Learning approaches: The Behaviourist Approach
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Who are the key psychologists?
Pavlov and Skinner
What does the behaviourist approach study?
Only behaviour that can be observed or measured
Does the behaviourist approach accept or reject introspection?
Reject
Why does the behaviourist approach reject introspection?
Concepts were vague and difficult to measure
What do behaviourists suggest about our learning processes?
They’re the same in all species so animals can replace humans as experimental subjects
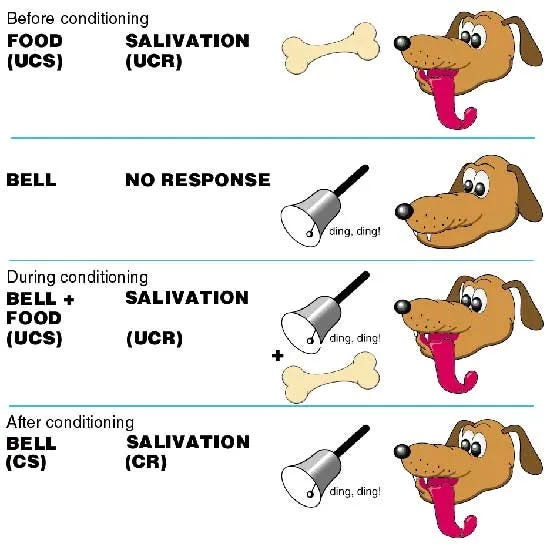
What is classical conditioning?
Associating two stimuli together to elicit a new learned response
Who studied Classical conditioning?
Pavlov
What was Pavlovs study called?
Pavlovs dogs
Describe Pavlovs study
What is operant conditioning?
Behaviour is shaped and maintained through consequences
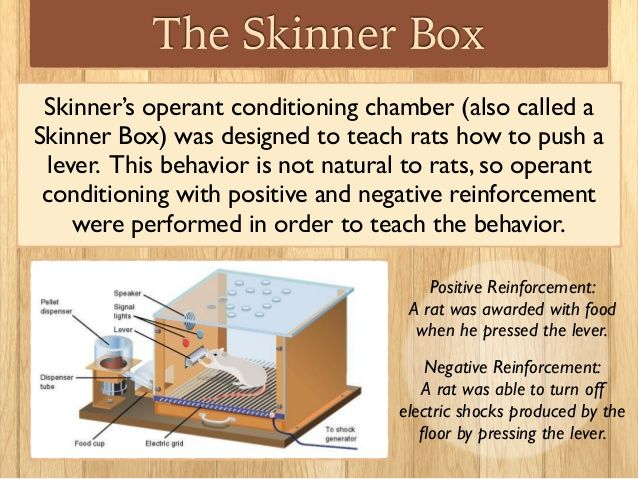
Who studied operant conditioning?
Skinner
What was Skinners study called?
Skinners box
Describe Skinners study
What are the 3 consequences of behaviour?
Positive reinforcement
Negative reinforcement
Punishment
What is positive reinforcement?
Recieving a reward when behaviour is performed
What is negative reinforcement?
Avoiding something unpleasant when a behaviour is performed
What is punishment?
An unpleasant consequence of behaviour
What does postivie/negative reinforcement lead to the increased likelihood of?
Repeated behaviour
What does punishment reduce the likelihood of?
Repeated behaviour
A03 Strength: Uses well-controlled research
Measures observable behaviour in controlled lab settings
Broken behaviour down into stimulus-response units and studied casual relationships
Behaviourist experiments have scientific credibility
A03 Strength: Real world application
Principles of conditioning have been applied to a range of real world behaviours
e.g token economy reward systems in prisons where desirable behaviour is rewarded with tokens in exchange for privileges
Increases value of approach as it has widespread application
A03 Limitation: Environmental determinism
All behaviour is determined by past experiences and ignores free will
Skinner - free will is an illusion and our past conditioning determines outcomes of situations
Extreme position which ignores influence of conscious decision making processes on behaviour
A03 Limitation: Ethical Issues
Animals kept in harsh conditions
Deliberately kept underweight so they were always hungry
Question of benefits vs costs
some would say the benefits outweigh the harm the animals experienced