12 - The Nervous System
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Postsynaptic Potentials
Neurotransmitter receptors cause graded potentials that vary in strength with
Amount of neurotransmitter released
Time neurotransmitter stays in area
Types of postsynaptic potentials
EPSP—excitatory postsynaptic potentials
IPSP—inhibitory postsynaptic potentials
Excitatory Synapses and EPSPs
Neurotransmitter binding opens chemically gated channels
Allows simultaneous flow of Na+ and K+ in opposite directions
Na+ influx greater than K+ efflux → net depolarization called EPSP (not AP)
EPSP help trigger AP if EPSP is of threshold strength
Can spread to axon hillock, trigger opening of voltage-gated channels, and cause AP to be generated
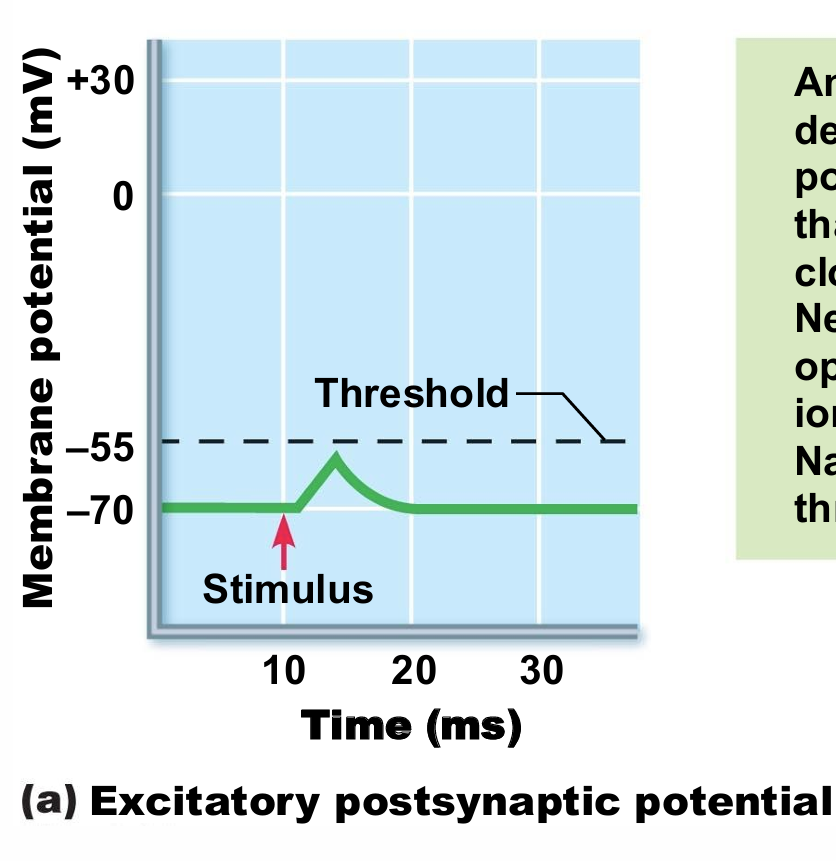
EPSP
a local depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane that brings the neuron closer to AP threshold. Neurotransmitter binding opens chemically gated ion channels, allowing Na+ and K+ to pass through simultaneously.
Inhibitory Synapses and IPSPs
