts
Contains chlorophyll, which absorbs sunlight and helps the plant to photosynthesise

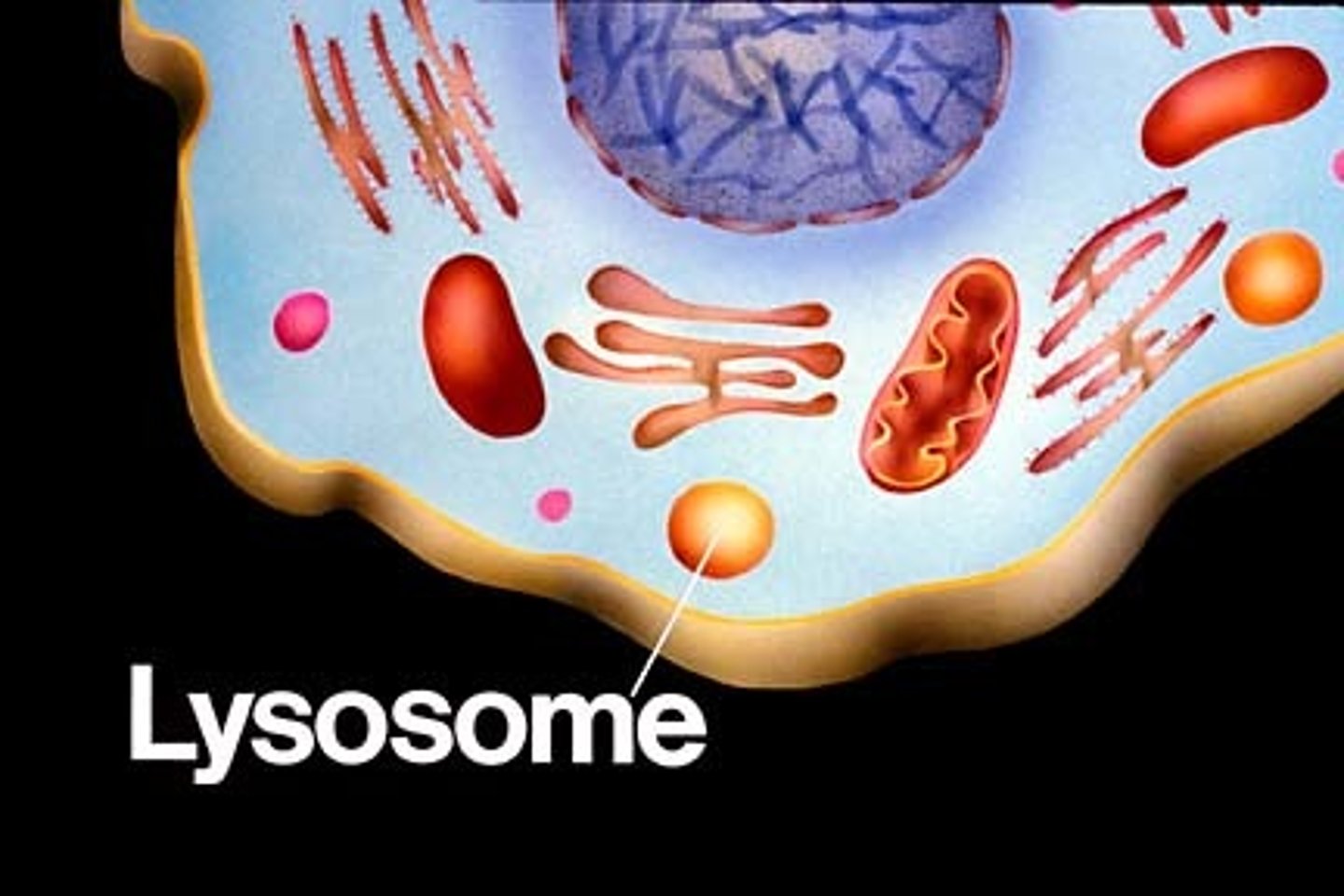
Lysosomes
Breaks down excess/worn-our organelles using digestive/hydrolytic enzymes
