Med-Surge Objective 5 Lecture 2 Electrolytes and Protein Imbalances in Nursing
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Solutes
Non-liquid substances present and transported within the fluids (ECF, ICF) in our bodies.
Common solutes
Glucose, Protein (amino acids), Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Antibodies, blood cells, Clotting factors, chemicals, salt, potassium, waste products (urea and creatinine).
Electrolytes
Minerals that are dissolved in our body fluids and have an electrical charge.
Cations
Electrolytes with a positive charge.
Anions
Electrolytes with a negative charge.
Chloride (Cl-)
An anion that is one of the electrolytes.
Bicarbonate (HCO3-)
An anion that is one of the electrolytes.
Phosphate (P04-)
An anion that is one of the electrolytes.
Sulfate (SO4-)
An anion that is one of the electrolytes.
Sodium (Na+)
A cation that is one of the electrolytes.
Potassium (K+)
A cation that is one of the electrolytes.
Calcium (Ca++)
A cation that is one of the electrolytes.
Magnesium (Mg++)
A cation that is one of the electrolytes.
Hydrogen ions (H+)
A cation that is one of the electrolytes.
Electrolyte functions
Regulate water distribution, nerve impulse transmission, muscle contraction, regulate enzyme reactions (ATP), regulate acid-base balance, blood clotting.
Nerve impulse transmission
The process that allows nerves to send messages.
Muscle contraction
The process influenced by electrolytes that allows muscles to contract and relax.
Blood pressure regulation
The control of blood pressure influenced by electrolytes.
Gland function
The proper functioning of glands influenced by electrolytes.
Practical nurse responsibilities
Knowledge of normal electrolyte concentrations, effects of imbalances, conveying results to PHCP, implementing PHCP orders for electrolyte monitoring.
Common electrolytes
Sodium, Potassium, Calcium, Phosphate, Magnesium.
Electrolyte concentrations
Differ in each of the fluid compartments; ICF has K+ as the most common cation and phosphate as the most common anion, while ECF has Na+ as the most common cation and chloride as the most common anion.
Blood samples
Obtained from the intravascular space and measured for various components.
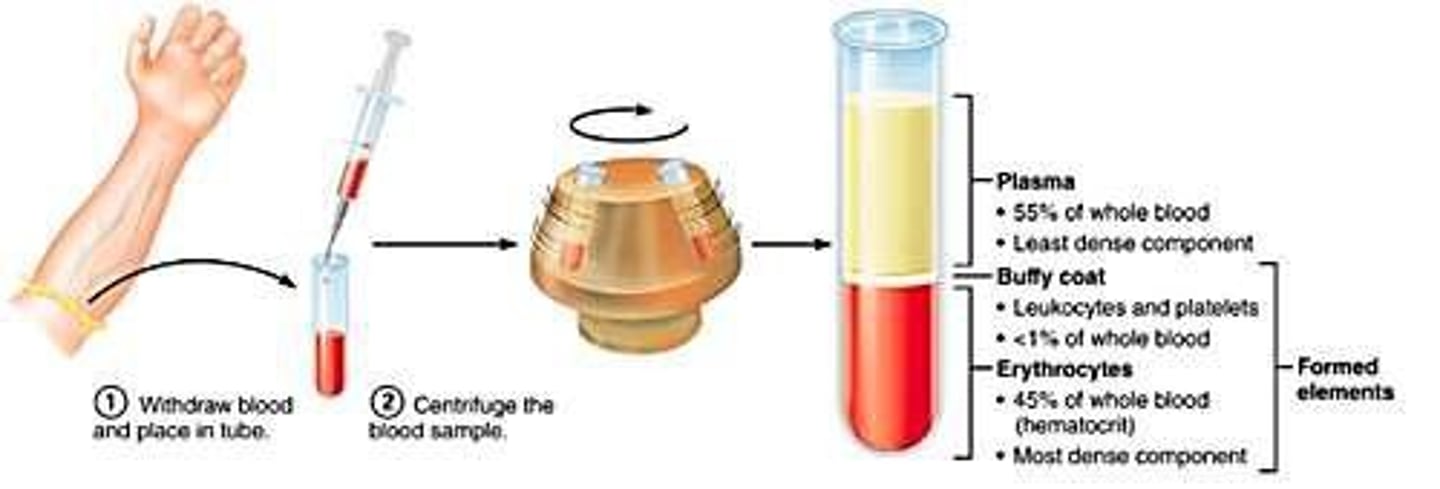
Serum levels
Many blood work/lab values are serum levels, not whole blood levels.
