HL PDA III Exam I - Med Chem of Benzos LOs
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is benzodiazepine pharmacophore?
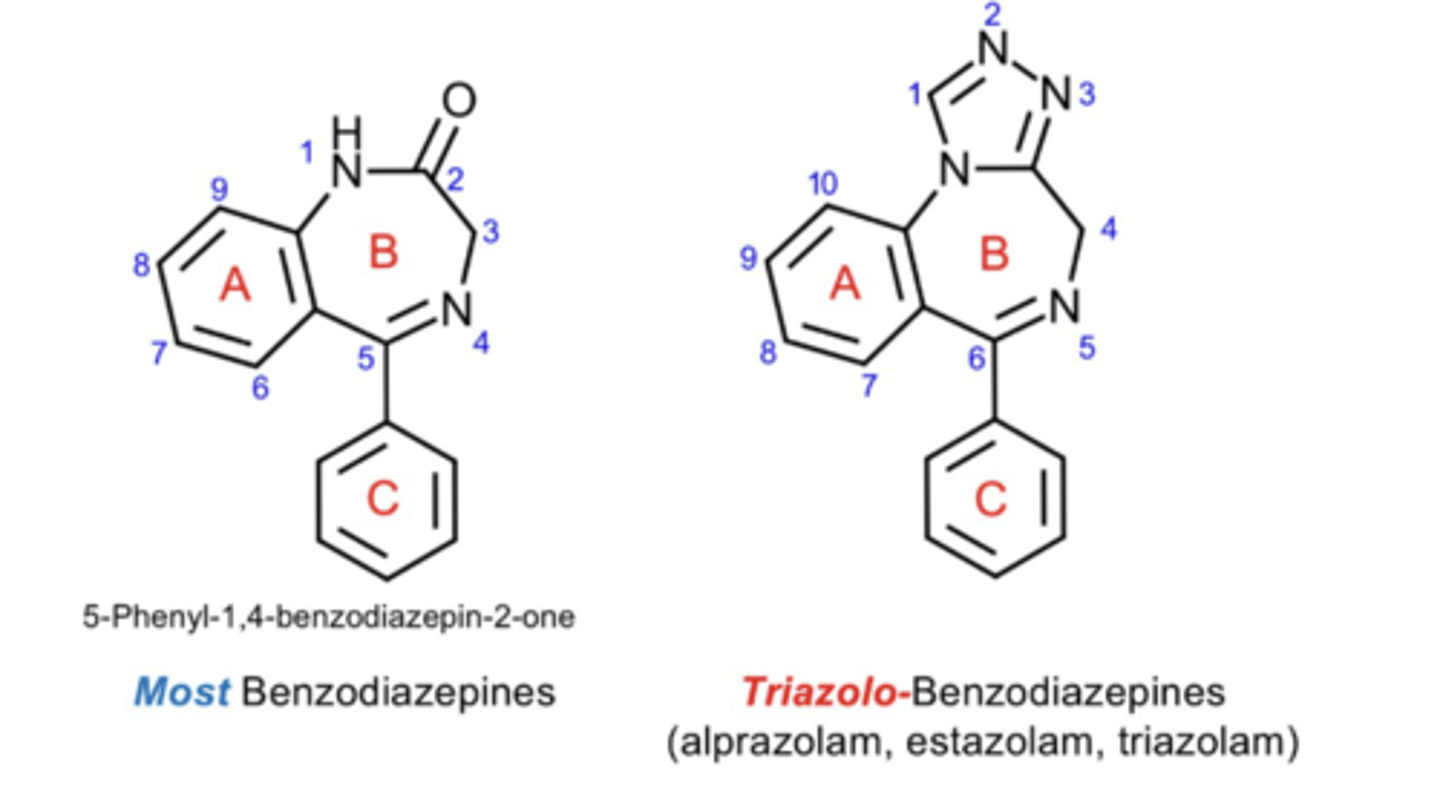
What substituents are on ring A of a benzo?
Position 7: EWG is required for GABAergic activity (can increase as EWG strength increases) → increases binding affinity
Also, must be a benzene ring (planer structure with pi bonding
True or False: in ring A, position 6, 8, or 9 of a benzo, placing an EWG will decrease activity
True
What is at position 1 of ring B of a benzo?
sterically small alkyl chain substitution (maintains activity)
What is at position 2 of ring B of a benzo?
proton accepting group that's required for GABA-A binding
Explanation: Lone pair of electrons on carbonyl oxygen interact with positively charged histidine residue in binding site. Substitution of the position 2 carbonyl with a thione retains activity (i.e., quazepam)
What is a thione?
