Composites
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
a combination of materials that exhibits a significant proportion of the properties of both constituent phases such that a better combination of properties is achieved
what is a composite
the dispersed component
the matrix
what are the two main components of composite materials
this is usually strong, stiff particles (particle reinforced composites), or fibres (fibre reinforced composite)
functions of the dispersed component:
improve strength
improve stiffness
improve creep resistance
dispersed component
a continuous phase which surrounds the other component in the composite, the dispersed phase
typically a polymer or metal
functions of the matrix:
transmit stress to dispersed component
protects dispersed component from corrosion and abrasion
provide toughness
good for ductility
prevents brittle crack propagation
the matrix
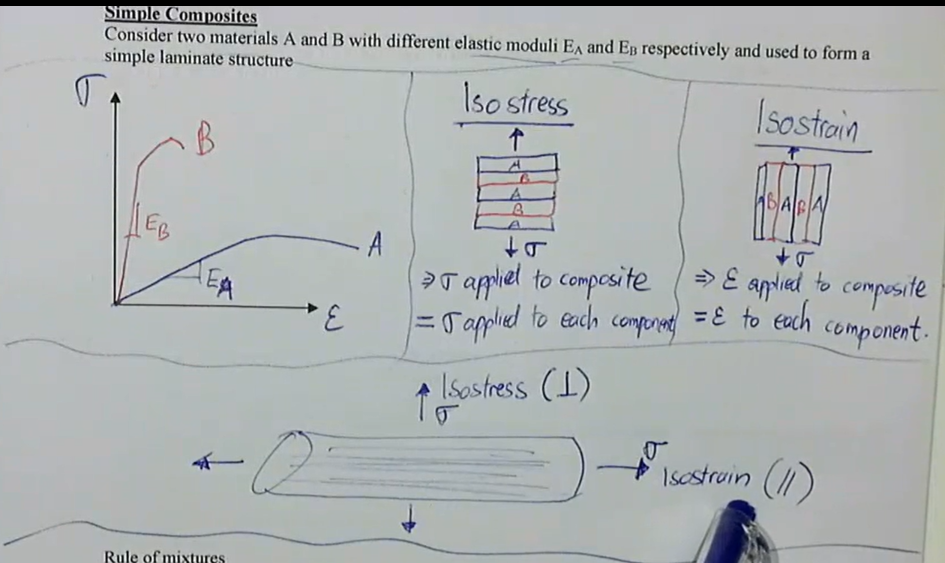
consider two materials A and B with different elastic moduli EA and EB respectively and used to form a simple laminate structure
can be done in two ways:
isostress:
stress applied to composite = stress applied to each component
applied perpendicular to material
isostrain
strain applied to composite = strain applied to each component
applied parallel to material
simple composites
for oriented continuous fibre composites
modulus of composite:
V = Volume fraction
E = Young’s Modulus
VA + VB = 1
isostrain stiffness (in direction of fibres) → EC - VAEA + VBEB = VAEA + (1 - VA)EB
isostress stiffness (perpendicular to fibres) → 1/EC = VA/EA + VB/EB = VA/EA + (1-VA)/EB
density of composite:
ρc = VAρA+ VBρB = VAρA + (1 - VA)ρB
specific modulus of composite:
indication of stiffness relative to weight
Ê = Ec/ρc
rule of mixtures