Rational Producer Behaviour
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Maximising Behaviour
Where firms all behave as rationally as possible and maximise profits
Economic Costs
Explicit + Implicit Costs
Explicit Costs
Costs that arise from firms purchasing FOPs
Implicit Costs
Opportunity costs that arise from using FOPs in a certain way
Theoretical revenue theory
Perfectly elastic demand (perfect competition)
So firms do not have to lower prices to attract more customers
Realistic revenue theory
In reality firms must lower prices to attract more customers
Depends on PED though
PED varies along the curve so at first it is elastic and firms will decrease the price
Eventually though the extra revenue gained from the increase in demand is outweighed by the revenue sacrificed from the units that were being sold at higher prices.
Normal Profit
TR = TC
Abnormal Profit
TR > TC
Losses
TC > TR
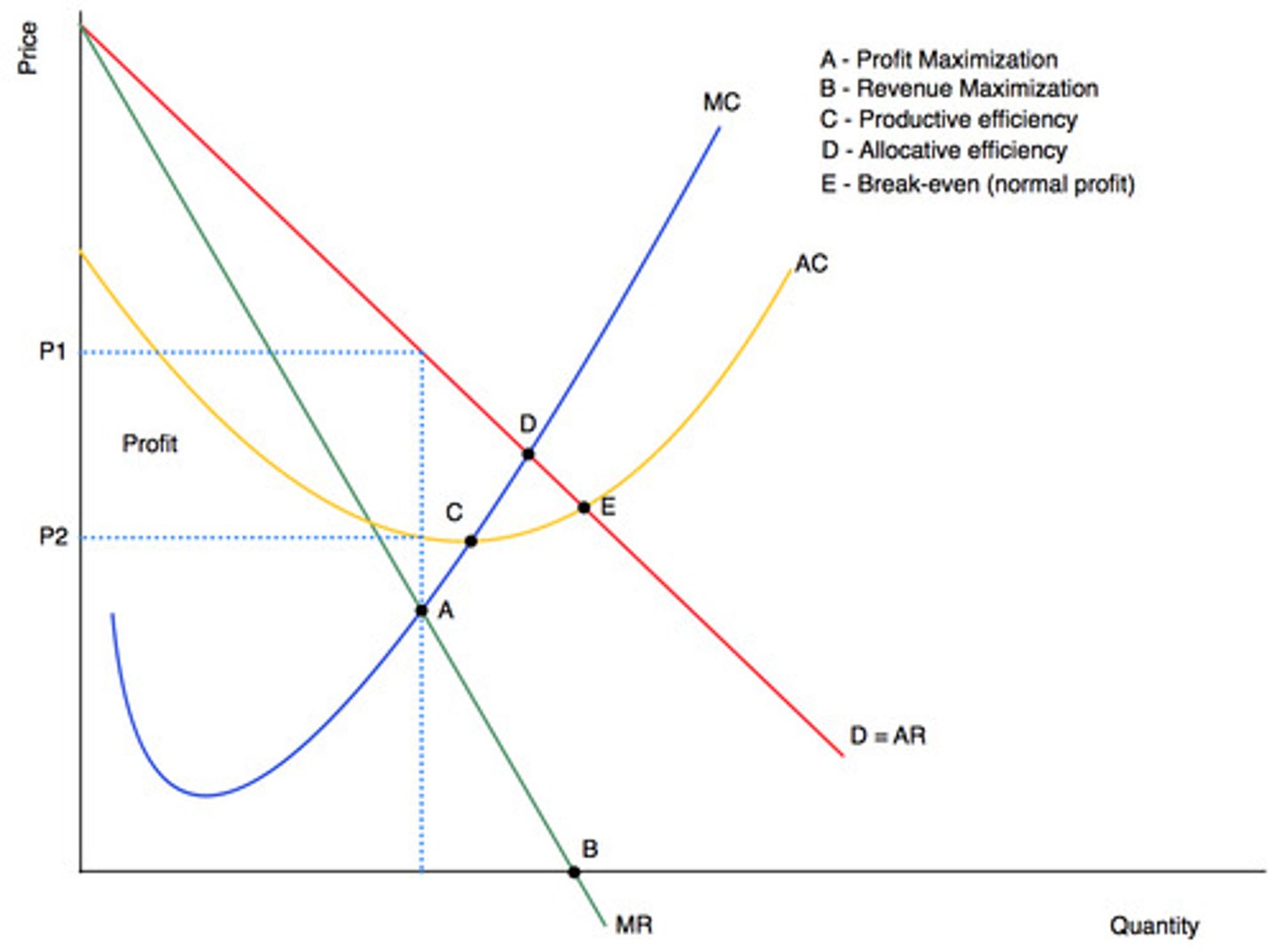
Point of profit maximisation
