Chapter 8: Supporting Structures & Periodontium
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Periodontium
consists of tissues that support the teeth
-2 units:
1. gingival
2. attachment
gingival unit:
free gingiva
attached gingiva
alveolar mucosa
attached unit:
cementum
PDL
alveolar bone
free and attached gingiva
-very dense mucosa
-thick epithelial covering
-keratinized cells
-called masticatory mucosa
* made to withstand the trauma from chewing forces
* also on hard palate
alveolar mucosa:
-lining mucosa
-tears and injures easily
-smooth, thin and nonkeratinized
- composed of loose connective tissue
-some muscle fibers
-loosely attached to underlying bone
-submucosa contains loose connective tissue and fat
gingival sulus
space between free gingiva and tooth
mucogingival junction
-Point at which the alveolar mucosa becomes gingiva
The free gingiva is located between
The gingival margin and the gingival sulcus
The attached gingiva is located beteen
The base of the sulcus and the mucogingival junction
free gingiva(collar)
-healthy: light pink, rarely exceeds 2mm in depth
- the bottom of the sulcus is influenced by the curvature of the cervical line
-gingival papilla(interdental papilla): gingiva found between teeth in the interproximal spaces
* inflammation is visible by color and shape changes
Free gingival groove
-can sometimes be present on the outside of the tissue
-marks the base of the sulcus
attached gingiva: Where does it extend?
Healthy appearance?
-extends apically from the base of the sulcus and is attached to the bone and the cementum by collagenous fibers
-has a stippling appearance(like an orange)
attached gingiva: characteristics
-highly keratinized
-covered with stratified squamos epthelium: most common of the multi layered epithelia; found as skin and mucosa
*stratified squamous means layers upon layers of very thin, flat cells
-rete peg formation: binding of the epithelium to the bone by collagen fibers (finger projections)
- lamina propria: connective tissue of gingiva
-darker skinned people have more melanin=darker pigment of gingiva
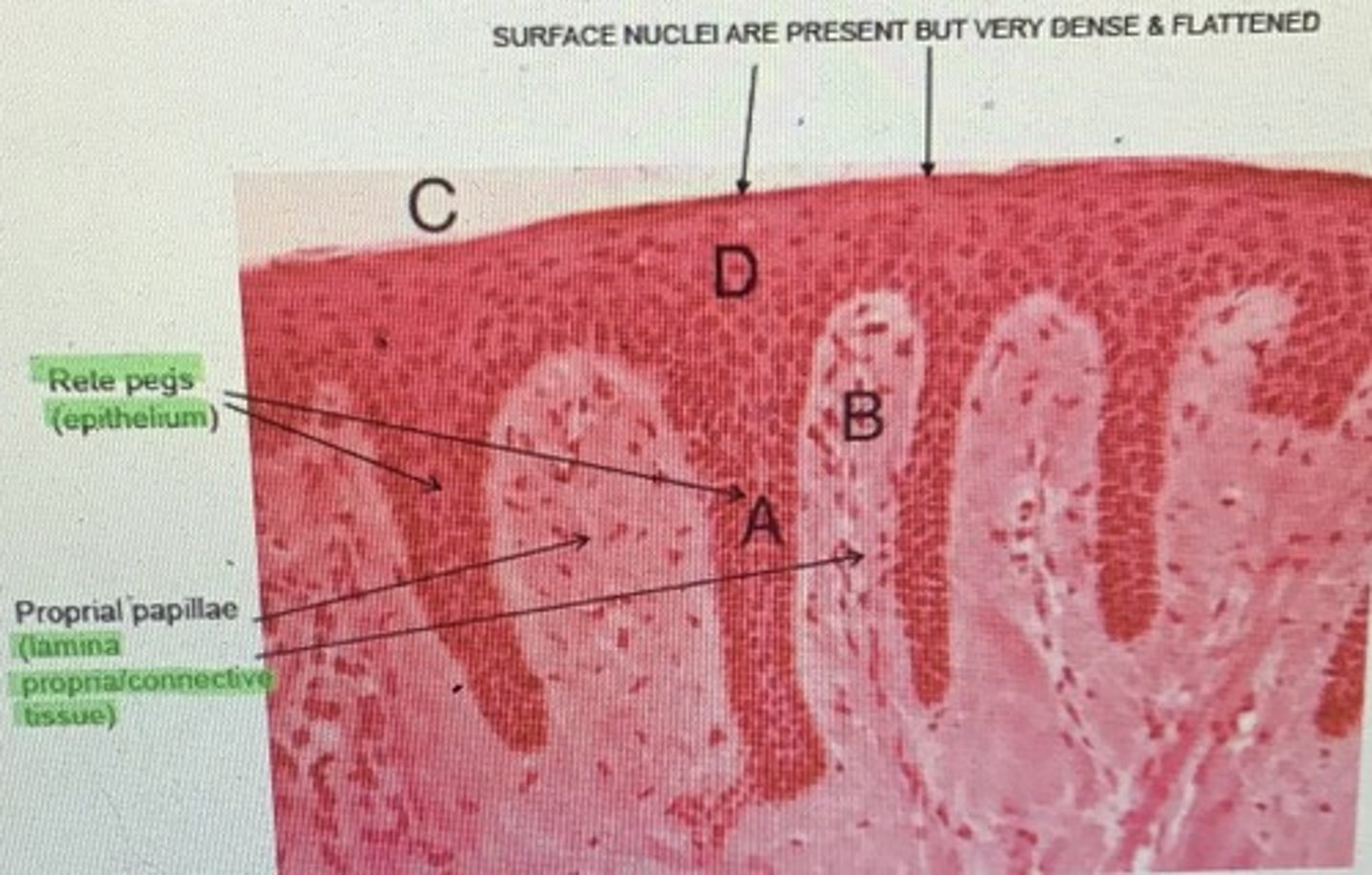
What is attached gingiva connected to?
