Disorders of the Pancreas
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Only the tail of the pancreas is _______, the majority of the pancreas is ______.
tail - intraperitoneal
most pancreas - retroperitoneal
What type of cell releases pancreatic lipase?
Acinar cells
Pancreatitis is often secondary to what 2 causes?
biliary tract disease and alcohol abuse
What are some pancreatic enzymes in body fluids?
lipase and amylase
The function of the ____ is to secrete pancreatic juice - alkaline fluid (pH 8) containing ~20 enzymes)
pancreas
______ is stimulated by acidic chyme; and is released into the blood by duodenal S cells
secretin
____ is stimulated by AAs, peptides, and fatty acids; and is released into the blood by duodenal I-Cells
CCK
The main inhibitor of exocrine secretion is ___
Somatostatin
What are some enzymes secreted by the pancreas?
amylolytic, lipolytic, and proteolytic
What are the 4 factors that prevent autodigestion of the pancreas and loss of any of these functions can lead to:
Premature enzyme activation
Autodigestion
Acute pancreatitis
1. Packaging of pancreatic proteases in proenzyme form
2. Intracellular calcium homeostasis
3. Acid-base balance
4. Synthesis of protective protease inhibitors
Most cases of acute pancreatitis are due to what?
biliary tract disease ( #1 = gallstones) or #2 = heavy EtOH intake
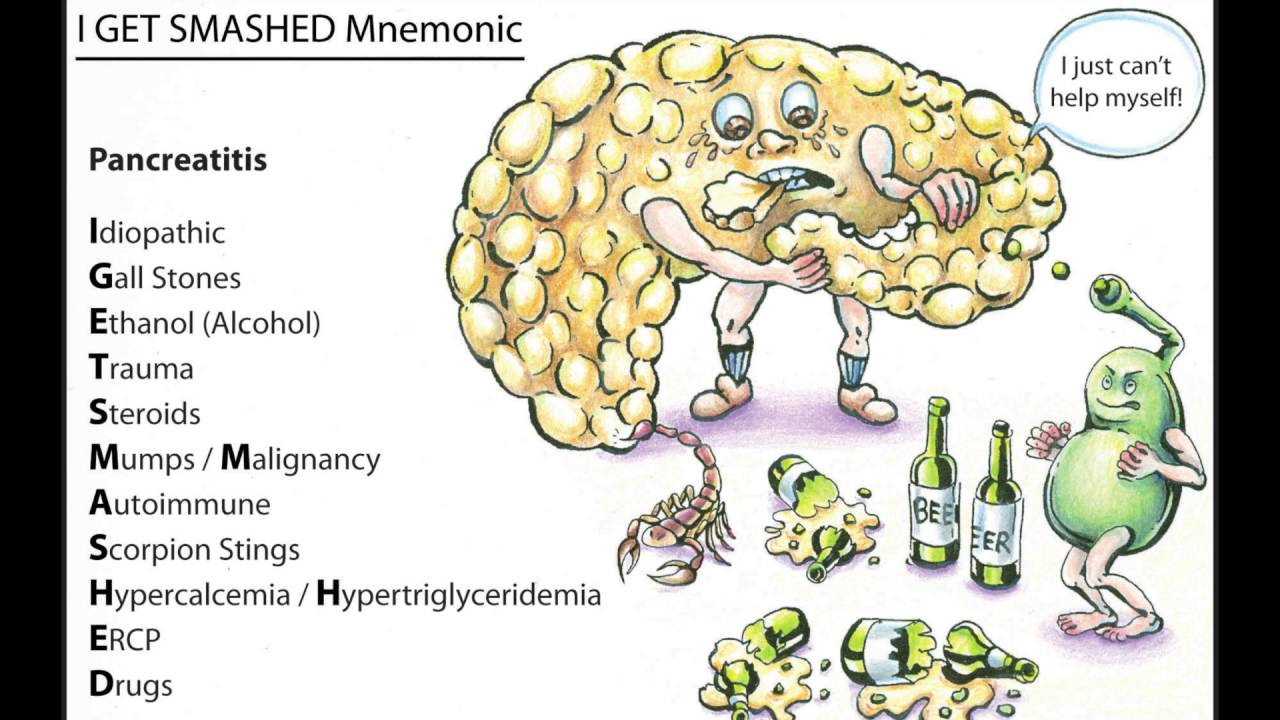
drugs, hypercalcemia, hypertriglyceridemia (3rd MCC), ERCP, dialysis are all other causes of what?