carbon double bonded to sulfur
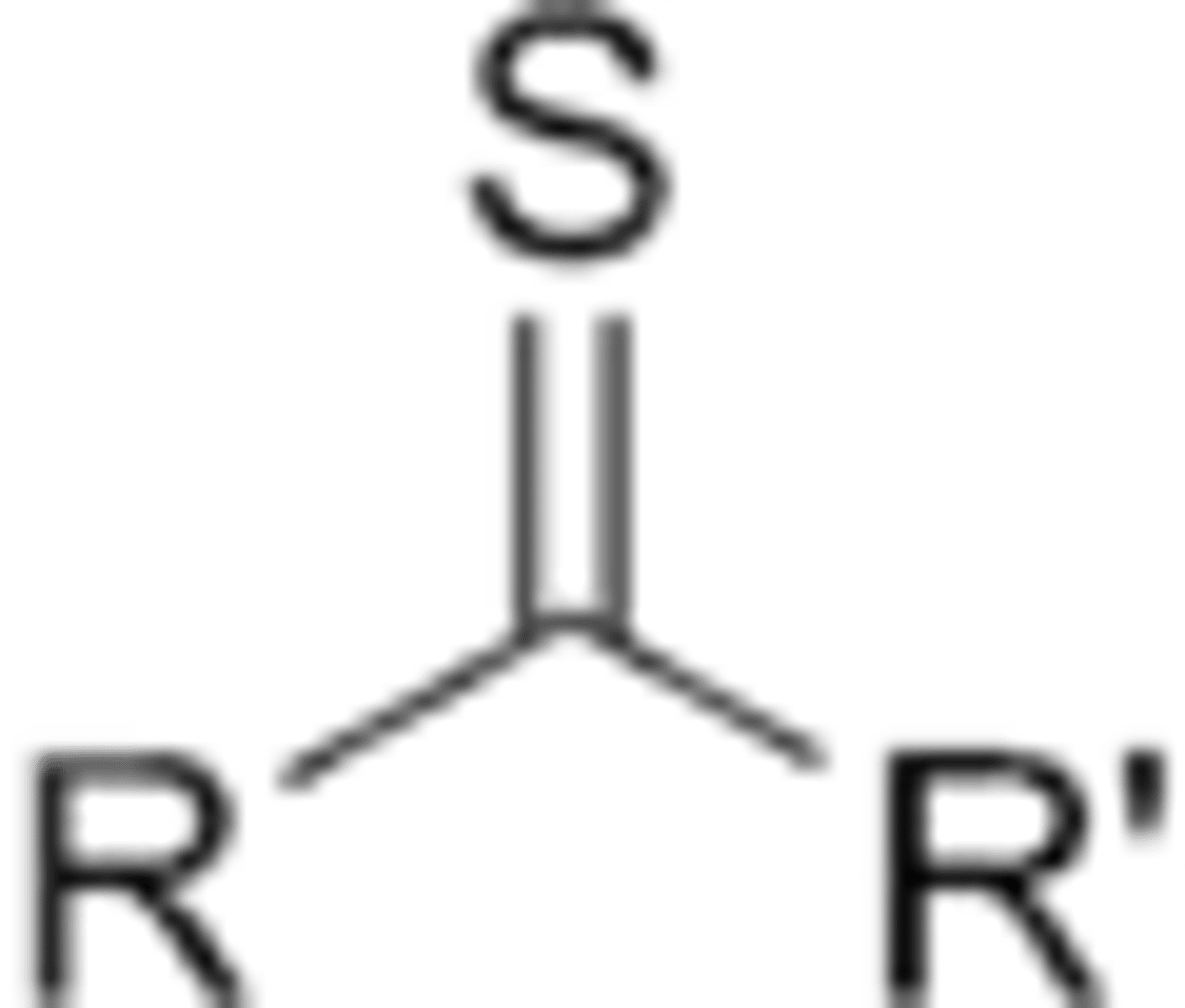
True or False: oxygen in a carbonyl vs a sulfur in a thione have different # of outermost shell electrons?
False
explanation: they are the same
What is at position 3 of ring B of a benzo?
alkyl substitution or OH substition
True or False: alkyl substitution at position 3 of ring B decreases activity
True
Explanation: 3-OH maintains activity
What decreases activity of a benzo between positions 4 and 5 of ring B?
saturated bonds
True or False: ring C is not needed for GABAergic activity
False
Explanation: ring C is not needed for GABA-A, but is necessary for allosteric/GABAergic activity
True or False: flumazenil has ring C and does not bind at BZRA receptor
False
Explanatino: flumazenil does NOT have ring C, does bind at BZRA receptor, and functions as an antagonist
True or False: all benzos have phenyl ring (ring C)
True
Explanation: this is because the pi bonding and hydrophobic interactions between ring C and residues in GABA-A binding site
What position on ring C are EWG at?