Plasma membrane
Controls what substances enter and leave the cell
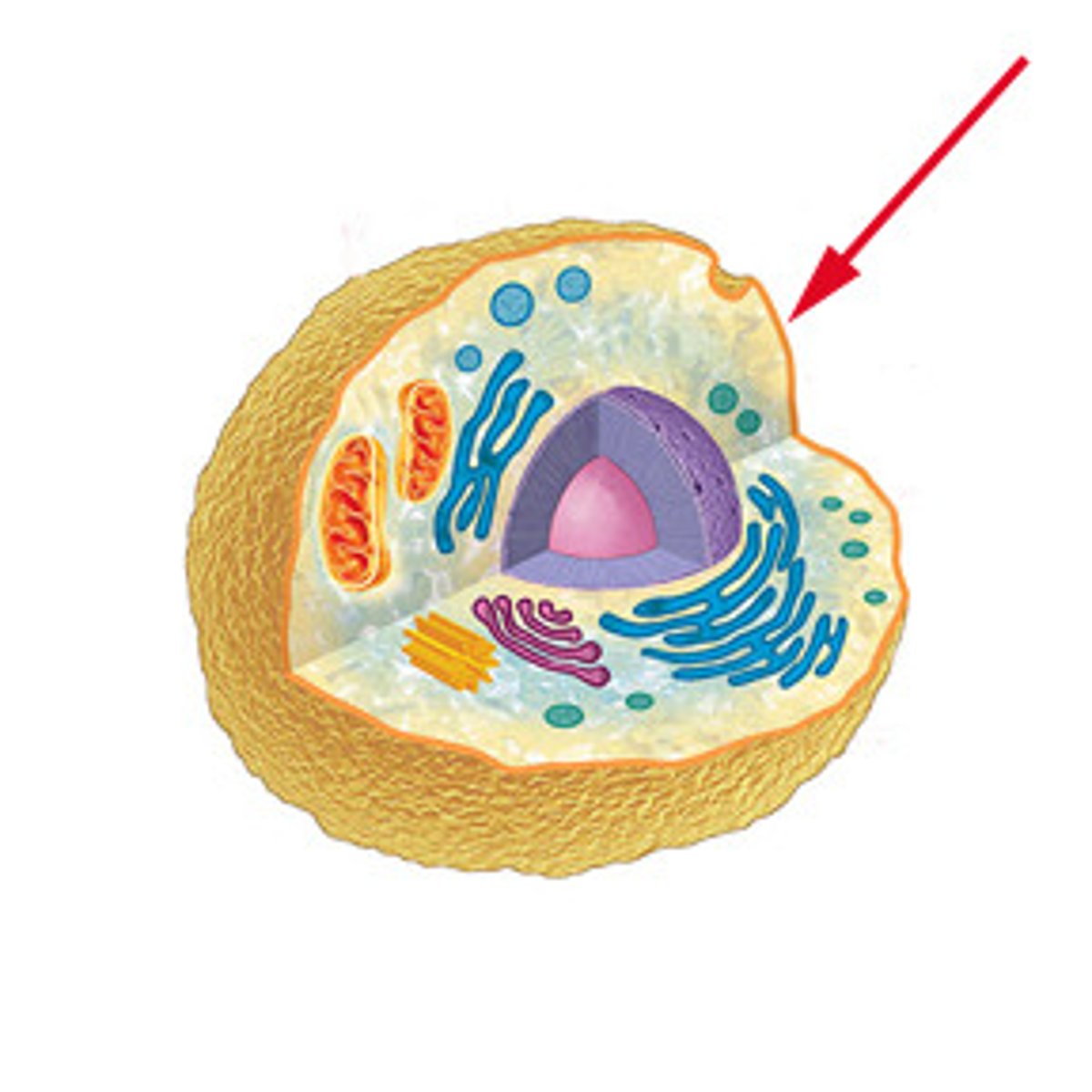
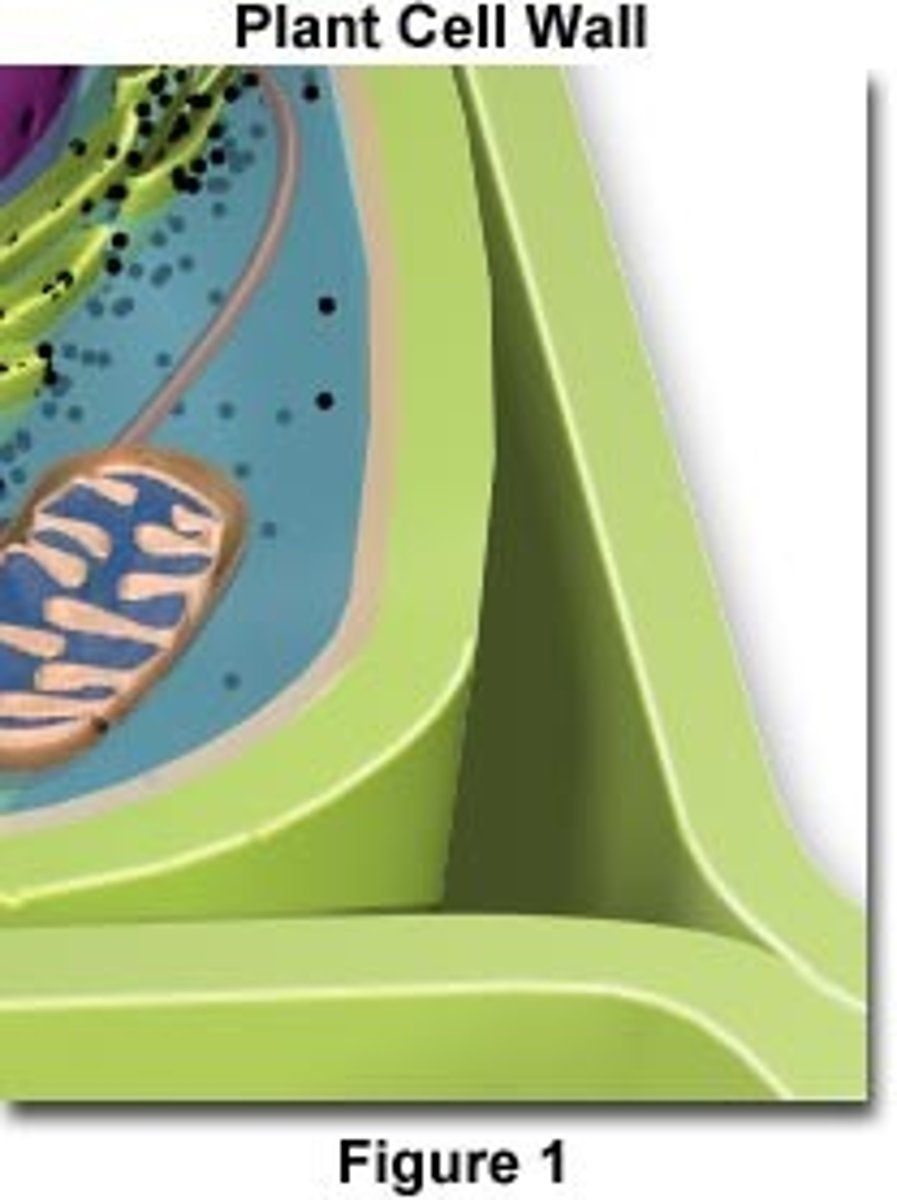
Cell wall