acute pancreatitis
A pt presents with complaints of N/V, fever, pallor, and ABRUPT/severe epigastric abd pain that radiates to the back and gets better when leaning forward. Upon PE there was NO guarding, rigidity or rebound tenderness. There is also absent bowel sounds. Her skin is pale, cool, and clammy. She has a + gray turner sign. Labs show elevated amylase and lipase. ---- what is the likely dx?
acute pancreatitis
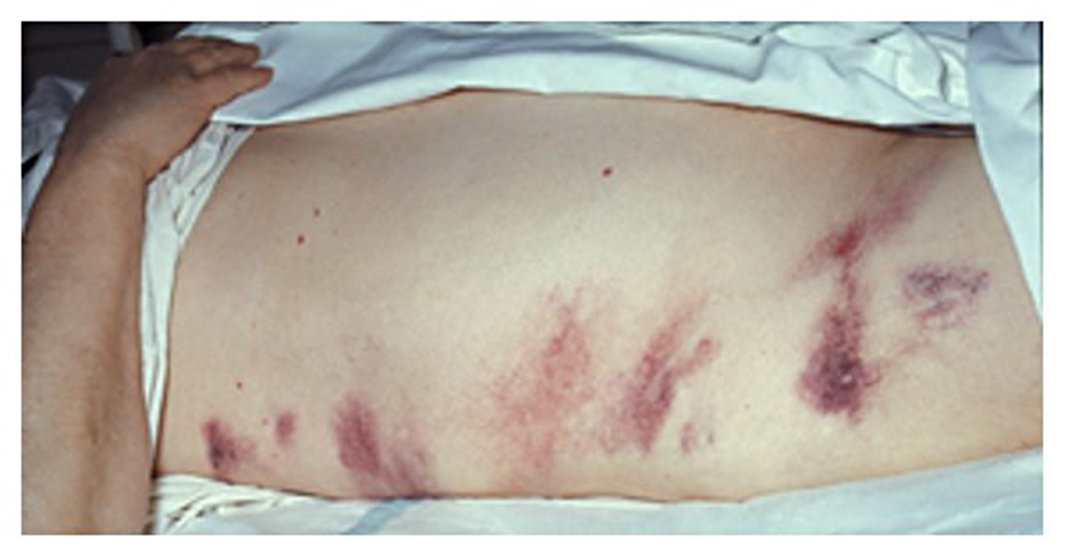
What is the sign characterized by a retroperitoneal hemorrhage and is associated with acute pancreatitis?
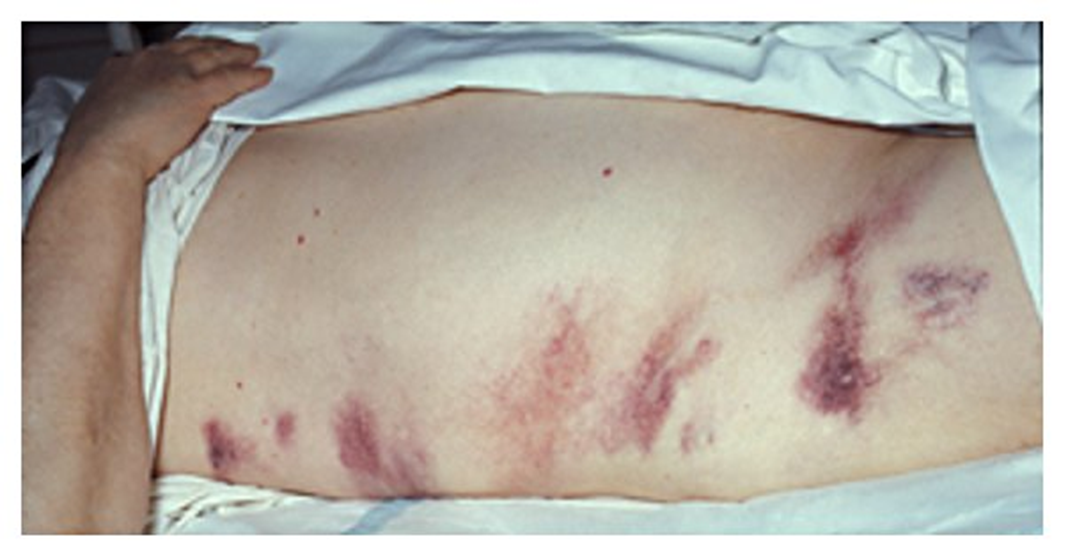
Gray Turner sign
What is the sign characterized by a intraperitoneal hemorrhage and is associated with acute pancreatitis?
