BIO Exam 1
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
What is defined by major geologic and biological events
Geologic Timescales
When did the earth form?
4.6 Billion Years Ago
What is the chemical soup?
early earth rich in water, CH4, NH3, and H2
What is crucial for the formation of bio molecules?
Oxygen
What was the Prebiotic Simulation Experiment?
An experiment performed by Stanley Miller to replicate pre-life conditions
What did the Prebiotic Simulation experiment create?
Amino Acids
What may have provided scaffolding to allow the formation of macromolecules?
Hot Clays
What is the formation of membranes from phospholipids?
Liposomes
What are the first membrane-bound aggregations of RNA, DNA, proteins, and lipids (Carol Woese)?
Progenotes
What is the Darwin Threshold?
error prone translation apparatus eventually attained modern levels of fidelity
What brought in molecular oxygen?
the origin of photosynthesis
What is evidence of early oxygenation?
Iron Deposits
The Endosymbiont Theory states what?
that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated as free living bacteria
What do Mitos and Chloros have in common with certain types of free-living bacteria?
Similiar sizes
What is similar in cyanobacteria and chloroplasts?
Photosynthetic pigments
What are mitochondria and chloroplasts both bound by?
two membranes
The two organelles (mitochondria and chloroplasts) replicate the same as what?
free-living bacteria by dividing
Mitochondria and Chloroplasts both have their own what?
DNA, RNA, and ribosomes
What does DNA show about mitos?
That they have a close relationship with bacteria
What does DNA show about chloros?
That they have a close relationship to cyanobacteria
What is the order of the Eras?
Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Caenozoic
Earliest fossils are from what?
Red Algae
What happened in the Cambrian period?
All major animal phyla evolve
What happened in the Ordovician Period?
the first jawless vertebrates appear, simple plants come to land
What happened in the Silurian Period?
First vascular plants appeared, first animals moved onto land
What happened in the Devonian Period?
the first amphibians appear, mysterious extinction
What happened in the Carboniferous Period?
First primitive reptiles evolve, when modern coal deposits were formed
What happened in the Permian Period?
Ends with catastrophic Permian-Triassic extinction
What is the Permian-Triassic Extinction?
The most severe extinction event in Earth’s history
What happened in the Cretaceous Period?
ended in Mass Extinction from a asteroid impact near the Yucatan Peninsula
Approximately how many eukaryotes are alive today?
7.4-10 million species
What is evolution?
the change in heritable characteristics of biological entities over time
What do Extant organisms provide?
clues through DNA, Embryonic development, and expressed structure
What do extinct organisms provide?
A rich fossil record
What is a fossil?
Any evidence of an organism that is older than 10,000 years old
How are compression fossils formed?
when fine sediment compresses a specimen (best for plants)
How are petrification fossils formed?
when an organism is buried, and dissolved minerals replace organic materials
How are impression fossils formed?
when an organism makes an impression in mud (can create trace fossils)
How are cast fossils formed?
when impressions are filled with mud, providing a mold
How does Intact Preservation Fossils form?
when tree resin traps an organism and hardens (amber)
What are bodies lodged in amber called?
Inclusions
What typically makes a good fossil?
rapid burial, anoxic conditions, or very dry conditions
What most likely destroys many fossils?
erosion and continental shift
What is relative dating?
A crude method in dating when fossils are dated
What is stratigraphy?
the study of rock layers and their chronological relations and composition
Wha is absolute dating?
Another crude method to dating fossils by using the fossil/specimen itself to determine the age
What is radiometric dating?
Another crude method to date fossils using radioactive isotopes as clocks
What is an isotope?
an atom with a different number of neutrons
What is half-life?
the amount of time it takes for half the isotopes in a sample to decay into the parent atom
What can Carbon 14 do?
age objects about 40,000 years old
What can Potassium 40 do?
age fossils dating 300,000 years or older
What is biogeography?
the study of how species are distributed across the planet
Who is the father of modern biology?
Alfred Russel Wallace
What is the Wallace Line?
a shift from more Australian-like fauna to more Asian-like fauna in Southeast Asia
What are Homologous structures?
structures which share a common ancestry
What are Vestigial structures?
structures with no apparent function, but may be a sign of share ancestry
What are analogous structures?
Structures which have similar functions, but different ancestral origins
What is Evolutionary development biology?
A way of looking at developmental pathways and how they are related
What are homeotic genes?
genes that lead to abnormal or misplaced structures when mutated
What is a genome?
the complete set of genes or genetic material of an organism
What are Ultra-conserved Elements?
are highly conserved regions of DNA that can be used to quantify differences in adjacent regions of DNA sequences
Who was the first to openly suggest that some groups may have arisen from a common ancestor?
Georges-Louis Buffon
Who proposed the theory of Uniformitarianism?
James Hutton
What is the theory of Uniformitarianism?
it suggests the slow processes of today occurred in the past
What is catastrophism?
it states that violent events are responsible for geologic formations of today
Who developed the principle of superstition?
Georges Cuvier
What is the principle of superposition?
it stated that lower rock layers were older than the ones above them
What did Charles Lyell argue?
that the Earth was not 6,000 years old, but rather hundreds of millions of years old
Who suggested the first way that species change?
Jean Baptiste Lamarck
What did Jean Baptiste Lamarck suggest?
that organisms acquired traits over their lifetimes and passed those on to successive generations (experiments showed otherwise)
Who was on the HMS Beagle ship?
