Atomic Theory, Models, and Subatomic Particles: Key Concepts for Chemistry
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

69 Terms
Dalton's Atomic Theory
1) all elements are composed of atoms (true)
2) all atoms of a given element are identical (false)
3) atoms of the same element have the same mass (false)
4) compounds consist of two or more elements combined in a fixed proportion (ex: H2O is always two atoms of hydrogen bonded to one atom of oxygen) (Law of definite proportions) (true)
5) chemical reactions occur when atoms are rearranged (true)

Dalton's atom
A Dense, hard, indivisible sphere with no subatomic particles

Thomson's plum pudding model
The atom is a sphere of positive charge with electrons embedded throughout (like chocolate chip cookies)
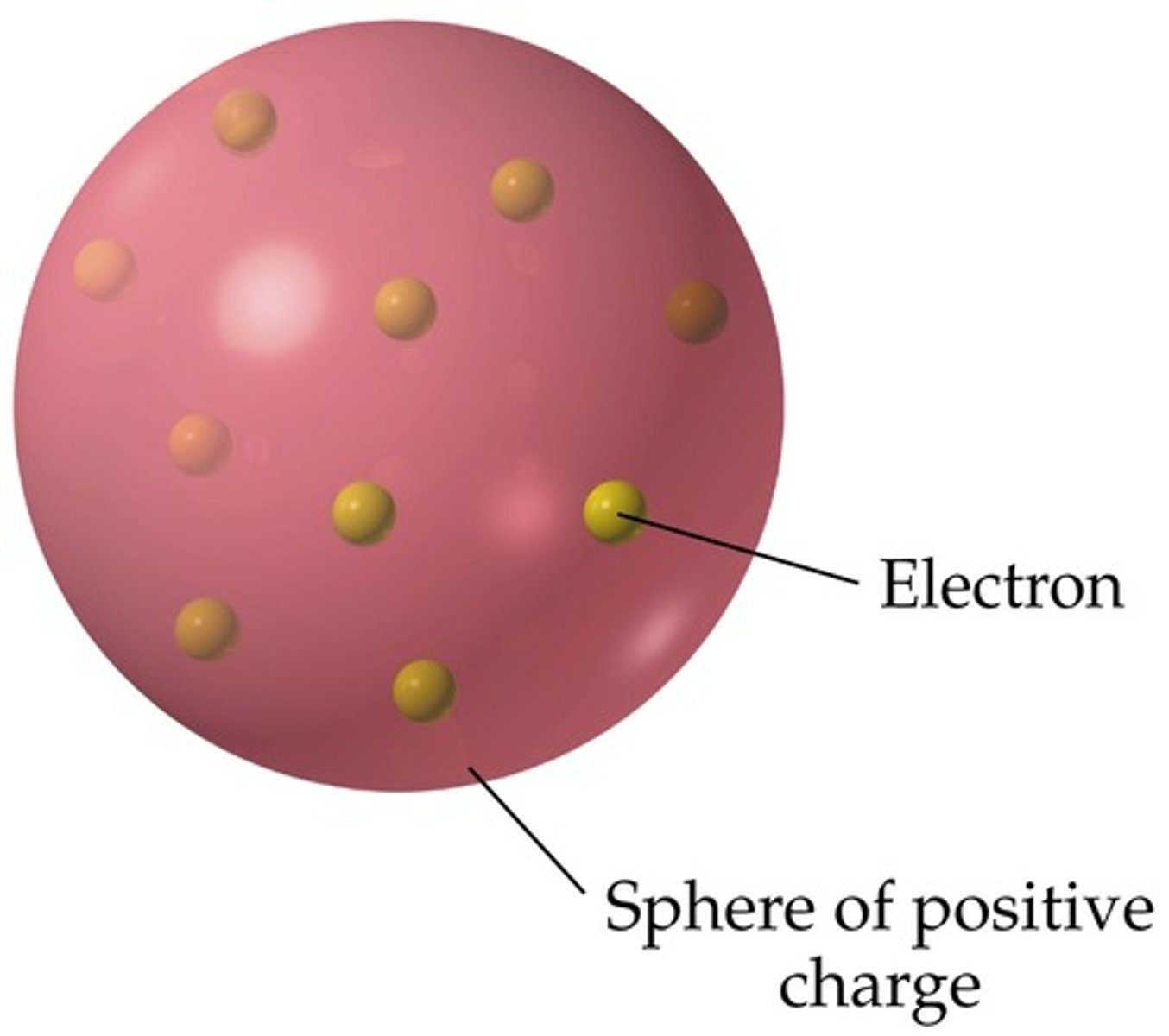
Thomson's discovery
Electron (experiment cathode ray tube)
What is a cathode ray tube?