Measurement of solutes
More solutes in fluid space means more concentrated; less solutes means less concentrated.
Units of measurement
Different units of measurement include mmol/L (Canada) and meq/dL (American).
Sodium (Na+)
Most abundant electrolyte in ECF, serum level 135-145 mmol/L, regulates volume of body fluids.
Hypernatremia
Condition characterized by serum level > 145 mmol/L caused by too much sodium or too little water.
Hyponatremia
Condition characterized by serum level <135 mmol/L caused by too much water or too little Na+.
Symptoms of Hyponatremia
Includes abdominal cramps, confusion, nausea/vomiting, headache, pitting edema, muscle weakness, and seizures.
Treatment of Hyponatremia
Includes diuretics, anti-emetics, dietary sodium consumption, and IV therapy with sodium chloride.
Symptoms of Hypernatremia
Includes intense thirst, dry mucous membranes, oliguria, confusion, agitation, and seizures.
Treatment of Hypernatremia
Encourages oral fluid intake, IV therapy, and avoiding overly rapid correction to prevent cerebral edema.
Nursing interventions for Na imbalances
Includes monitoring changes in level of consciousness, vital signs, intake and output, and serum sodium levels.
Potassium (K+)
Major cation in ICF with a serum level of 3.5-5.0 mmol/L, needed for nerve impulse and muscle fiber transmission.
Kidneys and Potassium
Kidneys eliminate 90% of K+; impaired renal function may lead to toxic levels being retained.
Foods high in sodium
Includes cured meats, pickled foods, canned soups, sausages, processed meats, and salad dressings.
Causes of Hyponatremia
Can be caused by profuse diaphoresis, excessive water ingestion, diuresis, Addison's disease, and certain medications.
Causes of Hypernatremia
Can be caused by profuse watery diarrhea, excessive salt intake, high fever, and severe burns.
S/S of Hypernatremia
Includes increased blood pressure, rough dry tongue, weight gain, and pulmonary edema.
Prevention of Hypernatremia
Involves monitoring client's diet and fluid consumption.
Hyperkalemia
too much potassium
Hypokalemia
too little potassium
Foods high in potassium
oranges, bananas, melons, tomato's, raisins, deep green and yellow vegetables
Hyperkalemia Serum level
Serum level >5 mmol/L
Causes of Hyperkalemia
Excessive potassium intake - IV fluids, potassium containing drugs, salt substitutes; Certain illnesses that cause a shift of potassium out of cells: acidosis, fever, blood infection (sepsis), crush injury's, tumor lysis syndrome, burns; Failure to eliminate - renal disease, potassium-sparing diuretics