Reduces postsynaptic neuron's ability to produce an action potential
Makes membrane more permeable to K+ or Cl
If K+ channels open, it moves out of cell
If Cl- channels open, it moves into cell
Therefore neurotransmitter hyperpolarizes cell
Inner surface of membrane becomes more negative…hyperpolarized state
AP less likely to be generated
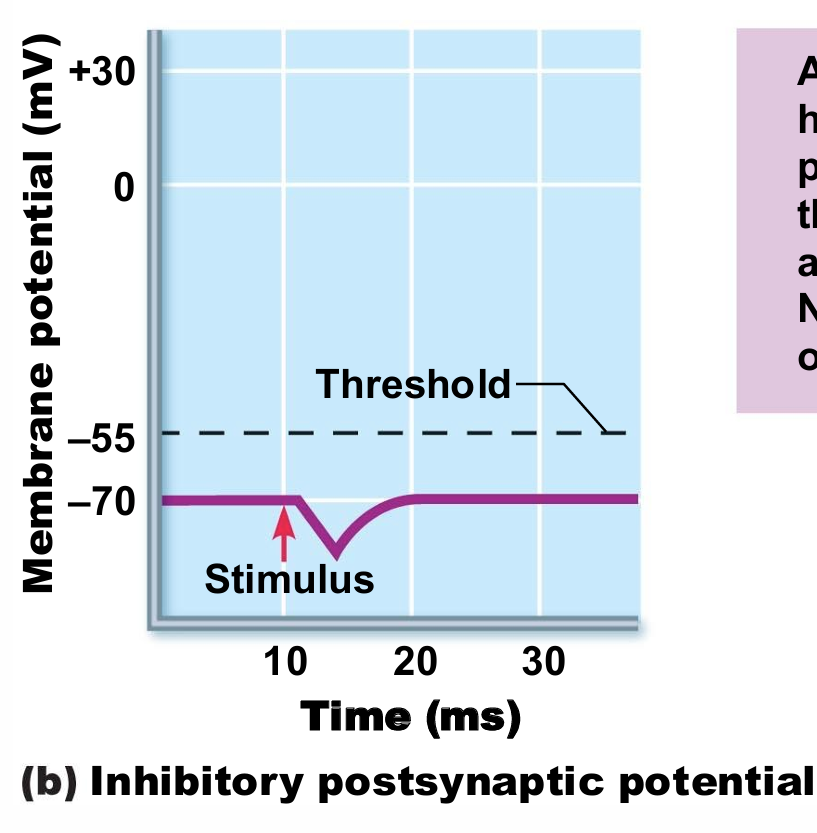
IPSP
local hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane that drives the neuron away from AP threshold. Neurotransmitter binding opens K+ or Cl– channels
Summation
Synaptic Integration
A single EPSP cannot induce an AP
EPSPs can summate to influence postsynaptic neuron
IPSPs can also summate
Most neurons receive both excitatory and inhibitory inputs from thousands of other neurons
Only if EPSP's predominate and bring to threshold→ AP
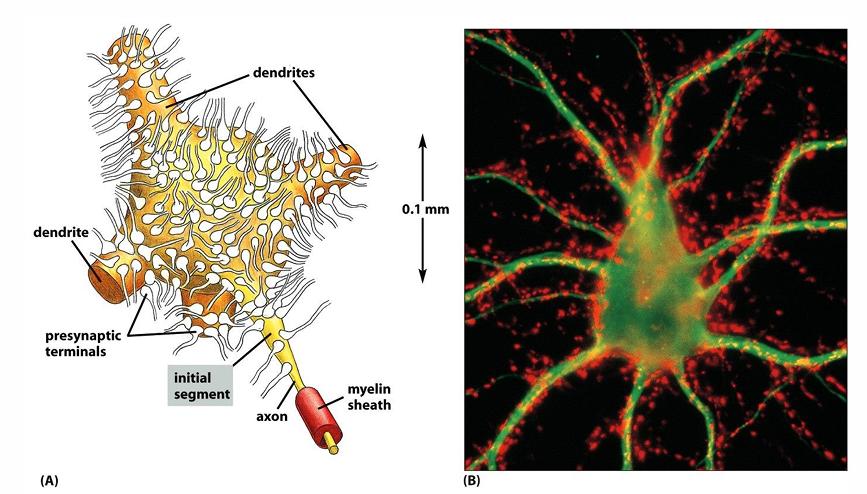
A single neuron can receive inputs from
thousands of other neurons and form synapses with thousands of other cells
Figure shows a single motor neuron and the nerve terminals that make synapses with it
Types of Summation
