Lecture 1 - Pharmacodynamics
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Define the term pharmacodynamics and distinguish it from pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics = effect of a drug on the body
(think dynamic is drug 1st)
Pharmacokinetics = effect of the body on a drug (ADME)
Understand how the physical properties of drugs and receptors determine their interactions
Drug + Receptor = Lock & Key = conformation determines function
RECEPTORS - interact with drug and initiate response
Physiological = bind to endogenous ligands made in body (B-andregenic)
Generalized = drug can bind but is not normally a receptor (Na+ channels)
DRUGS - interact with system to cause physiological effects
Small molecules = most traditional drugs (ibuprofen)/Lipinski 5
Large molecules/biologicals = peptides and antibodies (GLP1s)
Describe the types of bonds in drug receptor binding
most commonly hydrogen bonds, rarely covalent bonds
Define the term selectivity and describe its relationship to drug dose and side effects
Selectivity - drug’s ability to bind to specific receptors
most drugs bind to one receptor in multiple tissues
OR bind to different receptors as [ ] increases
necessary to determine the dose that will maximize beneficial effects while minimizing adverse ones
Define affinity and KD and the relationship between the two
Affinity - how strong attraction is between drug and receptor
KD - equilibrium dissociation constant; [ ] where 50% of receptors are bound by drug
Low KD = high affinity = high attraction
High KD = low affinity = low attraction
Understand the differences between full and partial agonists
Full agonist - binds with full potential
Partial agonist - can decrease full agonist if given together
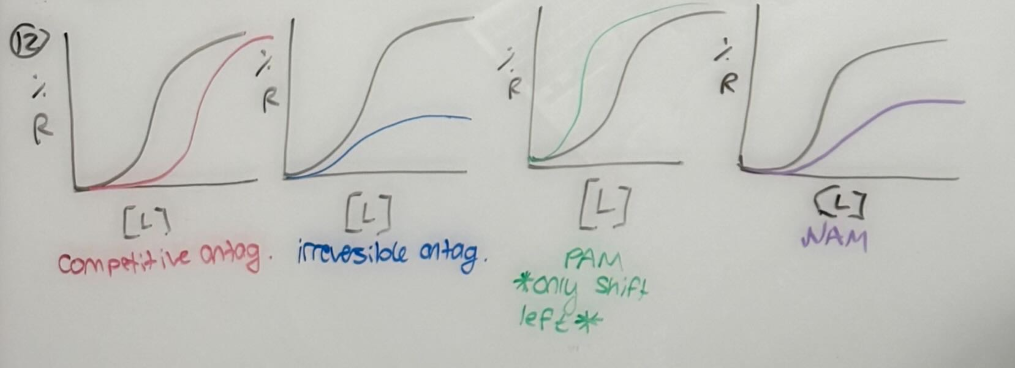
Understand the differences between competitive and irreversible non-competitive antagonists
Competitive antagonist - surmountable, more drug needed for effect
Irreversible non-competitive antagonists - insurmountable, covalent binding

Describe the difference between orthosteric and allosteric drugs and describe positive and negative allosteric modulators
Orthosteric - bind to primary agonist site of a receptor
Allosteric - bind to secondary agonist site of a receptor, up or down regulate binding/efficacy
PAM = more effective
NAM = less effective
Understand that many receptors can exist in an active signaling conformation in the absence of agonists and describe how inverse agonists work
Constitutive signaling - low levels of activation that happen without agonists
Agonists keep R* active conformation
Antagonists do no action but keep agonists from changing conformation
Inverse agonists promote R inactive = no constitutive signaling
Understand the relationship between drug-receptor interactions and the pharmacological effects of drugs in terms of potency and efficacy
Potency - how much [drug] is needed for desired effect?
Efficacy - how large is the effect?