Signs/Symptoms of Hyperkalemia
Muscle weakness particularly with lower extremities, cardiac changes - irregular pulse, cardiac arrest is extremely high, nausea/vomiting, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, numbness and tingling in fingers, face, tongue, irritability, anxiety
Hypokalemia Serum level
Serum level < 3.5 mmol/L
Causes of Hypokalemia
Nutritional deficit: Inadequate intake, alcoholism; Medications side effects: diuretics/corticosteroids; Illness processes: excessive vomiting & diarrhea
Signs/Symptoms of Hypokalemia
fatigue, weakness, nausea and vomiting, soft flabby muscles, weak irregular pulse, cardiac arrhythmias, polyuria, hyperglycemia, leg cramps, muscle weakness, and paresthesias, low blood pressure, death
Nursing Interventions for K+ Imbalances
Implementing orders from PCHP which treat the cause; Monitor for changes in pulse regularity, client reports palpitations, ECG changes will occur with both imbalances; Monitor and report VS, I & O, and serum potassium level, urine sample for testing, ensure adequate urinary output (0.5 ml/kg/hr); Alter nutritional sources of potassium to correct balance until resolved
Increasing oral sources of potassium
Increasing oral sources of potassium (bananas) until resolved
Eliminate oral sources of potassium
Eliminate oral sources of potassium (bananas) until resolved
Administer potassium supplements
Administer potassium supplements: oral or IV
IV solutions potassium limit
IV solutions should not exceed 60 mmol/L preferred
Severe cases potassium treatment
administer kayexelate, insulin infusion, or hemodialysis (Client very unstable- not signed to LPN)
Calcium CA++ Serum level
Serum level 1.15-1.35 mmol/l (Total non-ionized calcium: 2.1- 2.5 mmol/L)
Calcium in the body
Calcium is bound to proteins in the body (albumin), most of calcium (99%) is found in your bones/teeth
Functions of Calcium
Needed for nerve transmission, vitamin B12 absorption, muscle contraction & blood clotting
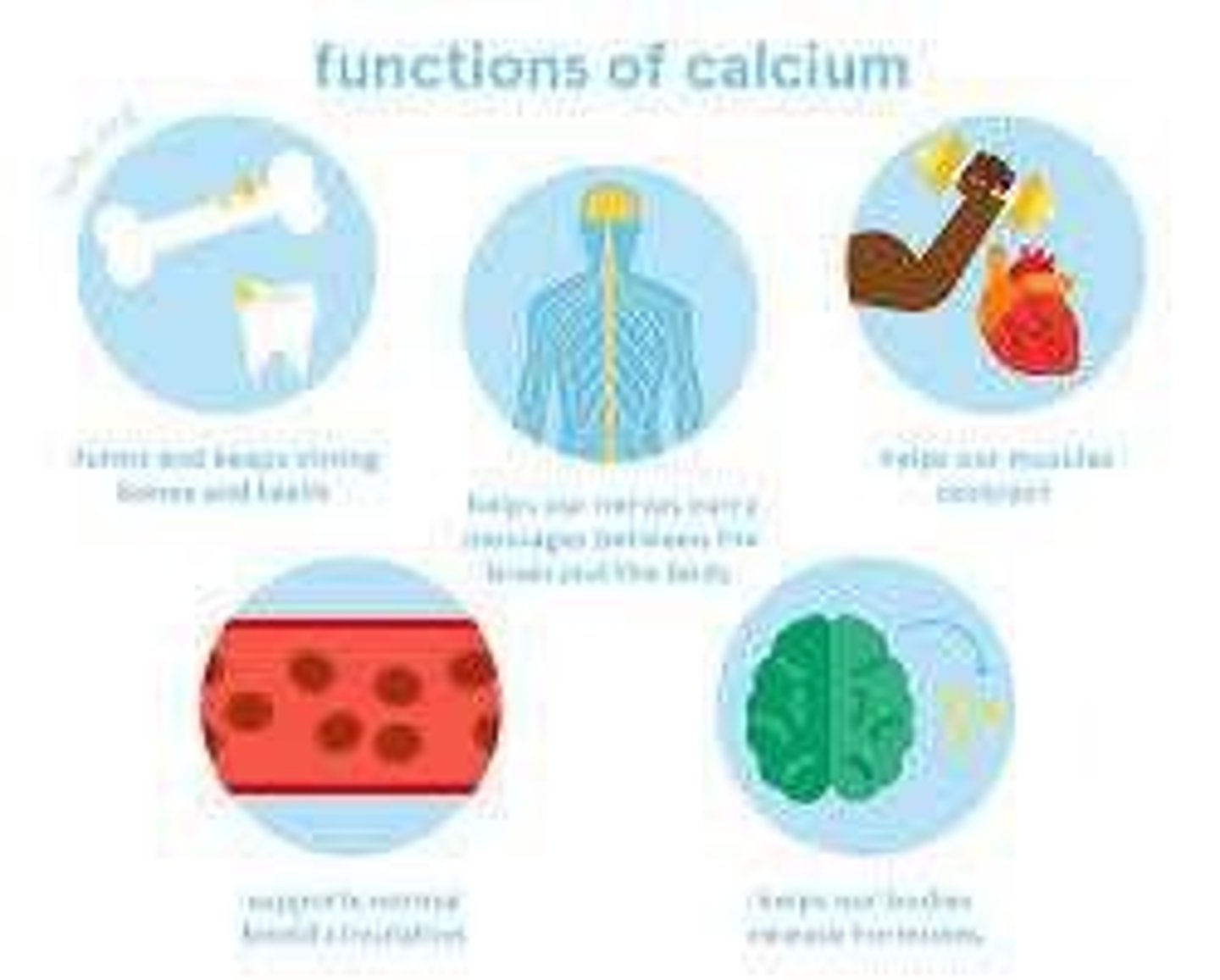
Regulation of Calcium levels
The level of calcium in the blood is regulated by the parathyroid hormone (PTH). When PTH excreted, calcium levels in body increase. Thyroid releases calcitonin (hormone) to decrease excess calcium.
Vitamin D
Needed for Ca absorption.
Inverse relationship with Phosphorus (PO4-)
Calcium and phosphorus levels affect each other inversely.
Hypercalcemia
Too much calcium in the blood.
Hypocalcemia
Too little calcium in the blood.