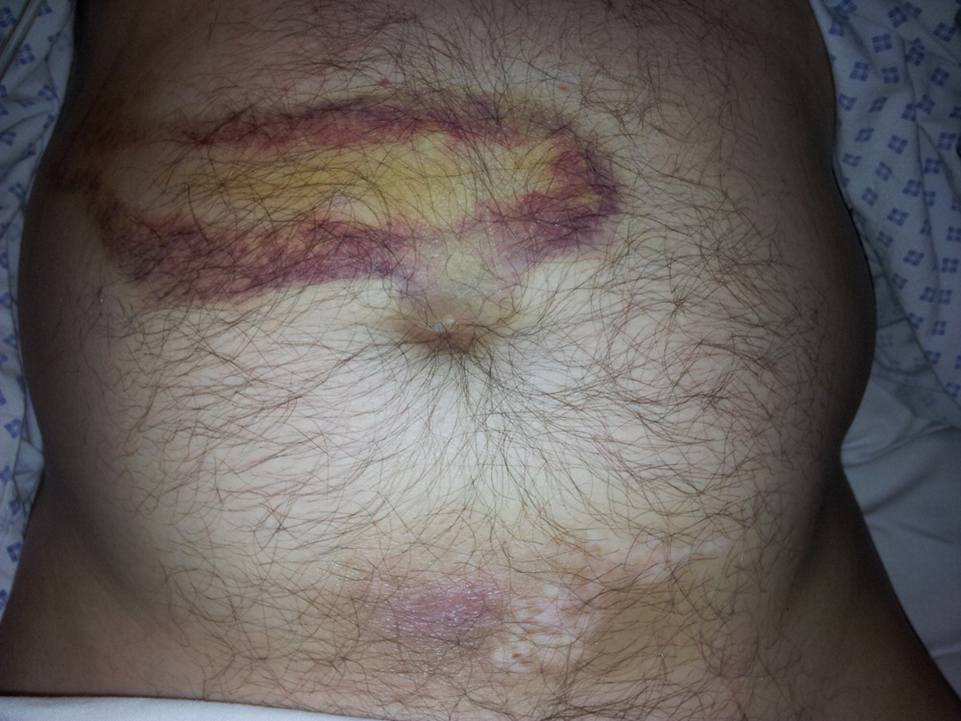
Cullen sign
Amylase or lipase: remains elevated longer and is more accurate for diagnosis?
lipase
ALT >150 suggests what?
biliary pancreatitis
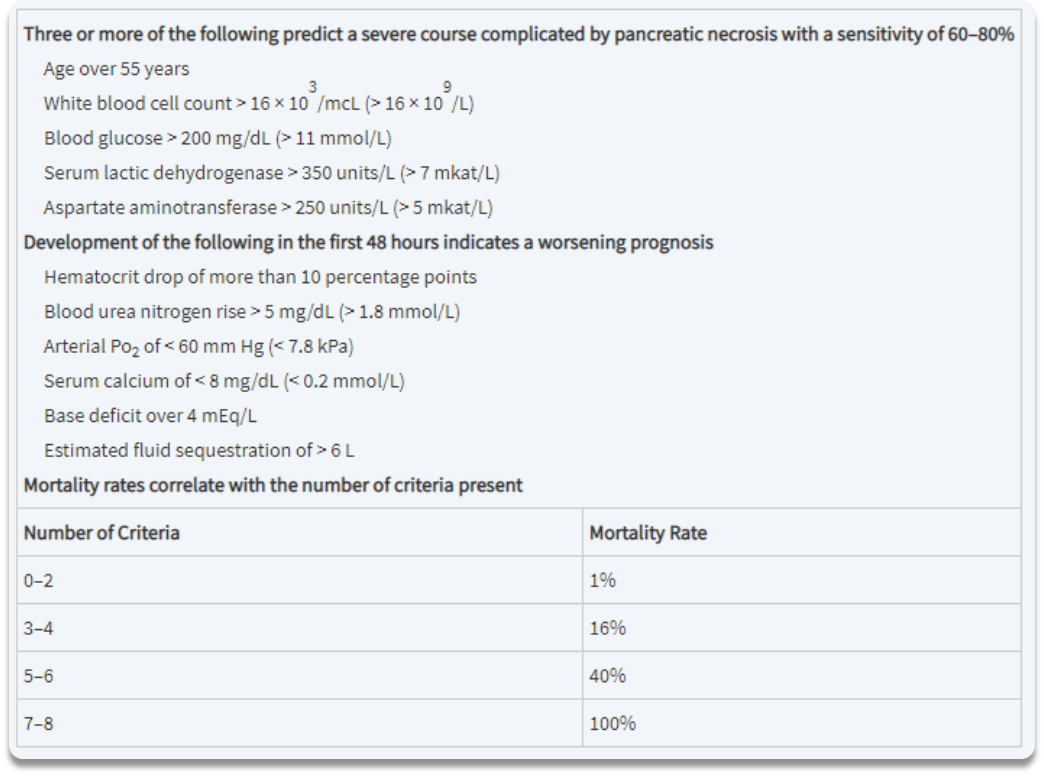
What diagnostic scoring system is used for acute pancreatitis?