Describe the function of second messengers in cellular communication
Second messengers = signal cascade = amplification relay
Interpret dose-response curves in terms of the relationship between a drug and its pharmacological effects
Define the terms effective dose 50 (ED50) and EMAX and describe how they relate to drug potency and efficacy
ED50/EC50 - [ ] or dose needed to reach 50% of max effect (potency)
EMAX - max effect produced by the drug or endogenous agonist (efficacy)
Determine ED50 from a dose response curve
ED50 on a given graph is the [ ] on the x-axis where the y-axis is at 50%
![<p>ED<sub>50 </sub>on a given graph is the [ ] on the x-axis where the y-axis is at 50%</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c9509748-ae92-4ce5-a898-ebec4e5b1a7b.png)
Rank drugs in terms of efficacy and potency based on their dose response curves
POTENCY - less drug for response is more potent
more left = more potent
more right = less potent
EFFICACY - height of graph
lower max peak = less effective
higher max peak = more effective
Relate drug effects to receptor binding: how does affinity/KD relate to potency/ED50
Low KD = Low ED50
High KD = High ED50
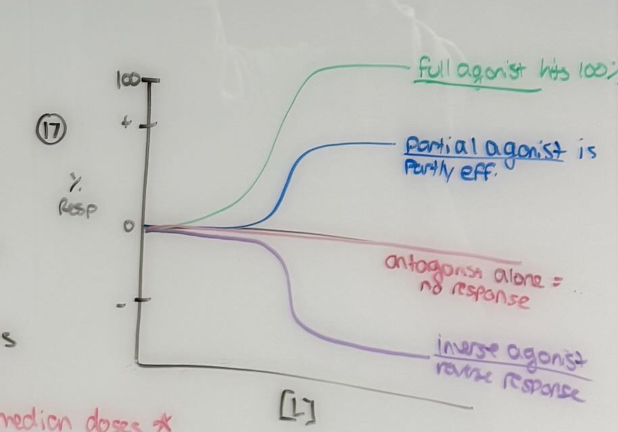
Classify drugs as full, partial or inverse agonists based on dose response curves
Full agonist should hit 100% (EMAX)
Partial agonist should be below 100%
Antagonist alone should be no response or 0%
Inverse agonist should reverse the response

Distinguish between quantal and graded dose responses
Quantal dose response - all or nothing effects
Y-axis is % of people responding
Graded dose response - effect has a scaling response
Y-axis is response E/EMAX
Recognize and interpret quantal dose response curves when plotted cumulatively or non-cumulatively
Quantal dose will have % population instead of % response (wrong in image)
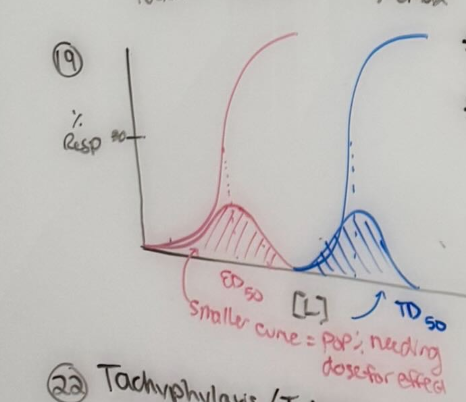
Define the terms median effective toxic and lethal doses (ED50 TD50 and LD50) determine their values from quantal dose response curves and use them to calculate a therapeutic index (TI) and margin of safety (MOS)
ED50 - median effective dose - [ ] needed to induce effect of drug in 50% of population
TD50 - median toxic dose - [ ] needed to induce adverse effects of drug in 50% of population
LD50 - median lethal dose - [ ] needed to kill in 50% of population
CALCULATIONS
TD50 or LD50 / ED50 = TI
TD1 or LD 1/ED99 = MOS
Rank drugs in terms of safety based on TI and margin of safety
Higher TI and MOS values = safer drug
Define tolerance, tachyphylaxis and sensitization and depict them in shifts on dose response curves
Tachyphylaxis/Tolerance - decreased response with multiple of the same doses
Densitize = receptor is phosphorylated » bind B-arrestin
Inactivation = long term change, remove receptor from membrane
Regulation - change # of receptors (ex. downregulation leads to tolerance)