Enzymes
1/20
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Enzymes are part of the _______ macromolecule.
Protein
They ___________________ in our bodies
Speed up chemical reactions
Enzymes act as a __________ to speed up chemical reactions in nature
Catalyst
In your body, reactions that have enzymes acting as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions are called __________.
Metabolism
What is a catalyst?
A type of protein that increases the speed of a chemical reaction. Example: Cleaning products that rid bacteria using enzymes.
How do catalysts speed up chemical reactions?
They lower the activation energy needed to start the reaction
Activation Energy (E)
The amount of energy required to start and maintain a chemical reaction
Enzymes are used up and can NOT be used mutliple times- true or false?
False
Enzymes usually end in:
-ase
Sugars usually end in:
-ose
Active Site
Where the substrate binds to the enzyme and initiates the enzyme’s function
Substrates
Other molecules involved in a chemical reaction- called the “reactants”
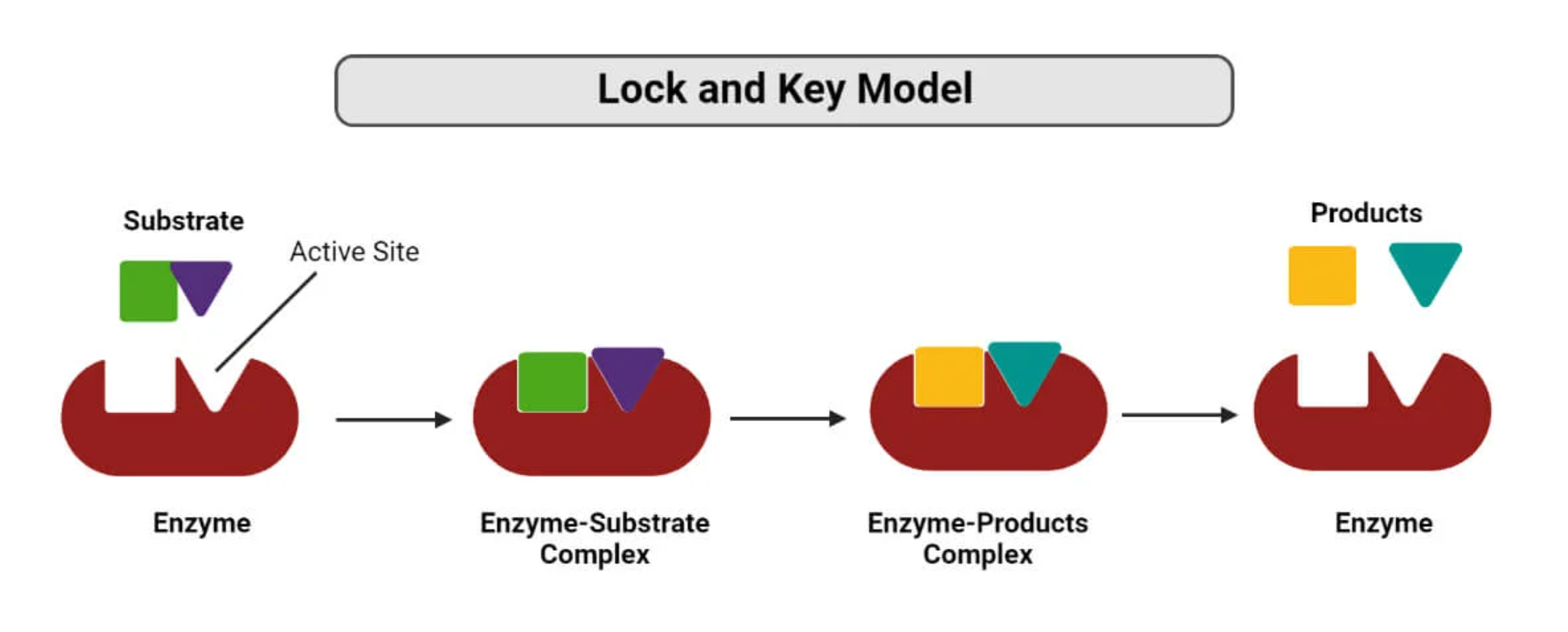
Lock and Key Model
The substrate fits perfectly to the enzyme
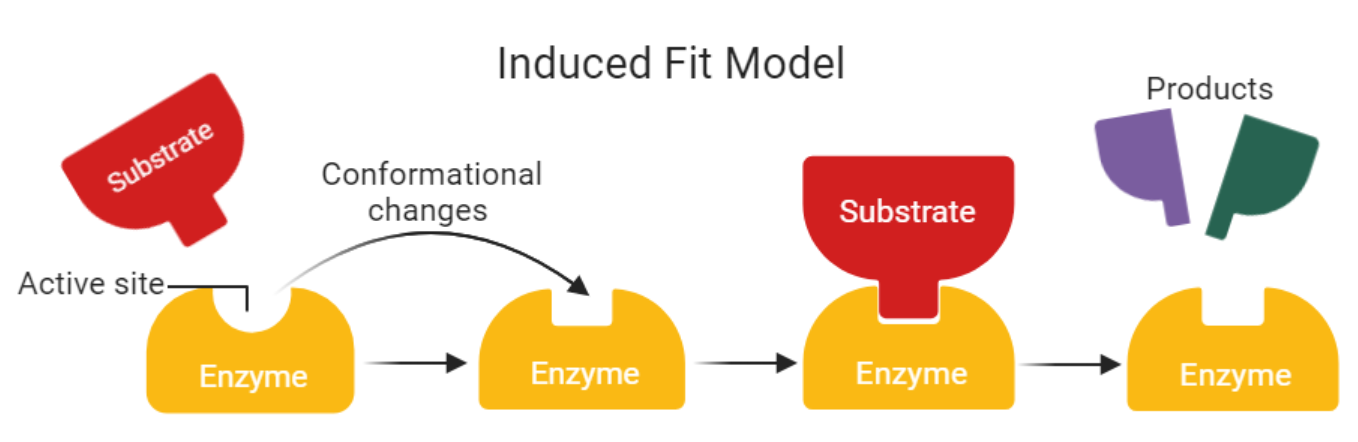
Induced Fit Model
Shape of the active site may change to fit the substrate shape
Anabolic Enzyme
Involed in building up long-chained molecules in the reaction products
Catabolic Enzyme
Breaks apart long-chained molecules in the reaction products
What affects the rate of enzyme activity?
Temperature and pH
Optimum Temperature
The most favorable temperature- you get the greatest number of interactions between the enzyme and substrate
Raising the temperature (boiling point)
Generally speeds up the reaction, but when the temperature is too high, causes the enzyme to denature (lose shape, lose function, doom)
Lowering the temperature
Molecules move slower, fewer interactions between the enzyme and substrate
pH effect on the enzyme
Changes in pH changes the protein shape, and changing the pH to extreme levels can cause the enzyme to denature