Quality Management - Chp 5
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What does makes a product of good quality?
reliability - performs consistently and does not break easily
durability - resistance to wear and tear
conformance - complies with the product standards
aesthetics - appealing to the senses
What is quality management?
oversees all activities involved in manufacturing the product to maintain a good standard of quality and ensures the product is capable of doing what it is designed to do
What does ISO stand for?
International Standards Organisation
What does ISO do?
sets the product standards for companies to follow, to ensure they meet consumer requirements
What does NSAI stand for?
National Standards Authority of Ireland
What does NSAI do?
it certifies companies that meet ISO standards
Give an example of a quality management principle:
customer focus - understand customer needs and requirements
leadership - create an environment in which the entire workforce is involved in achieving the organisations goals
involvement of people - involve all people and their abilities to deliver high quality goods
process/system approach - activities and resources should be managed as a process/in a system
continual improvement - the goal should be continuous improvement
factual approach - decision making based on analysis of data and information
mutually beneficial supplier relationship
Quality characteristic + example
general description of what a product is supposed to be/do
lightweight
operates quietly
Quality attribute + example
a specific description of what a product is supposed to be/do to achieve a certain characteristic
weighs less than 20g
produces noise less than 10db
What is meant by aesthetics?
refers to how a product looks/ appeals to the senses
What factors are considered when making a product aesthetically pleasing?
colour
proportion
texture
line, shape and form
balance
What is the impact of poor quality?
a poor quality product will usually secure less of a market than high quality product due to it being
unreliable
not durable
does not meet quality standards
a better quality product will generate more sales, and will have a longer life cycle
What does the product life cycle diagram show?
describes the life of a product from when it is introduced to the market, to when its sales fall and it is no longer sold
What are the stages of the product life cycle?
Introduction - product is entered into the market
Growth - product begins to build a market base, and sales rise when people find out about the product
Maturity - product sales are steady and at a peak
Decline - sales fall due to factors, such as outdated technology, pricing issues, economic state
What does a bathtub curve show?
shows the likelihood of a product failing over time
Bathtub Curve: Start of life
high failure rate until defective products are identified and discarded
Bathtub Curve: Mid-life
failures are low and consistent, any failures are random
Bathtub Curve: End life
there is a high-failure rate as age and wear have an effect on the product
What is the manufacturing cost dependant on?
- materials
- labour
- quality control costs
- overhead (fixed costs)
Quality's impact of manufacturing cost?
- costs more to make high quality: better skilled/educated work force, better quality materials more expensive
- poor quality products incur additional costs when sent back to be fixed, potential for legal costs
What does QA stand for?
Quality assurance
Quality assurance
involves systematically checking all relevant processes to ensure required standards are met
quality control staff check the product at each stage of its manufacture
What does QC stand for?
Quality control
What is quality control?
systematically checking all relevant processes to ensure that required standards are met
Tolerances
the amount of variance on a measurement of a product
What is meant by the cost of quality?
