chem - gravimetric analysis
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
what does gravimetric analysis do?
gravimetric analysis uses the mass of solids to determine the concentration of a species in a commercial product or water sample
precipitation reactions are used to remove the desired ions from sample
concentration is presented as a percentage by weight or in mgL^-1 (ppm)
choice of precipitate + requirements
a suitable precipitate must be formed to analyse a particular ion in the sample
the precipitate must:
have a known formula - desired ion
have low solubility - should not dissolve
be stable when heated (so it can be dried)
not form precipitates with other ions which could be present
precipitates formed for gravimetric analysis table
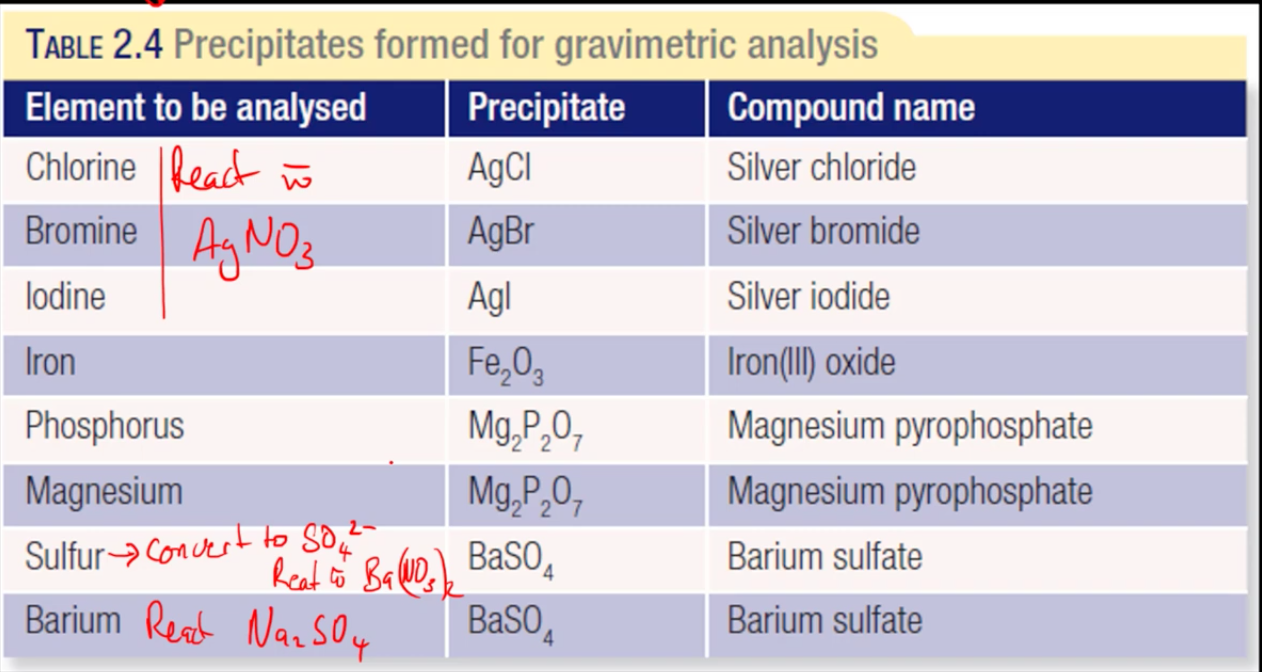
SNAPE
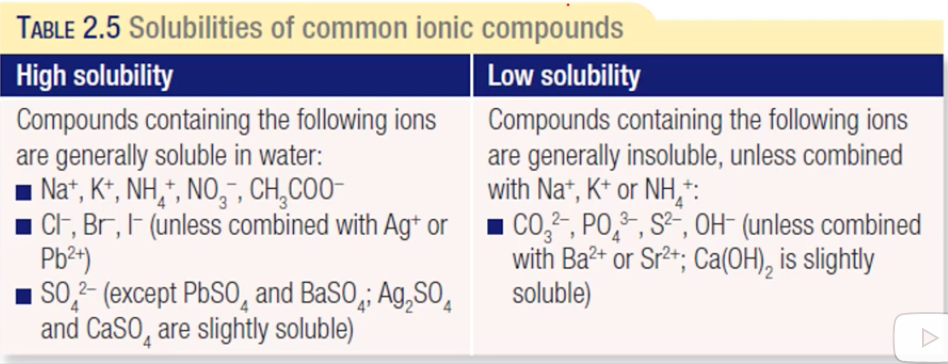
all nitrates, ammonium compounds, ethanoates and compounds of group 1 metals are soluble
solubilities of common ionic compounds
steps for typical gravimetric analysis (solid samples or solution samples)
for solid samples:
start with solid sample to be analysed - e.g. fertiliser, there identify lots of different ions within it
grind sample to a powder - increase SA, easy to dissolve
accurately weight mass of sample (this is used later to calculate the concentration of analyte), analyte = substance you are analysing for
add a solvent to dissolve the ion under analysis
for solution samples or continue through for solid samples:
filter solution to remove insoluble substances - don’t want to add to the final mass by leaving insoluble substances in there
discard insoluble residue
