Biology Practice Exam
4.6(14)
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:25 PM on 4/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
1
New cards
b. false
Heritability is an estimate of genetic determination of a genotype on a phenotype.
a. true
b. false
a. true
b. false
2
New cards
b. false
In sexual selection, “intersexual competition” refers only to male-male competition and “mate choice” refers only to female choice of potential mating partners.
a. true
b. false
a. true
b. false
3
New cards
b. false
Only monophyletic groups share common ancestors.
a. true
b. false
a. true
b. false
4
New cards
b. false
Populations of asexually reproducing organisms cannot evolve as fast as sexually reproducing organisms.
a. true
b. false
a. true
b. false
5
New cards
a. true
Hybrid zones both reinforce and relax species barriers.
a. true
b. false
a. true
b. false
6
New cards
c. 0.75
I am so confident in your knowledge of evolutionary biology, I think you can calculate allele frequencies without an equation! Let’s say that the frequency of the dominant H allele in a population (p) is 0.25. What is the frequency of the recessive h allele (q)?
a. 0.35
b. 0.11
c. 0.75
d. 0.25
a. 0.35
b. 0.11
c. 0.75
d. 0.25
7
New cards
b. no
In the allele frequency example above (when p = 0.25), if the allele frequency of q is 0.67 in the next generation, do we think that population is under Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?
a. yes
b. no
a. yes
b. no
8
New cards
d. Most effective in small populations
Which of the following conditions does not describe the factors necessary for Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?
a. No mutation. Allele frequency does not change, and no new alleles are added.
b. No selection. Different genotypes have equal survival and reproduction.
c. Mating is random.
d. Most effective in small populations.
a. No mutation. Allele frequency does not change, and no new alleles are added.
b. No selection. Different genotypes have equal survival and reproduction.
c. Mating is random.
d. Most effective in small populations.
9
New cards
b. population bottleneck
A hard frost in southern Florida nearly killed all the individuals of a population of green iguanas. Even though the iguana population recovered in numbers after a couple of years, the genetic variation within that population remained low. What is the most likely cause of the diminished genetic variation?
a. founder effect
b. population bottleneck
c. gene flow
d. natural selection
a. founder effect
b. population bottleneck
c. gene flow
d. natural selection
10
New cards
a. no selection is acting
In a gene that encodes for antibiotic resistance, the rate of nonsynonymous substitutions to synonymous substitutions (dN/dS) is 2/2 = 1, then:
a. no selection is acting
b. there is positive selection
c. there is purifying selection
d. there is disruptive selection
a. no selection is acting
b. there is positive selection
c. there is purifying selection
d. there is disruptive selection
11
New cards
c. cryptic
Even trained biologists have difficulty telling females of Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila sechellia apart, and yet these species are reproductively isolated. Thus, these species are considered ______ species.
a. lineage
b. morphological
c. cryptic
a. lineage
b. morphological
c. cryptic
12
New cards
d. 66
A diploid fish hybridizes with a closely related tetraploid. If the haploid number is 22, how many chromosomes would the hybrids be expected to have?
a. 11
b. 22
c. 44
d. 66
a. 11
b. 22
c. 44
d. 66
13
New cards
a. an increase in the oxygen concentration
Suppose that you are the scientific consultant on a sci-fi movie set up twenty million years from now. In the movie, there are very large flying insects inhabiting Earth. What is the most likely atmospheric change that has occurred?
a. an increase in the oxygen concentration
b. a decrease in the carbon dioxide concentration
c. an increase in the carbon dioxide concentration
d. a decrease in the oxygen concentration
a. an increase in the oxygen concentration
b. a decrease in the carbon dioxide concentration
c. an increase in the carbon dioxide concentration
d. a decrease in the oxygen concentration
14
New cards
c. D is equally closely related to F and H
Which of these statements is true?