A device that emits a beam of particles, typically electrons.
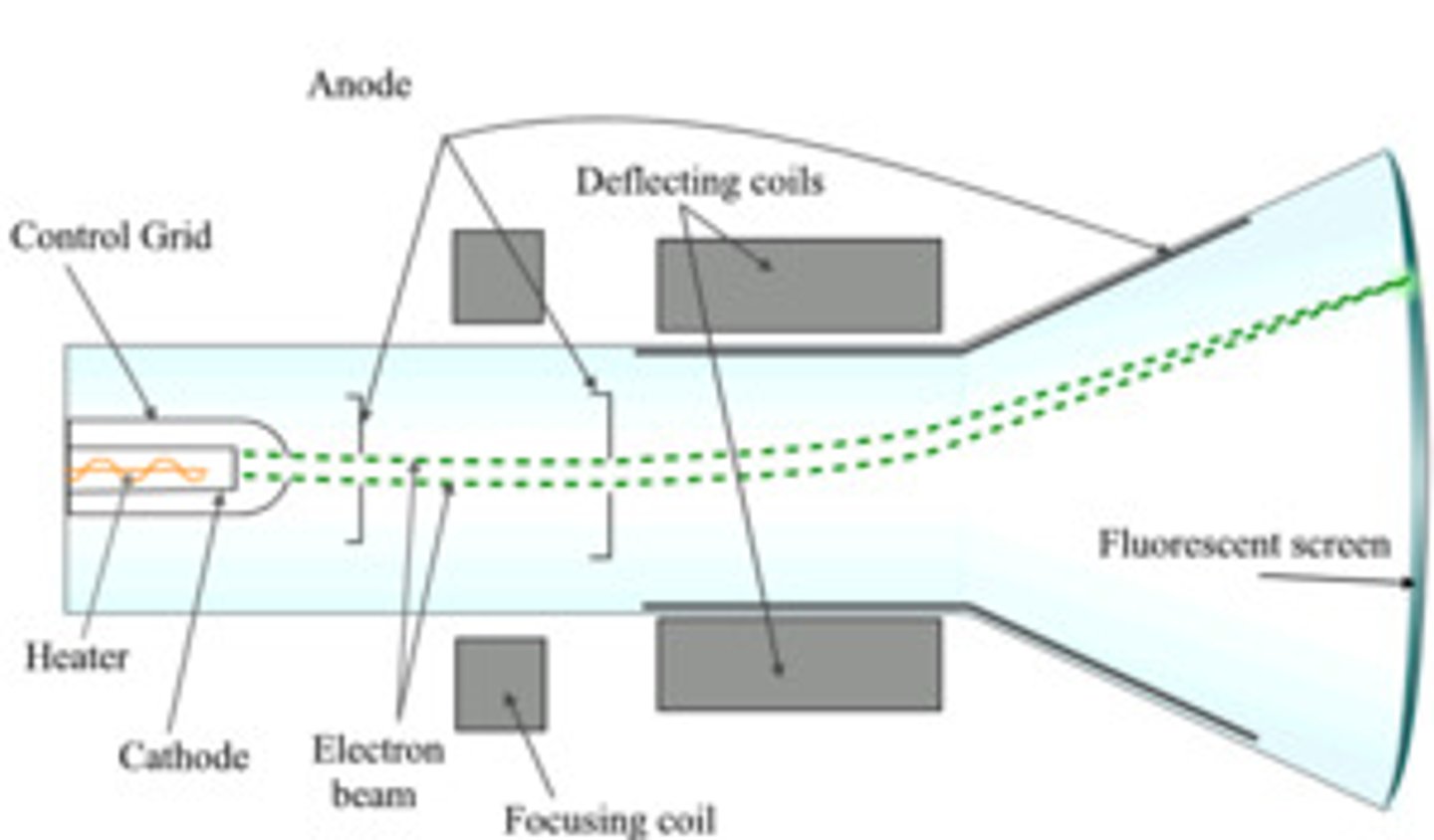
What happens to a beam of particles in a cathode ray tube when it passes through two charged plates?
