FAMILY STUDIES MIDTERM TEST
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
BENEFITS OF HAVING CHILDREN
when young:
more comfortable
age gap smaller
less chance of medical issue
BENEFITS OF HAVING CHILDREN
when older:
good income
financially stable
More experience
Define parent
is anyone who is biologically or legally a mother or father
Define parenting
Means using the skills to care for and raise a child to adulthood
Healthy reasons for parenting
share your life
ready to love a child
guide someone to become an adult
Unhealthy reasons
to solve problems with a partner
to receive money
children may bring prestige
Qualities needed by parents
Unconditional love
Patience
Support
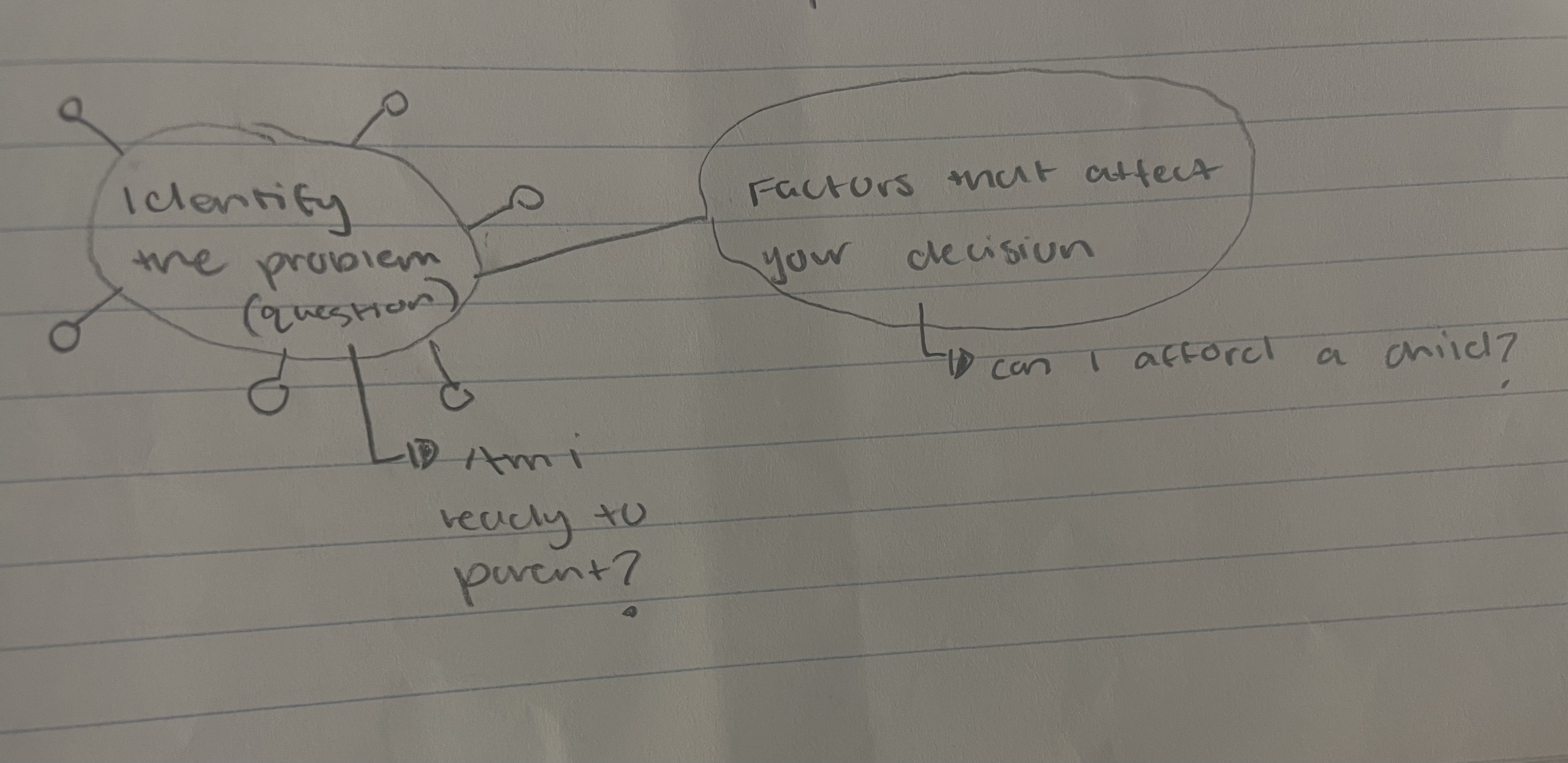
DECISION MAKING
uninformed decisions
flip a coin or rock/paper/scissors
based on how you feel at the moment
choose not to decide + then live with what happens
DECISION MAKING
Informed decisions
gather all the information you need to make a choice
consider advantages and disadvantages
DECISION MAKING

DECISION MAKING
what are the 8 factors influencing the decision to parent?