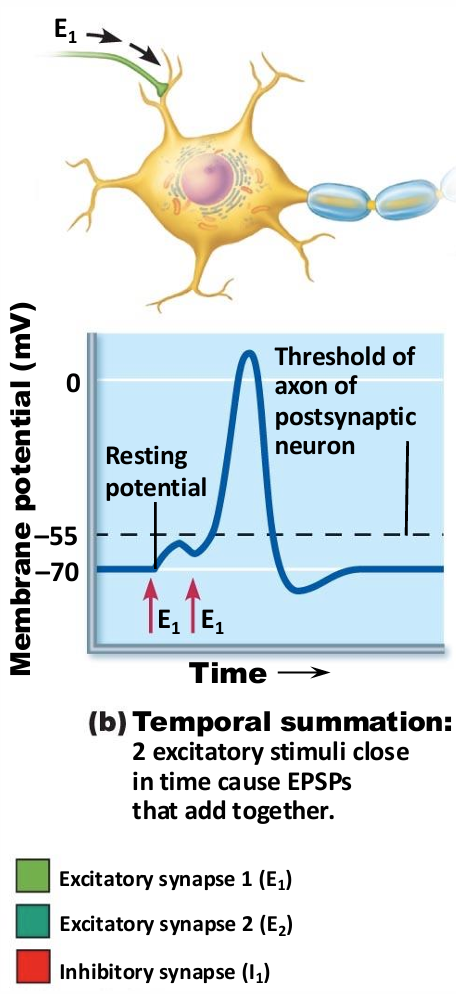
temporal summation
spatial summation
Temporal summation
One or more presynaptic neurons transmit impulses in rapid-fire order
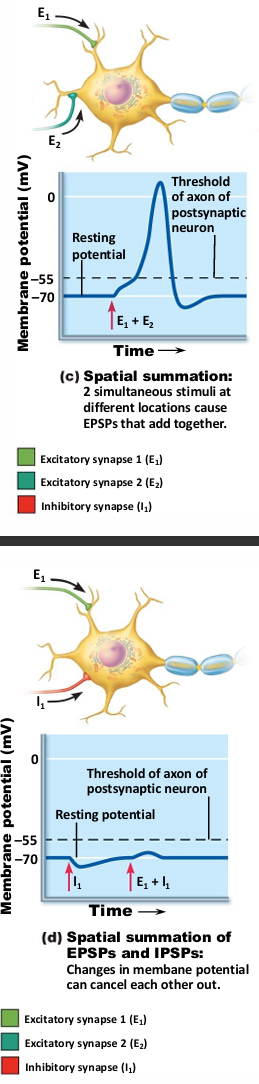
Spatial summation
Postsynaptic neuron stimulated simultaneously by large number of terminals at same time
Grade potentials vs Action Potential
Grade Potential
take place cell body and dendrite
short distance
various magnitudes (drop off as get further)
summate
chemically gated channels
Action Potential
start in axon hillock and proceed down axon
long distance
all or none
do not summate
voltage gated channels
Synaptic Potentiation
integration
Repeated use of synapse increases ability of presynaptic cell to excite postsynaptic neuron
Ca2+ concentration increases in presynaptic terminal and postsynaptic neuron
Brief high-frequency stimulation partially depolarizes postsynaptic neuron
Chemically gated channels (NMDA receptors) allow Ca2+ entry
Ca2+ activates kinase enzymes that promote more effective responses to subsequent stimuli