The beam is attracted towards the positive charge.
What conclusion did J.J. Thomson draw from his experiments with cathode rays?
He concluded that atoms contain negatively charged particles.
Ernest Rutherford's model
Nuclear model
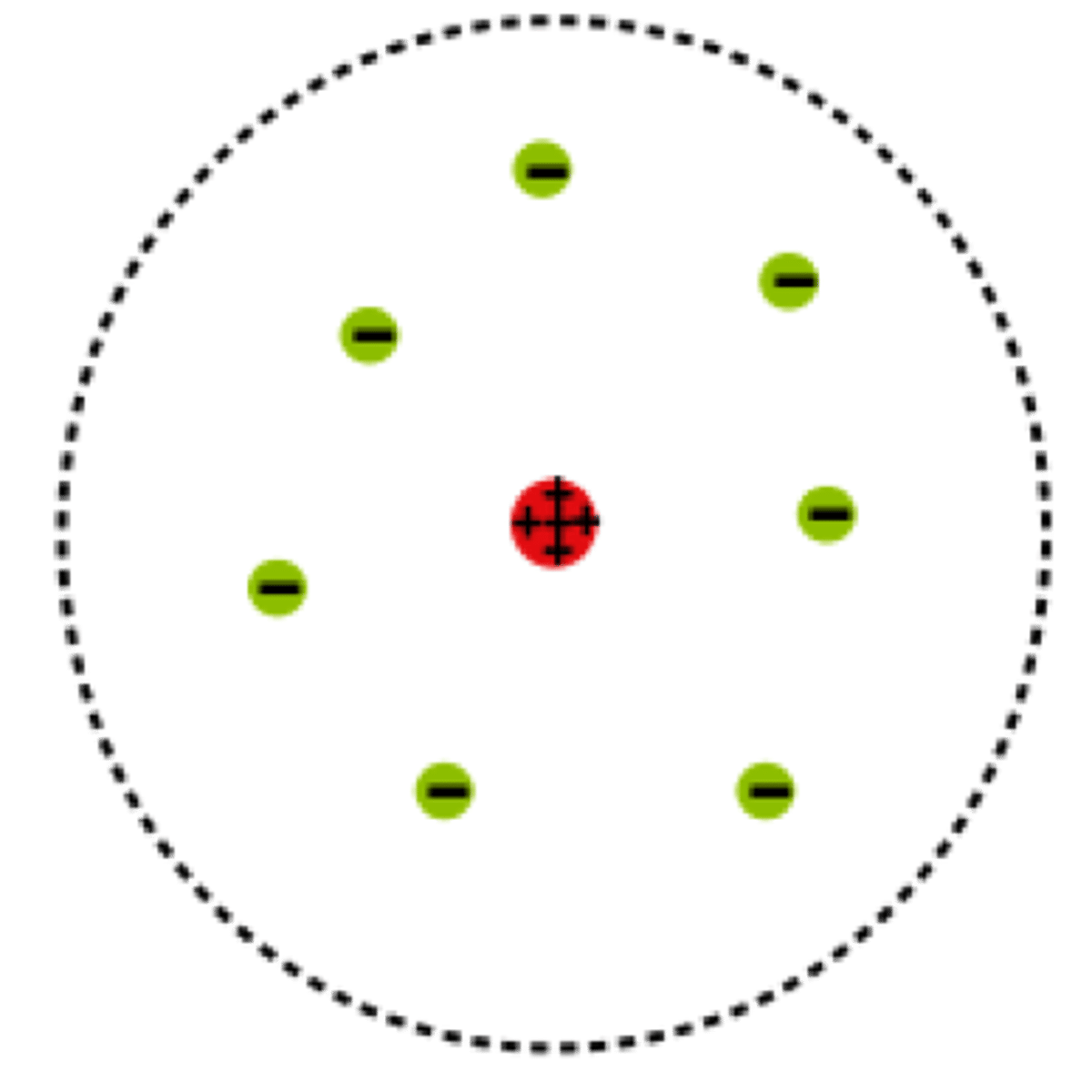
What is the nuclear model?
Central positive nucleus, surrounded by empty space with electrons scattered around it
What two properties of the atom did Ernest Rutherford discover?
1) Had a small, positive, dense nucleus
2) Was mostly empty space
What experiment did Ernest Rutherford conduct?
Gold foil experiment
What observations were made in the gold foil experiment?