Ranson criteria (know at least presentation criteria!)
What two signs will you see on KUB imaging for acute peritonitis?
sentinel loop and colon cut off sign
should you get a CT of the abd with or without for acute pancreatitis?
WITH
What is the diagnostic imaging of choice for acute pancreatits?
CT Abd WITH contrast
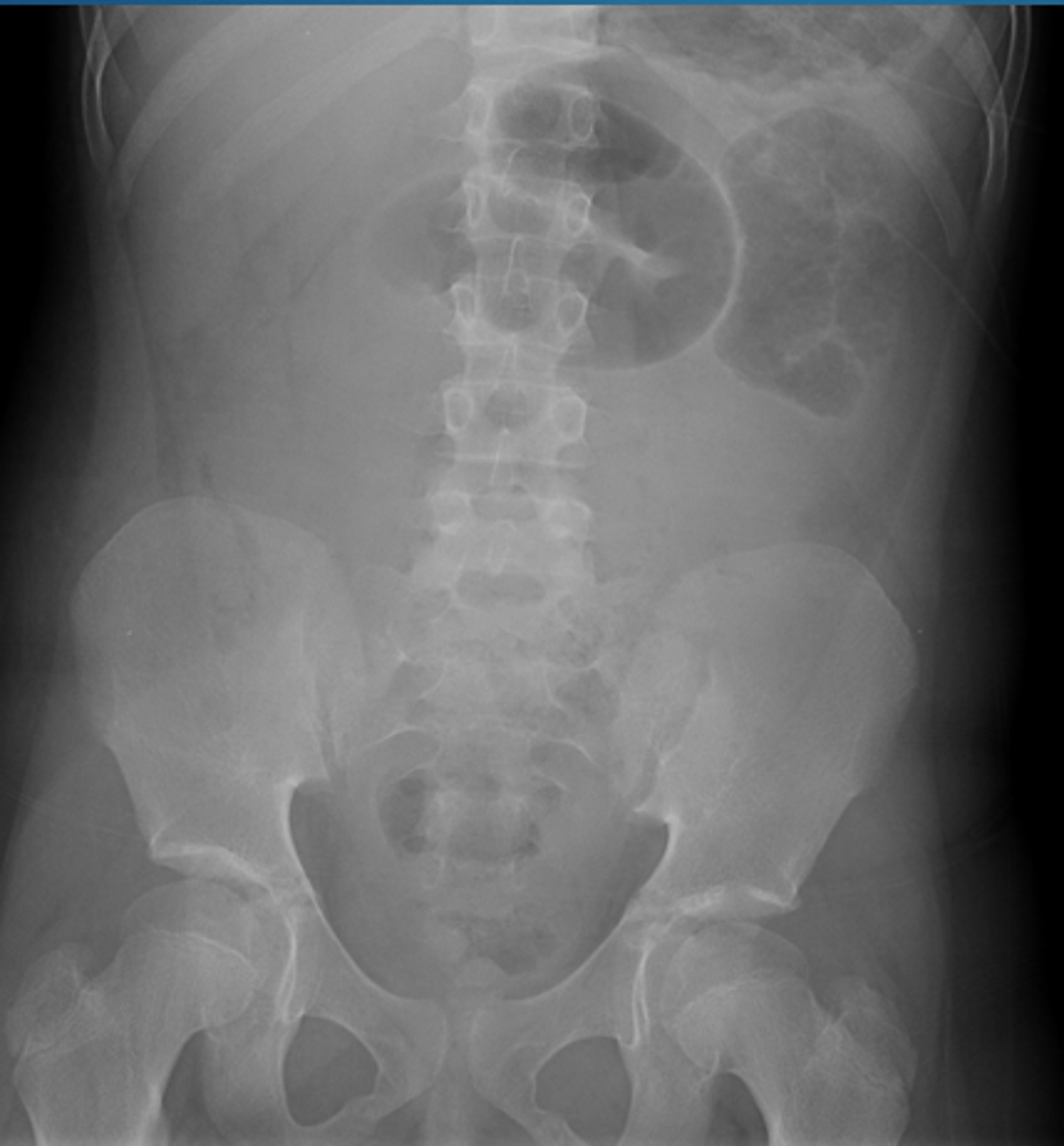
What KUB sign when diagnosing acute pancreatitis is defined by a localized ileus (segment of air-filled small intestine) most commonly in the LUQ?
