periodic trends: atomic radius
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
atomic radius
*The Atomic Radius of an element is an estimate of the size of an atom is nucleus to its outer shell:
Atomic radius is usually measured in angstroms (A), An angstroms 1x10-10m
trends of atomic radius
Atomic radius gets smaller as you move left to right on an the periodic table
why does the atomic radius get smaller as u move left to right on periodic table
The number of protons and electrons increases
The number of attractions between opposite charges increases → The last shell is pulled closer to the nucleus (Shrinking effect)
-Atomic radius gets larger as you go from top to bottom on the periodic table
Li< Na<K
why ?
The number of shells increase (distance from nucleus to last she’ll)
1 The attraction force exerted by the nucleus decrease)
electrons inner Shells repel each other (shielding effect)
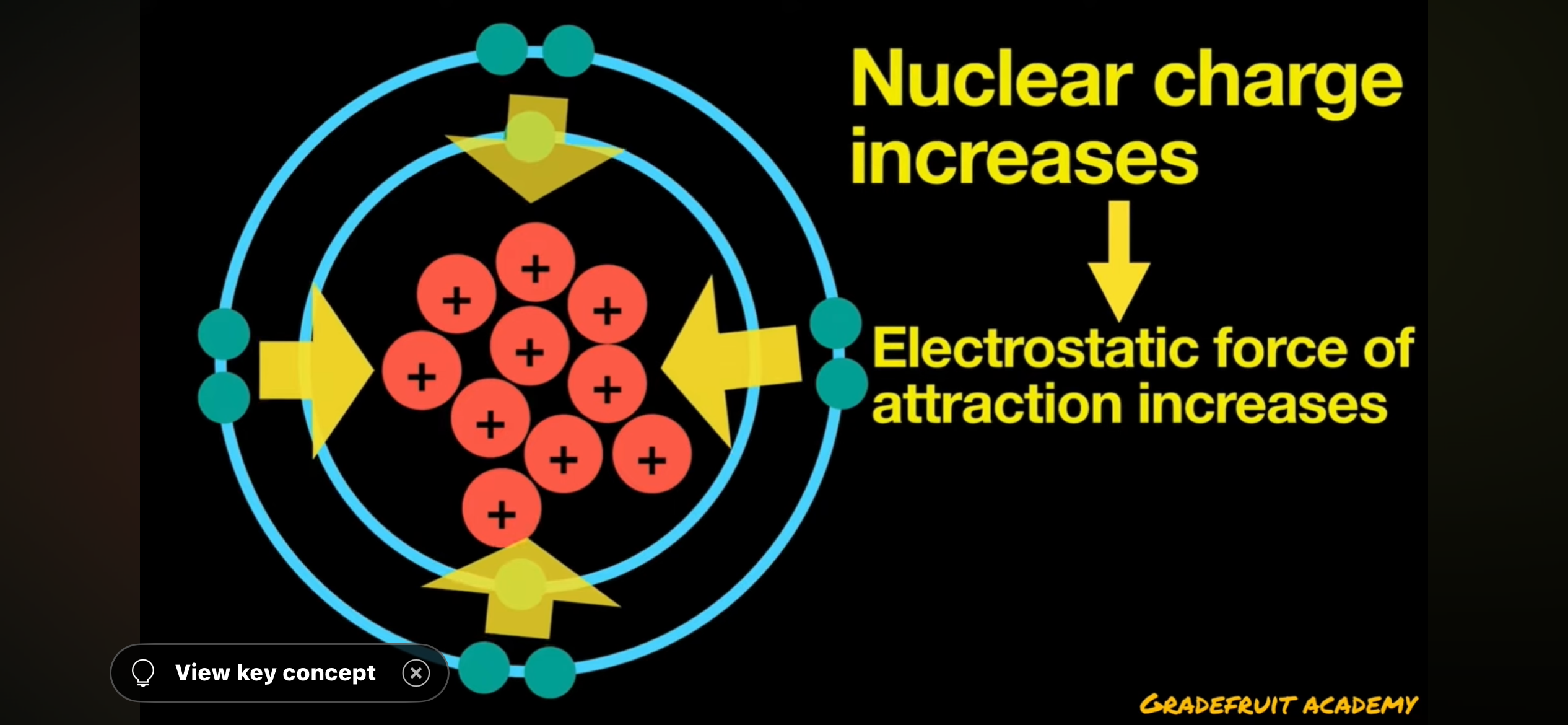
nuclear charge
positive charge of the nucleus
strength of nuclear charge depends on __
number of protons
what happens when number of protons increase
nuclear charge increases
what happens when nuclear charge increases