Made of cellulose that strengthens the cell and gives it support
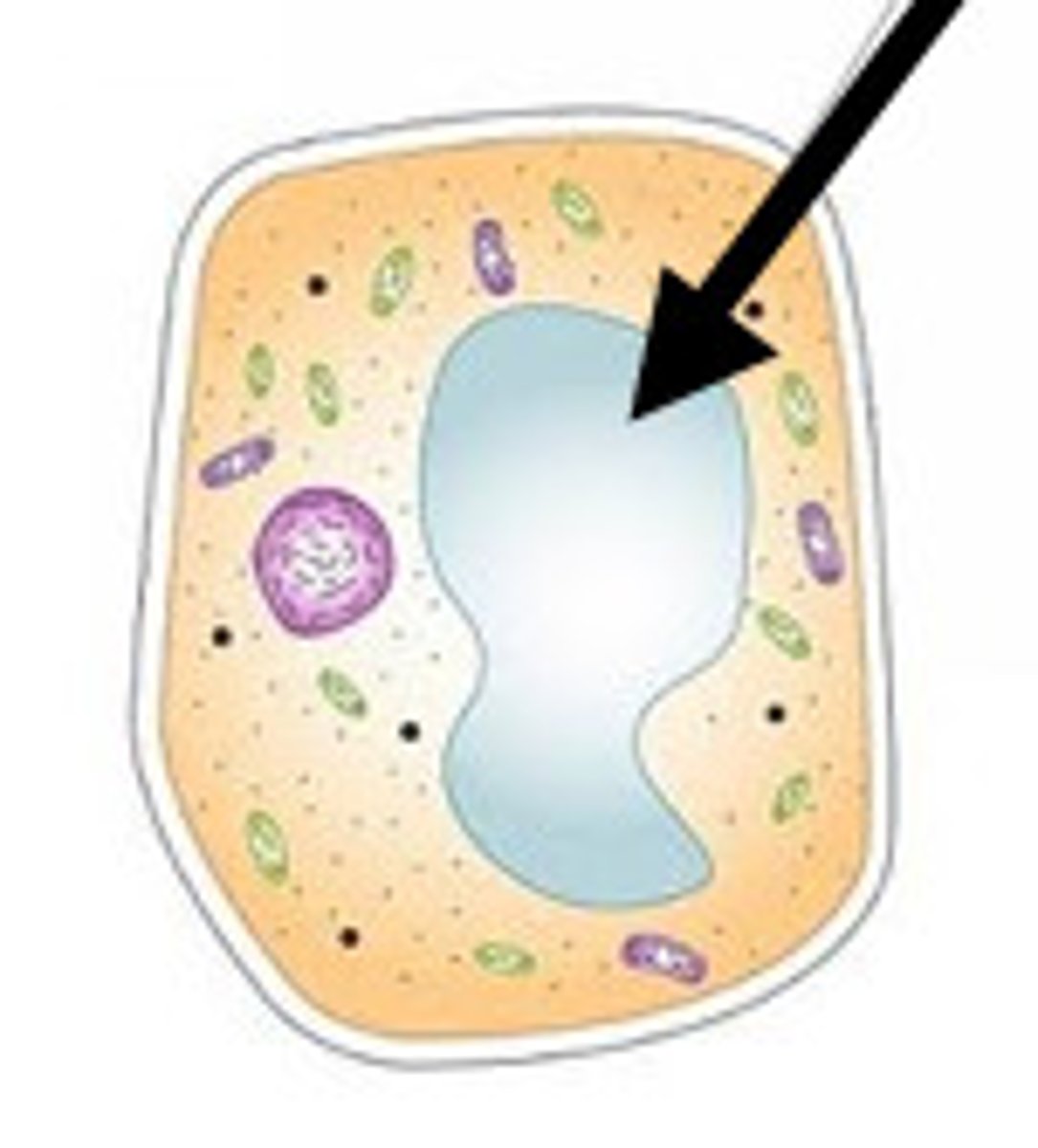
Vacuole
Filled with cell sap, keeps cells rigid to support the plant
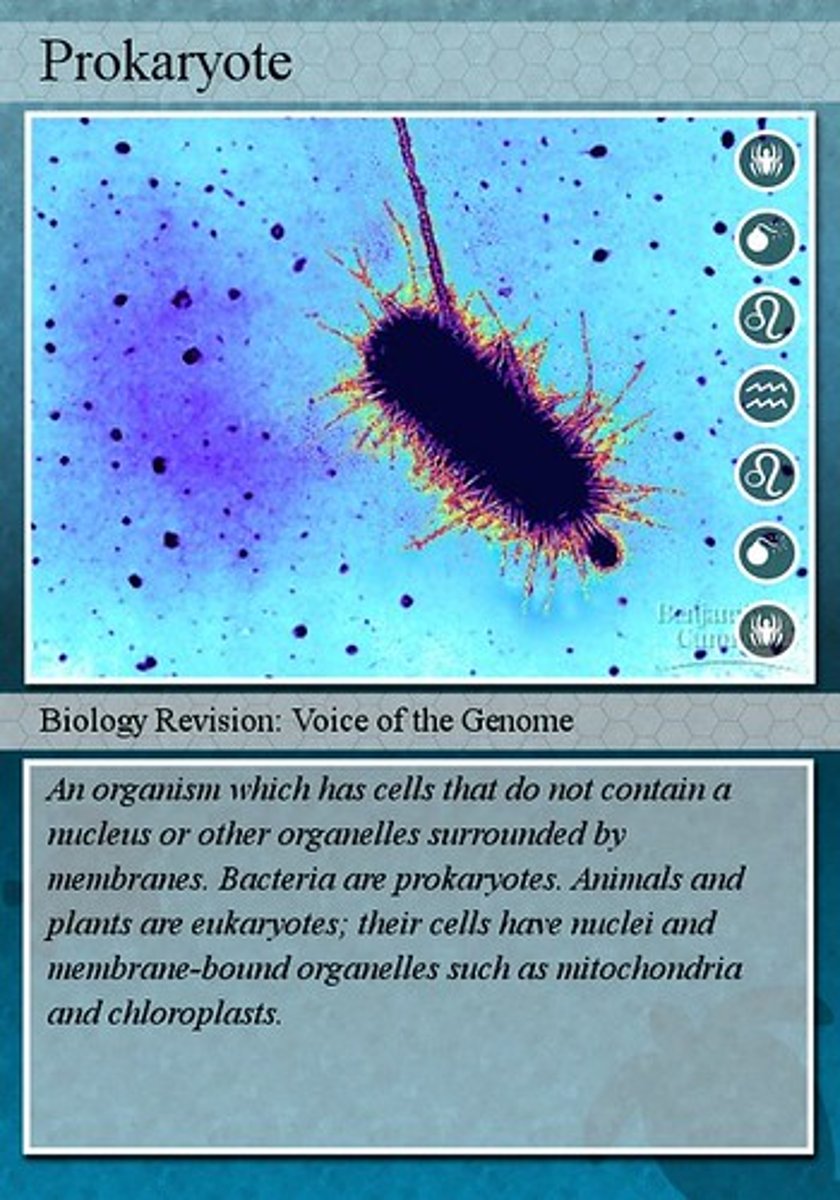