a. D is a sister species to C
b. D is more closely related to E than G
c. D is equally closely related to F and H
d. D is more ancient than G or H
a. D is a sister species to C
b. D is more closely related to E than G
c. D is equally closely related to F and H
d. D is more ancient than G or H
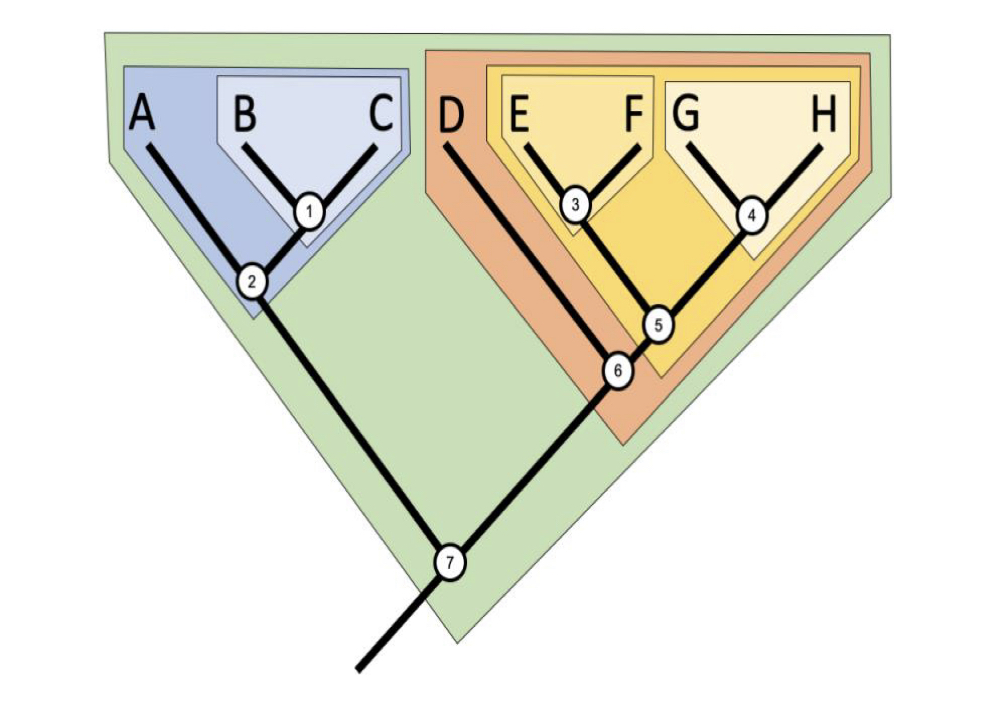
15
New cards
c. 6
Which number represents the most recent common ancestor of D, E, or F?
a. 7
b. 5
c. 6
d. none, it is not a clade
a. 7
b. 5
c. 6
d. none, it is not a clade
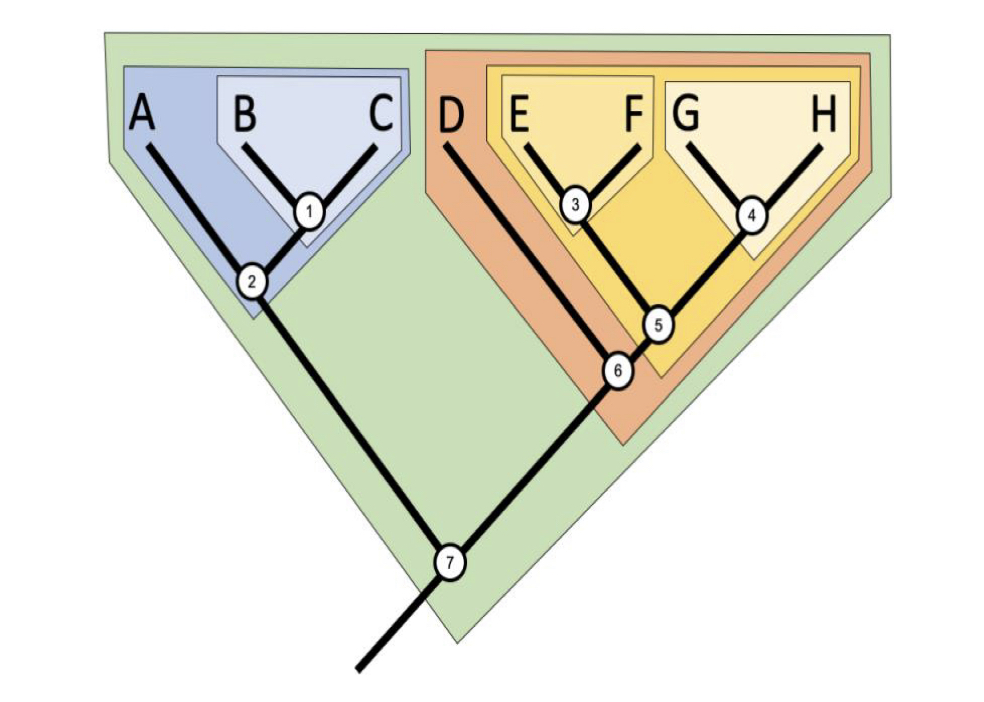
16
New cards
b. B, C, and D
Which of the following species grouping would create a polyphyletic group?