Presynaptic Inhibition
Excitatory neurotransmitter release by one neuron inhibited by another neuron via an axoaxonal synapse
Less neurotransmitter released
Smaller EPSPs formed
Types of Synaptic Integration
Summation
Synaptic Potentiation
Presynaptic Inhibition
Neurotransmitters
Language of nervous system
100 neurotransmitters have been identified
Most neurons make two or more neurotransmitters
Neurons can exert several influences
Usually released at different stimulation frequencies
Classification of neurotransmitters
chemical structure
function
Effects – excitatory versus inhibitory
Actions – direct versus indirect
Chemical structure classification of neurotransmitters
Acetylcholine
Nicotinic vs muscarinic receptors
Biogenic amines
Catecholamines
Indolamines
Amino acids
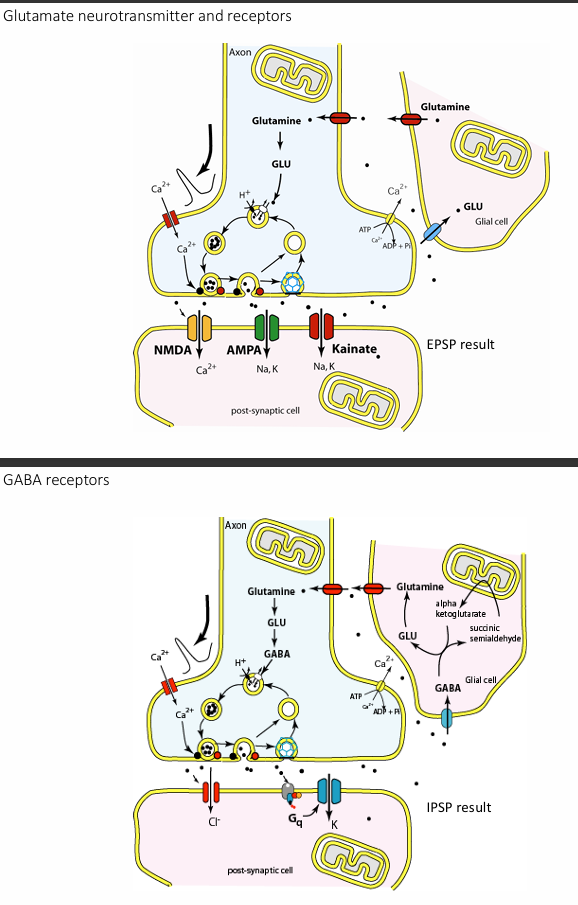
Glutamate
Aspartate
Glycine
GABA
Peptides - Neuropeptides
Substance P
Endorphins
Gut-brain peptides
Purines
ATP
Adenosine
Gases and lipids - gasotransmitters
Nitric Oxide
Carbon Monoxide
Hydrogen sulfide gases
Endocannabinoids
Direct action