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus.
It's DNA is suspended freely in the cytoplasm
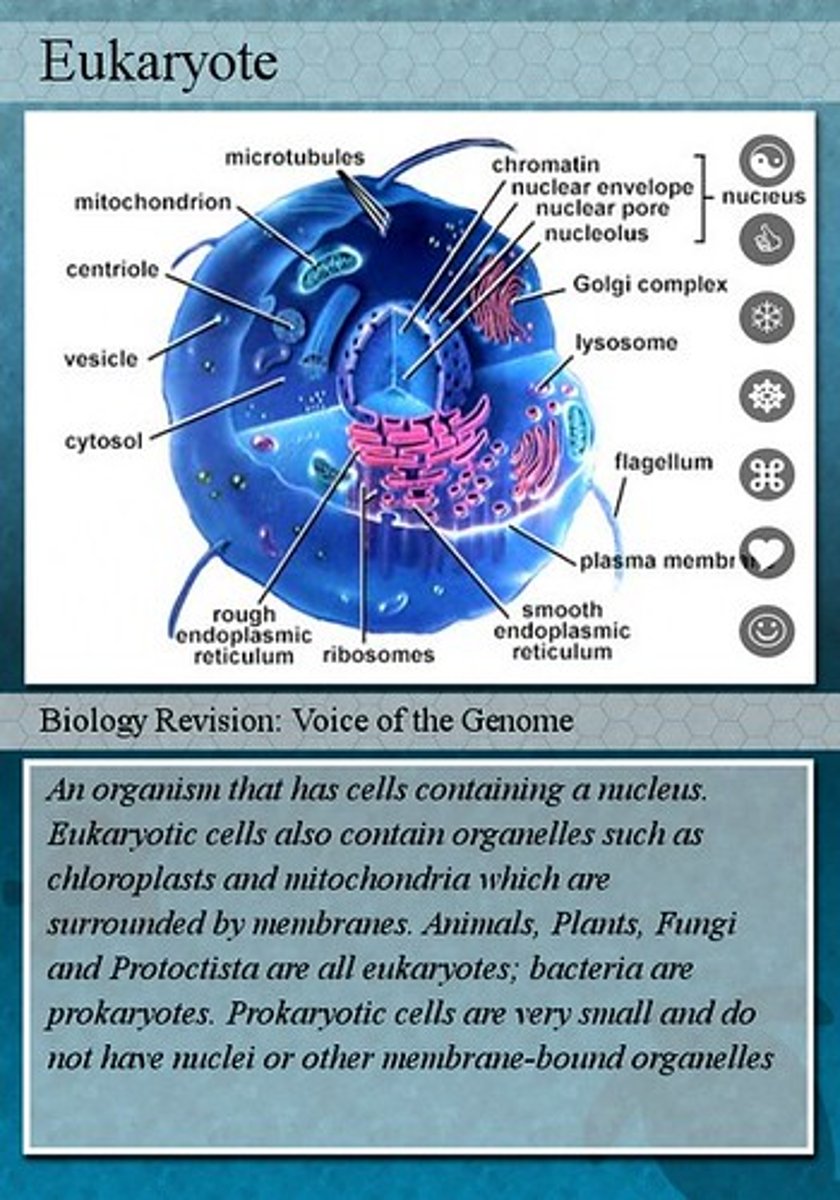
Eukaryote
An organism that contains a nucleus.