sentinel loop
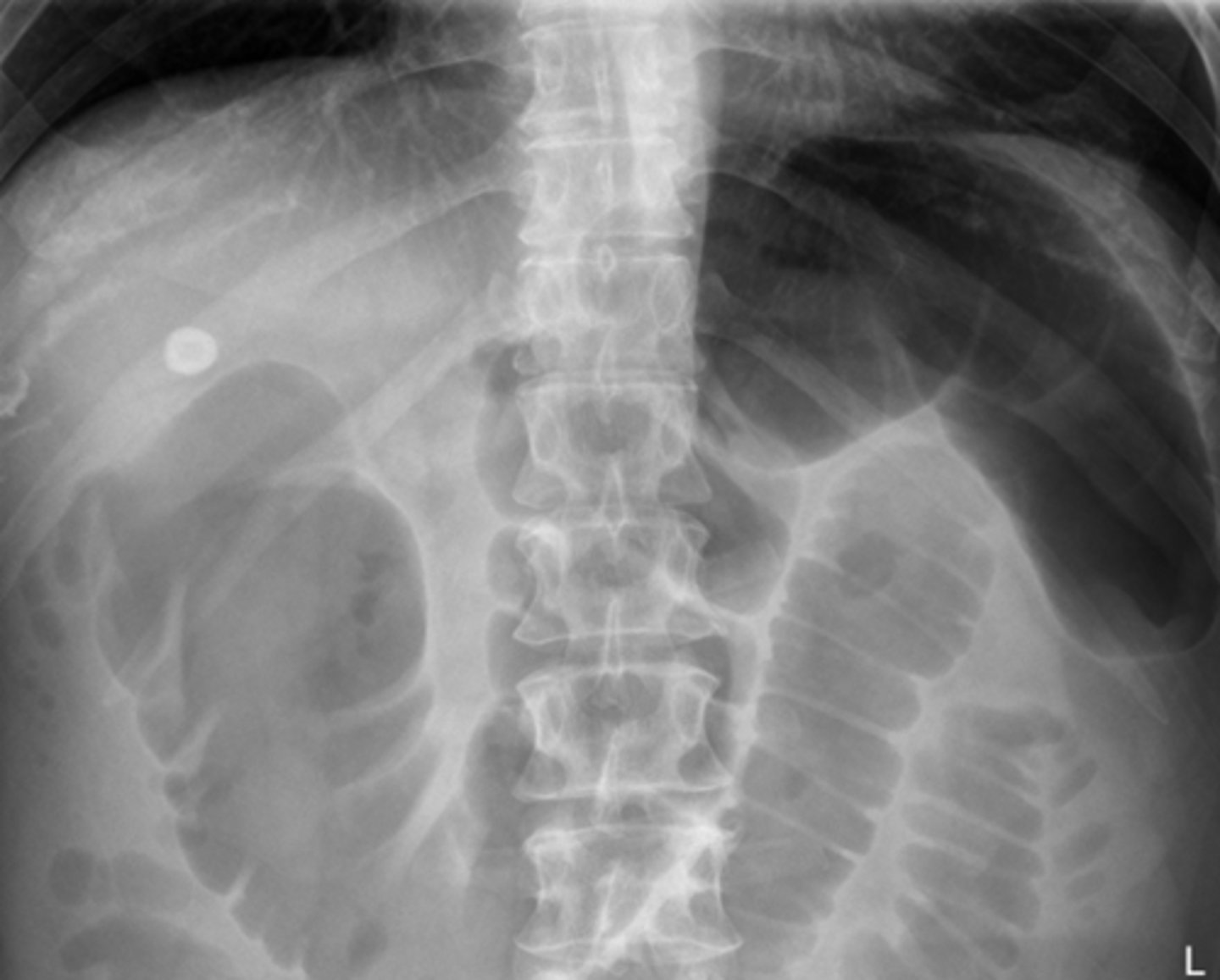
What KUB sign when diagnosing acute pancreatitis is gas filled segment of transverse colon abruptly ending at the area of pancreatic inflammation?
colon cut off sign
Pancreatic calcifications are sign in what stage of pancreatitis?
