Integumentary System- Chapter 3.2
integumentary system- largest organ of the body that forms a physical barrier between the external environment and the internal environment that it serves to protect and maintain %%(skin)%%
Functions:
Skin is also critically important in %%regulating body temperature%%, due to the extensive array of tiny capillaries and sweat glands that lie near the surface of the skin.
It is also involved in certain %%chemical processes%% in the body.
Keratin:
keratin- a %%tough protein%% also found in hair and nails that adds structural strength, helps to protect the skin against damage
keratinocytes- produce keratin
- Keratin and naturally occurring oils in the skin assist in serving as a %%water barrier%%, and keratin prevents water from entering the body during bathing or swimming.
Melanin:
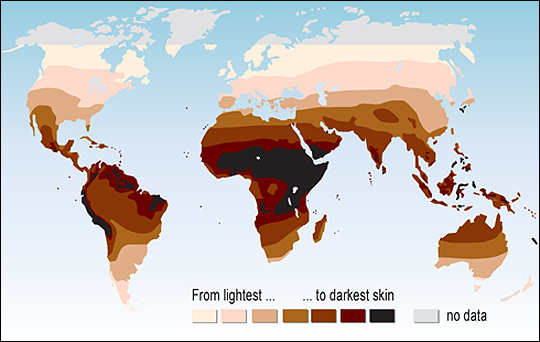
Melanocytes- produce %%melanin%%, a pigment that %%protects%% the body from harmful %%UV radiation%%
Melanin- primarily responsible for %%human skin color%%
- Exposure to sunlight causes melanocytes to produce more melanin.
Freckles- clusters of melanocytes
Albinism- %%prevents the normal production%% of melanin, and produces very little pigment in the skin, hair, and eyes.
Light skin is good for rapid Vitamin D production, and dark skin is better for protection from Atoo much UV.
Appendages of the Skin:
Sweating:
Process of sweating- the body %%eliminates chemical waste%% products, including urea, uric acid, and salts
sudoriferous glands- distributed in the %%dermis%% over the entire body (%%sweat glands%%)
eccrine glands- the major sweat glands of the body, cover most of the body, open directly onto the skin
- fluid secreted by the sweat glands is acidic, and helps to protect the body against bacterial infections
Sebum:
sebaceous glands- located all over the body except for the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, produce an oily substance called %%sebum%%
sebum- an oily and slightly waxy substance found on the skin, helps to keep the %%skin and hair soft%%but also contains chemicals that kill bacteria \n
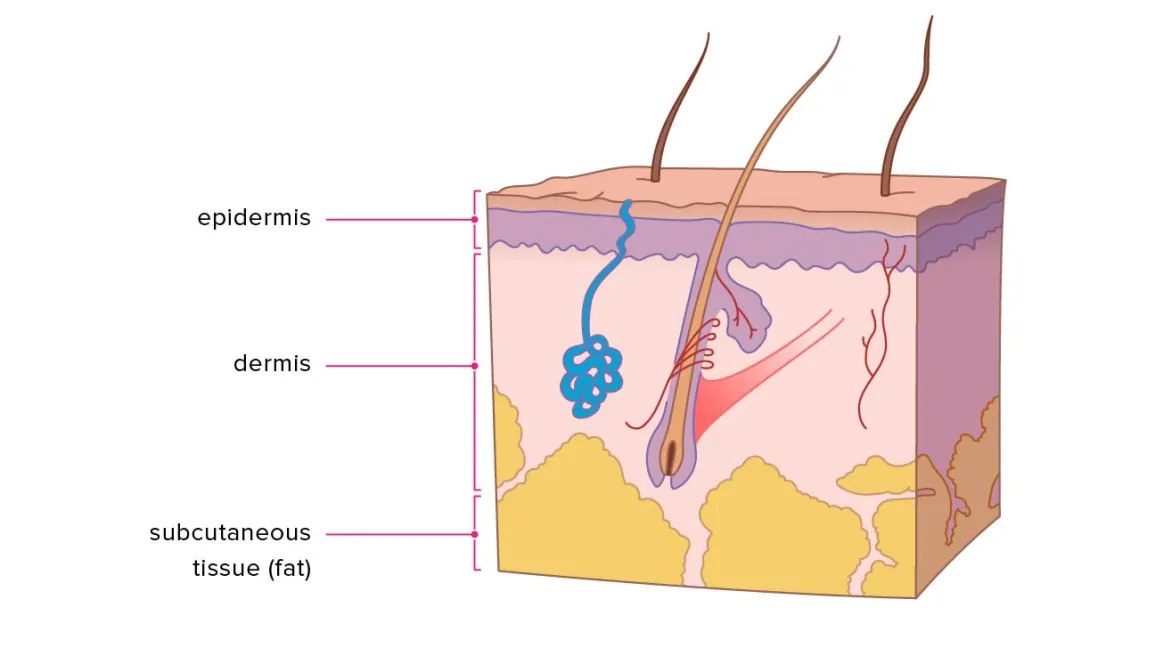
Anatomy of the Skin:
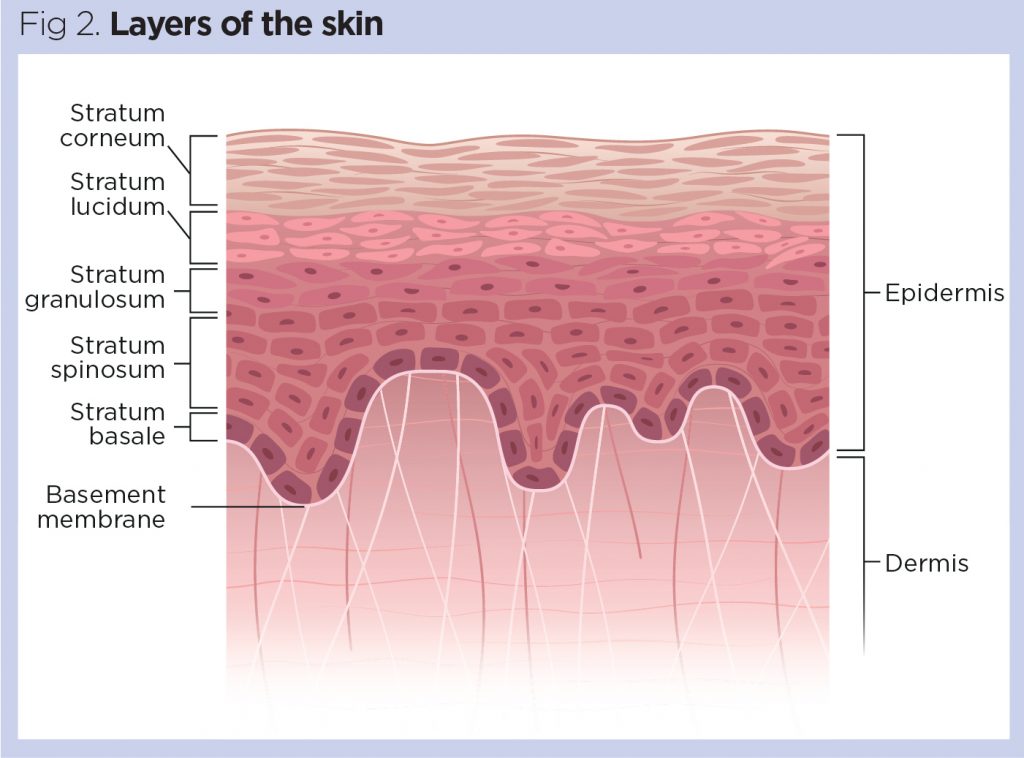
Epidermis:
Epidermis- the surface epithelium of the skin, overlying the dermis.