a. A, B, and C
b. B, C, and D
c. E, F, and G
a. A, B, and C
b. B, C, and D
c. E, F, and G
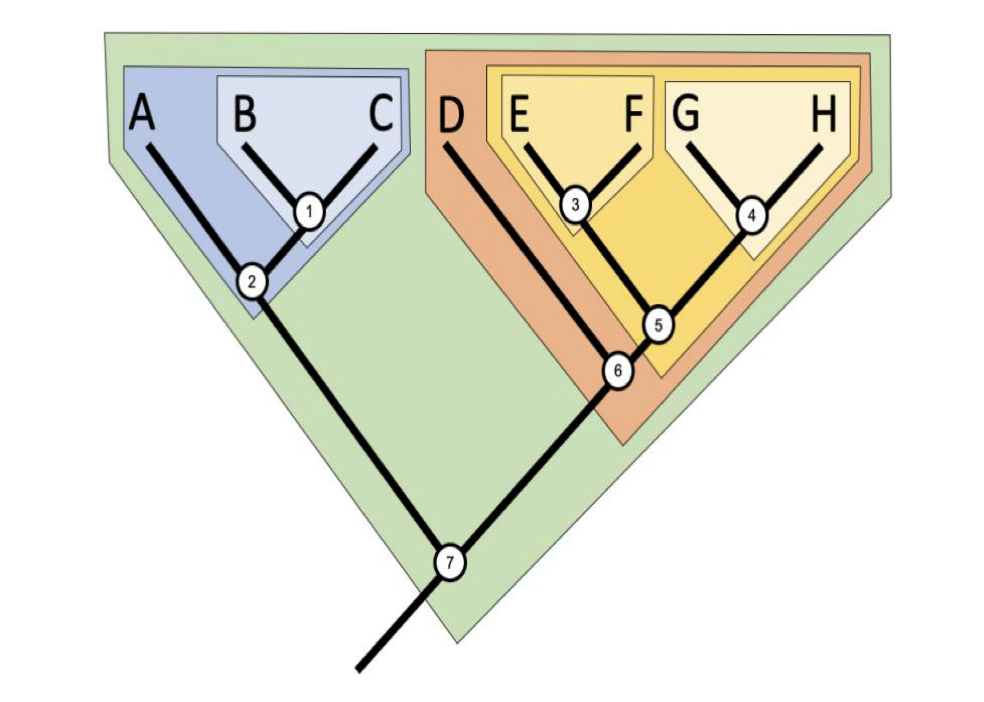
17
New cards
b. disruptive selection
Which mode of selection is most likely to lead to an increase in phenotypic variation?
a. directional selection
b. disruptive selection
c. stabilizing selection
a. directional selection
b. disruptive selection
c. stabilizing selection
18
New cards
c. both A and B
In a corn breeding program, which of the following factors would increase the response to selection?
a. increased inheritability
b. greater selection differential
c. both A and B
d. neither A nor B
a. increased inheritability
b. greater selection differential
c. both A and B
d. neither A nor B
19
New cards
b. derived
The common ancestor of humans and the other “great apes” walked on all fours, whereas humans are bipeds (i.e., they walk on two feet). Bipedalism is therefore the _______ trait.
a. ancestral
b. derived
c. convergent
d. phylogenetically uninformative
a. ancestral
b. derived
c. convergent
d. phylogenetically uninformative
20
New cards
d. all of the above
50 birds are blown off course during a migration and land on an uninhabited island with a new food resource. After 10 generations, which of the following evolutionary processes would explain why the allele frequency of this new population differs from their ancestral population?
a. genetic drift
b. founder’s effects
c. directional selection
d. all of the above
a. genetic drift
b. founder’s effects
c. directional selection
d. all of the above
21
New cards
b. gene flow
In the hypothetical bird population described in the previous example, which evolutionary process would explain how allele frequencies began to appear more similar to the ancestral populations over time?
