Chpt 14 The Brain
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
Elevated ridges
Gyri
Deep grooves
Fissures
What are the six regions of the brain?
Cerebrum (lateral ventricles)
Cerebellum
Diencephalon (slit like cavity)
Mesencephalon (same as midbrain)
Pons
Medulla oblongata
The ventricles of the brain are filled with what?
CSF
Each cerebral hemisphere contains what and is separated by what?
One large lateral ventricle
Separated by a thin medial partition (septum pellucidum)
The lateral ventricles communicate with the third ventricle via what?
Interventricular foramen (foramen of Monro)
The third ventricle is the ventricle of what?
The diencephalon
Which ventricle extends into the medulla oblongata, is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord, and connects with the third ventricle?
Fourth ventricle
What cavities are connected by the cerebral aqueduct (Sylvius)?
Third and fourth ventricles
What are the three layers of cranial meninges and what do they protect the brain from?
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Pia mater
Protect the brain from cranial trauma

This cranial meninges layer has an inner fibrous layer (meningeal layer) and an outer fibrous layer (endosteal layer) fused to the periosteum with venous sinuses (big veins in cranium filled with blood) between the two layers
Dura mater
What are the folded inner layers of dura mater that extend into and divide the cranial cavity while stabilizing and supporting the brain and contain collecting veins (dural sinuses)?
Dural folds
What are the three largest dural folds?
Falx cerebri: extension of dura matter between left + right cerebral hemispheres
Tentorium cerebelli: Like tent over cerebellum
Falx cerebelli
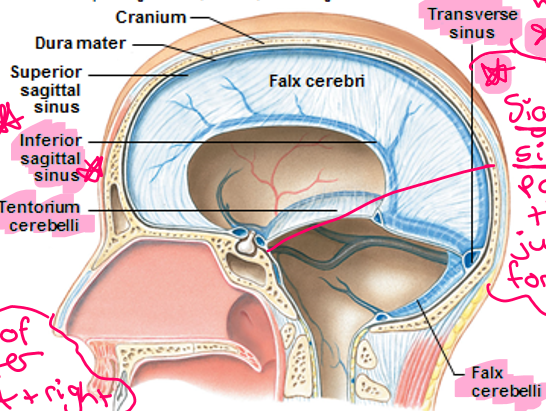
Fluid goes in this sinus
Transverse sinus
This sinus passes through the jugular foramen
Sigmoid sinus
This mater is spider-like, covers the brain, contacts the meningeal layer of dura mater, and holds subarachnoid space
Arachnoid mater
This space is filled with serous fluid
Subdural space
This mater is attached to the brain’s surface by astrocytes and fused with tissue of the brain to supply blood
Pia mater
This surrounds all exposed surfaces of the CNS (including in cavities and the subarachnoid space) and interchanges with the interstitial fluid of the brain
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
What are the three main functions of CSF?
Cushions delicate neural structures
Supports brain (absorbs trauma to head, protection)
Transports nutrients, chemical messengers, and waste products
What is CSF produced by?
The choroid plexus of each ventricle
This barrier is one of two that isolates the CNS neural tissue from general circulation, is formed by tight junctions, and allows for diffusion of lipid-soluble compounds (O2, CO2), steroids, and prostaglandins?
Blood ECF Barrier
What controls the blood-brain barrier by releasing chemicals that control the permeability of the endothelium?
Astrocytes
This barrier is formed by special ependymal cells (tight junctions), surrounds capillaries of choroid plexus, limits movement of compounds transferred, and allows chemical composition of blood and CSF to differ
Blood-CSF Barrier
Does CSF have any proteins or blood cells in it?
No
How is the medulla oblongata connected to the spinal cord, pons, and cerebellum?
