Chapter 18: Introduction to Darwinian Evolution
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Convergent evolution
organisms evolved similar characteristics as a result of exposure to similar environmental challenges [natural selection]
Homologous
two different related species share a common ancestor with different adaptations of common ancestral feature
Homoplasy
two different, unrelated species that do not share a common ancestor share similar traits
Macroevolution
major evolutionary changes that occur over a long period of time resulting in large phenotypic changes such as the formation of new species
Microevolution
more minor evolutionary changes that occur over just a few generations (allele level)
Modern synthesis
an explanation of evolution that incorporates many aspects of biology such as molecular genetics, phylogeny, natural selection, mutations, etc.
Population
a group of individuals of the same species
Species
a group of successfully interbreeding organisms that also produce fertile offspring that interbreed
Vestigial structure
remnants of structures that were present and functional in the ancestral organisms
Two species have homologous structures. What can we infer?
A.) The structures are identical
B.) The structures have the same function
C.) The species have very different ancestors
D.) The species are related by a common ancestry
E.) The structure have the same function, and they are identical
D.) The species are related by a common ancestry
Natural Selection
Mechanism where organisms with best chance of survival pass on their genes
Evolution
gradual change in traits over time (accumulation of heritable traits)
-modifications can occur in just a few generations
Things to keep in mind with respect to evolution (4)
-organisms survive as a result of changes that occur in gene pool
-do not change to survive
-modifications or changes may not result in a more complex or ordered state
-natural selection favors genetic change supporting survival
(two population may diverge to the point of becoming different species )
Biological species are similar organisms capable of two major things
interbreeding and producing fertile offspring
Population
is a group of individuals of one species (live in same geographic area at same time)
Leanardo da Vinci
fossils as extinct animals/organisms
Hutton
Gradualism
Curvier
punctuated equilibrium
-catastrophes= mass extinction → new species fill void
Malthus
geometric vs arithmetic growth
-favorable variations for survival tend to be preserved, unfavorable ones eliminated
Jean Baptiste de Lamarck
traits acquired during one’s lifetime passed to offspring (natural phenomenon involved and evolutionary change occurs)
Lamarck
use vs disuse: extension of neck causes elongation so offspring will have longer neck
Darwin
(natural selection): variety of necks, longer necks
-reach higher leaves (one possibility)
-mate selection (males use necks to fight)
-heat regulation (vary amount of body surface in sun)
(genetic drift favors longer neck)
Darwin proposed that evolution occurs by natural selection based upon 4 observations…
-Variation: characteristics not same in all individuals in a population
-Overproduction: more offspring produced than can survive
-Limits on population growth: number of survivors limited by competition for resources
-Differential reproductive success (survival of the fittest): most favorable combination of characteristics likely to survive and reproduce
Explain the fossil record
relationships/lineage/progression: connections between living and dead
DNA analysis changing historical relationships (genetic relationships)
Other fossil evidence (preserved footprints and embryos)
Homology Requirements
similar in origin, implies common ancestor: monophyletic
-diff species
-different adaptation/variation of common ancestral feature
-occurs as part of divergent evolution
Homoplasy: example
similar in appearance but not origin (same species, no common ancestor)
-birds compared to insects: vertebrate vs. invertebrate- wings (flight) evolved independently, not from a common ancestral feature
Analogous Structures
have a similar function but anatomically different
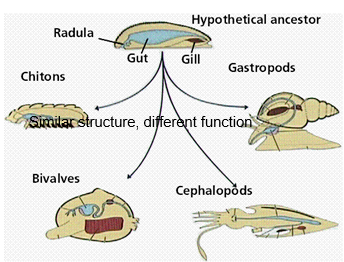
Homology Example vertebrates and mollusks
vertebrates: humerus→ ulna and radius
mollusks: foot for movement, anchoring, feeding
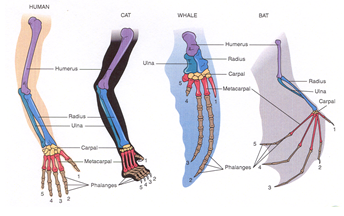
Convergent Evolution
(gives rise to homoplasy)
-similar natural selection pressure produce similar result (e.g. wings and flight)

Homology or Homoplasy
Homology: skeletal features (comes from common ancestor [both vertebrates])
Homoplasy: red in color (evolved separately)
Vestigial Structure
Remnants of past structure: overtime useful structure becomes smaller→ loss of function or may degenerate entirely
Vestigial Structure Examples (6)
-palmaris longus
-plica semilunaris (3rd eyelid blinks horizontally and still present in other animals)
-human fused tailbones, third molar wisdom teeth, muscles that move ears
-pelvic bones in other animals
-secum and appendix in humans
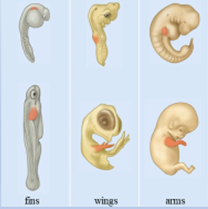
Explain
How and when genes are switched on and off during development results in diversity of form in species with similar genes
-fish, chickens, and humans are vertebrates (strikingly similar genes)
-different developmental pathways, different results (fins, wings, or limbs)