Integumentary system (part 4)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
list the vesiculobullous disorders
impetigo, herpes simplex, varicella, herpes zoster, erythema multiforme, dyshidrosis
describe the presentation of impetigo
erythematous papules that have honey-colored crust. Highly contagious, caused by staph
describe presentation of herpes simplex
cluster of multiple vesicles - painful erosion of the vesicle with ulcer formation
what is the hallmark of varicella
lesions present and in all stages simultaneously
list the stages of varicella
red papule --> vesicle --> pustule --> ulceration --> crusted lesion
what two disorders are caused by the varicella zoster virus
herpes zoster (shingles)
varicella (chicken pox)
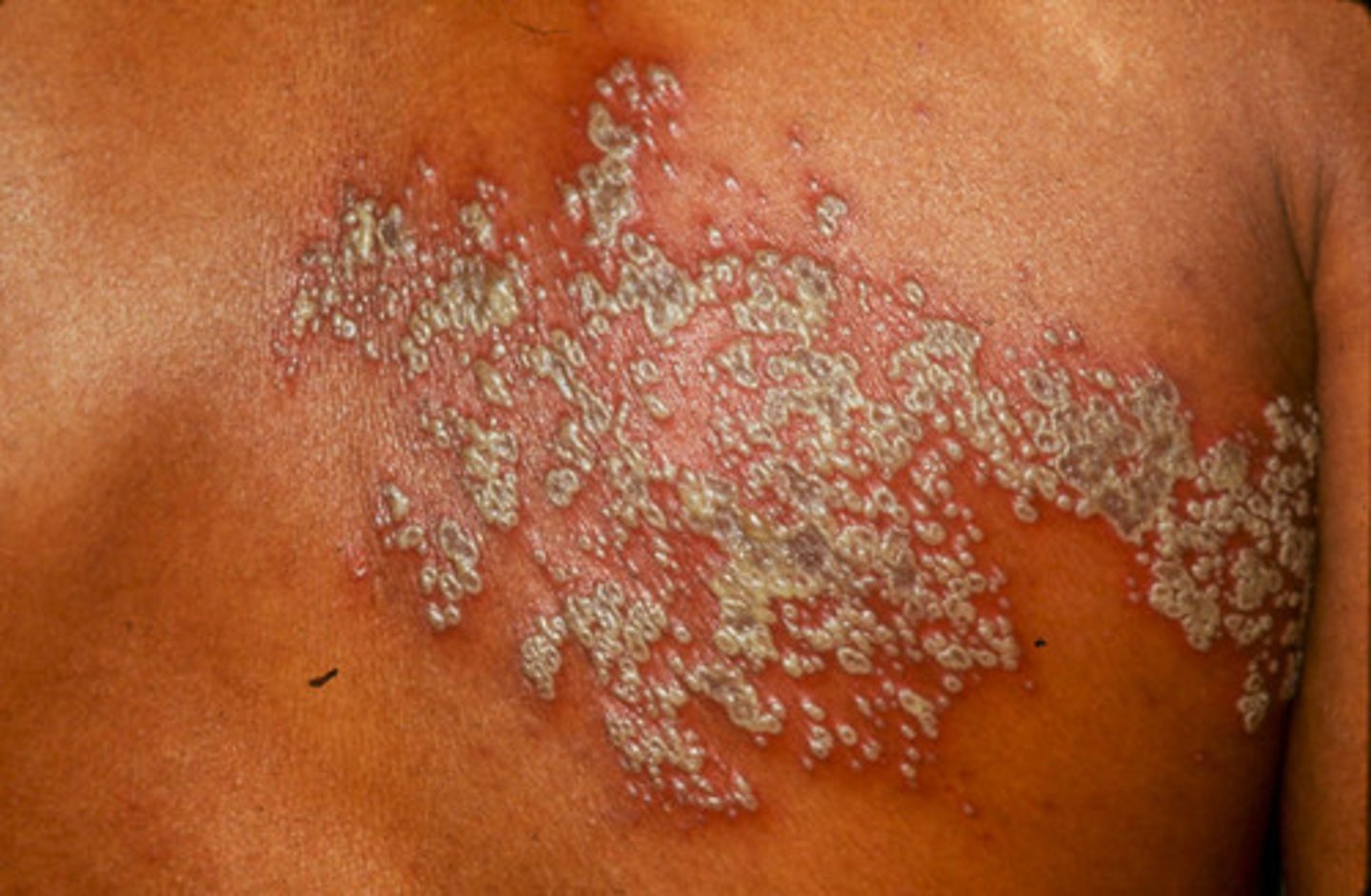
what is the hallmark for shingles
presents along a dermatome and is usually unilateral
herpes zoster
viral disease affecting the peripheral nerves, characterized by painful blisters that spread over the skin following the affected nerves, usually unilateral; also known as shingles
describe the presentation of erythema multiforme minor
flat, reddened macules and/or plaques. Lesions may have a target appearance or the bull's-shaped lesions with 3 zones of color
what can the erythema multiforme minor lesions progress to
vesicles or bulla
what causes erythema multiforme minor
herpes virus
what causes erythema multiforme major
infection like herpes virus or mycoplasma
or response to medicine
what lab changes might you see in a patient with erythema multiforme
decreased WBC and RBC
Increased sed rate, BUN and creatinine
what is dyshidrosis
vesicular disorder that typically affects the hands and feet
what is dyshidrosis associated with
excessive moisture or sweating of the hands/feet
small vesicles that itch and burn which crust over
list the inflammatory disorders
acne vulgaris, rosacea, cellulitis, boil/abscess, folliculitis
what are the 4 components of rosacea
facial flushing, papules or pustules, rhinophyma, dry eyes
how can rosacea be differentiated from acne
no comdeones present
what usually causes boils or abscesses
staphylococcal infections of hair follicles or sebaceous glands
what typically causes cellulitis
staph or strep infections
what is folliculitis
inflammation of hair follicles, typically associated with staph
list the types of hyperplasia disorders
verruca (warts), corns & calluses, molluscum, skin tag, epidermal inclusion cyst
what is the difference between a corn and a callus
callus is thick skin with indistinct borders, painless
corn has distinct borders and is painful
true/false: molluscum is contagious
true
describe molluscum
white or flesh-colored firm dome-shaped papule with a small dimple center
describe epidermal inclusion cysts
lesions with a cheesy discharge and a foul odor
nodular and firm
subcutaneous lesions and tender
what is tinea pedis
fungal infection on the soles of the feet and webs of the toes. scaly rash with maceration
what is tinea capitis
fungal infection that invades the hair shaft causing breakage
what is tinea corporis
ringworm found on non-hairy extremities and trunk
annular lesion with scaling and central clearing with well defined borders
what will a tick bite that is affected by lyme disease or rocky mountain spotted fever be marked by
round target-like lesion