a. genetic drift
b. gene flow
c. disruptive selection
d. all of the above
a. genetic drift
b. gene flow
c. disruptive selection
d. all of the above
22
New cards
c. the origin of life
The Miller-Urey Experiment sought to replicate the conditions for:
a. Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
b. speciation
c. the origin of life
d. allopatric speciation
a. Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
b. speciation
c. the origin of life
d. allopatric speciation
23
New cards
d. A and B but not C
The fact that genes often interact with each other within genomes to produce complex phenotypes is fundamental to which of the following:
a. Dobzhansky-Muller model
b. developmental biology
c. Mendelian inheritance
d. A and B but not C
e. all of the above
a. Dobzhansky-Muller model
b. developmental biology
c. Mendelian inheritance
d. A and B but not C
e. all of the above
24
New cards
c. comparisons with known holotypes
Which of the following tools would best be used to describe a fossilized dinosaur bone that was dislodged during an earthquake, where it fell into a riverbed and washed up by your feet?
a. stratigraphy
b. carbon-14 radioisotope dating
c. comparisons with known holotypes
a. stratigraphy
b. carbon-14 radioisotope dating
c. comparisons with known holotypes
25
New cards
a. gene flow
Which of the following phenomena would likely decrease speciation rates?
a. gene flow
b. geographic barriers
c. polyploidy
d. sexual selection
a. gene flow
b. geographic barriers
c. polyploidy
d. sexual selection
26
New cards
c. the rate of fixation of new neutral mutations equals the mutation rate
Molecular clocks are based on which of the following pieces of information:
a. phylogenies can only be built using protein polymorphisms
b. the rate of fixation of new alleles is faster in smaller populations
c. the rate of fixation of new neutral mutations equals the mutation rate
d. speciation rates are constant across populations of different sizes
a. phylogenies can only be built using protein polymorphisms
b. the rate of fixation of new alleles is faster in smaller populations
c. the rate of fixation of new neutral mutations equals the mutation rate
d. speciation rates are constant across populations of different sizes
27
New cards
d. all of these are necessary
Which of the following is necessary for runaway sexual selection to occur?
a. a conspicuous trait exists in one sex
b. preference for the conspicuous trait in another sex
c. inheritance of the conspicuous trait
d. all of these are necessary
e. all but one of these are necessary
a. a conspicuous trait exists in one sex
b. preference for the conspicuous trait in another sex
c. inheritance of the conspicuous trait
d. all of these are necessary
e. all but one of these are necessary
28
New cards
b. heterotropy
Which of the following mechanisms produces phenotypes by changing the location of gene expression in developing organisms:
a. heterochrony
b. heterotropy
c. heterometry
a. heterochrony
b. heterotropy
c. heterometry
29
New cards
c. ecological speciation
The Sawyer family built a farm in a savannah ecosystem where a local population of dung beetle usually prefer to live and mate among tall grasses. A subset of the population begins collecting cow dung and mating/laying eggs in the Sawyers’ barn. This situation may lead to:
a. sexual antagonism
b. temporal isolation
c. ecological speciation
d. adaptive radiation
a. sexual antagonism
b. temporal isolation
c. ecological speciation
d. adaptive radiation
30
New cards
d. the differential survival and reproduction of individuals
Natural selection can be defined as:
a. the generation of random variation in traits
b. the potential for species to radiate into new environments
c. the processes by which individuals to resemble their parents
d. the differential survival and reproduction of individuals
a. the generation of random variation in traits
b. the potential for species to radiate into new environments
c. the processes by which individuals to resemble their parents
d. the differential survival and reproduction of individuals
31
New cards
c. disruptive
Some coastal lakes in British Columbia are inhabited by a marine species of stickleback fish. Individuals that are larger than average are good at catching large prey, while individuals that are smaller than average are better at avoiding being preyed on. Individuals with intermediate phenotypes are not good at either task. Which type of selection is operating on these coastal lakes?