MC = MR
Point of allocative Efficiency
MC = AR
Point of productive efficiency
MC = AC
Other goals of a firm
Corporate Social Responsibility
Satisficing
Growth Maximization
Revenue Maximization
Market Structure
Identifies how a market is made up in terms of:
Number and size of firms
Control over price and output
Barriers to enter and exit
Nature of product (Degree of homogeneity)
Characteristics of Perfect Competition
Large number of firms
Products are homogeneous
No barrier to enter or exit
Firms are price takers
Each producer has very little market share
Perfect information
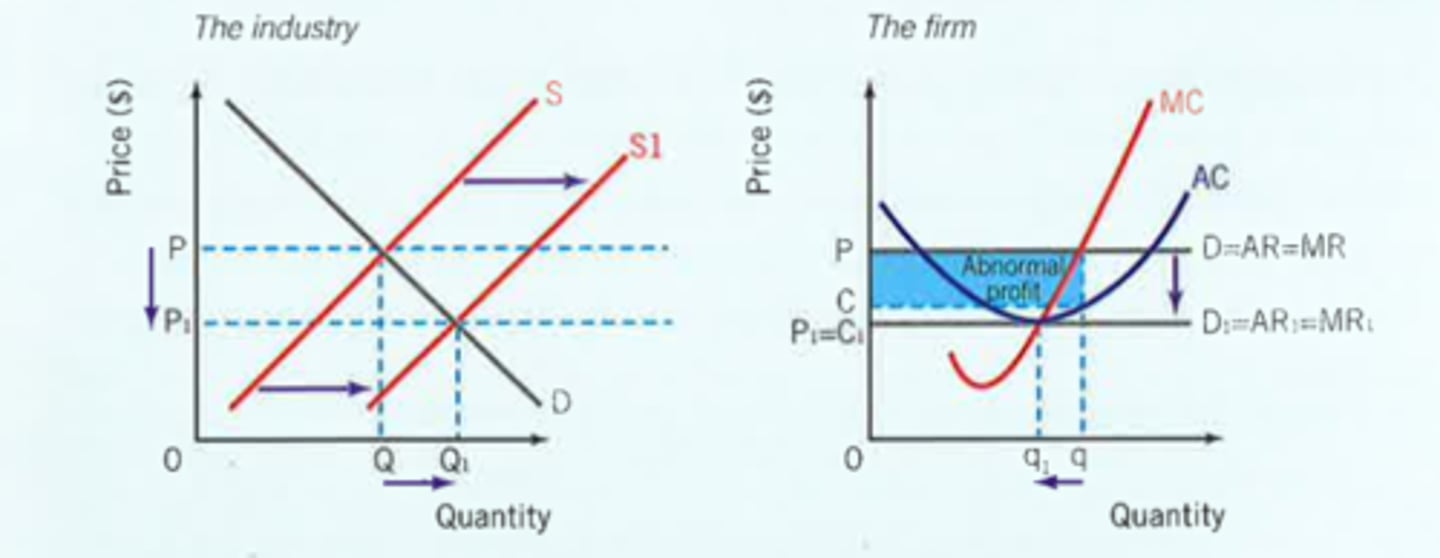
Perfect Competition (Short run abnormal Profits to Long run normal profits)
Abnormal profits made in short run
No barriers to entry and perfect knowledge causes supply to shift right causing market price to decrease
Demand then decreases for all firms and AR will decrease. This will continue until all firms are producing normal profit.