ortho
Explanation: this increases binding affinity to GABA-A receptor
True or False: adding EWG to meta and para positions on ring C will sterically hinder binding to GABA-A receptor
True
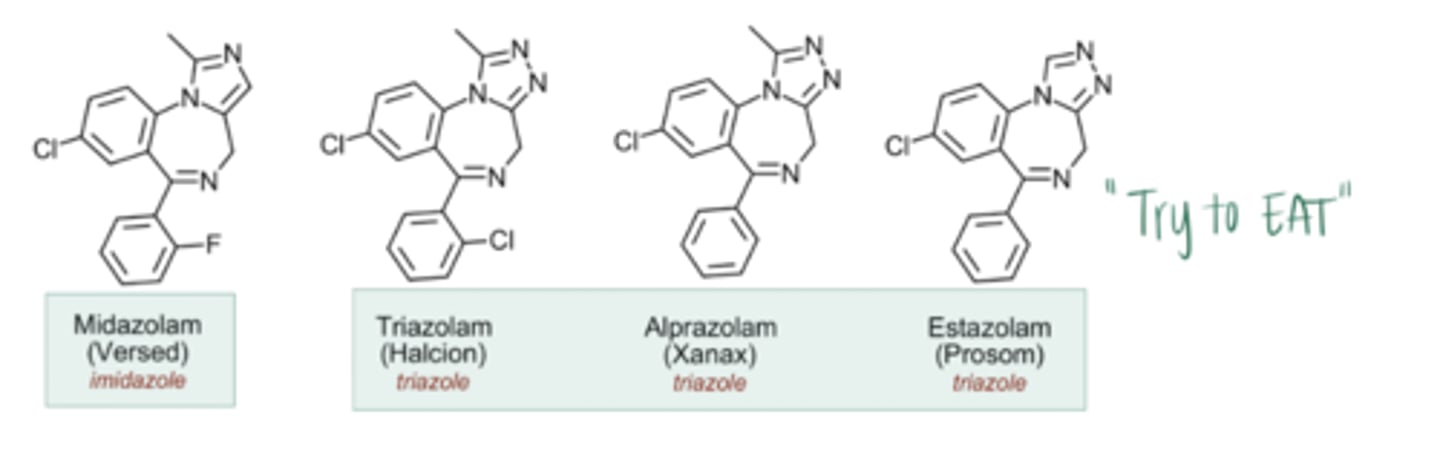
What are the characteristics of imidazo- and triazo- benzos?
greater binding affinity for GABA-A,
more potent,
shorter acting
Describe the effect of a 3-hydroxy substituent on the metabolism of benzodiazepines and explain the clinical importance of that effect:
The Problem: Benzos with alkyl substituents at position 1 have a long t1/2, gradually undergoing CYP450 N-dealkylation → active metabolites (can also have long t1/2) → hangover effect
The Solution: synthesizing benzos with a 3-OH group results in shorter duration of action → glucuronidation (instead of CYP) → quickly excreted into the urine
Describe the effects of imidazole and triazole chemistry on potency and metabolism of benzodiazepines:
The Problem: Benzos with alkyl substituents at position 1 have a long t1/2, gradually undergoing CYP450 N-dealkylation → active metabolites (can also have long t1/2) → hangover effect → excessive duration of GABAergic activity
The Solution: Synthesizing an aromatic ring at position 1 removes the possibility of active, long-acting metabolites from CYP450 N-dealkylation → imidazole and triazole benzos have active metabolites that are shorter acting → shorter onset and greater potency. Having a methyl group on the imidazole or triazole ring at the alpha carbon allows for hydroxylation (via CYP) → short t1/2 metabolite → rapid glucuronidation (via UGT) → renal excretion
True or False: benzos are hydrophilic
False
Explanation: they are lipophilic
What does having a high logP value indicate?
lipophilic
True or False: low pKa = uncharged at physiological pH
True
What are benzo formulation issues and a possible solution?
Aq formulations are difficult with older benzos because they are insoluble in water unless a salt form is made using a strong acid (i.e., HCl), BUT salt forms of older benzos are unstable in an aq environment causing ring opening and decreased drug activity
Solution: diazepam and lorazepam are formulated in cosolvents (i.e., propylene glycol, benzyl alcohol) to maintain solubility within special storage and/or extra care (i.e., dilution) when injecting IV because of side effects
What makes midazolam's formulation different than most benzos?
Aq formulations work well for midazolam because it has a higher pKA (6.2) so it’s water AND fat soluble, the HCl salt of midazolam is stable in aq environment as well
This is done by buffering midazolam HCl to pH = 3 so it remains charged and in the solution → exists in stable ring-opened state → converts back to the active, ring-closed, mostly uncharged molecule at physiological pH