Intro to Psych Unit 1
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
Mental processes include . . .
Cognitions (thoughts), feelings (affect), states of consciousness
Structuralism
an early school of psychology that used introspection to explore the elemental structure of the human mind
William James
founder of functionalism; studied how humans use perception to function in our environment
Functionalism
A school of psychology that focused on how our mental and behavioral processes function - how they enable us to adapt, survive, and flourish.
Sigmund Freud
Austrian physician whose work focused on the unconscious causes of behavior and personality formation; founded psychoanalysis.
Psychoanalysis
Freud's theory of personality, which attributes thoughts and actions to unconscious motives and conflicts; the techniques used in treating psychological disorders by seeking to expose and interpret unconscious tensions, the "talking cure"
Talking cure
a therapy in the form of a discussion of psychological distress with a trained professional, leading to the elimination of distressing symptoms
John B Watson
founder of behaviorism
Behaviorism
A scientific approach to the study of behavior that emphasizes the relationship between environmental events and an organism's behavior (stimulus -> response)
Humanistic Psychology
An approach to psychology that emphasizes the role of free choice and our ability to make conscious, rational decisions about how we live our lives
Abraham Maslow
Humanistic psychologist known for his "Hierarchy of Needs" and the concept of "self-actualization"
Self-actualization
according to Maslow, one of the ultimate psychological needs that arises after basic physical and psychological needs are met and self-esteem is achieved; the motivation to fulfill one's potential
Carl Rogers
Humanisic; self-concept and unconditional positive regard drive personality
Margaret Washburn
first woman to earn a Ph.D. in psychology
Mary Whiton Calkins
American psychologist who conducted research on memory, personality, and dreams; first woman president of the American Psychological Association
Francis Cecil Summer
first African American to earn a PhD in psychology, father of African American psychology
Cognitive psychology
the scientific study of all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating
Biological psychology
a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior
Computational psychology
Uses theoretical analysis, computer science, and mathematical modeling to understand how the brain and nervous system function, develop, and their cognitive processes. It often involves creating models and simulations to study biological processes and behaviors.
Developmental psychology
a branch of psychology that studies physical, cognitive, and social change throughout the life span
Social psychology
the scientific study of how we think about, influence, and relate to one another
Cultural psychology
the study of how cultures reflect and shape the psychological processes of their members
Clinical psychology
area of psychology that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of psychological disorders and other problematic patterns of behavior
Health psychology
the subfield of psychology concerned with ways psychological factors influence the causes and treatment of physical illness and the maintenance of health
Descriptions
perceivable information
Goals of psychology
describe, explain, predict, control
Mirror neurons
Frontal lobe neurons that fire when performing certain actions or when observing another doing so. The brain's mirroring of another's action may enable imitation, language learning, and empathy.
Theory
A scientific theory is a logical explanation for the relevant data or facts scientists have observed regarding certain phenomena
Hypothesis
A statement that proposes the existence of a relationship between variables; typically, as a tentative explanation for cause and effect
Variables
anything that varies
Operational definitions
specific explanations of abstract concepts that a researcher plans to study
Sample
a subset of the population
Representative sample
A sample in which critical subgroups are represented according to their incidence in the larger population that is being studied
Random sample
A sample group of a larger population that is selected by randomization procedures
Convenience sample
a form of nonprobability sample using respondents who are convenient or readily accessible to the researcher—for example, employees, friends, or relatives
W.E.I.R.D
Western, Educated, Industrialized, Rich, Democratic (96% of research comes from WEIRD countries)
Case study
an observation technique in which one person is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles
Observational method
the technique whereby a researcher observes people and systematically records measurements or impressions of their behavior