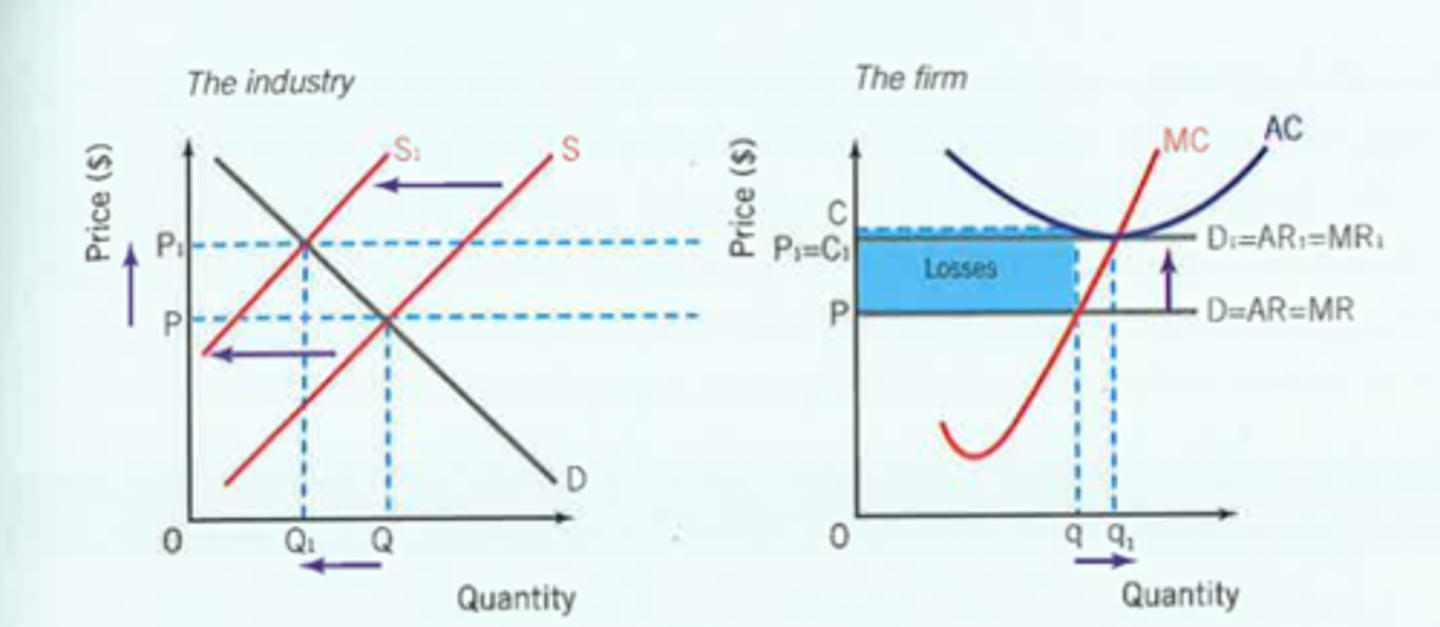
Perfect Competition (Short run losses to Long run normal profits)
Losses are made in the short run
No barriers to exit and perfect knowledge causes supply to shift left causing market price to increase
Demand then increases for all firms and AR will increase. This will continue until all firms are producing normal profit.
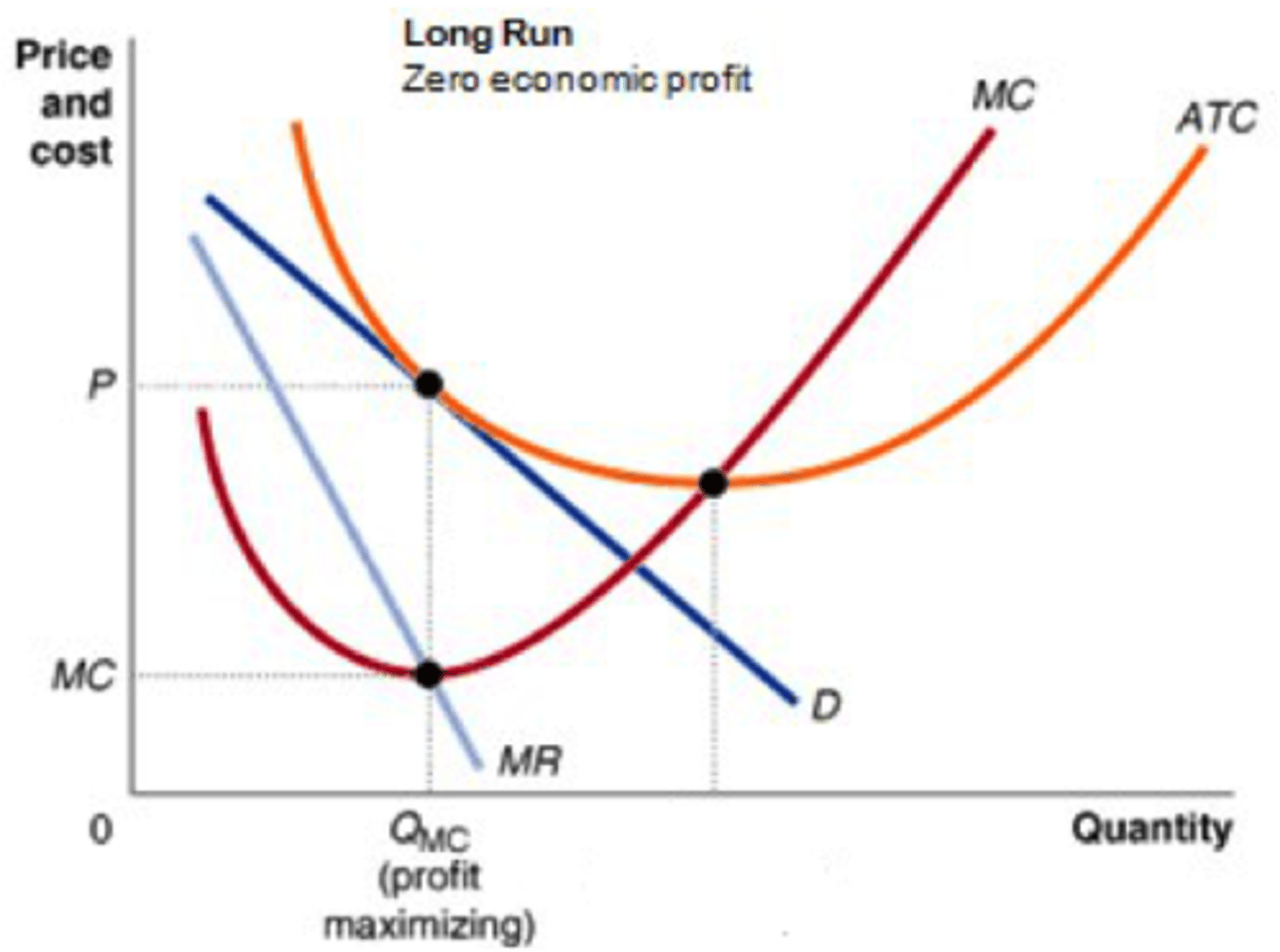
Efficiency in perfect competition
SR: MC = MR, MC = AR
LR: MC = MR, MC = AR, MC = AC
Advantages of Perfect Competition
Allocative Efficiency
Productive Efficiency
Low prices for consumers
Competition leads to shutting down of inefficient producers
Lack of market power leads to no market failure
Disadvantages of Perfect Competition
Unrealistic assumptions
Limited possibilities to gain economies of scale due to long run normal profits
Lack of product variety
Limited ability to engage in RnD
Characteristics of Monopolistic Competition
Large number of firms
Low barriers to entry or exit
Product differentiation
Firms still have low market share
Firms are price makers
Monopolistic Competition (Short-run abnormal profits to Long Run Normal profits)
Firms are attracted to the abnormal profits and enter the market
Demand is now competed away from existing firms causing demand curve to shift left.