Neurotransmitter binds to and opens ion channels
Promotes rapid responses by altering membrane potential
Examples: ACh and amino acids
Indirect action
Neurotransmitter acts through intracellular second messengers, usually G protein pathways
Broader, longer-lasting effects similar to hormones
Biogenic amines, neuropeptides, and dissolved gases
Neurotransmitter receptors types
Channel-linked receptors
Mediate fast synaptic transmission
G protein-linked receptor
Oversee slow synaptic responses
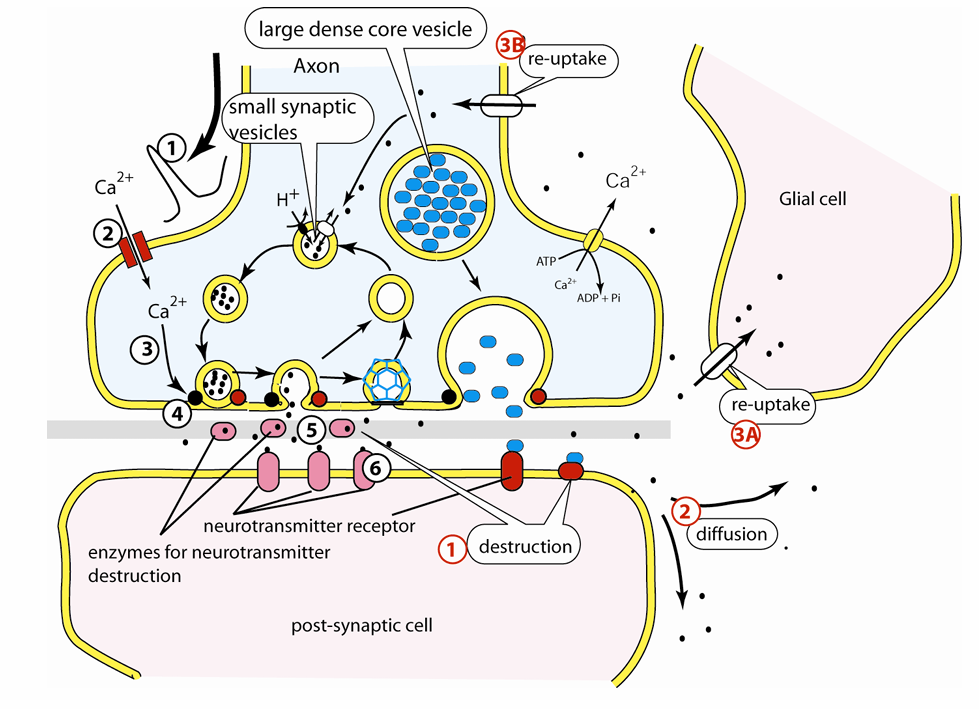
General mechanism of the origin and termination of neurotransmission (diagram)
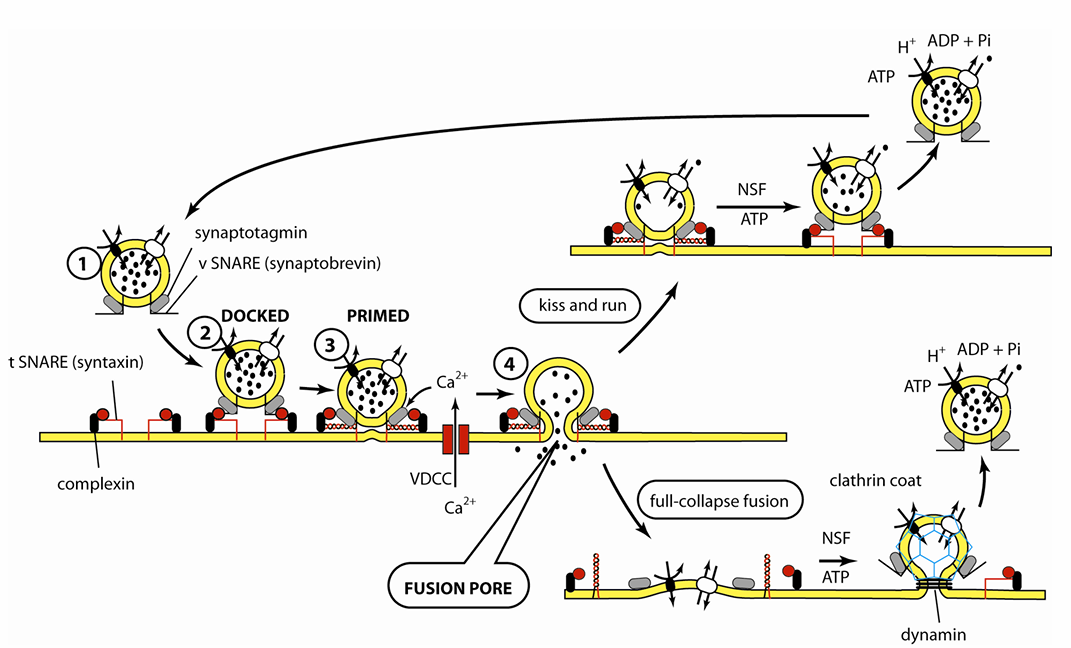
Mechanism of vesicle fusion and recycling (diagram)
Acetylcholine
ACh
First identified; best understood
Released at neuromuscular junctions, by some ANS neurons, by some CNS neurons
Synthesized from acetic acid and choline by enzyme choline acetyltransferase
Degraded by enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
Bind to
Nicotinic receptors (ion channels, fast, sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system)