Inferiorly connected is the spinal cord
Superiorly connected is pons
Posterior to it is the cerebellum
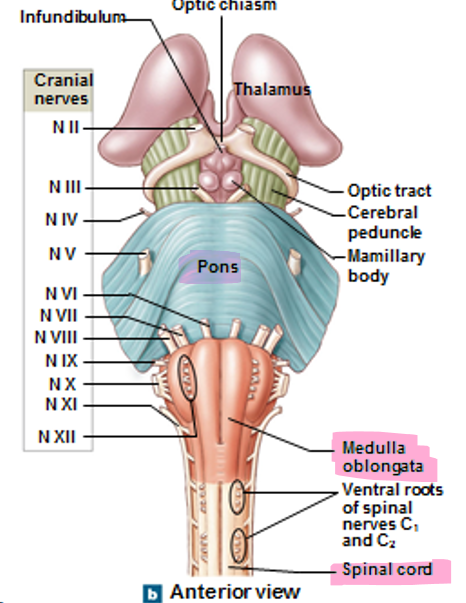
What are the superficial structures (5) of the medulla oblongata?
Pyramids/decussation of pyramids (descending tracts)
Olives (somatic motor relay)
Fasiculus gracilus (lateral) and cuteatus (medial)(sensory, ascending tract)
Inferior cerebeller peduncle (fibers that connect medulla to cerebellum)
What are the three nuclei groups of the medulla oblongata?
Autonomic nuclei
Sensory nuclei
Motor nuclei
The cardiovascular center (heart rate + how strong heart beats), the respiratory center (how deep + fast you breathe), and the reticular formation (alertness) are all part of which nuclei?
Autonomic
Cranial nerves VIII(8), IX(9), X(10), XI(11), and XII(12) along with relay stations belong to which nuclei?
Sensory and motor
Pons involved what sensory and motor nuclei of cranial nerves?
V, VI, VII, VIII
The apneustric center and pneumotaxic center of pons function to do what?
Modify respiratory rhythmicity center activity sent by medulla
Nuclei of pons process and relay information to and from where?
Cerebellum
Along with ascending and descending fibers, these fibers link pontine nuclei with opposite cerebellar hemisphere?
Transverse
This connects the cerebellum, pons, and medulla
Middle cerebellar peduncle
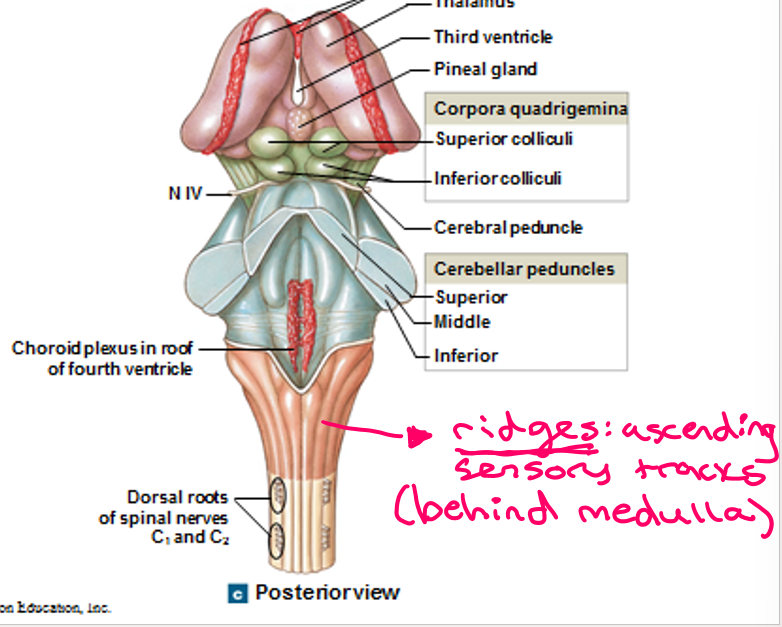
This is the posterior portion of the midbrain with two pairs of sensory nuclei (corpora quadrigemina)
Tectum
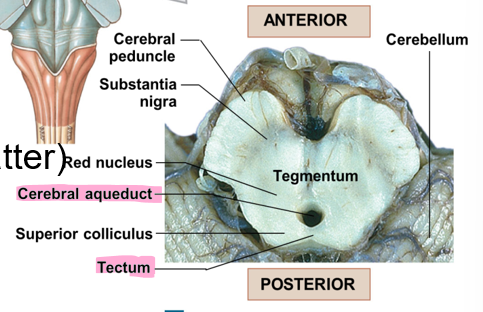
What is the difference between the superior colliculus and the inferior colliculus of tectum?