Demand shifts until firms are making normal profits

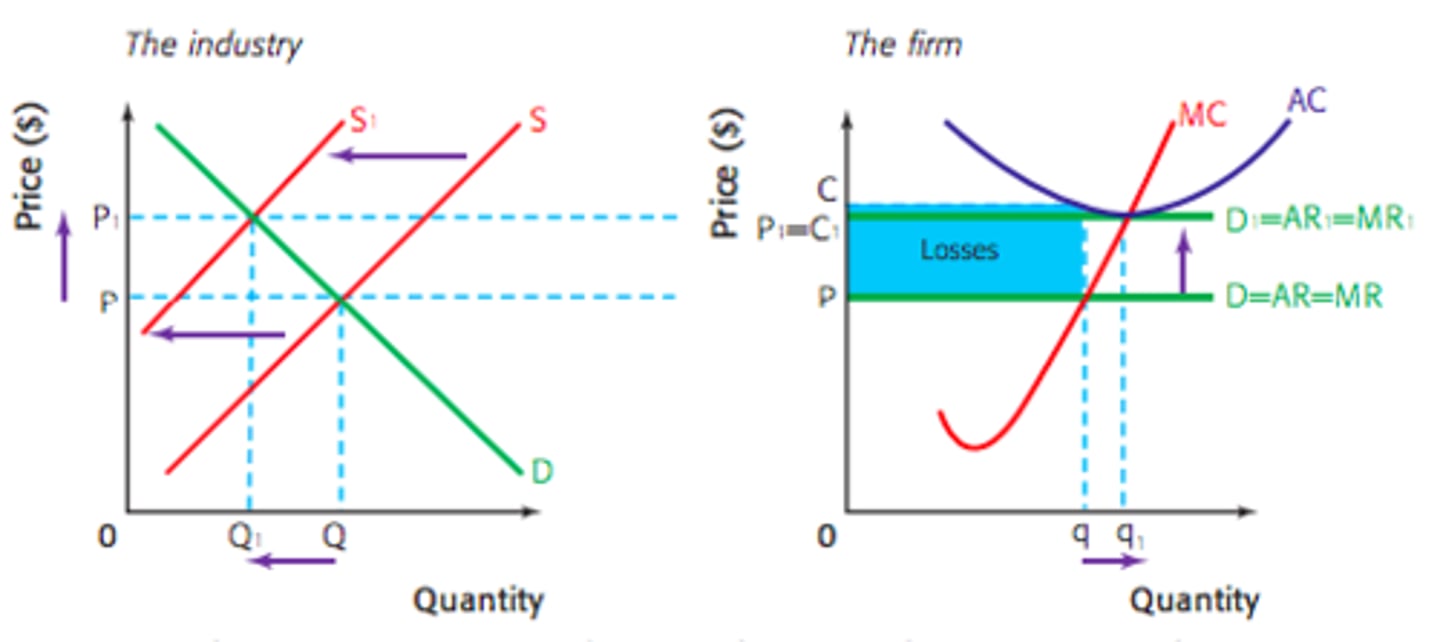
Monopolistic Competition (Short-Run losses to long run normal profits)
If losses are being made, firms will start to leave
Remaining firms see an increase in demand
Demand curve shifts right until firms are making normal profits
Firms compete through non-price competition e.g product differentiation
Efficiencies in Monopolistic Competition
SR: MC = MR
LR: MC = MR
Little bit of market fialure as firms are not allocatively efficient
This is because of the consumers desire for variety which makes them better off
Government will choose not to intervene however as firms do not dominate the market
Monopolist
Industry that consists of a firm that dominates the market with a very large market share
Natural Monopolies
A firm that has economies of scale so large that it is possible for the single firm alone to supply the entire market at a lower average cost
Characteristics of a Monopoly
Only one firm produces the product so the firm is the industry
High barriers to entry
Could earn abnormal profits in the long run
Reasons monopolies have so much power
Economies of Scale
Legal Barriers
Brand Loyalty
Anti-competitive Behaviour
Economies of Scale
Increasing output leads to lower long run average costs
Types of Economies of Scale
Specialisation
Bulk Buying (Transport too)
Financial Economies
Large Machines
Promotional Economies
Natural Monopoly Graph
A natural monopoly occurs when there are only enough economies of scale to support one company
The firm is the industry so there is only one graph.