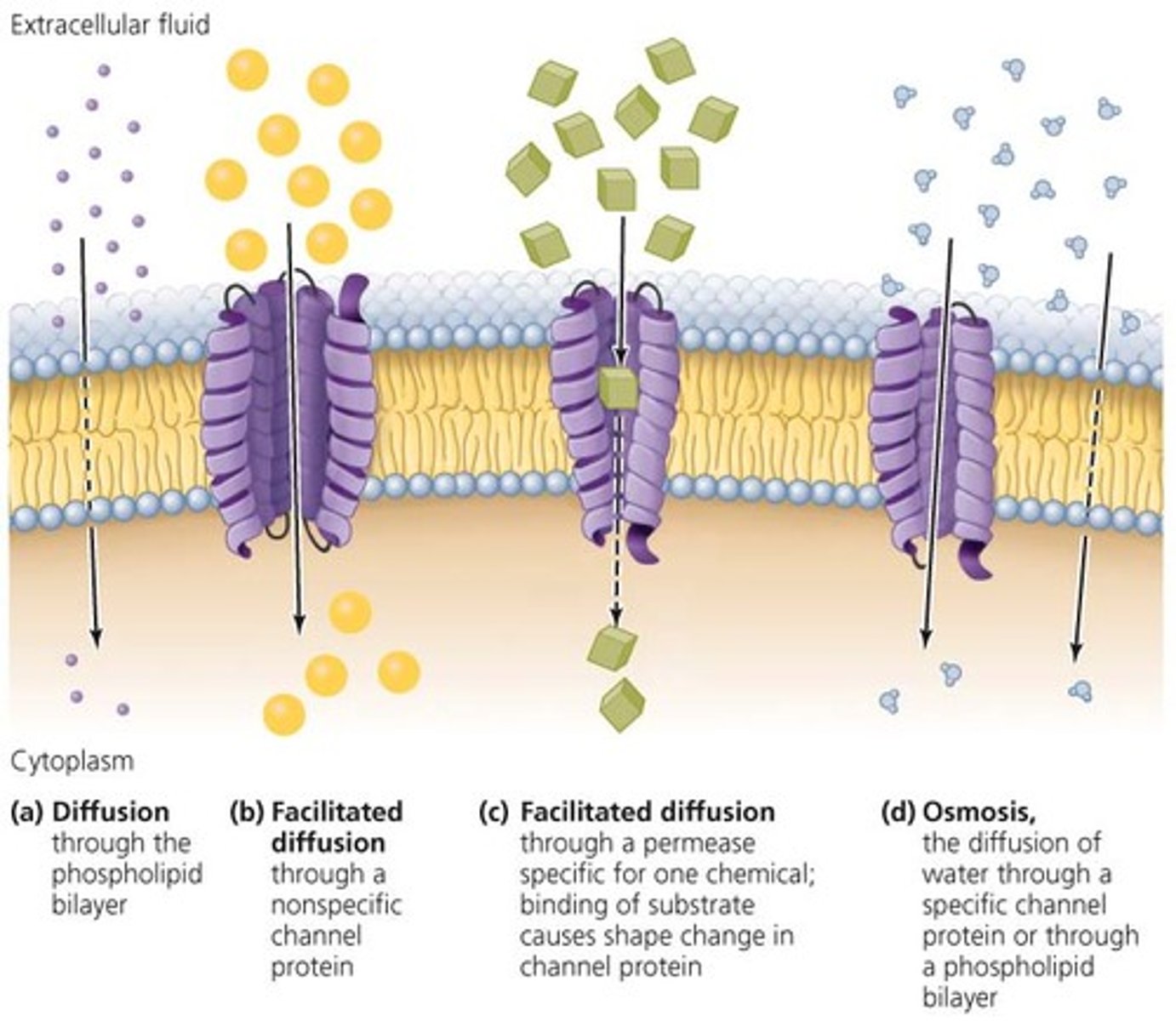
Passive transport
The movement of substances across a cell that doesn't use energy
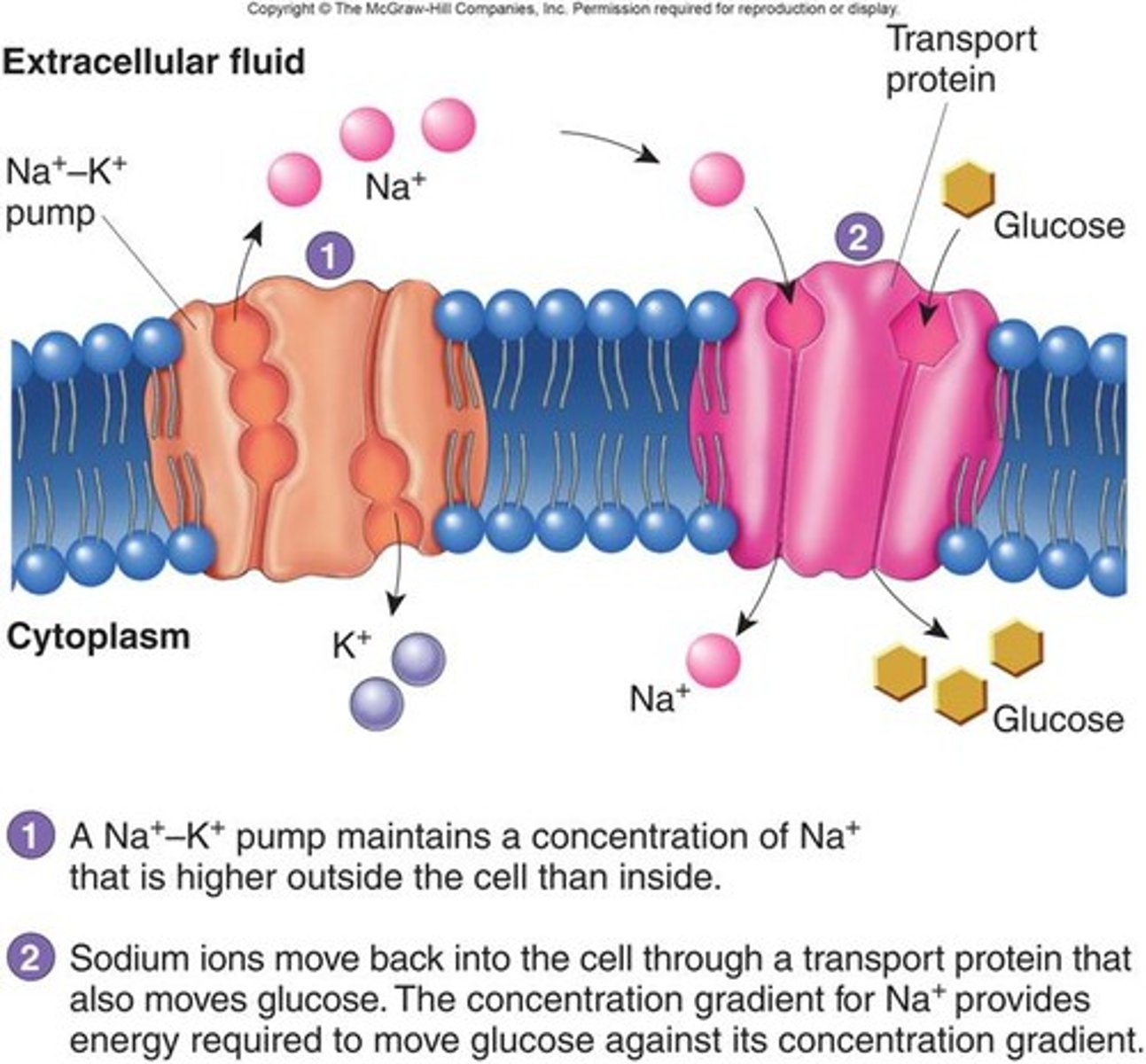