keep filtrate - solution which has been filtered
add a substance to filtrate which will form a precipitate with the analyte
filter under vacuum to remove as much solvent as possible (can also rinse with distilled water)
precipitate can be washed at this time to remove all soluble ions
dry precipitate in oven (100-110 degrees celsius) - remove all water
ensure the precipitate does not melt below this temperature
drying should be completed to a constant mass - e.g. you dry it for a few days and measure it at each day, and when the mass of ppt. becomes constant over a few days you know all the water has evaporated
weigh precipitate and record mass
use stoichiometry to determine mass of ion in precipitate
calculating the concentration of an analyte
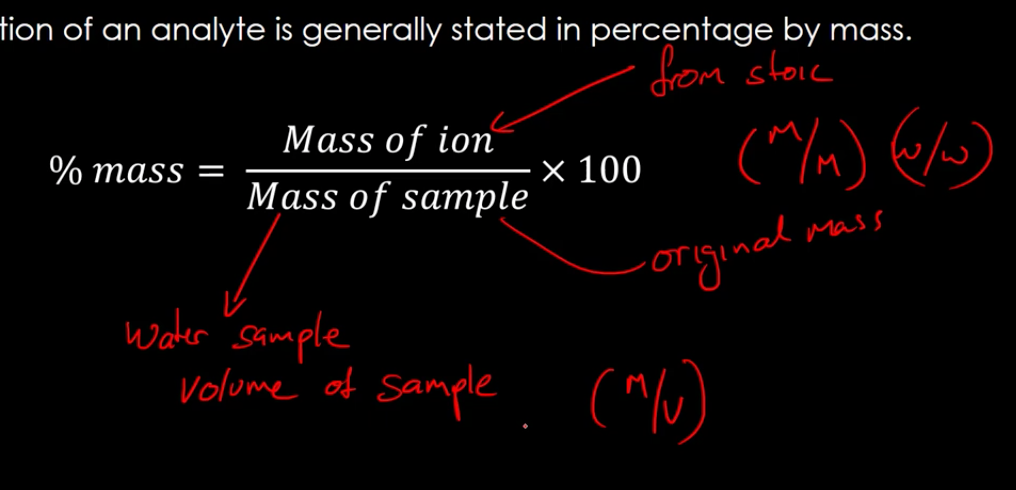
the conc. of an analyte is generally stated in percentage by mass
illustrated steps of gravimetric analysis
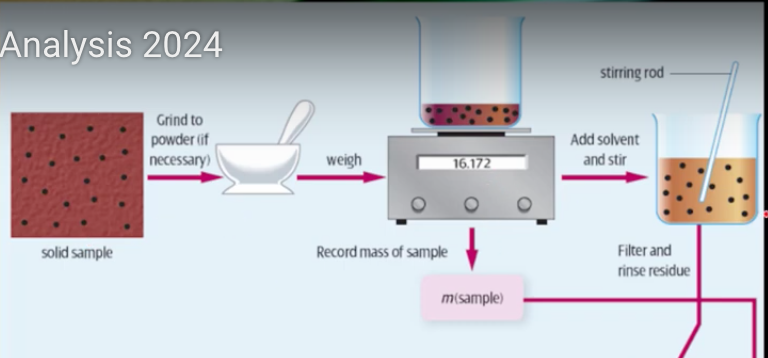
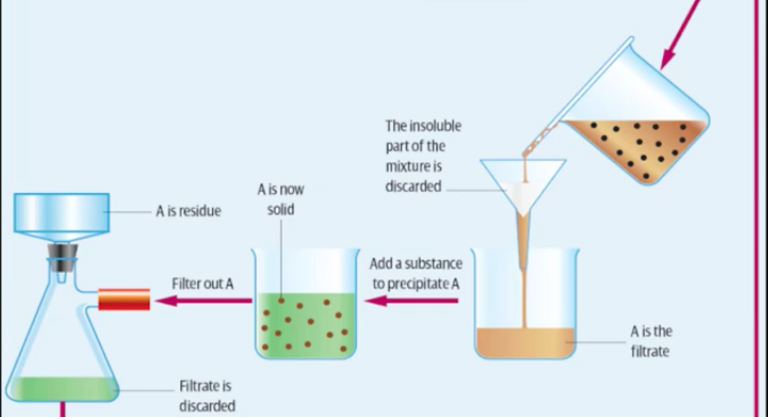
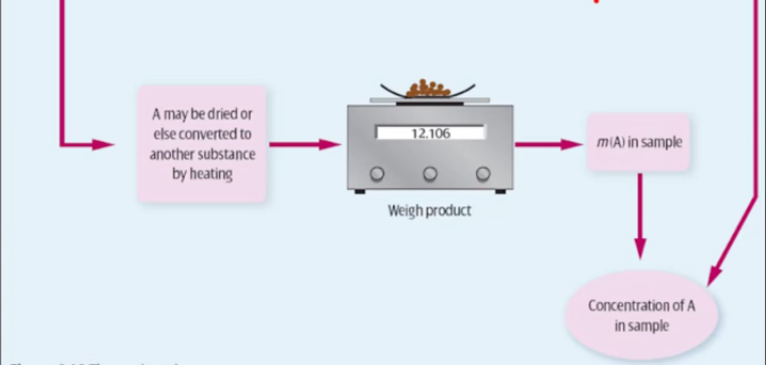
*for a water sample would start at ‘add a substance to precipitate A’
errors in gravimetric analysis
assumptions made:
analyte is only substance which dissolves in solvent - FROM SOLID
analyte = only substance which is precipitated *ask about this
drying precipitate:
any solvent leftover will add to final mass
dry, weigh, repeat until constant mass
ensure all of analyte is precipitated from solution:
add excess reactant to ensure full precipitation - to ensure reaction is completed fully
rinsing equipment properly
spillage or splashing of solution may lose analyte
not weighing all of precipitate:
some may be left in funnel or on glass rod etc.