If another firm enters the market the demand of the original firm is competed
Monopolist Graph
Monopolist demand curve tends to have very low elasticity as there are very few (or no) substitutes
Firm will produce at MC = MR
They earn abnormal profits
If firms enter monopolies can employ predatory pricing
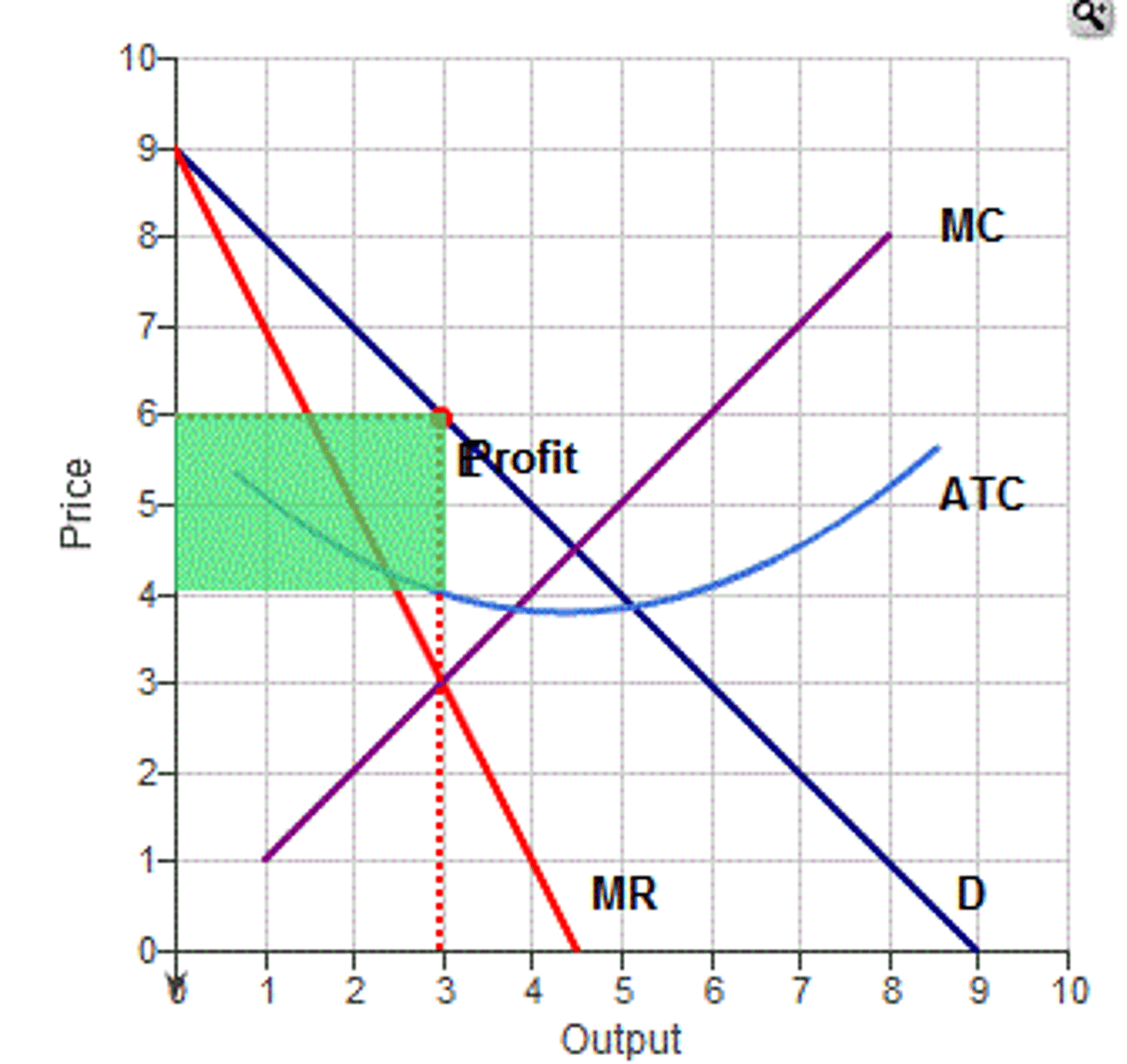
Advantages of a monopoly in comparison to perfect competition
Marginal Cost of the monopoly will be lower than the marginal cost of a firm in competition as they can achieve economies of scale
P.C produces at MC = AR but Monopoly produces at MC = MR
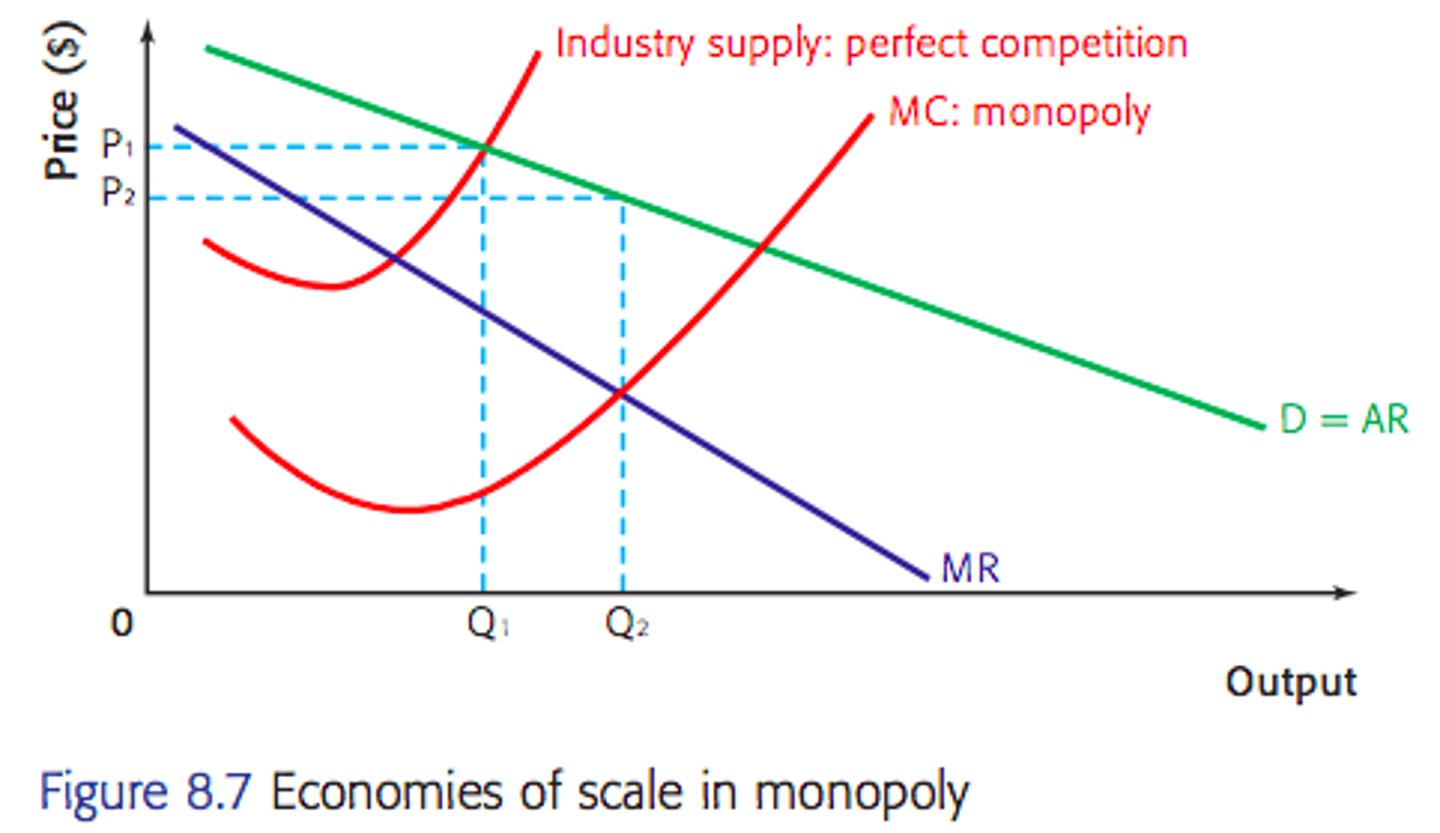
Disadvantages of a monopoly in comparison to perfect competition
Monopolies don't take advatnage of E.O.S
P.C produces at MC = AR but Monopoly produces at MC = MR
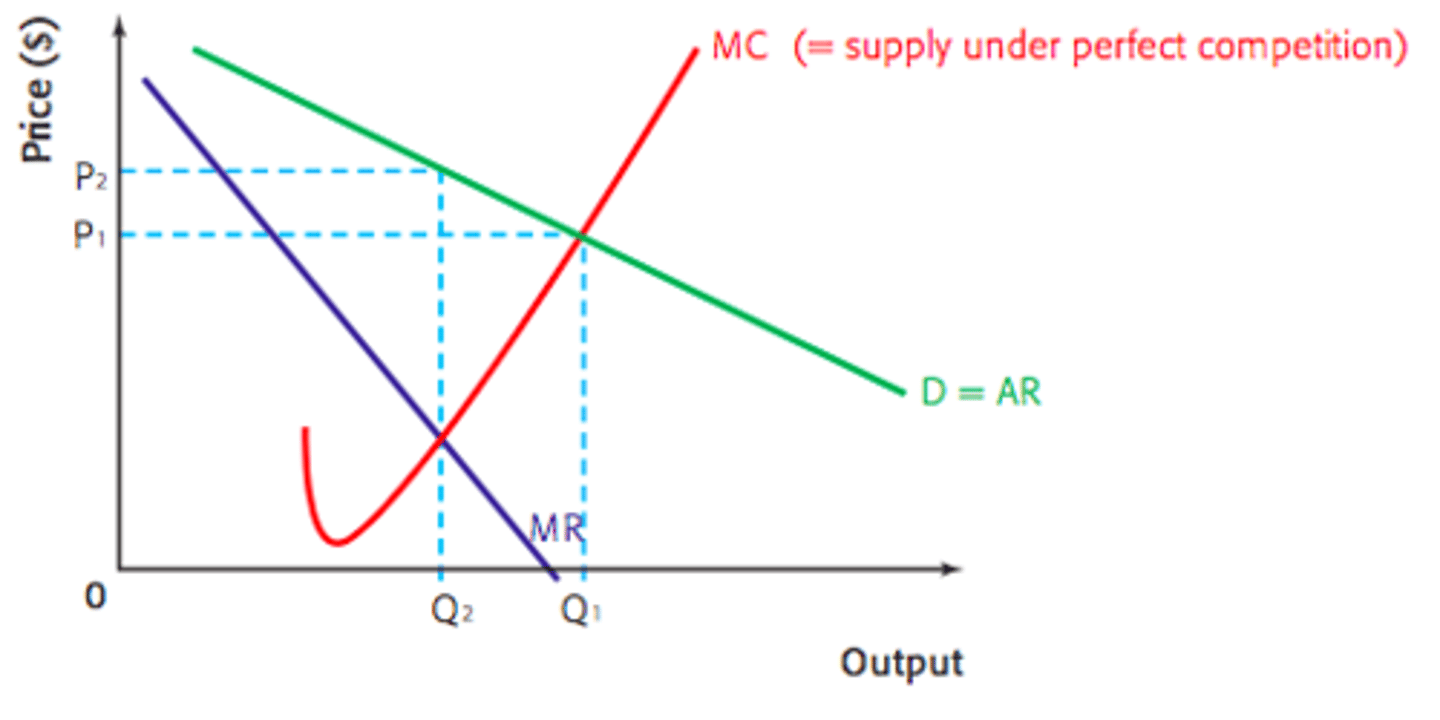
Regulating natural monopolies through marginal cost pricing
Brings market to allocative efficiency and solves market failure