muscarinic receptors (G-protein coupled receptors, slow, parasympathetic nervous system – rest and digest)
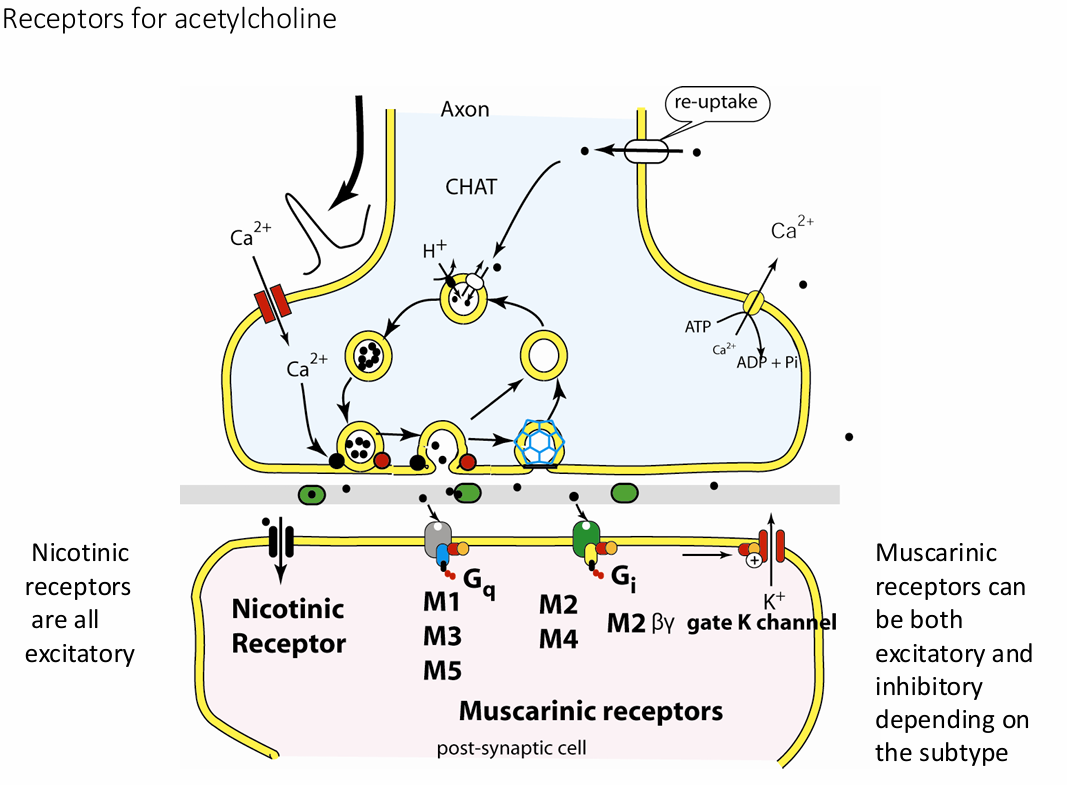
_ nerves secrete ACh
Cholinergic
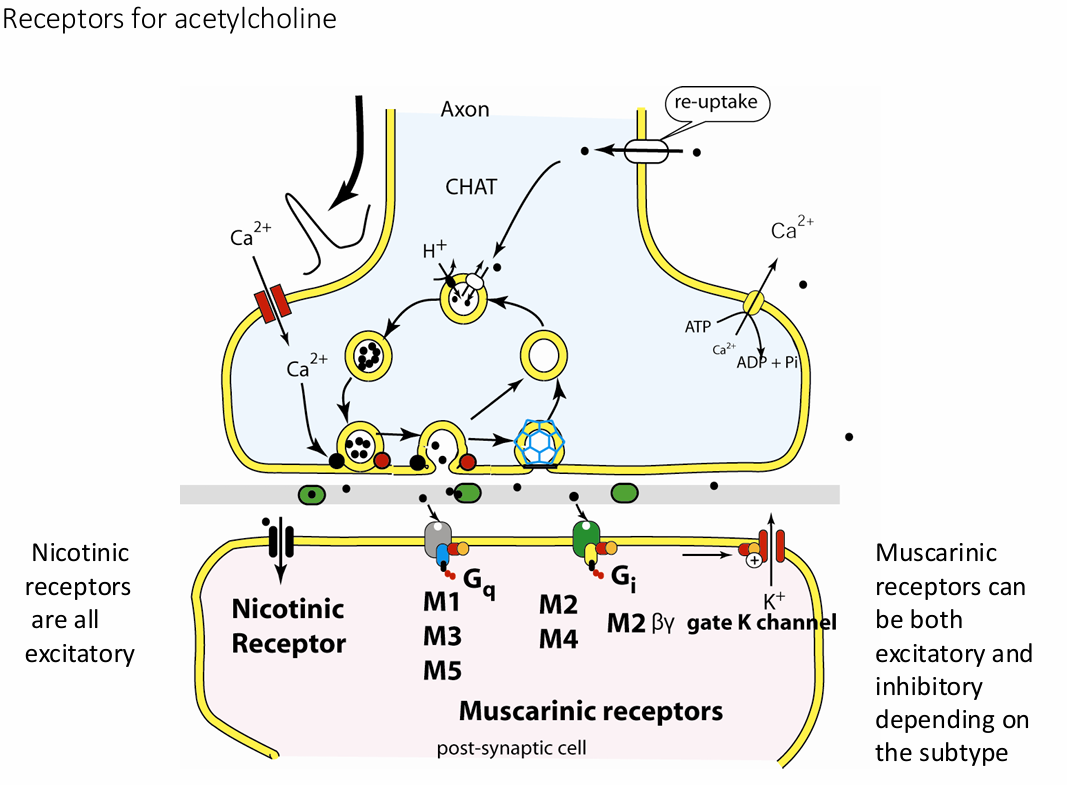
Nicotinic receptors
ion channels, fast, sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
get their name from nicotine
Nicotine selectively binds to the nicotinic receptors
are all excitatory
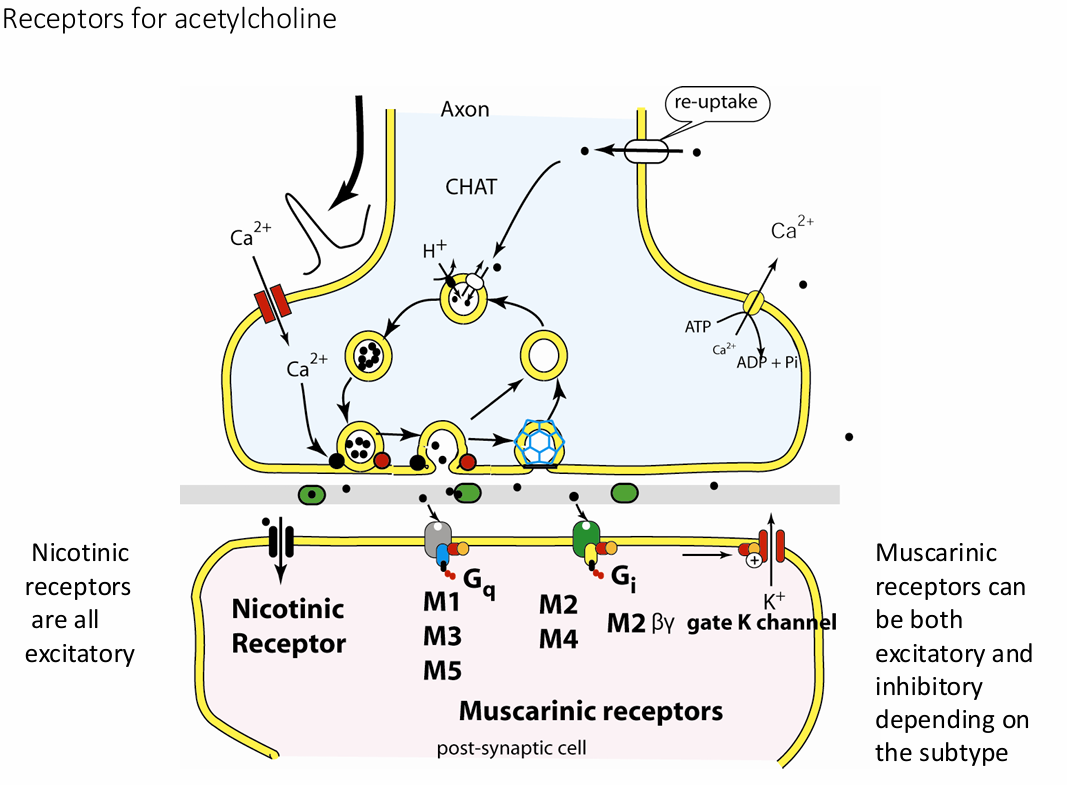
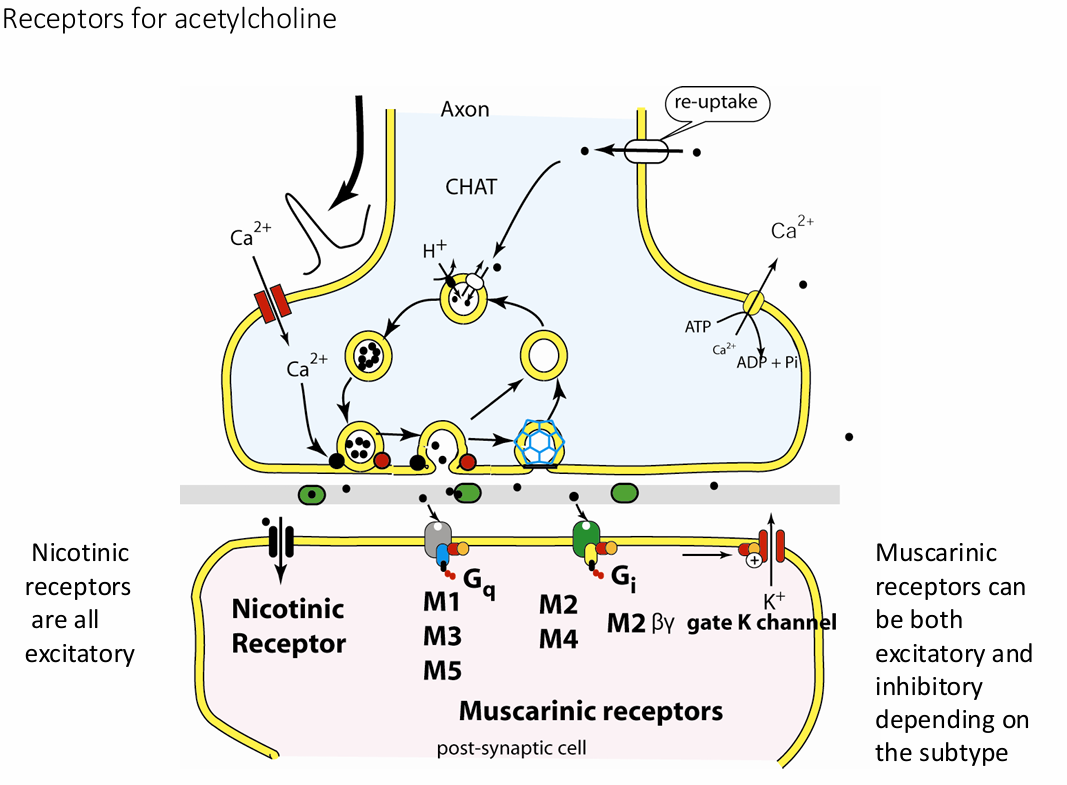
muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
G-protein coupled receptors, slow, parasympathetic nervous system – rest and digest
gets their name from a chemical that selectively attaches to that receptor muscarine
Muscarine is a natural product found in certain mushrooms
can be both excitatory and inhibitory depending of the subtype
Biogenic amines
Broadly distributed in brain
Play roles in emotional behaviors and biological clock
Some ANS motor neurons (especially NE)
Imbalances associated with mental illness
Catecholamines
Indolamines