1) Most alpha particles travel through the foil undeflected.
2) Some alpha particles are deflected by small angles.
3) Occasionally an alpha particle travels back from the foil.
What interpretations were made in the gold foil experiment?
1) The atom is mostly empty Space
2) The nucleus is positively charged as as well as the alpha particle
3) The nucleus carries most of atoms mass
A piece of gold was bombarded with...
Alpha particles which have a positive charge
Based on Thompson's model of the atom, what should've happened?
All of the particles should have passed straight through the foil, but they didn't
Most alpha particles...
Passed straight through the foil
A small amount of alpha particles...
Bounced backwards or deflected to a side of an angle
Conclusion of gold foil experiment
The atom has a small, dense positive nucleus, and is composed of mostly empty space
Neil's Bohr model of atom
1) Planetary model
2) Place electrons and energy levels outside the nucleus
3) electrons travel in a fixed path or orbit around nucleus
Planetary model
Electrons orbit, the nucleus (Planets Around the sun)
What model did Bohr build upon?
Rutherford's model
How did Bohr explain the stability of electrons around the nucleus?
He stated that electrons could only occupy certain energy levels.
What restriction did Bohr add to the movement of electrons?
Electrons do not have the freedom to move in any orbit; only certain energy levels are allowed.
What must an electron do to move from a lower energy level to a higher energy level?
It must absorb the right amount of energy from another source.
What is the relationship between photon energy and energy levels?
Photon energy is equal to the energy difference between two energy levels.
What charge do protons have?
Positive
What is the mass of a proton approximately equal to?
One AMU
What is necessary for an atom to exist?
Protons
What do protons balance in an atom?
Charge (with electrons)
What role do protons play in the structure of an atom?
They provide structure (an atom can't exist without them)
What do protons give to an atom?
Identity
What happens if you change the number of protons in an atom?
You change the element
What is the charge of a neutron?
No charge/neutral
How does the size of a neutron compare to a proton?
Slightly larger than a proton
What is the mass of a neutron in atomic mass units (AMU)?
Approximately one AMU
What role do neutrons play in an atom?
They stabilize the atom by providing mass
What happens if you change the number of neutrons in an atom?
You change its stability and mass
What are isotopes?
Atoms of the same element with different masses (different number of neutrons)
What is the charge of an electron?
Negative
How does the mass of an electron compare to that of a proton?
1/2000 of a proton
How significant is the mass of an electron?
Negligible (Too small to measure)
What do electrons balance in an atom?
Charge (with protons)
What role do electrons play in chemical reactions?
They interact with other electrons to bond.
What happens to the reactivity and charge of an atom if the number of electrons changes?
They change (chemical reactivity and charge).
Ion
Charged at formed by adding/subtracting electrons
If adding electrons...
Charge decreases (Negative)
If subtracting electrons...
Charge increases (Positive)
anion
A negatively charged ion (p
Cation
A positively charged ion (p>e)
atomic mass
Protons + neutrons (Top left of symbol)
Atomic number
Number of protons, Bottom left of symbol (If neutral, p = e)
Charge
Protons - electrons (Top right of element symbol)
Name notation
Only used for neutral atoms (p=e)
Who was Democritus?
A Greek philosopher who developed the first atomic theory.
What are atoms according to Democritus?
Very small indivisible parts that make up matter.
How did Democritus believe atoms differ?
Atoms differ in shape and size.
What did Democritus believe about the identity of atoms?
He believed that all atoms were identical and that everything was made of the same element.
Law of conservation of mass
In a chemical reaction matters neither created or destroyed
Law of definite proportions
A specific chemical compound always contains the exact same proportion of elements by mass
Law of multiple proportions
Elements can combine a different simple ratios to make different compounds
Who believed that matter was made up of 4 main elements?
Empedokles
What are the 4 main elements according to Empedokles?
Earth, air, fire, and water
Who added that there were 4 basic properties of the elements?
Aristotle
What are the 4 basic properties of the elements according to Aristotle?
Hot, cold, wet, and dry
How many basic properties can each of the elements have?
2 basic properties
Who were the main philosophers associated with atomism?
Democritus and Leucippus
What term did atomists use to describe small, individual particles?
Atomos
According to atomists, what are the two fundamental components of existence?
Atoms and the void
What did atomists believe about the nature of atoms?
Atoms were constantly in motion and indestructible