-connected to bone by a meshwork of collagenous fibers made by fibroblasts
-collagen fibers are embedded in the cementum on one end.
* the ends of these fibers are called sharpey’s fibers
Types of gingival fibers
-gingival
-transeptal fibers (in between teeth)
-circular fibers
Functions of circular fibers:
-keep gingiva closely attached to tooth
-prevent free and attached gingiva from being peeled away from tooth
-prevent apical migration of epithelial attachment and resist gingival recession
- blood supply from supraperiosteal vessel that originates from the lingual, mental, buccal, infraorbital, and palatine arteries.
alveolar mucosa:
What does it join and what is it continuous with?
-joins attached gingiva at mucogingival junction
-continuous with the rest of the vestibule
Attachment unit:
1. cementum
2. PDL
3. alveolar bone
1. hard, bonelike tissue covering rots of tooth
2. soft connective tissue that surrounds roots and connects teeth to alveolar bone
3. thin covering of bone that surrounds teeth
functions of attachment unit:
-supportive: supports and prevents movement
-nutritive: by blood vessels and nerves
-formative: replace cementum, PDL, and alveolar bone with specialized cells called cementoblasts, fibroblasts, and osteoblasts
-sensory: by blood vessels and nerves
Attachment unit: cementum
cellular and acellular
cellular cementum
- formed by cementoblasts
-cementoblasts become embedded in the cementum
-covers the apical portion, sometimes forms over acellular cementum
-collagen fibers embedded
acellular cementum
- formed by cementoblasts
-free of embedded cementoblasts; clear without structure
-covers cervical 3rd, sometimes covers almost all root except apical area
-collagen fibers embedded
cementocytes
cementoblasts trapped in their own cementum
Attachment unit: alveolar bone
Alveolar bone proper/ cribiform plate/ lamina dura (radiographic name): type of bone that lines the sockets where roots sit
- thin and compact
- small openings for vascularity
2 layers
- compact lamellar bone
- layer of bundle bone into which the periodontal fibers insert
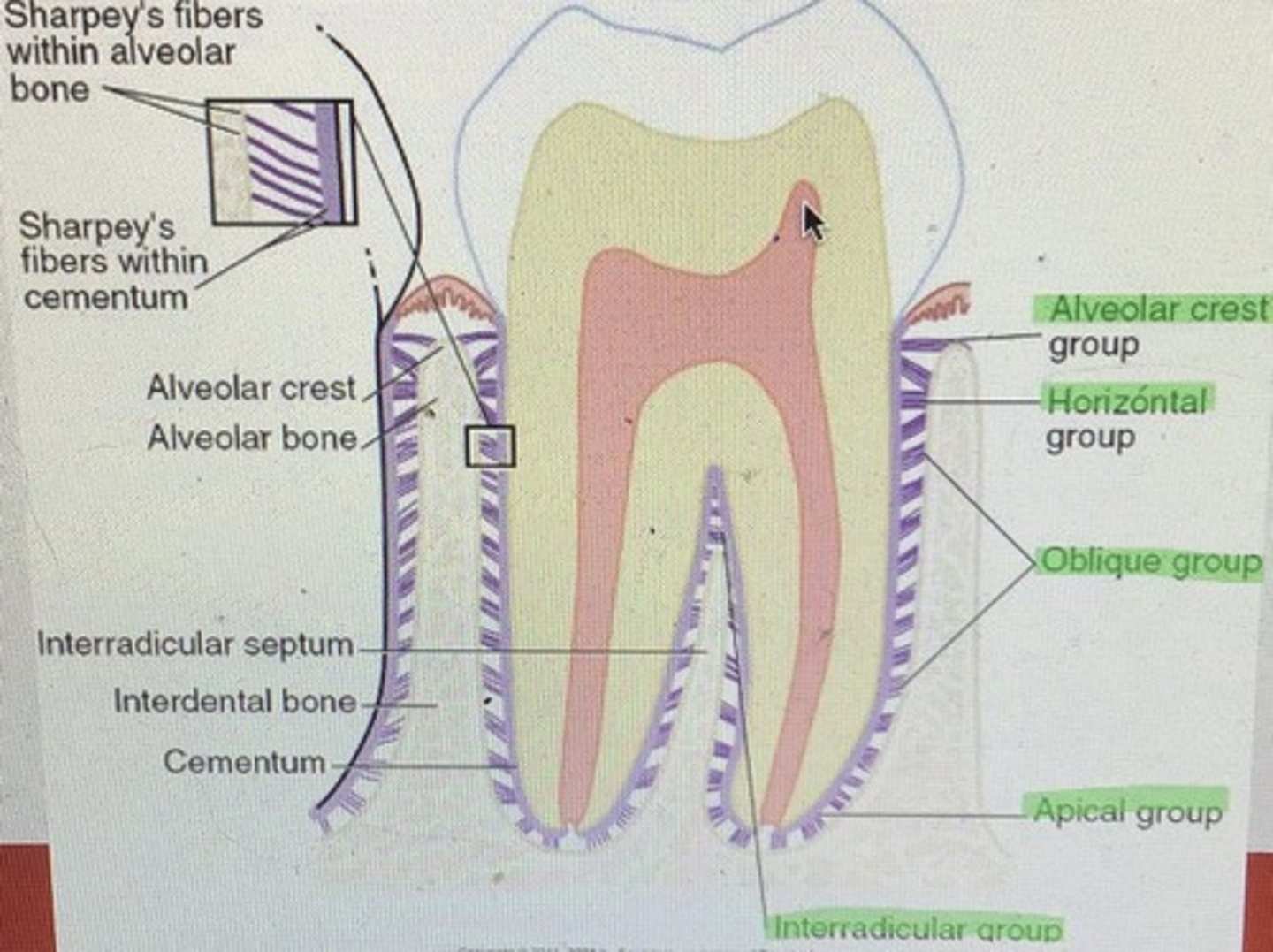
* core of the fibers remain uncalcified in the calcified tissues of bone or cementum (sharpey’s fibers)
alveolus
-socket in which the tooth rests
trabeculae
interlacing meshwork that makes up the softer cancellous(spongy) bony framework
apposition
-addition of new layers of bone, bone may be laid down on one end and resorbed on the other(orthodontics)
-the bone is extremely active
organic matrix and inorganic matter of alveolar bone
Organic: collagen and intercelluar substance
Inorganic: apatite crystals of calcium, phostphate, carbonates
Stresses placed on bone
-loss of function
-occlusal stress: supporting bone becomse thicker and more trabecular
-undergoes resorption with pressure exerted