Catecholamines
type of Biogenic amines
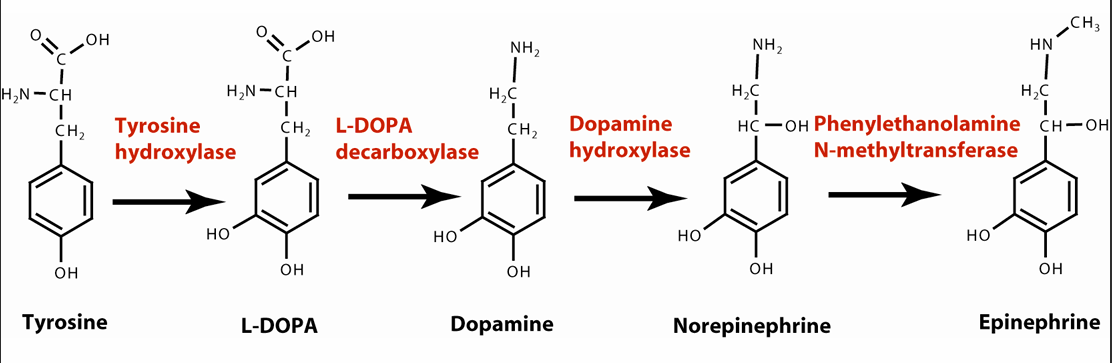
Dopamine, norepinephrine (NE), and epinephrine
Synthesized from amino acid tyrosine
Adrenergic or “working on adrenaline” nerve cells
Indolamines
type of Biogenic amines
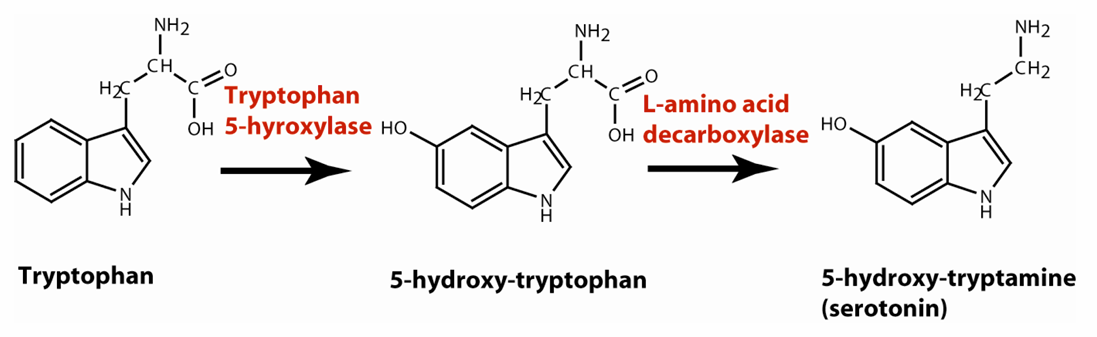
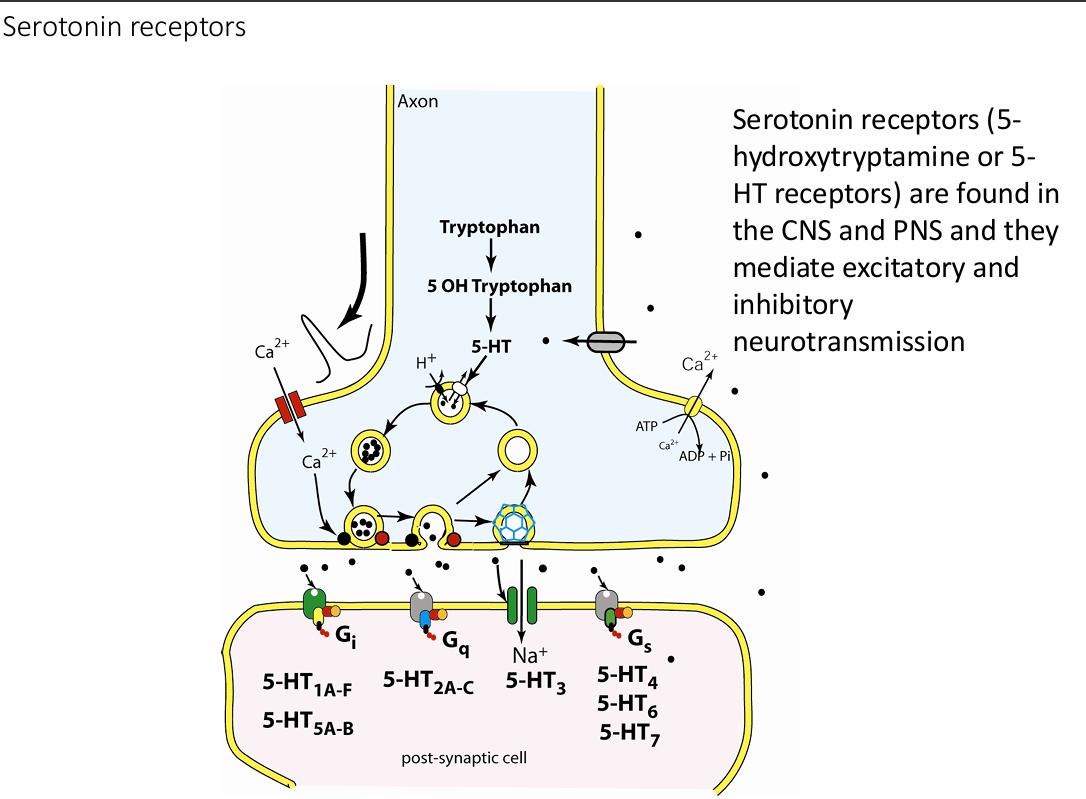
Serotonin and histamine
Serotonin synthesized from amino acid tryptophan; histamine synthesized from amino acid histidine
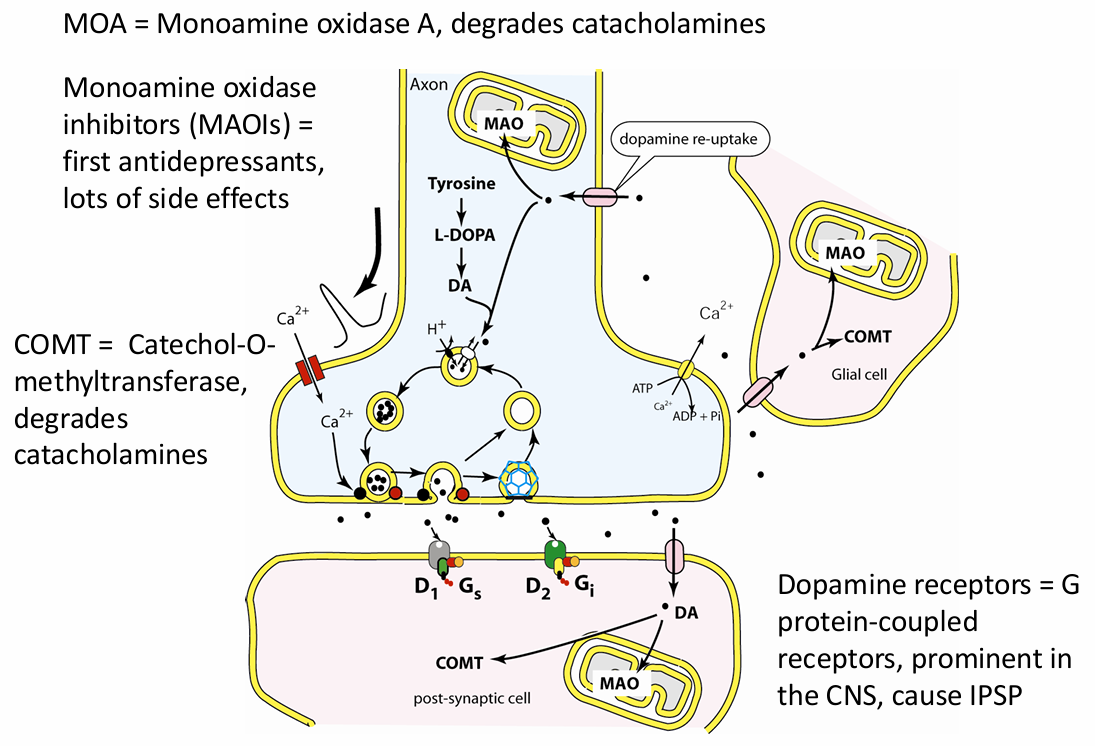
Dopamine receptors and degradation
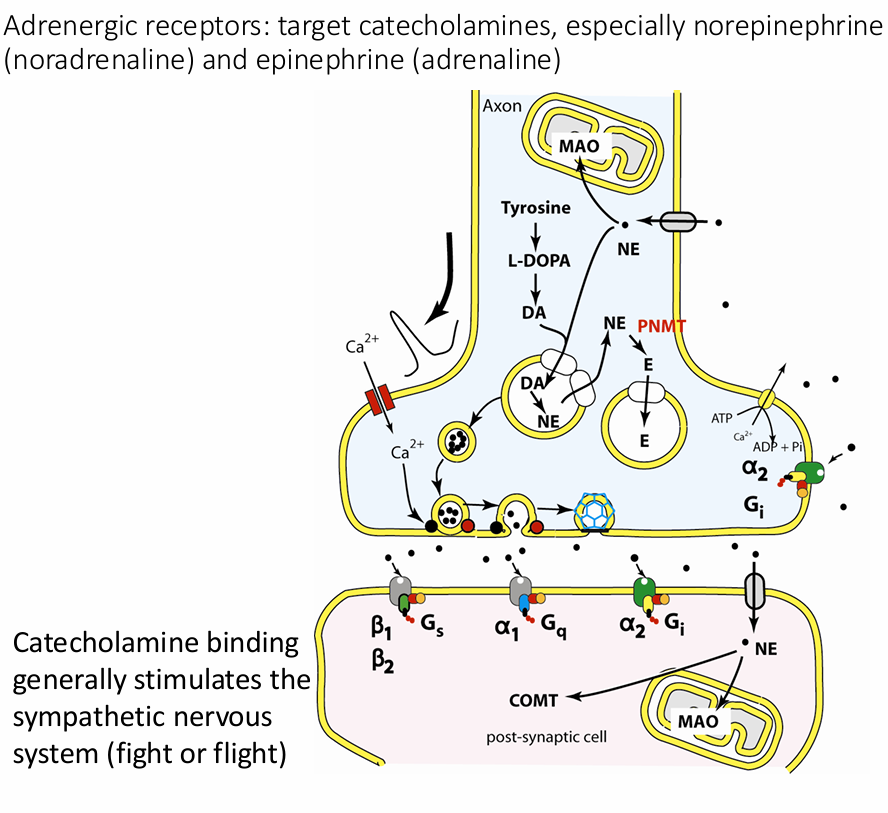
Adrenergic receptors
target catecholamines, especially norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline)
Serotonin receptors
Amino acid Neurotransmitters
Glutamate - excitatory
Aspartate
Glycine
GABA—gamma (γ)-aminobutyric acid - inhibitory
neuropeptides
Substance P
Mediator of pain signals
Endorphins
Beta endorphin, dynorphin and enkephalins
Act as natural opiates; reduce pain perception
Gut-brain peptides
Somatostatin and cholecystokinin
Purines as Neurotransmitters
ATP!