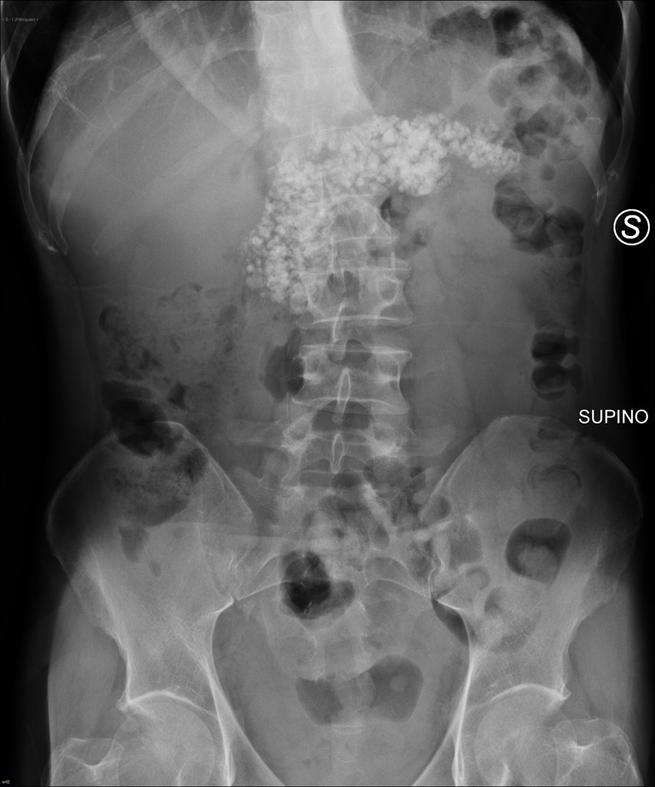
chronic pancreatitis
What are some complications acute pancreatitis?
Pre-renal azotemia
ARDS
Pancreatic abscess
Fluid collection/necrosis
Hemorrhage
What is the tx for mild acute pancreatitis?
NPO or clear liquids only, IVF, analgesics (diluadid 1mg q4h IV)
**think NPO, fluids, pain!
**mild dz is more common, subsides in several days
What is the tx for severe acute pancreatitis?
NPO
IVF
ICU monitoring
Surgical consult
Hypocalcemia → calcium gluconate
Coagulopathy or hypoalbuminemia → FFP or serum albumin
Colloid administration à increased risk of ARDS
Enteral nutrition vs. parenteral nutrition
IVF abx
What is the IVF ABX PROPHYLAXIS tx for severe acute pancreatitis?
imipenem or cefuroxime
What is the IVF ABX CONFIRMED INFECTION
tx for severe acute pancreatitis?
imipenem or meropenem
What are the complications of acute pancreatitis and how are you treating them?
necrotizing pancreatitis → necrosectomy
abscess → percutaneous or surgical drainage
pancreatic pseudocyst → monitor or surgical correction
What are the risk factors for chronic pancreatitis?
"TIGAR-O"
Toxic-metabolic, idiopathic, genetic, autoimmune, recurrent and severe acute pancreatitis or obstructive
EtOH
