Enzymes: Classification of Enzymes
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
oxidoreductase
transfer elctrons or H atoms
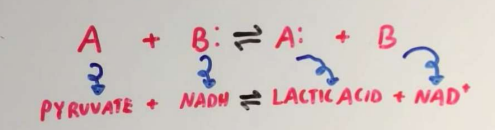
xanthine oxidase
an oxidoreductase that Converts hypoxanthine → xanthine → uric acid.
xanthine oxidase hyperactivity
________________ → hyperuricemia & gout
allopurinol
competitive inhibitor of xanthine oxidase
Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH)
an oxidoreduc tase that Converts lactate to pyruvate.
Marker: ↑ in hemolysis, MI, liver disease, some cancers.
Cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYPs)
an oxidoreductase that Metabolize drugs in liver
Variability in CYP activity affects drug dosing, toxicity, resistance.
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD)
an oxidoreductase that Produces NADPH in RBCs.
Deficiency → hemolytic anemia when exposed to oxidative stress (e.g., fava beans, sulfa drugs).
xanthine oxidase
lactate dehydrogenase
cytochrome P450 enzymes (CPYs)
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD)
Examples of oxidoreductases
transferase
transfer groups to other m molecules
AST & ALT
transferase:
Markers: ↑ in hepatitis, liver injury, MI (AST also in heart).
GGT
transferase:
Marker: ↑ in alcoholic liver disease, cholestasis.
CK & CK-MB
transferase:
Marker: ↑ in myocardial infarction, muscular dystrophies
AST
ALT
GGT
CK & CK-MB
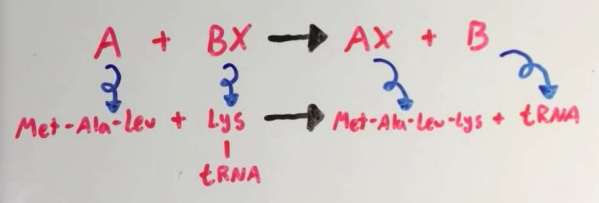
peptidyl transferase
examples of transferases
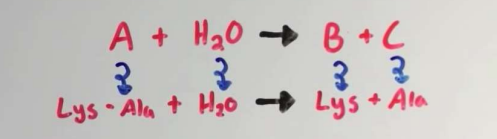
hydrolase
breaks molecules apart with water (hydrolysis reaction)
Amylase & Lipase
hydrolase:
Digest starches and lipids
Markers: ↑ in acute pancreatitis
acetylcholinesterase
hydrolase:
Breaks down acetylcholine → choline + acetic acid in synapses.
ensures stimuli are brief and controlled
organophosphates
acetylcholinesterase is inhibited by ______________ → cholinergic crisis
myasthenia gravis
Drugs inhibit acetylcholinestarease to treat ______________
cholinergic crisis
caused by an excess of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) at nerve and muscle junctions, leading to overstimulation of cholinergic receptors
due to inhibition of acetylcholinesterase
life threatening
Acid phosphatase (ACP)
hydrolase:
Marker: ↑ in prostate carcinoma (historical use), bone diseases.
amylase
lipase
acetylcholinesterase
acid phosphatase (ACP)
examples of hydrolases
lyase
addition, transfer, or removal of groups to double bonds
non-hydrolytic transfer of groups

pyruvate decarboxylase
lyase:
Involved in metabolism (lab teaching).
histidine ammonia-lyase
Disease link: Deficiency → histidinemia, a rare inherited metabolic disorder
arginosuccinate lyase
pyruvate decarboxylase
histidine ammonia-lyase
examples of lyase
isomerase
transfer of functional group/s within molecules
change sthe structure/ isomeric form

Phosphoglucose isomerase (PGI)
isomerase:
Glycolysis (glucose-6- phosphate fructose-6-phosphate).
Clinical note: Deficiency → nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia.
Triosephosphate Isomerase (TPI)
isomerase:
Clinical note: Rare * deficiency → progressive neuromuscular disorder.
phosphoglucose isomerase (PGI)
triosephosphate isomerase (TPI)
examples of isomerase
ligase
combines/ysnthesizes molecules through condensation reactions
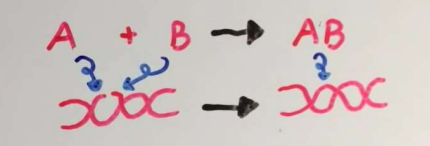
DNA ligase
ligase:
repairs DNA strand break
immunodeficiency & cancer
defects in DNA ligase → predisposition to ______________ and __________
glutamine synthetase
ligase:
glutamate + ammonia + ATP → glutamine
nitrogen assimilation and ammonia detoxification in brain
hepatic encephalopathy
dysregulation of Glutamate synthetase is linked to ______________
leads to brain dysfunction due to liver dysfunction
subtle cognitive changes to severe confusion, personality alterations, disorientation, lethargy, and coma.
DNA ligase
Glutamine synthetase
examples of ligases
oxidoreductases
transferases
hydrolases
lyases
isomerases
ligases (synthetases)
List the 6 classifications of enzymes in chronological (IUPAC)