Adenosine
Potent inhibitor in brain
Caffeine blocks adenosine receptors
Act in both CNS and PNS
Produce fast or slow responses
Induce Ca2+ influx in astrocytes
gasotransmitters
gases and lipids
Nitric oxide (NO), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen sulfide gases (H2S)
Bind with G protein–coupled receptors in the brain
Lipid soluble
easily get into membrane
Synthesized on demand
NO involved in learning and formation of new memories; brain damage in stroke patients, smooth muscle relaxation in intestine
H2S acts directly on ion channels to alter function
Endocannabinoids
Act at same receptors as THC (active ingredient in marijuana)
Most common G protein-linked receptors in brain
Lipid soluble
Synthesized on demand
Believed to be involved in learning and memory
May be involved in neuronal development, controlling appetite, and suppressing nause
Classification of Neurotransmitters: Function
Great diversity of functions
Can classify by
Effects – excitatory versus inhibitory
Actions – direct versus indirect
Classification of Neurotransmitters: Effects
excitatory versus inhibitory
based on receptor present
Neurotransmitter effects can be excitatory (depolarizing) and/or inhibitory (hyperpolarizing)
Effect determined by receptor to which it binds
GABA and glycine usually inhibitory
Glutamate usually excitatory
Acetylcholine and NE bind to at least two receptor types with opposite effects
ACh excitatory at neuromuscular junctions in skeletal muscle
ACh inhibitory in cardiac muscle
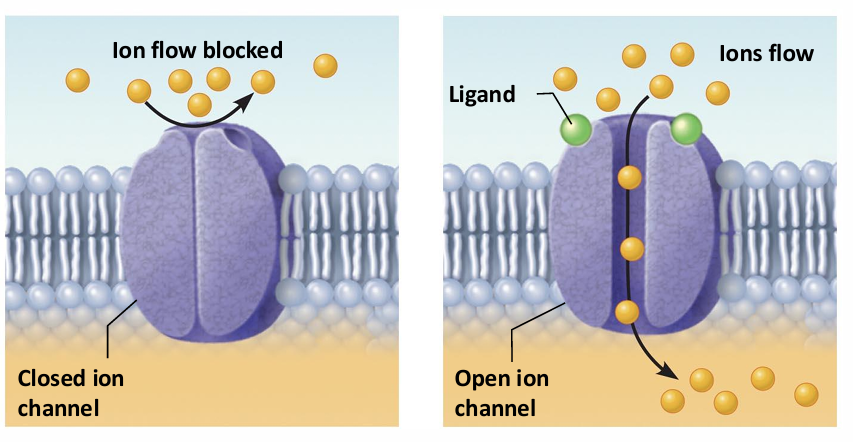
Ionotropic Mechanism of Action
Channel-Linked (Ionotropic) Receptors
Ligand-gated ion channels
Action is immediate and brief
Excitatory receptors are channels for small cations
Na+ influx contributes most to depolarization
Inhibitory receptors allow Cl– influx that causes hyperpolarization
Metabotropic Mechanism of Action
G Protein-Linked Receptors
Responses are indirect, complex, slow, and often prolonged
Transmembrane protein complexes
Cause widespread metabolic changes
Examples: muscarinic ACh receptors, receptors that bind biogenic amines and neuropeptides
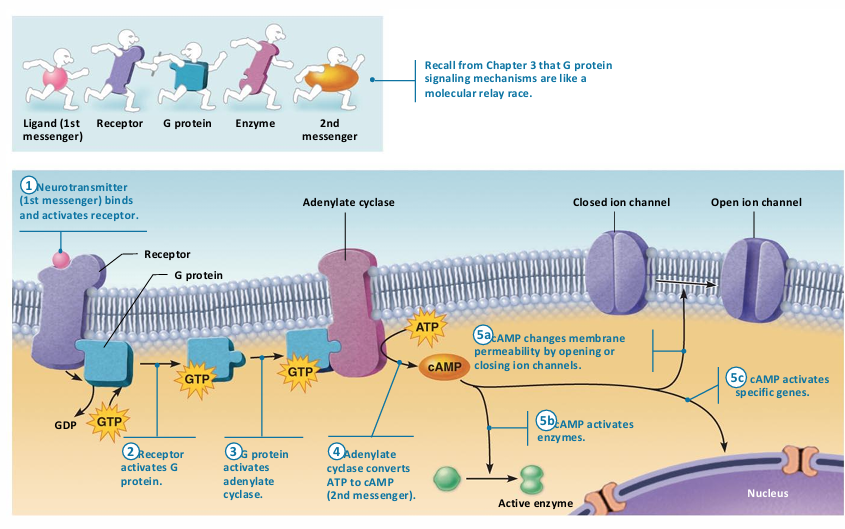
G Protein-Linked Receptors: Mechanism Steps
Neurotransmitter binds to G protein–linked receptor
G protein is activated
Activated G protein controls production of second messengers, e.g., Cyclic AMP, cyclic GMP, diacylglycerol, or Ca2+
Second messengers
Open or close ion channels
Activate kinase enzymes
Phosphorylate channel proteins
Activate genes and induce protein synthesis