Superior colliculus is visual, associated with the reflex of turning your head away from a bright light
Inferior colliculus is auditory, associated with the reaction of turning your head with a loud noise
The tegmentum of the midbrain contains what two structures?
Red nucleus (many blood vessels)
Substantia nigra (pigmented gray matter)
These are nerve fiber bundles on ventrolateral surfaces that contain descending fibers
Cerebral peduncles
*NOT to be confused with “cerebellar”, leads to spinal cord
These are ridges that are narrow and highly folded on the surface of the cerebellum
Folia
The cerebral aquaduct is present where?
In the midbrain
Cerebellar hemispheres are separated at the midline by what?
Vermis
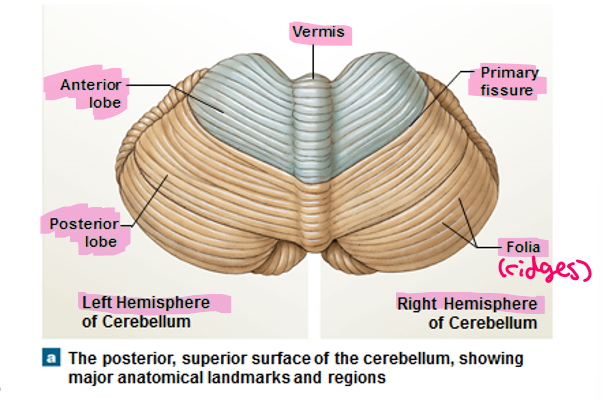
Anterior and posterior lobes of the cerebellum are separated by what?
Primary fissure
The narrow band of the cortex (cerebellum)
Vermis
Below the fourth ventricle, 3rd lobe
Flocculonodular lobe
This is the outer, darker layer in the cut section of the cerebellum
Cortex
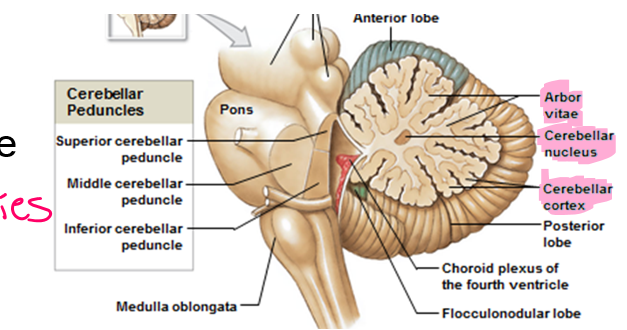
These are large, branched cells of the cortex that receive input from up to 200,000 synapses
Purkinje cells
This structure is seen in the cut section of the cerebellum to relay information to Purkinje cells
White matter or Arbor vitae (“tree of life”)
Embedded in arbor vitae with clusters of cell bodies (unmyelinated)
Cerebellar nuclei
Tracks link cerebellum with brain stem, cerebrum, and spinal cord
Superior, middle, and inferior regions
Cerebellar peduncles
This cerebellar peduncle goes from the cerebellum to the cerebrum
Superior
This cerebellar peduncle goes from muscle contraction to the cerebellum
Inferior
This cerebellar peduncle goes from the stimulus to the cerebellum
Middle peduncle
What are the two functions of the cerebellum?
Adjusts postural muscles
Fine-tunes conscious and subconscious movements
This is a disorder of the cerebellum that results in damage from trauma or stroke, intoxication (temporary impairment), and disturbs muscle coordination
Ataxia
What structures are included in the diencephalon?