money a business loses because its product was of insufficient quality, for example
repairing a damaged product
recalling and replacing defective products
dealing with legal action
PDCA/PDSA/Deming cycle
four step process for the continuous improvement of manufacturing processes and products
plan - recognise the opportunity, collect data and develop plat
do - implement the plan
study - analysis the results of the chage
act - include new changes and go through the cycle again with new plan, keep all parts of the plan that went well excluding all the negatives
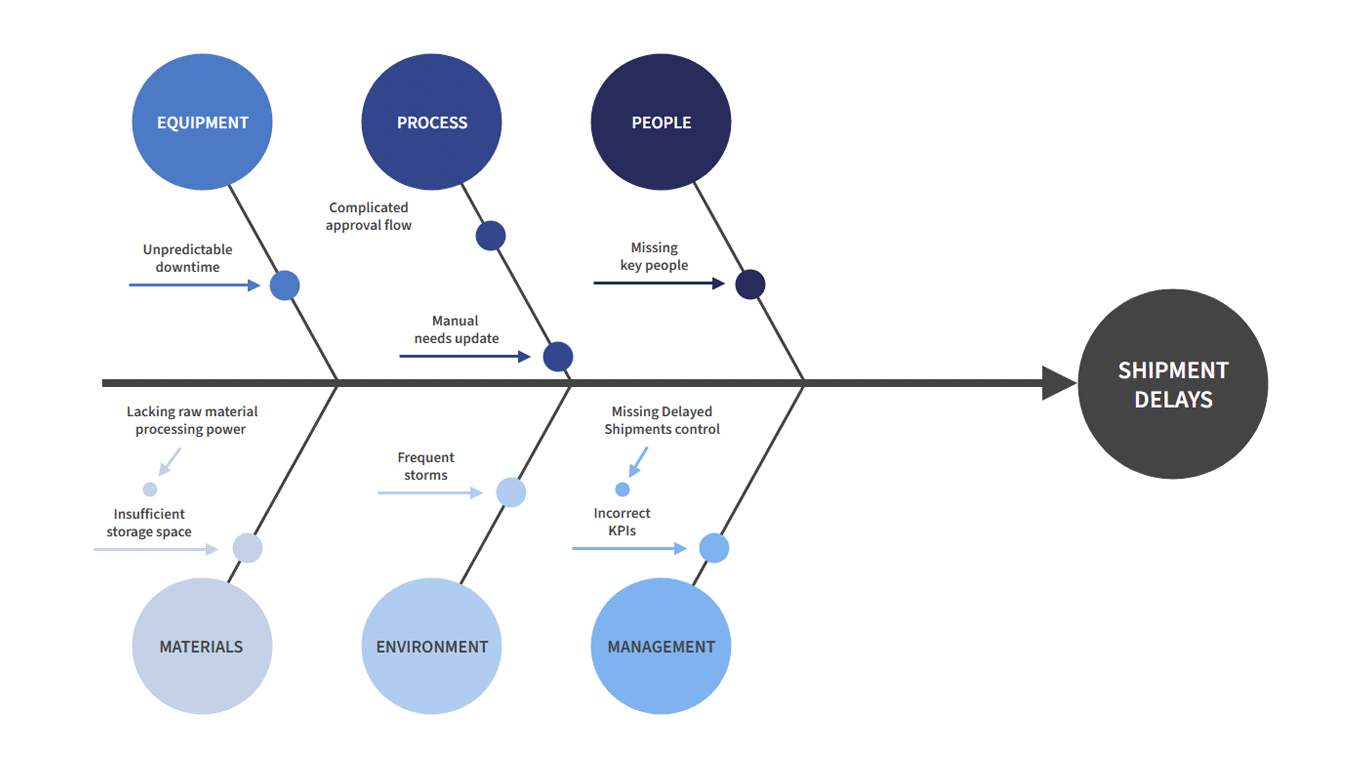
What is another name for a cause + effect diagram?
fishbone diagram
Give an example of a cause and effect diagram:
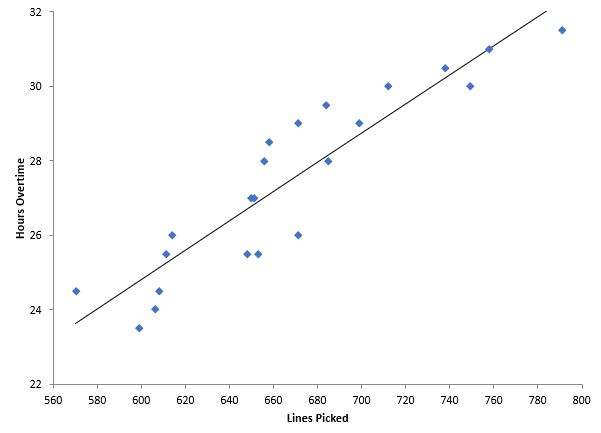
What does a scatter diagram show?
used to investigate the effect of an independent variable on the dependent variable
What is meant by statistical measurement?
collection and analysis of data in a systematic way
What is Planned Obsolesence?
company planning on their product to fail after a certain time period, forcing the consumer to buy more of the product