Hypercalcemia Serum Level
Serum level > 1.35 mmol/L; total Calcium > 2.5 mmol/L.
Causes of Hypercalcemia
Includes hyperparathyroidism (2/3), cancer (1/3), vitamin D overdose, and thiazide diuretics.
S/S of Hypercalcemia
Deep bone pain, pathological fractures, kidney stone formation, muscle weakness, decreased reflexes, anorexia, N/V, polyuria, dehydration, and mental changes.
Hypocalcemia Serum Level
Serum level is < 1.15 mmol/L (total calcium < 2.1 mmol/L).
Causes of Hypocalcemia
Includes low oral intake, loop diuretics, and parathyroid disorders.
S/S of Hypocalcemia
Fatigue, EKG changes, cardiac arrhythmias, numbness/tingling, laryngeal spasms, muscle cramps/tetany, seizures, depression, anxiety, and confusion.
Nursing Interventions for Calcium Imbalances
Implement orders from PCHP, modify calcium intake, monitor changes in muscle, nerve sensation, bleeding, and mental status.
Hypercalcemia Nursing Interventions
Reduce nutritional intake of Ca and increase fluid intake.
Hypocalcemia Nursing Interventions
Increase nutritional intake of Ca and implement safety precautions.
Phosphate (PO4-)
Serum level 1.0-1.5 mmol/L; primary anion in ICF.
Hyperphosphatemia
Too much phosphate in the blood; serum level > 1.5 mmol/L.
Causes of Hyperphosphatemia
Includes excessive ingestion of phosphorus foods, phosphate-containing laxatives, and diseases like DKA.
S/S of Hyperphosphatemia
Muscle problems, tetany, rhabdomyolysis, and possible skin crystals causing itching.
Hypophosphatemia
Too little phosphate in the blood; serum level < 1.0 mmol/L.
Causes of Hypophosphatemia
Includes malnourishment, aluminum-containing antacids, and illnesses like burns and DKA.
S/S of Hypophosphatemia
Weak bones leading to pain and fractures, fatigue, and anorexia.
Hyperphosphatemia
Decrease oral sources of phosphorus or administer prescribed supplement to decrease absorption.
Hypophosphatemia
Increasing oral sources of phosphorus (drinking low-fat or skim milk) if mild, or prescribed supplement (may cause diarrhea).
Nursing interventions for PO4 imbalances
Implementing orders from PCHP which treat the cause, modifying oral sources of phosphate until resolved absorption, and monitoring for changes in muscle tone, notifying PHCP of changes, VS, I & O, and serum phosphate levels.
Magnesium (Mg+)
Helps to maintain normal nerve and muscle function, supports a healthy immune system, keeps the heart beat steady, helps bones remain strong, helps to regulate blood glucose levels, and aids in the production of energy and protein.
Serum magnesium level
0.65-1.05 mmol/L.
Hypermagnesemia
Serum levels > 1.05 mmol/L; causes include clients with kidney failure given magnesium salts or taking drugs that contain magnesium.
Symptoms of Hypermagnesemia
Lethargy, drowsiness, N/V, deep tendon reflexes are lost, somnolence, respiratory and cardiac arrest.
Hypomagnesemia
Serum levels < 0.65 mmol/L; causes include high levels of certain hormones, diabetes, malabsorption, impaired GI absorption caused by diarrhea, vomiting, nasogastric suction, and decreased intake due to malnutrition or chronic alcohol use.
Symptoms of Hypomagnesemia
N/V, sleepiness, weakness, personality changes, muscle spasms, cardiac arrhythmias, tremors, and loss of appetite. If severe, hypomagnesemia can cause seizures, especially in children.
Foods high in magnesium
Green vegetables, nuts, bananas, peanut butter, and chocolate.
Magnesium excretion
Excreted by kidneys.
Majority of magnesium in the body
Uncharged and bound to proteins or stored in bone; very little magnesium circulates in the blood.
Concentration camps example
Irregular heart rhythm and even death due to acute (sudden) drops.
Client education for phosphorus
Education on food high in phosphorus.
Muscle tone monitoring
Monitor for changes in muscle tone and notify PHCP of changes.
Serum phosphate levels monitoring
Monitor serum phosphate levels as part of nursing interventions.
Vitamin D role
Helps in the absorption of phosphorus.
Kidney failure and magnesium
Clients with kidney failure may have increased magnesium levels due to magnesium salts or drugs.
Symptoms of magnesium deficiency
Muscle spasms, tremors, and cardiac arrhythmias.
Severe hypomagnesemia consequences
Can cause seizures, especially in children.