Active transport
The movement of substances across a cell that does use energy
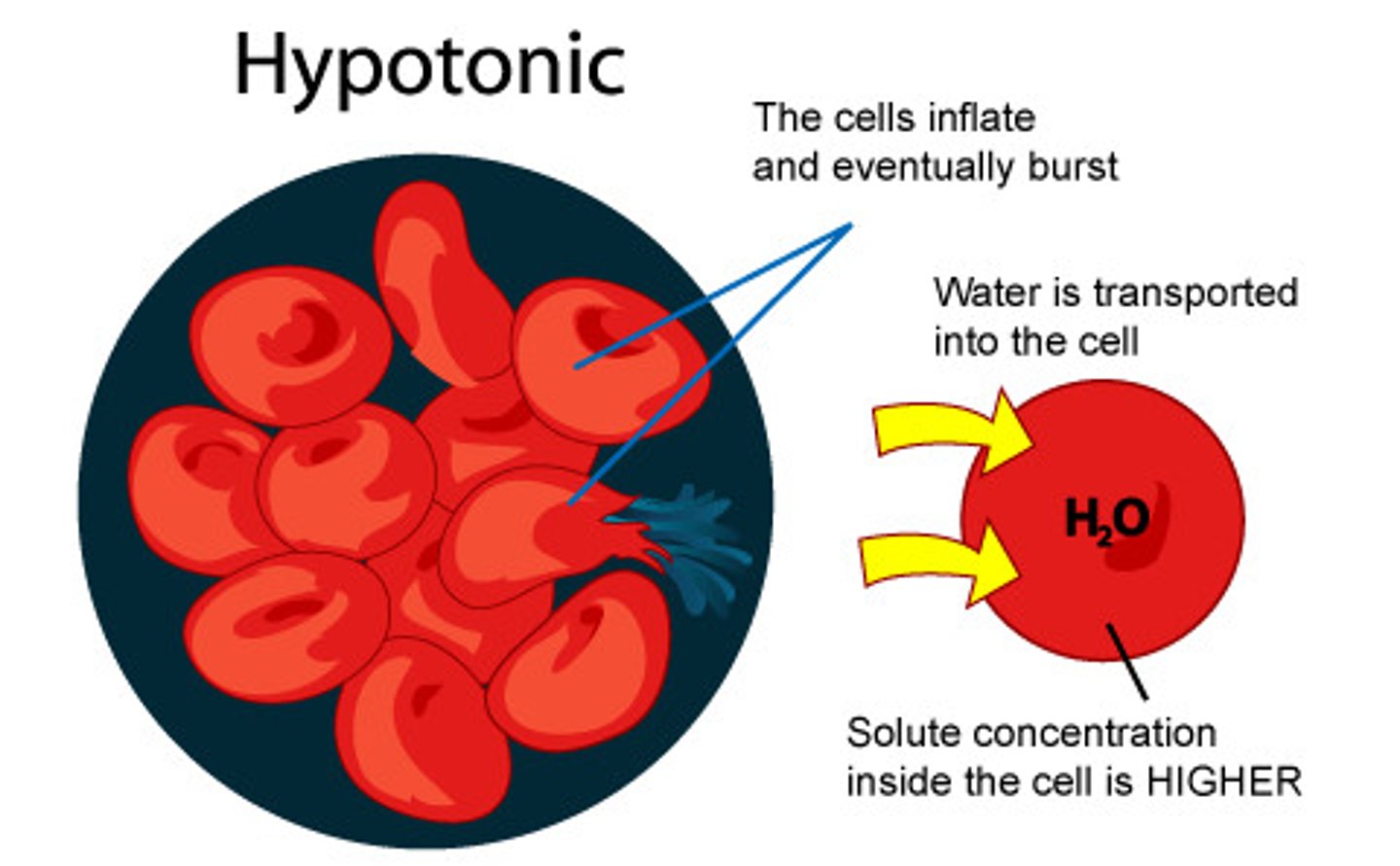
Hypotonic