-opposition when tension placed on it
bundle bone
-when numerous layers of bone are added to the socket wall.
-forms immediate attachment of the PDL
PDL: purpose and 5 groups
Attaches cementum to alveolar bone
Hammock
Shock absorption
Fluids help buffer
Contains fibroblasts and small blood/ lymph vessels and nerves
1. alveolar crest: cervical area of tooth to alveolar crest
2. horizontal group: running horiz. from tooth to alveolar bone
3. oblique: running obliq. from cementum to bone
4. apical group: radiating apically from tooth to bone
5. interradicular: btwn root of multi-rooted teeth
Forces that allow for movement
1. mesial drift: allows tooth to move forward in mouth
2. active eruption force: causes tooth to migrate occlusally until it occludes with antagonist
orthodontic corrective forces:
placement of pressure causing appliance
traumatic occlusal forces
premature contact of occlusion
Masticatory occlusal forces
Tooth occlusion during chewing
Sharpey's fibers can be found in all of the following except one
a) cementum
b) dentin
c) PDL
d) alveolar bone
e) they are in all of the above
b) dentin
The thin, soft, smooth alveolar mucosa is highly keratinized. The thinker, stipples attached gingiva is keratinized, contains rete pegs, and is covered with stratified squamous epithelium. (T/F)
The first is false, second is true
The periodontal ligament provides a hammock of tissue bundles that support the tooth within the bone. Each of the following is true regarding the PDL except one.
a) the main portion of the PDL is composed of osseous trabeculae
b) fluids with the PDL act as a hydraulic pressure system on the alveolar wall
c) PDL fibers tie the tooth to the bone
d) PDL fibers prevent the tooth from being pushed into the bone
e) the PDL contains small blood and lymph vessels and nerves
a) the main portion of the PDL is composed of osseous trabeculae
The mucogingival junction joins the free and attached gingiva. There is a raised line on the surface of the mucogingival junction. (T/F)
Both statements are false
Each of the following structures is a component of the gingival unit except one
a) free gingiva
b) alveolar mucosa
c) PDL
d) attached gingiva
c) PDL
Interdental papilla is classified as attached gingiva (T/F)
False
The periodontium, composed of tissue that support the teeth, include which of the following structures
Attached gingiva
All of the above
Cementum
Dentin
Alveolar bone
Attached gingiva
Cementum
Alveolar bone
PDL fibers that extend from the tooth to the the alveolar crest are called
Alveolar crest fibers
With regard to apposition and resorptio, on which tissues are these activities most active
Bone
Inflammation of the gingiva papilla is easily recognized because the area takes on a color that is more red than normal (T/F)
Both the statement and reason are correct and related