- The epidermis contains five layers of tissue.
- From superficial to deep (the outside going in), these are the %%stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, and stratum basale%%.
- The epidermis completely replaces itself every 25 to 45 days.
Layers of the Epidermis:
Stratum Corneum- the %%oldest%% layer of cells
dust- (dead) cells that %%shed%% from the stratum corneum
Stratum Lucidum- %%clear%% layer of dead, keratinized cells
- This is only present in areas of the body with %%thick skin%%.
Epidermal Ridges- %%increases surface area%% for oxygen, diffusion from the dermis
- This causes finger and footprints to be made.
Stratum Granulosum- produces a large amount of %%keratin%%, die eventually due to %%lack of oxygen%%
Stratum Spinosum- cells begin forming desmosomes to attach to each other in layers.
Stratum Basale- deepest layer with melanocytes
Merkel cells- located in the stratum basale, function as %%touch receptors%%
Cells in the Epidermis:
Epidermal dendritic cells- respond to the presence of foreign bacteria or viruses by initiating an immune system response
Dermis:
Dermis- thick layer of living tissue below the epidermis which forms the true skin, containing blood capillaries, nerve endings, sweat glands, hair follicles, and other structures
Papillary Layer- dermal papillae that %%protrude%% from the surface up into the epidermis
Reticular Layer- collagen and elastic fibers in this region have an %%irregular arrangement%%, it includes blood and lymphatic vessels, sweat and oil glands, involuntary muscles, hair follicles, and nerve endings
- When the two %%separate%%, they form %%blisters%%, or a “fluid filled pocket".
- Some of the dermal papillae contain capillaries that supply nutrients to the epidermis. Other dermal papillae contain nerve endings involved in sensing touch and pain. \n
Hypodermis:
Hypodermis (subcutaneous fascia)- a %%storage%% repository for fat
- %%not a part of the skin, but connects%% the skin to the underlying tissues
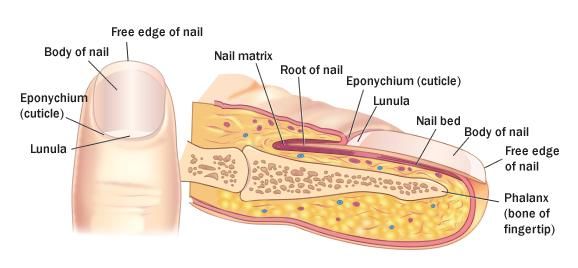
 Nails:
Nails:
Nails- a more compacted, keratinized version of the stratum %%corneum%%
Cuticle- overlap of the stratum corneum, %%keeps bacteria away%% from nail root
Bed- contains tissue from stratum basale and spinosum
Matrix- contains cells that constantly divide