When a solution has a lower concentration of solutes than another solution
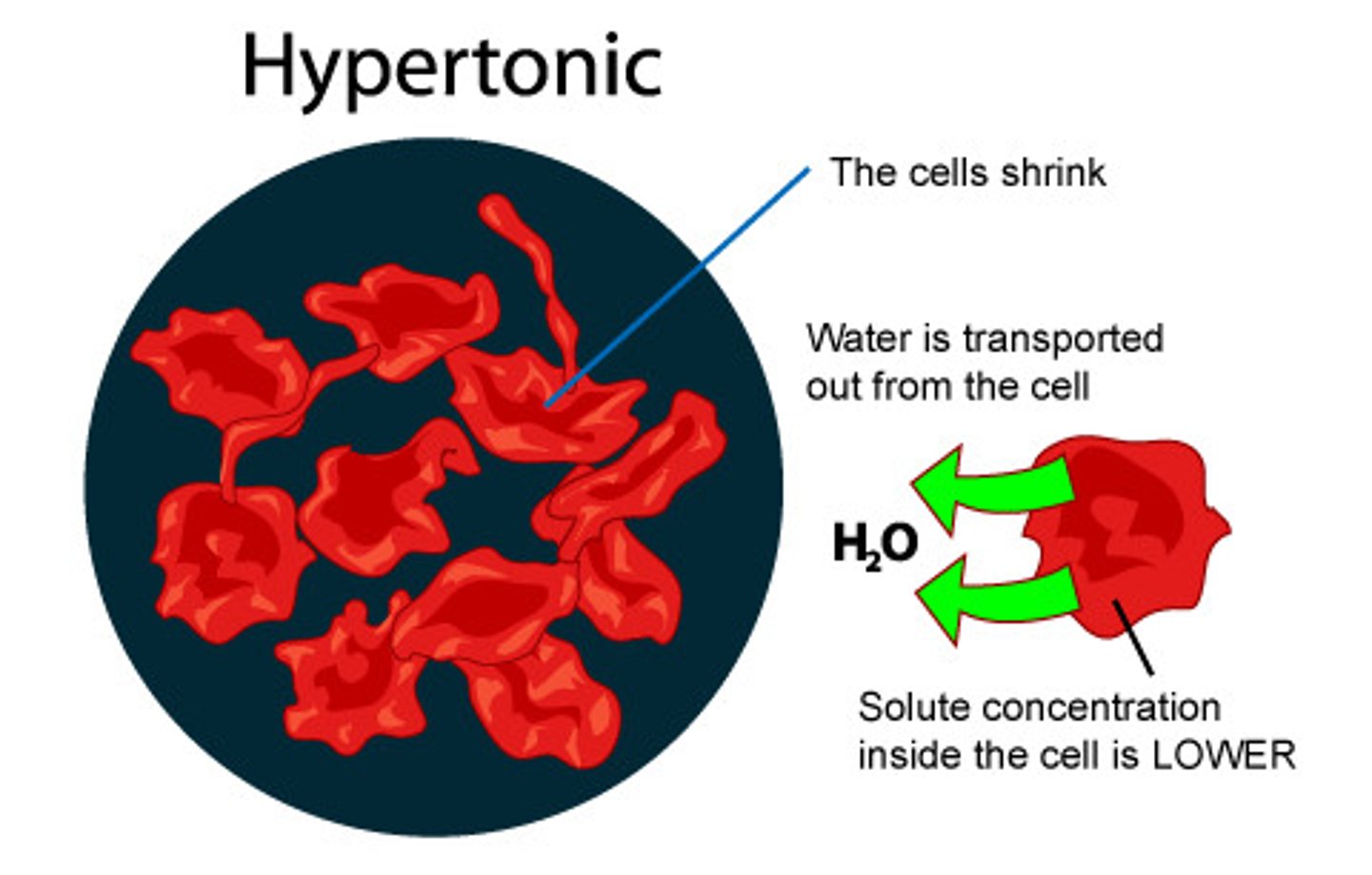
Hypertonic
When a solution has a higher