Topic 12 - Executive Functions
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
given by Lily
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Why do we play?
happens in animals across the kingdom like crows and ravens, lizards, bees, etc
most times doesn’t lead to better hunting, improve reproduction, or social bonding so why? → gives change to stimulate loss of control and unpredictable circumstances in a safe and rewarding way
the extended juvenile period in animals that do play behaviour means they can practice how to react to unexpected things in development of executive functioning
also beneficial for practicing emotional regulation
Characteristics of Play
distinguished from functional behaviours
voluntary
modified relative to functional contexts
repeatedly performed, but not invariantly
evident in healthy unstressed animals
Dysexecutive Syndrome
people with frontal damage have bad judgement and decision making, are impulsive and make risky decisions, often abuse drugs and alcohol, behave in socially inappropriate ways
Executive Functions
frontal cortex is separated into primary motor, premotor, and prefrontal regions
PFC is a part of the brain divided into subregions
major regions are dorsolateral region, rostral or fronto-polar, ventrolateral, and medial region
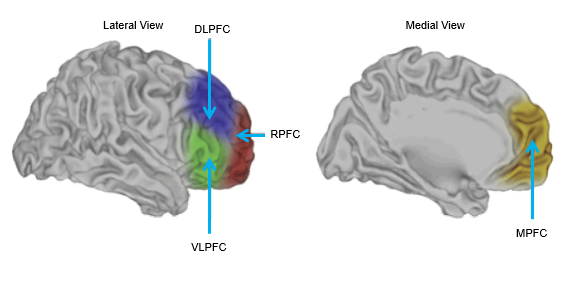
What’s special about the prefrontal cortex?
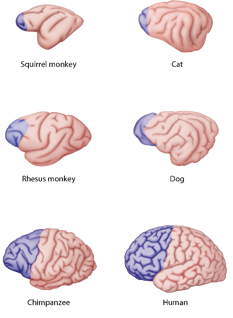
develops last in the brain
is disproportionately large compared to other animals
ratio of frontal to rest of neocortex
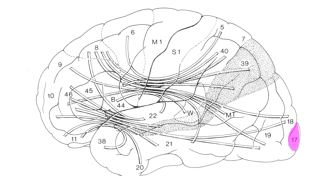
widespread connectivity (cortico-cortical and cortico-subcortical) through direct and rapid communication via long-range white matter tracts
connections multimodal association cortices, especially those temporal and parietal regions
high-level integration of behaviour
Consciousness and the Frontal Lobes
visual awareness may depend on 1 to 1 direct connections to frontal cortex
not aware of what goes on in V1 (not conscious of what is being processed in this region)
Executive Functions
there is little that is exactly defined, they’re more of a cloud of our most complex behaviours
abstract reasoning
decision making
impulse control
planning
multi-tasking
cognitive flexibility
error correction, etc
Four Domains of Executive Functions
inhibitory control
set-shifting aka task switching
working memory updating
planning
unity (higher order) and diversity (subcategories) model - breaking down higher order functions into diverse categories that connect exetensively
Convergent vs. Divergent Thinking
convergent: you either know the answer or you don’t so you converge on one answer, usually what IQ tests ask you
divergent: processes that one might use to solve tasks where you don’t know the one single answer, kind of like thinking outside the box
Stroop Task
measures how well you can inhibit their prepotent responses
say the colour not read the word that is written, reaction time and accuracy is recorded and compared against norms
Luria’s Test
examiner and patient face each other and place both hands palm down on the table
examiner taps once and asks patient to copy, then examiner tests inhibitory functioning by saying “if i tap once you tap twice, and if i tap twice, you tap once”
frontal patient won’t be able to inhibit the reflexive action of copying
another test is fist, edge, palm: patient is asked to make a fist, turn hand so it rests on side, turn palm back down to table
examiner measures number of correct sequences
more repetitions = more difficult to do for frontal patients especially over time
Verbal Fluency
inertia - slow to start, slow to continue
preservation - getting stuck on a word and repeating it
rule breaking - not doing what the task asked
poor strategy use - our words tend to be grouped by semantic meaning, or clustered phonetically, etc

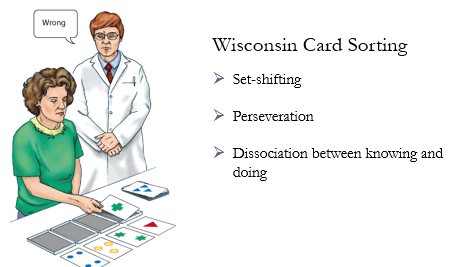
Wisconsin Card Sorting
testing set-shifting (mental flexibility)
patient is given 4 example cards that differ in some ways and have to sort a deck as indicated by the example
patient is not told how to sort, only feedback on whether the card placed is correct or incorrect
after doing 10 cards right, experimenter silently switches the rule and says whether patient is right or wrong
very irritating and common for patients to abandon the test out of frustration, but also indicated inability to self-regulate behaviour and emotional responses appropriately
we can measure what errors they made like preservation and can even tell you what the category is and continue to sort it wrong → dissociation between learning and doing
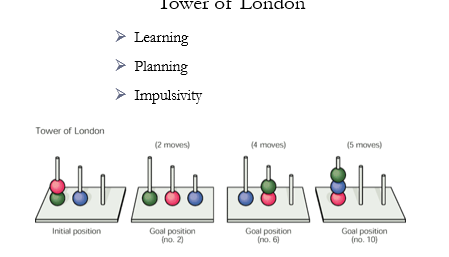
Tower of London
measures planning, learning, and impulsivity