a. stabilizing
b. directional
c. disruptive
d. sexual
a. stabilizing
b. directional
c. disruptive
d. sexual
32
New cards
a. no mutation, no migration; 1 generation
After a hurricane, snails are washed out by the currents and the new population has a different genotypic frequency. First, which of these statements includes some of the assumptions for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? Second, how many generations of random mating will be required to restore the genotypic frequencies to Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
a. no mutation, no migration; 1 generation
b. no selection, no mutation; 2 generations
c. no mutation, non-random mating; 1 generation
d. no mutation, large population size; 2 generations
a. no mutation, no migration; 1 generation
b. no selection, no mutation; 2 generations
c. no mutation, non-random mating; 1 generation
d. no mutation, large population size; 2 generations
33
New cards
d. interaction between alleles at different loci
Which is an assumption of the Dobzhansky-Muller model of speciation?
a. natural selection
b. temporal selection
c. chromosomal rearrangements, particularly centric fusions
d. interaction between alleles at different loci
a. natural selection
b. temporal selection
c. chromosomal rearrangements, particularly centric fusions
d. interaction between alleles at different loci
34
New cards
a. insects resistant to Bt pass this Bt resistance on to their offspring
Bacillus thuringienses (Bt) bacteria produce a natural insecticide. Widespread use of Bt by in pest control has led to Bt resistance among insects. Why is this occurring?
a. insects resistant to Bt pass this Bt resistance on to their offspring
b. Bt-resistant insects increase in the population by chance
c. in the presence of Bt, individual insects evolve to become Bt resistant
d. natural selection causes insects to generate genes providing resistance to Bt
a. insects resistant to Bt pass this Bt resistance on to their offspring
b. Bt-resistant insects increase in the population by chance
c. in the presence of Bt, individual insects evolve to become Bt resistant
d. natural selection causes insects to generate genes providing resistance to Bt
35
New cards
a. it drives more allele frequency change in small populations than large populations
Which statement about genetic drift is true?
a. it drives more allele frequency change in small populations than large populations
b. it is how natural selection operates
c. it increases the amount of genetic variation in a population
d. it changes allele frequencies by moving alleles from one population to another
a. it drives more allele frequency change in small populations than large populations
b. it is how natural selection operates
c. it increases the amount of genetic variation in a population
d. it changes allele frequencies by moving alleles from one population to another
36
New cards
a. most polymorphic alleles found in natural populations are neutral
According to the neutral theory of molecular evolution,
a. most polymorphic alleles found in natural populations are neutral
b. nearly all mutations have some effect on the organism
c. the rate of fixation of neutral mutations is much faster in smaller populations than it is in large ones
d. mutations must be neutral
a. most polymorphic alleles found in natural populations are neutral
b. nearly all mutations have some effect on the organism
c. the rate of fixation of neutral mutations is much faster in smaller populations than it is in large ones
d. mutations must be neutral
37
New cards
b. early bacteria generated free oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis
Which statement about oxygen and ancient Earth is true?
a. the atmosphere of early Earth contained almost as much free oxygen as present-day Earth, but most of this oxygen was lost in the Cambrian
b. early bacteria generated free oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis
c. oxygen-generating cyanobacteria have gone extinct
d. the evolution land plants reduced atmospheric oxygen concentrations
a. the atmosphere of early Earth contained almost as much free oxygen as present-day Earth, but most of this oxygen was lost in the Cambrian
b. early bacteria generated free oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis
c. oxygen-generating cyanobacteria have gone extinct
d. the evolution land plants reduced atmospheric oxygen concentrations
38
New cards
c. sexual selection
Males of many birds have bright colors and other conspicuous characters that do not appear to improve survival (and potentially may be deleterious) but their carriers nonetheless reproduce frequently. This represents a case of:
a. sympatric speciation
b. reproductive isolation
c. sexual selection
d. genetic conflict
a. sympatric speciation
b. reproductive isolation
c. sexual selection
d. genetic conflict
39
New cards
a. gene flow
Which of the following processes will decrease the rate of genetic differentiation between populations?
a. gene flow
b. hybrid incompatibility
c. genetic drift
a. gene flow
b. hybrid incompatibility
c. genetic drift
40
New cards
b. genetics
“The Evolutionary Synthesis” occurred about 100 years after Darwin published On the Origin of Species. This event sought to synthesize evolutionary biology with which discipline?
a. biogeography
b. genetics
c. medicine
d. conversation biology
a. biogeography
b. genetics
c. medicine
d. conversation biology