concentration of solutes than another solution
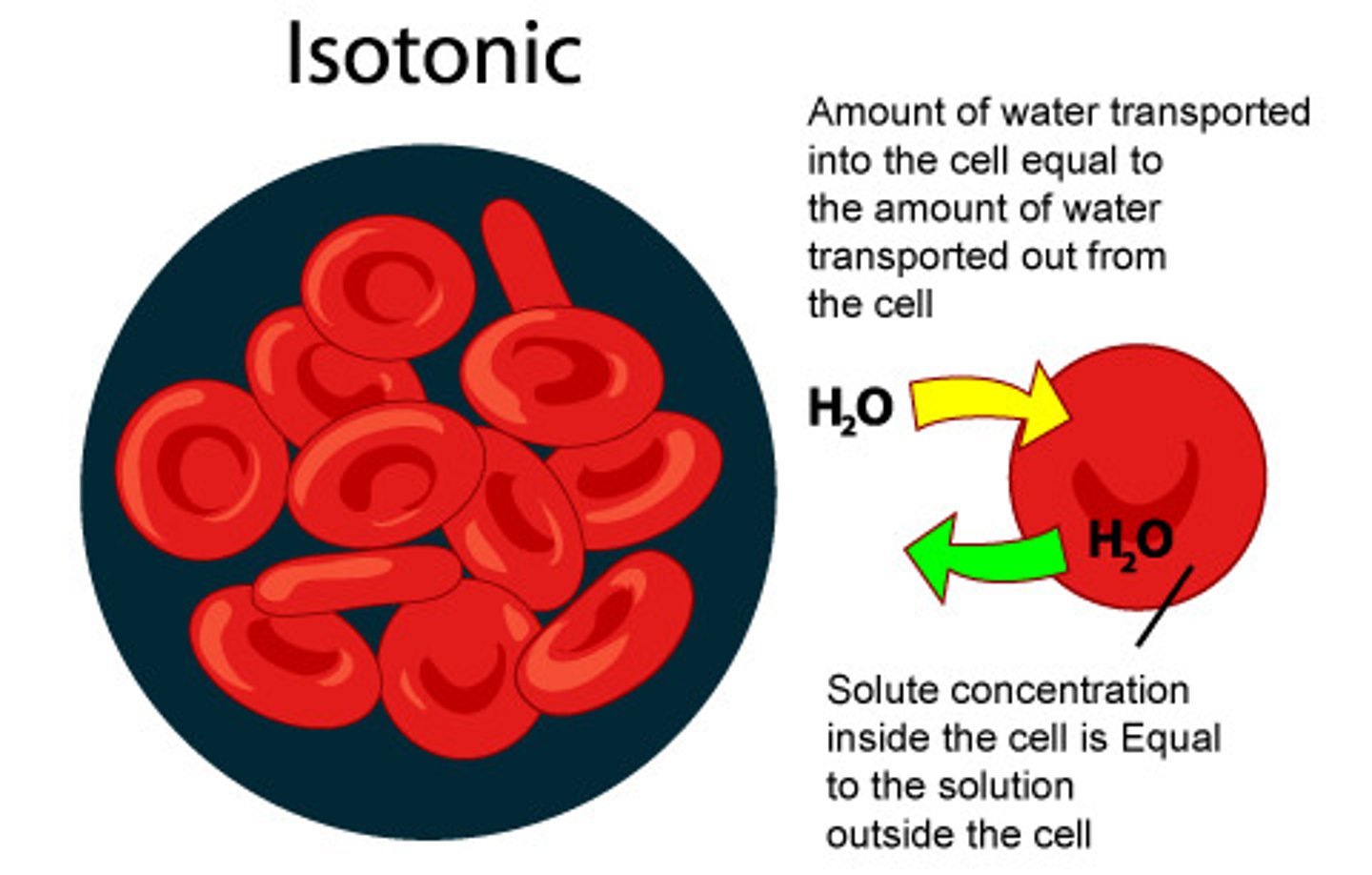
Isotonic
When the concentration of two solutions is the same