electrostatic force of attraction also increases which makes atomic radius smaller
what causes atomic radius to get bigger
shipping effect because electrons in inner shell repel electrons in outer shell which prevents electrons in outer shell from fully experiencing the nuclear charge
effective nuclear charge
the net positive pull that an electron actually feels from the nucleus after you subtract the “shielding” effect of the other electrons
effective nuclear charge formula
nuclear charge - shielding effect
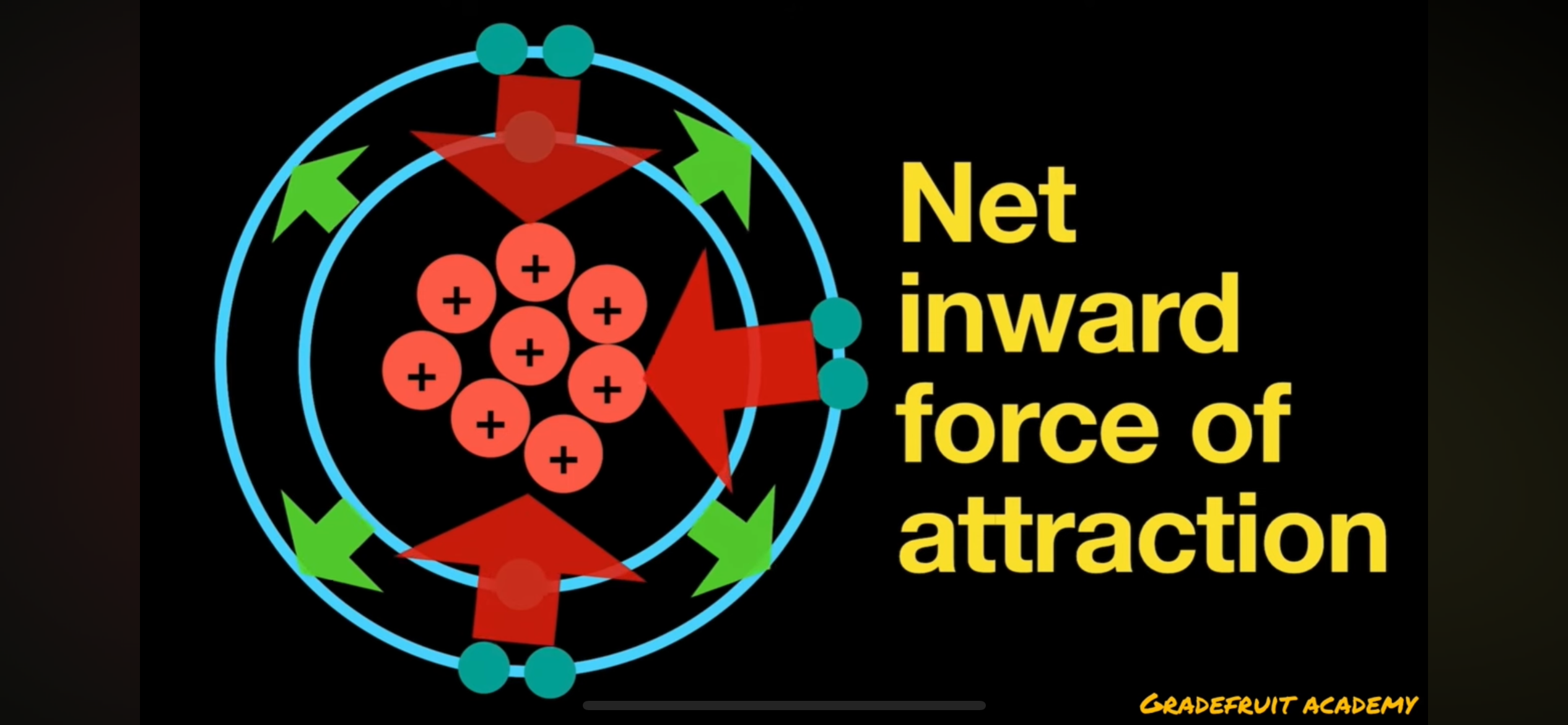
what happens if nuclear charge is greater than shielding effect
effective nuclear charge increases and there will be a net inward force of attraction between nucleus and valence electrons as it is stronger than the shielding effect between the electron shells
Which has a larger radius: a neutral atom or its cation/anion? Explain.
Neutral atom > cation radius (cation loses shell, stronger pull). Anion > neutral atom (extra electron repulsion expands shell)
Explain why atomic radius increases down a group (top → bottom).
Increases top → bottom down a group (more shells = bigger atom).