social + cultural influences
Education
Finances
Parenting partnership
Personal maturity
Age
Health
Life experience
SOCIAL + CULTURAL INFLUENCES
name the 4 influences that play a role in becoming a parent
a) family
b) friends
c) community
d) media
SOCIAL + CULTURAL INFLUENCES
affect our beliefs/values about parenting
family - have children
friends - are having children
community - part of religion + have children
media - being trendy (having a baby is fashionable)
EDUCATION
doesnt make you a better parent
the less it is you will be unemployed
may lead to better paying job
FINANCES
having more money does not make you a better parent
lack of money- stressful, unable to meet childs needs
more money spent on boys bcus of food
PARENTING PARTNERSHIP
married, living together, committed
team effort
2 role models
PERSONAL MATURITY
age doesnt determine personal maturity
combo of emotional & intellectual maturity
experiences in life
AGE
physical maturity
best age: early 20s to mid 30s
men may be able to father a child their entire life
HEALTH
consider both parents
both must be healthy
physical + mental health
drugs/alcohol harms mom/child
LIFE EXPERIENCE
how you were raised can affect how you raise your children
happy: raise child same way you were raised
sad: difficulty parenting bcus no role models growing up
experience with children: babysitting, siblings/neice’s/nephews
TYPES OF PARENTHOOD
Biological parenthood
2 parents living with their biological children
TYPES OF PARENTHOOD
Adoptive parenthood
process of taking a child legally and raising it as their own
TYPES OF PARENTHOOD
Reasons for adopting
couple has physical conditions
wants to adopt a child who needs a home
couple has disease that may be inherited by the child
TYPES OF PARENTHOOD
Foster parenthood
Parents who provide home to children in need of care
They are paid
In MB- they fall under a government agency “Child family services”
Lasts until child turns 18 yrs or if child is adopted
TYPES OF PARENTHOOD
Parenthood by marriage
occurs when someone without children marries someone with children
may choose to legally adopt the child
blended family- consists of 2 adults and children from previous marriages
TYPES OF PARENTHOOD
Single parenthood
usually from divorce or death of spouse
woman chooses to raise child by herself
around 26% of single parent families
TYPES OF PARENTHOOD
Teenage parenthood
raise child on own: single parent family
raise child with partner: nuclear family
raise child with fam support: extended family- several generations in same household
TEEN PREGNANCY AND PARENTING REALITIES
Sources of help
friends
father of child
family
social services (doctor, cfs)
TEEN PREGNANCY AND PARENTING REALITIES
Alternative choices
raise child herself
raise with parents
Adoption or abortion
TEEN PREGNANCY AND PARENTING REALITIES
Consequences
drop out of school
loss of freedom
need income
change in social life
Adoption
in MB- occur under legislation of The adoption act and The child family services act
Protects the child and birth/adoptive parents
Steps in adopting a child
1-9
Interview and application appointment
Education seminar
Adoption file development
Homestudy
Approval
Matching process
Matched
Placement
Finalization
Interview and application appointment
process and procedures are explained
Takes two hours
Education seminar
Presentations from birth/adoptive parents/lawyers
Get legal documents
Adoption file development
Complete legal documents to create adoption file
File may include letters and photos about adoptive parents
Home study
Involves at least 4 interviews
To decide if you are responsible and capable to become a parent
Provide medical reports, criminal checks, etc.
Approval
If adoptive parents meet requirements, they are approved for placement
File can be shown to birth parents
Matching process
Birth mother sees options, is shown the adoption file and chooses family
Being chosen to adopt could take weeks, years or not happen at all
Matched
adoptive parents are given information about the birth mother
Adoption agency arranges a meeting between the birth mother and adoptive parents
If they all agreed to proceed with the adoption, legal documents are signed about the intent to place the child
Placement
Birth mother must wait 48 hours after birth to sign her consent for adoption
Birth parents have 21 days to revoke consent
Lawyer files court documents after 21 days
Finalization
After placement, birth parents receive support and adoptive family is super supervised until the adoption is final.
TEENAGE FATHERS: THE MISSING FATHER MYTH
forgotten partners, irresponsible
Eager to help their partner and child
Anxious to participate in parenting of their children
Lower incomes, less education
Bewildered
Little idea of what a father is supposed to do
Drop out of school
Those who had dropped out of school had resumed their education
Degrassi Junior High