Natural observation
observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate and control the situation
Observer bias
tendency of observers to see what they expect to see
Generalizability
the extent to which we can claim our findings inform us about a group larger than the one we studied
Survey
a technique for ascertaining the self-reported attitudes or behaviors of a particular group, usually by questioning a representative, random sample of the group
Correlational Method
a research procedure used to determine how much events or characteristics vary along with each other
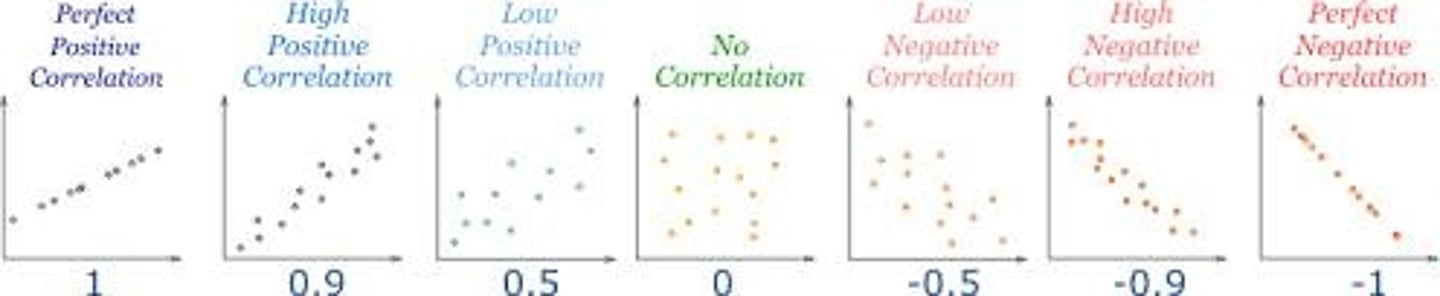
Coefficient of correlation
a statistical index ranging from -1.00 to +1.00 that indicates the direction and degree of correlation
3 key elements of experiments
manipulation of an independent variable and measure of the outcome or dependent variable, random assignment, control over the research environment
Independent variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.
Dependent variable
The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable.
Random assignment
assigning participants to experimental and control conditions by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differences between those assigned to the different groups
Experimental group
In an experiment, the group that is exposed to the treatment, that is, to one version of the independent variable.
Control group
In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.
Quasi-experiments
comparisons of groups that differ in exposure to a variable of interest that cannot be manipulated for ethical or practical reasons
Statistics
Mathematical methods for describing and interpreting data
Measure of central tendency
mean, median, mode
Descriptive statistics
numerical data used to measure and describe characteristics of groups. Includes measures of central tendency and measures of variation.
Variability
in a set of numbers, how widely dispersed the values are from each other and from the mean
Normal distribution
A function that represents the distribution of variables as a symmetrical bell-shaped graph.
Measure of variability
A measure that indicates whether distribution scores are clustered closely around their average or widely spread out
Range
the difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution
Standard deviation
a computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score
Inferential statistics
numerical methods used to determine whether research data support a hypothesis or whether results were due to chance
statistical significance
a statistical statement of how likely it is that an obtained result occurred by chance
Psychology
The scientific study of behavior and mental processes
Scientific method
careful observation of events in the world, the formation of predictions based on these observations, and the testing of these predictions by the manipulation of variables and systematic observation
Behavior
The observable actions by which an organism adjusts to its environment
Wilhelm Wundt
german physiologist who founded psychology as a formal science; opened first psychology research laboratory in 1879
Behavioral Neuroscience
Everything psychological is simultaneously biological
Nervous system
Carries information to and from different parts of the body
3 Basic Types of Neurons
Sensory, Motor, and Interneurons
Sensory Neurons
Messages from sensory receptors to central nervous system
Motor Neurons
Carry messages from central nervous system to muscles
Interneurons
Intermediary between sensory and motor neurons
How Neurons Communicate
Chemical and electrical activity
Chemical activity
presynaptic neuron -> postsynaptic neuron, neurotransmitters
Presynaptic neuron
conducts impulses toward the synapse
Postsynaptic neuron
transmits impulses away from the synapse
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
Electrical Activity
resting potential and action potential
Resting Potential
the state of the neuron when not firing a neural impulse
Action Potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
Glial Cells
Support cells that assist neurons by providing structural support, nutrition, and removal of cell wastes, and manufacturing myelin
Serotonin
A neurotransmitter that contributes to the regulation of mood, appetite, and sleep.
Dopamime
A neurotransmitter involved in control of movement and sensations of pleasure
Acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that plays a key role in muscle movement, arousal, attention, learning, and memory.
Endorphins
Neurotransmitters that act as natural painkillers and are involved in pleasure and reward.
Norephinephrine
A neurotransmitter involved in arousal and mood
GABA
A neurotransmitter involved in sleep and inhibits movement
Glutamate
A neurotransmitter involved in learning, memory, formation, nervous system development, and synaptic plasticity