Charles E. Darwin
Whose essay provided Darwin with some insight?
Thomas Malthus’ essay on the Principle of Population
What did the essay on the Principles of Population say?
stated that resources are finite, and that not all organisms survive to reproduce
Darwin termed what?
Natural selection, the preservation of favorable traits over inferior ones
What is artificial selection?
humans acted as the agents of selection
What is the issue with blending inheritance?
it would mean that favorable variations would be diluted out
What did Gregor Mendel do?
his fertilization experiments with pea plants demonstrated a mechanism of inheritance that would validate Darwin
What is the modern evolutionary synthesis?
it unified Mendel’s and Darwin’s ideas, adding that mutations are responsible for observed variation
What is a mutation?
a change in nucleotide sequence
On what level does evolution act on?
the population, which consists of interbreeding members of the same species
What is responsible for variability?
variations of genes called Alleles
What is a Gene Pool?
the entire collection of genes and their alleles in a population
What is phenotype?
the physical manifestation of an organisms genetic make up
What is a variation that helps an organism survive?
adaptation
What does Fitness refer to?
an organism’s genetic contribution to the next generation
What is Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
a set of theoretical circumstances where allele frequencies do not change
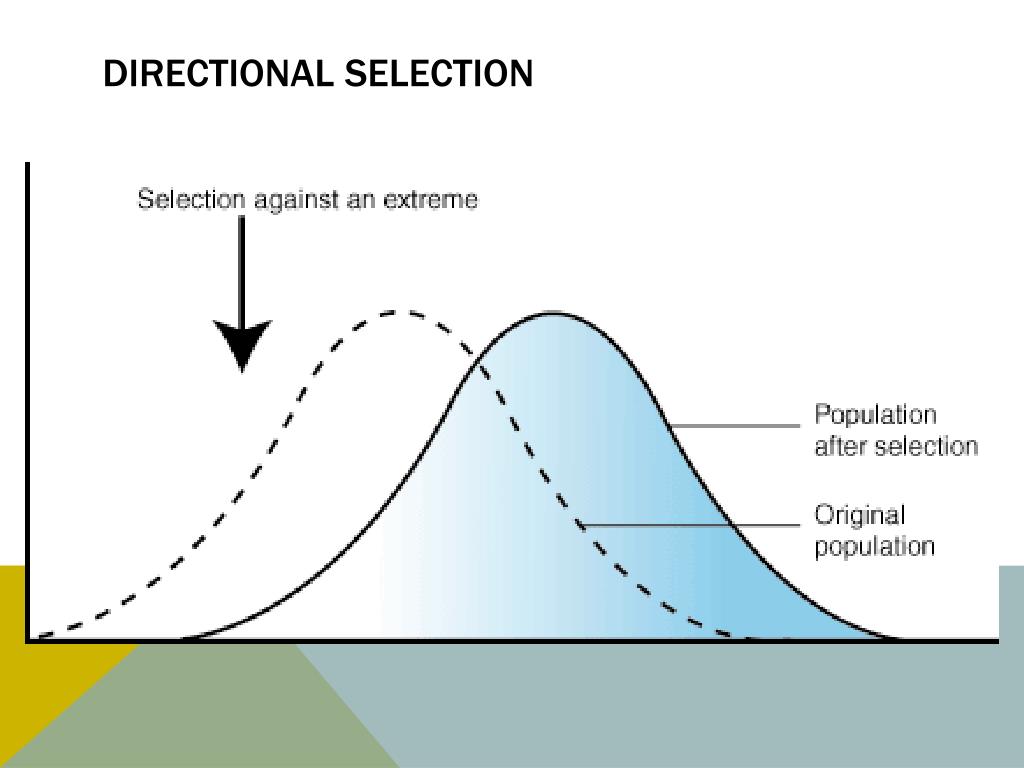
What is Directional Selection?
one extreme phenotype is fittest, and the environment selects against other variations.
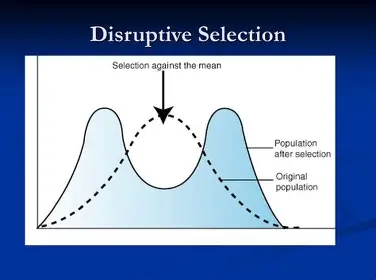
What is Disruptive Selection?
occurs when two or more extreme phenotypes are selected
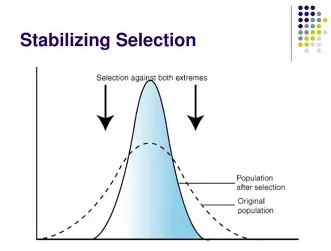
What is Stabilizing Selection?
occurs when extreme variations are selected against, and intermediate are favored
What is balanced polymorphism?
genes that maintain multiple alleles
When does Heterozygote advantage occur?
when an individual with two different allele is favored over individuals
What is Sexual Selection?
a type of natural selection on variation in the ability to obtain mates
What is Sexual Dimorphism?
a difference in appearance between males and females of species (prominent in species who compete for mates)
What is Intrasexual selection?
where members of the same sex compete
What is intersexual selection?
were members of the opposite sex do the selecting
What is Genetic drift?
a change in allele frequencies that happens purely by chance (impact small populations)
What is genetic drift an example of?
sampling error
What are Genetic Bottlenecks?
they occur when there is a loss of alleles
What is the founder affect?
when a loss in alleles is the result of a small population becoming isolated
What is the microevolutionary processes?
the various modes of selection and their impact on allele frequency