Government must pay for the firms fixed costs as they only generate enough revenue for their variable costs
Regulating natural monopolies through average cost pricing
Improves market failure but doesn't solve
Oligopoly
A market dominated by a few producers, each of which has control over the market
High Market Concentration
Concentration ratio
The extent to which a market or industry is dominated by a few leading firms
Characteristics of an Oligopoly
No single theory of how firms determine price and output
Product Branding
Significant Barriers of entry
Interdependent Decision Making
Non-Price Competition
Mutually Interdependent
Price competition makes them worse off
Collusive Oligopoly
When firms in the market collude to fix prices and act like a monopoly
Also known as formal collusion or cartel
Governments often ban this type of behavior
Informal Collusive Oligopoly (Tacit Collusion)
Price leadership is when one firm has a clear dominant position in the market
Firms will often follow their pricing strategies which can influence the market
Non-Collusive Oligopoly
When they do not collude in any way and each firm behaves independently
However, they do try and predict what the other firms will do.
This causes prices to be rigid as it will make them worse off
Advantages of Oligopolies
Economies of scale can be achieved
Product innovation can be pursued due to high abnormal profits
Technological innovations can occur
Production innovation results in higher choice
Disadvantages of Oligopolies
Welfare loss, allocative inefficiency and market failure
Higher prices and low quantities of output compared to perfect competition and monopolistic
Loss of consumer surplus
Higher production costs
Possibly less innovation
Difficult to determine if firms are colluding
Importance of non-price competition for Oligopolies
Better quality of service
Longer opening hours
Extended warranties
Discounts on product upgrades
Contractual relationships with suppliers