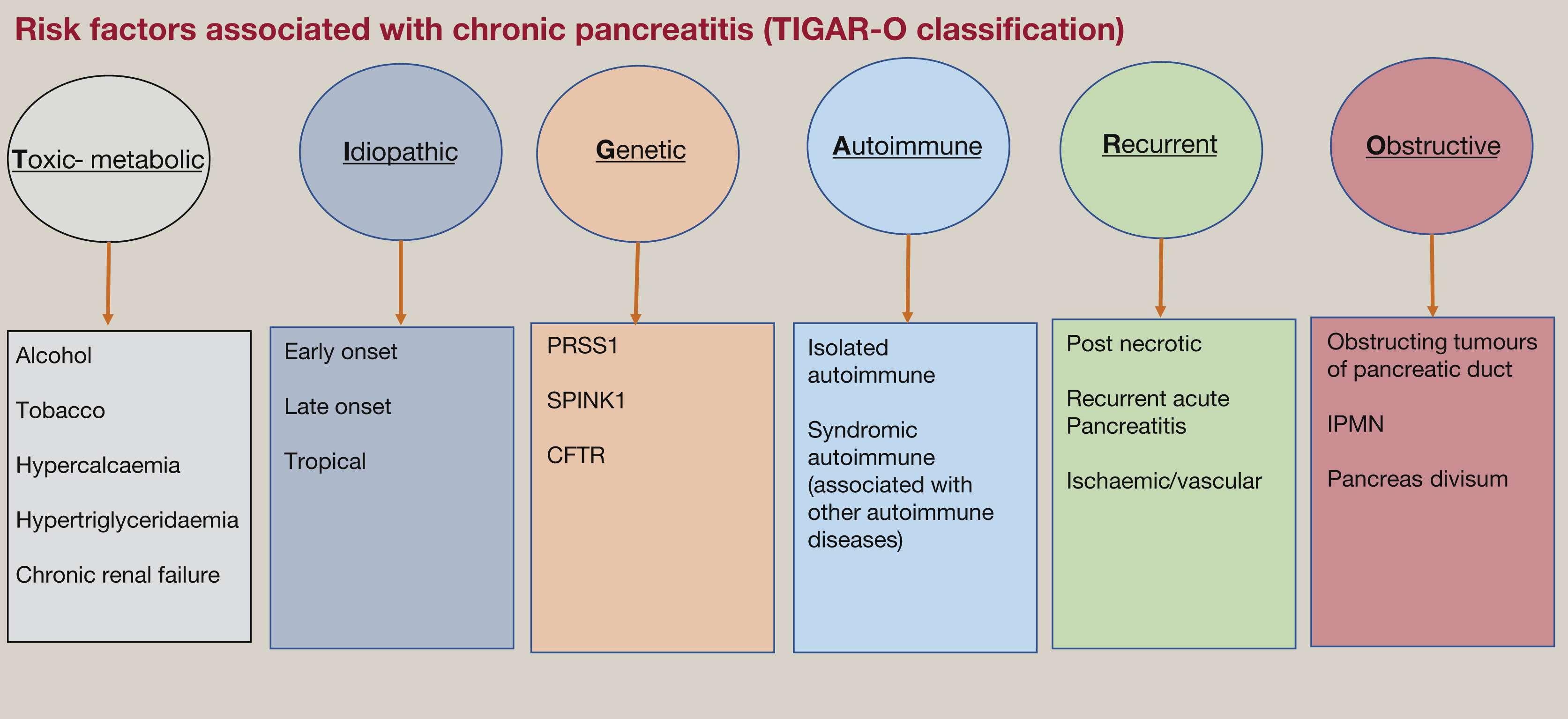
acute vs chronic pancreatitis?
similar to acute, but not as severe and has less hemodynamic issues
A pt presents with complaints of PERSISTENT recurrent episodes of epigastric or LUQ pain, anorexia, N/V/C, WL, and flatulence. She complains of frequent steatorrhea. PE shows tenderness over the pancreas during attacks as well as guarding. ----- what is the likely dx?
chronic pancreatitis
What is a common symptom for chronic pancreatitis?
steatorrhea- bulky, foul, fatty stools may occur late in course (bc they can’t digest fats!)
What are some labs/ diagnostics associated with chronic pancreatitis?
Amylase and lipase may be elevated during attack however NL values do not exclude diagnosis
ALP and bilirubin - compression of bile duct
Glycosuria
Excess fecal fat
Secretin stimulation test - pancreatic exocrine insufficiency
Genetic mutations
IgG4 levels, ANA
Pancreatic biopsy
What is the gold standard for dx of chronic pancreatitis IF IMAGING FAILS?
HISTOLOGY
What is the initial dx imaging study of choice for chronic pancreatitis?
CT
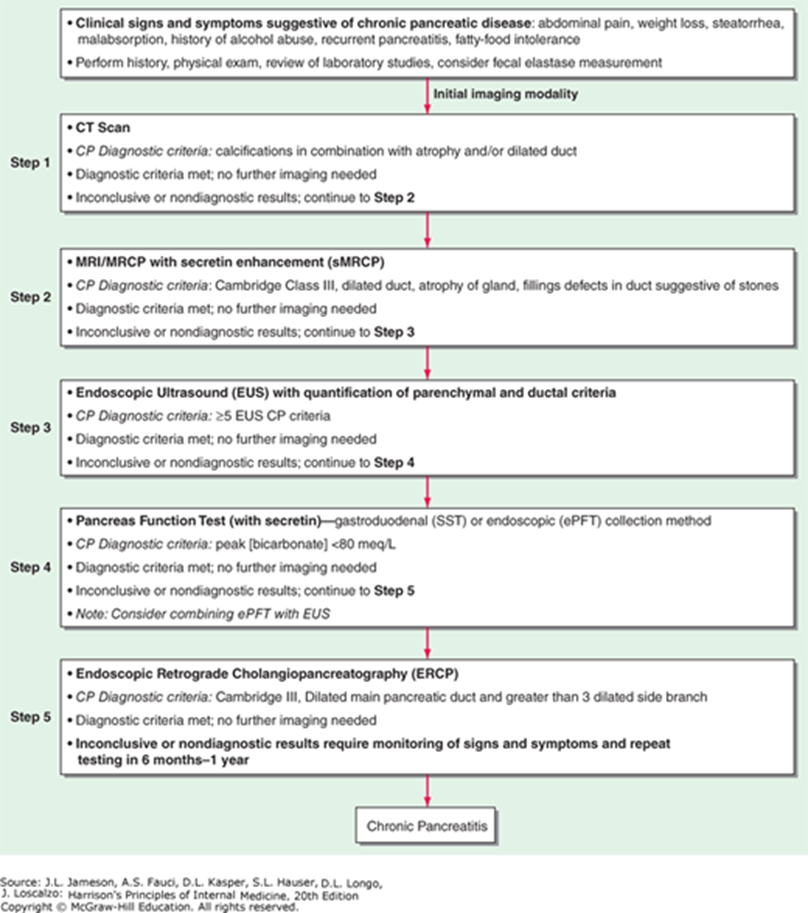
What is the most sensitive (but also invasive) imaging study for chronic pancreatitis and what will you see?