given a starting position of coloured balls on pegs, a goal, and number of moves to get there
goals start simple and get harder
frontal patients find it hard to plan and will be impulsive, and when given the chance to correct to see if they learn from mistakes you see preservative errors
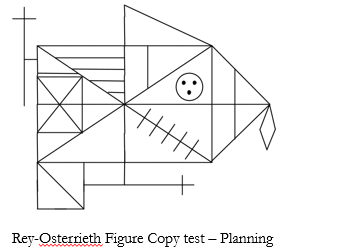
Complex Copying Task
measures planning and organizational strategies
frontal patients don’t do planning and strategy and go right into doing what they want to do, copy isn’t terrible but there is lack of forethought to what they were doing
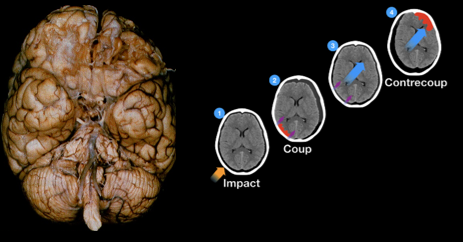
Traumatic Brain Injury
usually from acceleration-deceleration
two mechanisms of injury:
impact itself makes makes coup then force of impact causes brain to shift and hit opposite of impact point, the countercoup
brain shifting by velocity of the impact makes axons tear - diffuse axonal shearing throughout the brain, not just at impact sites
orbitofrontal cortex is prone to injury, since bony protrusions tear tissue when brain jostles
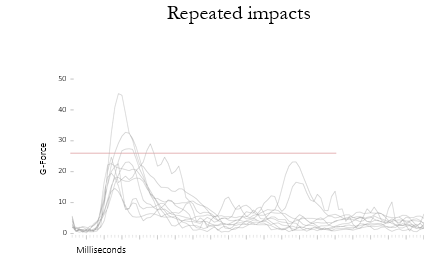
Repeated Impacts
impact is really harmful and consequences can cause brain fog, tension headaches, dizziness, memory trouble, and frontal damage effects as previously discussed
Impulsivity and Disinhibition
little forethought, leaping before looking, lack of planning
inappropriate social behaviours
short fuse
hyper or hypo sexual arousal
increased reckless behaviour
increased drug use
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy
repeated exposure to TBIs causes this neurodegenerative condition
tissue loss leads to enlarged ventricle space and sulcal widening, as well as trademark issues with frontal damage (poor ability to sustain attention, impulsive and aggressive behaviour, increased risk of depression and suicidal ideation)
Utilization Behaviour
aka environmental dependency syndrome bby L’Hermitte
patients feel compelled to use objects placed in front of them for what they’re designed for inappropriate situations
sat in front of patient with objects on the table and not say anything, but patients may have just assumed the item being there means they had to do something with it
some behaviours were bizarre and not explained by effects of expectation alone
some behaviours were imitative to what L’Hermitte did
intentional and meaningful interaction with object based on its function and many cases were guided by who the patient was (context dependent)
smokers would light cigarette, nonsmokers offered one to L’Hermitte
nurse with injection
Mirror Neurons
originally discovered in monkeys by Rizzolatti and his group
are neurons that fire when monkey physically does something while observing someone else do the same action, initially seen in premotor cortex or monkey but has been found beyond in humans
activity starts with simple imitation like making faces at a baby that it copies so mirror neuron system helps us learn motor behaviours
mix of people trained in ballet and Capoeira and monitored brain activity and found that when dancers watched videos of dance they were trained in, dorsal premotor region activity was highest so they are mentally mimicking what they are seeing
theory of mind: understanding that others have mental states like intentions and beliefs that autistic patients find hard
Working Memory
relies on dorsolateral prefrontal cortex function to hold and manipulate information; is goal-driven
Association of Exposure to Television Violence on Executive Functioning and White Matter Volume
evidence supporting idea that violence on TV makes you more violent is thin and not well-established empirically, or if those who have a tendency to violent behaviour prefer violent TV
violent TV in childhood seems to predict adult aggression maybe from imitation (mirror neurons)
developing belief systems (violence is more reasonable if exposed at developing age)
desensitization (get used to it over time)
poor cognitive control and inhibition - aggression in adulthood from poorer cognitive control and inhibiting emotional responses
study had 65 men in minimal game players refrain from gaming during the week where they recorded past watching habits and current watching habits for the week, as well as MRIs of the brain
executive functioning was tested by participants completing tasks like stroop, counting interference, go and no-go,
found that 2 components related to media viewing: violent TV exposure scores negatively correlated with factor of attention-inhibition → the more violent TV they were exposed to the lower their capacity for attention and inhibitions, same as video games
white matter volume has negative corr with violent TV in the right hemisphere superior longitudinal fasciculcus