Thalamus, epithalamus, and hypothalamus
The pineal gland is found here and it secretes melatonin
Epithalamus
This structure filters ascending sensory information for primary sensory cortex (over 90%), relays information between basal nuclei and cerebral cortex, and is made up of multiple thalamic nuclei
Thalamus
What are the 7 functions of the hypothalamus?
Controls autonomic function (Confused)
Coordinates activities of nervous and endocrine systems (Cats)
Secretes hormones (ADH and OT)(Steal)
Produces emotions and behavioral drives(Pizza)
Coordinates voluntary and autonomic functions(Causing)
Regulates body temperature (ex. chills, preoptic area)(Random)
Controls circadian rhythms (suprachiasmatic nucleus, SAD)(Chaos)
Supraoptic nucleus of the hypothalamus
ADH
Paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus
OT
The feeding and thirst centers are controlled by what structure?
Hypothalamus
The preoptic area is part of the hypothalamus to do what?
Regulate body temperature
The suprachiasmatic nucleus is part of the hypothalamus to do what?
Control circadian rhythms
What is the largest part of the brain?
The cerebrum
This structure controls all conscious thoughts and intellectual functions and processes somatic sensory and motor information
The cerebrum
This is found in the cerebral cortex and basal nuclei
Gray matter
This is found deep to the cortex and around the basal nuclei
White matter
Increases the surface area with a number of cortical neurons including pre-central and post-central and cingulate
Gyri of neural cortex
Shallow depressions in between gyri including central, calcarine, and parieto-occipital
Sulci
Deep depressions including longitudinal, transverse, and lateral
Fissure
Divisions of hemispheres including frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal, and insula
Lobes
How many pairs of cranial nerves are connected to the brain?
12
What are the classifications of cranial nerves?
Sensory
Somatic sensory: touch, pressure, vibration, temperature, and pain
*Special sensory: taste, smell, sight, hearing, balance
Motor: axons of somatic motor neurons
Mixed: mixture of motor and sensory fibers
Cranial nerve I
Olfactory (smell)
Cranial nerve II
Optic (smell)
Cranial nerve III
Oculomotor (motor)
Cranial nerve IV
Trochlear (motor)
Cranial nerve V
Trigeminal (mixed)
Cranial nerve VI
Abducens (motor)
Cranial nerve VII
Facial (mixed)
Cranial nerve VIII
Vestibulocochlear (smell)
Cranial nerve IX
Glossopharyngeal (tongue, mixed)
Cranial nerve X
Vagus (mixed)
Cranial nerve XI
Accessory (sternocleidomastoid, trapezius, motor)
Cranial nerve XII
Hypoglossal (motor)
Association fibers are found where?
White matter of the cerebrum
These fibers are connections within one hemisphere on the same side that are arcuate (short) and longitudinal (longer)
Association fibers
Commissural fibers are found where?
White matter of the cerebrum
These fibers connect the two hemispheres
Commissural fibers
Where are projection fibers found?
White matter of the cerebrum
These fibers connect with the cerebrum in lower areas
Projection fibers
What are the two major basal nuclei (or basal ganglia)?
Caudate nucleus and lentiform nucleus
This nucleus is a curving, slender tail in a “C” shape
Caudate nucleus
This nucleus is found more internally including the globus pallidus and putamen
Lentiform nucleus
What are the four functions of the basal nuclei?
Subconscious control of skeletal muscle tone (Sally)
Functionally linked with substantia nigra (Fixed)
The coordination of learned movement patterns (walking, lifting, rhythmic movement)(The)
Dysfunction may lead to Parkinsonism (inhibited, abnormal) and Chorea (sudden movements, impulse)(Drain)
What sulcus separates motor and sensory areas?
Central sulcus
What is the gyrus of the primary motor cortex and what does it do?
Precentral gyrus including voluntary movements (facial, hands, etc.)
What are the cells of the primary motor cortex?
Pyramidal cells including neurons with axons to brain stem to spinal cord
What are the three motor areas of the cerebrum?
Primary motor cortex (voluntary movements)
Premotor cortex
Frontal eye field (for eye movement)