ECRP- shows dilated ducts, intraductal stones, strictures, pseudocysts
What will EUS (2nd test) show for suspected chronic pancreatitis?
Hyperechoic foci with shadowing indicative of calculi in the main pancreatic duct and lobularity with honeycombing of the pancreatic parenchyma
What are some chronic pancreatitis complications?
OPIOID addiction
Diabetes
Pancreatic pseudocyst and/or abscess
Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency
Malnutrition
Pancreatic Cancer
What is the treatment for chronic pancreatitis?
Low fat diet
ETOH cessation
Avoid opioids- NSAIDs, APAP, tramadol, TCA
Pancreatic enzyme replacement
Surgical intervention
What composes ranson criteria?
three or more of the following predict a severe course complicated by pancreatic necrosis:
age >55yo
WBC count >16,000
Blood glucose >200
Serum Lactic dehydrogenase >350
Aspartate aminotransferase >250
What is another name for direct bilirubin?
A. Conjugated
B. Unconjugated
A!
What is the most common cause of acute liver failure?
A. Augmentin (amoxicillinc-clavulanic acid)
B. Acetaminophen
C. Ketamine
B!
What type of hernia is depicted by A?
A. Indirect inguinal hernia
B. Direct inguinal hernia
C. Femoral hernia
A!
Which of the following is associated with inflammatory bowel disease?
A. Primary biliary cirrhosis
B. Primary sclerosing cholangitis
C. Hemochromatosis
D. Rotor syndrome
B!
Which of the following is not a component of Charcot’s triad?
A. Fever/chills
B. Jaundice
C. AMS (altered metal status)
D. RUQ pain
C!
Which of the following is not commonly seen in hemochromatosis?
A. Kayser–Fleischer rings
B. Arthralgias
C. ED
D. Insulin resistance
A! (wilson’s disease)
What test is available for PSC
A. ANA
B. AMA
C. P-ANCA
D. Lactoferrin
C! (you see PSC w/ UC and P-ANCA is + in UC)
What test is available for PBC
A. ANA
B. AMA
C. P-ANCA
D. ASCA
B! *look up smooth muscle AMA
A 38 yo male with hepatic failure, what should you consider?
A. Wilson’s disease
B. Hemochromatosis
C. PBC
A!
(B is over 50)
Treatment of Wilson’s
A. Penicillamine
B. Phlebotomy
C. Phenobarbital
D. Ursodeoxycholic acid
A!
25 yo female with a history of DVT presents with acute liver failure and ascites. What do you suspect?
A. PSC
B. Budd Chiari
C. Hep C
D. Acute mesenteric ischemia
B!
45 year old female with RUQ pain, jaundice, fever. What do you need to rule out?
A. Cholecystitis
B. Cholangitis
C. PUD
B!
A patient with bleeding presents with elevated PT/INR. IV Vit K fails to improve bleeding time. What could this suggest?
A. Liver failure
B. Malabsorption
C. Protein C deficiency
A!
*improved with Vit. K can indicate malabsoroption
Criteria for acute pancreatitis?
A. Ranson’s
B. Rome
C. PECARN
A!
What can predict necrosis in acute pancreatitis?
A. Triglycerides >1000
B. Creatinine > 1.8 at 48 hours
C. HCT < 30 early in course
B!
What is the most common cause of death in chronic pancreatitis?
A. Cancer
B. ARDS
C. CKD
A!
What is the most common cause of cancer? not type!
Thromboembolic events